12-事件循环机制、宏任务和微任务
# 浏览器的事件循环机制(重要)
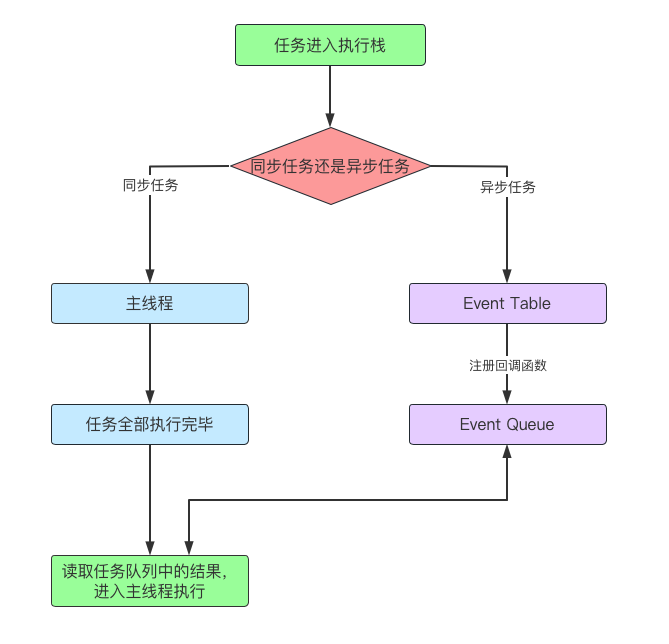
执行顺序如下:
同步任务:进入主线程后,立即执行。
异步任务:会先进入 Event Table;等时间到了之后,再进入 任务队列 (Event Queue)排队(排队是因为同一时间,JS 只能执行一个任务),先进先出。比如说,
setTimeout(()=> {}, 1000)这种定时器任务,需要等一秒之后再进入 Event Queue。当主线程的任务执行完毕之后,此时主线程处于空闲状态,于是会去读取 Event Queue 中的任务队列,如果有任务,则进入到主线程去执行。
# Node.js 事件循环机制
浏览器的 EventLoop 依据的是 HTML5 规范。而 Node.js 的 EventLoop 是由Node.js底层的 libuv 规定的。 libuv是一个专注于异步IO的跨平台库。
Node.js的事件循环中,有六个队列。其中,微任务有两个队列,宏任务有四个队列。
一、微任务队列:
- 顺序1:next tick queue。比如:process.nextTick
- 顺序2:other queue。比如:Promise的then回调、queueMicrotask
二、宏任务队列:
- 顺序3:timer queue。比如:setTimeout、setInterval
- 顺序4:poll queue。比如:IO事件
- 顺序5:check queue。比如:setImmediate
- 顺序6:close queue。比如:close事件
参考链接:
- 【荐】浏览器及nodeJS中的EventLoop事件循环机制:https://www.cnblogs.com/weiyongchao/p/13766429.html
- 浏览器和Node 事件循环的区别:https://github.com/Advanced-Frontend/Daily-Interview-Question/issues/26
# 宏任务和微任务
JS中的任务分为同步任务、异步任务。
JS中的异步任务分为宏任务(macrotask)、微任务(microtask)。在早期,异步任务中只有宏任务,没有微任务。后来的语言标准中,推出了“微任务”,因为希望微任务能够尽早执行。
# 宏任务、微任务分类
事件循环的队列中,有两个队列。
1、宏任务队列,包含这些任务:
- ajax 网络请求
- setTimeout、setInterval
- DOM事件
- UI渲染
- I/O文件读写操作。
2、微任务队列,包含这些任务:
- Promise的then回调
- Mutation Observer API:监听DOM节点变化。
- queueMicrotask():可直接将某个任务加入到微任务队列中。
在执行一个 Promise 对象时,当走完 resolve() 进入 fulfilled状态后,会立刻把 .then()里面的代码加入到微任务队列当中。
# 任务的执行顺序
JS中的任务执行顺序:同步任务 --> 微任务 --> 宏任务。
在执行任何一个宏任务之前(不是队列,是一个宏任务),都会先查询微任务队列中是否还有任务需要执行:
- 当前宏任务执行之前,必须要保证微任务队列是空的。
- 如果微任务队列不为空,那就优先执行微任务队列中的任务。
# 任务执行顺序的面试题
实际开发中,基本不会出现下面这些题目,因为很多时候我们无法精准控制异步任务的执行顺序。但是它们在面试中出现的频率特别高,因为熟悉这些思维训练,有利于考察我们对JS单线程、事件循环机制、宏任务和微任务等原理的掌握程度。
# 题 1:宏任务和微任务的执行顺序
setTimeout(() => {
// 宏任务
console.log('setTimeout');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve();
console.log('promise1'); // 同步任务
}).then((res) => {
// 微任务
console.log('promise then');
});
console.log('同步任务'); // 同步任务
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
打印结果:
promise1
同步任务
promise then
setTimeout
2
3
4
上方代码执行的顺序依次是:同步任务 --> 微任务 --> 宏任务。
# 题 2:在宏任务中嵌套了微任务
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
console.log('setTimeout'); // 宏任务
}, 0);
console.log('promise1');
}).then((res) => {
// 微任务
console.log('promise then');
});
console.log('同步任务');
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
打印结果:
promise1
同步任务
setTimeout
promise then
2
3
4
上方代码解释:在执行宏任务的过程中,创建了一个微任务。但是需要先把当前这个宏任务执行完,再去创建并执行微任务。
# 题3:综合题
console.log("script start")
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("setTimeout1");
new Promise(resolve => {
resolve();
}).then(() => {
new Promise(resolve => {
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log("then1");
});
console.log("then2");
});
});
new Promise(resolve => {
// 下面这两行代码,即便调换顺序,也不影响打印结果
console.log("promise1");
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log("then3");
});
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("setTimeout2");
});
console.log('同步代码');
queueMicrotask(() => {
console.log("queueMicrotask")
});
new Promise(resolve => {
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log("then4");
});
console.log("script end");
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
打印结果:
// 第一次循环
script start
promise1
同步代码
script end
// 第二次循环
then3
queueMicrotask
then4
// 第三次循环
setTimeout1
then2
then1
// 第四次循环
setTimeout2
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 题4:async await 题目
代码举例:
console.log('script start')
async function async2() {
console.log('async2')
}
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2();
console.log('async1 end')
}
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0)
async1();
new Promise(resolve => {
console.log('promise1')
resolve();
}).then(function () {
console.log('then1')
})
console.log('script end');
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
打印结果:
script start
async1 start
async2
promise1
script end
async1 end
then1
setTimeout
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 赞赏作者
创作不易,你的赞赏和认可,是我更新的最大动力:
