-
Java异常处理机制
异常概念与简单使用
异常是阻止当前方法或作用域继续执行的问题,在程序中导致程序中断运行的一些指令。
1.什么是异常
2.try与catch关键字
在程序中出现异常,就必须进行处理import org.testng.annotations.Test; //public class testetre { // @Test // public void dfds(){ // System.out.println("哈哈哈"); // } //} /** 异常处理 1.Throwable是异常的基类,分为Error和Exception,在编程中我们关注Exception 2.Exception分为编译器异常(受检)和运行期异常(非受检) 3.异常会导致程序中断无法继续执行, 4.在开发中,我们需要把可能出现异常的代码使用try语句块包裹起来 5.处理异常,可以让程序保持运行状态 6.catch可以有多个,顺序为从子类到父类 */ public class testetre{ public static void main(String[] args){ /** * 除法运算 */ div(10,0); } private static void div(int num1,int num2){ int[] arr ={1,2,3,4,5}; try { System.out.println(arr[5]); // int result = num1/num2; // System.out.println("result="+result); }catch (ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("除数不能为0"); }catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("数组下标越界"); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("出错啦"); } System.out.println("程序结束"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
try_catch_finally的使用
3.异常处理过程分析
- 一旦发生异常,则系统会自动产生一个异常类的实例化对象
- 此时如果存在了try语句,则会自动找到匹配的catch语句执行,如果没有异常处理,则程序将退出,并由系统报告错误
- 所有的catch根据方法的参数匹配异常类的实例化对象,如果匹配成功,则表示由此catch进行处理
4.finally关键字
在进行异常的处理之后,在异常的处理格式中还有一个finally语句,那么此语句将作为异常的统一出口,不管是否产生了异常,最终都要执行此段代码
import org.testng.annotations.Test; //public class testetre { // @Test // public void dfds(){ // System.out.println("哈哈哈"); // } //} /** 异常处理 1.Throwable是异常的基类,分为Error和Exception,在编程中我们关注Exception 2.Exception分为编译器异常(受检)和运行期异常(非受检) 3.异常会导致程序中断无法继续执行, 4.在开发中,我们需要把可能出现异常的代码使用try语句块包裹起来 5.处理异常,可以让程序保持运行状态 6.catch可以有多个,顺序为从子类到父类 */ public class testetre{ public static void main(String[] args){ /** * 除法运算 */ // div(10,0); method(); } private static void div(int num1,int num2){ int[] arr ={1,2,3,4,5}; try { System.out.println(arr[5]); // int result = num1/num2; // System.out.println("result="+result); }catch (ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("除数不能为0"); }catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("数组下标越界"); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("出错啦"); }finally { System.out.println("程序执行完毕"); } System.out.println("程序结束"); } private static int method(){ int a = 10; int b = 5; try { System.out.println("a="+a); System.out.println("b="+b); int c = a/b; System.out.println("a/b="+c); return c; }catch ( Exception e){ //代码测试时使用 e.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println("finally,"); } return -1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
_throw_throws与异常规则
throws关键字主要在方法的声明上使用,表示方法中不处理异常,而交给调用处处理。实际上对于Java程序来讲,如果没有加入任何的异常处理,默认由JVM进行异常的处理操作。
throw关键字表示在程序中手动抛出一个异常,因为从异常处理机制来看,所有的异常一旦产生之后,实际上抛出的就是一个异常类的实例化对象,那么此对象也可以由throws直接抛出。
异常处理的语法规则- try语句不能单独存在,可以和catch、finally组成try…catch…finally、try…catch、try…finally三种结构,catch语句可以有一个或多个,finally 语句最多一个,try、catch、finally这三个关键字均不能单独使用
- try、catch、finally三个代码块中变量的作用域分别独立而不能相互访问
- 多个catch块时候,Java虚拟机会匹配其中一个异常类或其子类,就执行这个catch块,而不会再执行别的catch块。
import org.testng.annotations.Test; import java.util.InputMismatchException; import java.util.Scanner; //public class testetre { // @Test // public void dfds(){ // System.out.println("哈哈哈"); // } //} /** 异常处理 1.Throwable是异常的基类,分为Error和Exception,在编程中我们关注Exception 2.Exception分为编译器异常(受检)和运行期异常(非受检) 3.异常会导致程序中断无法继续执行, 4.在开发中,我们需要把可能出现异常的代码使用try语句块包裹起来 5.处理异常,可以让程序保持运行状态 6.catch可以有多个,顺序为从子类到父类 */ public class testetre{ public static void main(String[] args){ /** * 除法运算 */ // div(10,0); // method(); // try { // div(20,0); // }catch (Exception e){ // e.printStackTrace(); // } // System.out.println("over"); input(); } private static void div(int num1,int num2){ int[] arr ={1,2,3,4,5}; try { System.out.println(arr[5]); // int result = num1/num2; // System.out.println("result="+result); }catch (ArithmeticException e){ System.out.println("除数不能为0"); }catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("数组下标越界"); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println("出错啦"); }finally { System.out.println("程序执行完毕"); } System.out.println("程序结束"); } private static int method(){ int a = 10; int b = 5; try { System.out.println("a="+a); System.out.println("b="+b); int c = a/b; System.out.println("a/b="+c); return c; }catch ( Exception e){ //代码测试时使用 e.printStackTrace(); }finally { System.out.println("finally,"); } return -1; } //自动补全:alt+/ private static int div2(int a,int b)throws ArithmeticException{ try { int c= a/b; return c; }catch (ArithmeticException e){ throw new ArithmeticException("除数不能为0"); } } private static void input(){ //ctrl+shift+o 导包 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); try { int num = input.nextInt(); System.out.println(num); }catch (InputMismatchException e){ System.out.println("输入不匹配"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
自定义异常与assert
在Java中,已经提供了很多的异常类的定义,但是我们在实际项目开发中,可能需要使用一些自己的异常类,那么可以通过集成Exception类或已有的异常类的方式完成一个自定义异常类的操作。
classNotFoundException
DataFormatException
RuntimeException
ArithmeticException
IndexOutOfBoungsException
NullPointerException
ClassCastException/** * 自定义异常通常都是通过继承一个异常类来实现的 * 1.Throwable * 2.Exception * 3.RuntimeException * * 自定义异常的实现是重写父类的构造方法 * 异常对象本身是没有实际功能,只是一个有意义的标识 */ public class MyException extends Exception{ public MyException(){ super(); } public MyException(String message){ super(message); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
示例:排错法
user.javapublic class User { private String username; private String password; private int age; private String sex; public User(String username,String password,int age,String sex) { super(); this.username = username; this.password=password; this.age=age; this.sex=sex; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "username='" + username + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", sex='" + sex + '\'' + '}'; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
UserService.java
public class UserService { public User login(String username,String password)throws MyException{ if("admin".equals(username)){ throw new MyException("用户名错误"); }else if ("12345".equals(password)){ throw new MyException("密码错误"); } User user = new User("admin","12345",18,"男"); return user; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
LoginDemo.java
import java.util.Scanner; public class LoginDemo { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入用户名:"); String name = input.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入密码:"); String pass = input.nextLine(); UserService us = new UserService(); try { User user=us.login(name,pass); System.out.println("登录成功"); System.out.println(user); } catch (MyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
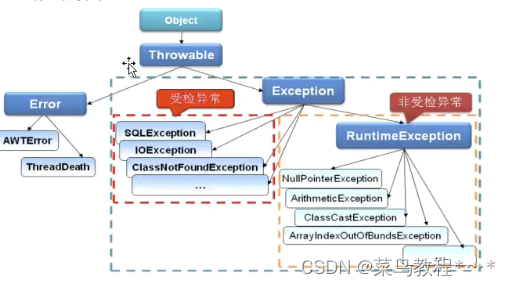
受检异常:Exception
定义方法时必须声明所有可能会抛出的Exception:在调用这个方法时,必须捕获它的checked exception,不然就得把它的exception传递下去;exception是从java.lang.Exception类衍生出来的。例如:IOException,SQLException就属于Exception
非受检异常:RuntimeException
在定义方法时不需要声明会抛出runtime exception;在调用这个方法时不需要捕获这个runtime Exception;runtime exception是从java.Lang.RuntimeException或java.lang.Error类衍生出来的。例如:NullPointException,IndexOutOfBoundsException就属于runtimeexception
assert关键字,表示断言
当程序执行到某个固定位置的时候,程序中的某个变量的取值肯定是预期的结果,那么这种操作可以使用断言完成。
断言的操作语法:
assert表达式; -
相关阅读:
vant weapp的custom-tab-bar显示红点
学长告诉我,大厂MySQL都是通过SSH连接的
TRex学习之旅九
kubernetes集群安装
【Linux】【驱动】设备树中设备节点的挂载
redis常用命令
关于使用ScriptObject作为项目数据配置
C++ Reference: Standard C++ Library reference: C Library: cmath: remainder
没有学过C语言可以学Java吗?
vue.js生命周期函数
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/fanfangyu/article/details/126926204
