JavaIO流05
4.常用的类04
4.4节点流和处理流03
4.4.8打印流-PrintStream和PrintWriter
打印流只有输出流,没有输入流
1.简单介绍及应用
- PrintStream是字节打印流


例子1:演示PrintStream(字节打印流/输出流)
package li.io.printstream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintStream; /** * 演示PrintStream(字节打印流/输出流) */ public class PrintStream_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintStream out = System.out; //在默认情况下,PrintStream 输出数据的位置是 标准输出,即显示器 out.print("jack,hello"); /** * public void print(String s) { * if (s == null) { * s = "null"; * } * write(s); * } */ //因为print底层使用的是write,所以我们可以直接调用write进行打印/输出 out.write("Hello北京".getBytes()); out.close(); //我们可以去修改打印流输出的位置/设备 // 1.修改为打印到d:\f1.txt // 2."落霞与孤鹜齐飞,秋水共长天一色" 这句话就会打印到d:\f1.txt里 // 3.System.setOut底层: /** * public static void setOut(PrintStream out) { * checkIO(); * setOut0(out);//native方法 ,修改了 out * } */ System.setOut(new PrintStream("d:\\f1.txt")); System.out.println("落霞与孤鹜齐飞,秋水共长天一色");//打印到d:\f1.txt } }
运行结果:


如上所示:在修改了打印流 输出的位置/设备之后,再调用System.out.println方法,打印/输出的地方就变为指定的文件路径,点击System.setOut方法,可以看到底层是调用了setOut0方法,该方法是本地方法(native)。它会去修改out,即修改输出数据的位置:


- PrintWriter是字符打印流


例子2:
package li.io.printstream; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; /** * 演示PrintWriter的使用方式 */ public class PrintWriter_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(System.out); //向PrintWriter构造器中传入一个FileWriter对象 PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\f2.txt")); printWriter.print("hi,北京你好~"); printWriter.close();//flush()+关闭流,才会将数据写入到文件中 } }

4.5Properties类
- 看一个需求:
如下一个配置文件 mysql.properties:
ip=192.168.0.13 user=root pwd=12345
问编程读取ip、user、pwd的值是多少要怎么做?
分析:
- 传统的方法
- 使用Properties类可以方便实现
例子:传统方法
在scr文件夹下创建一个mysql.properties文件,内容为

package li.io.properties_; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; public class Properties01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //读取mysql.properties文件,并得到ip,user,pwd //创建 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties")); String line = ""; //读取 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {//循环读取 String[] split = line.split("="); System.out.println(split[0] + "值是: " + split[1]); } //关闭 br.close(); } }

如上所示,如果mysql.properties的参数很多,并且要求读取修改其中一项或者n项参数,那么使用传统的读取方法,就需要我们对读取的参数进行条件判断,一旦要读取的参数过多,代码就会变得非常繁琐。这时候就需要使用到Properties类。
4.5.1基本介绍
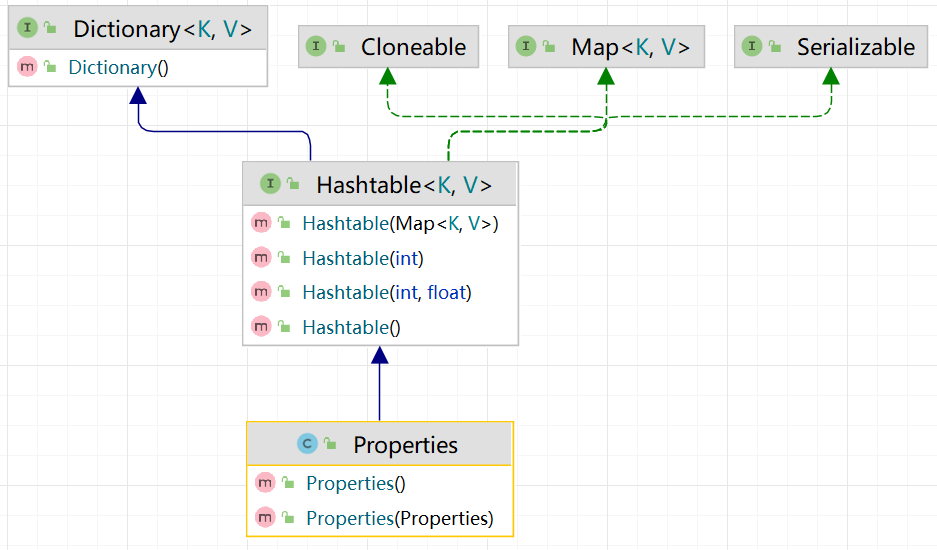
Properties是Hashtable的子类,是专门用于读写配置文件的集合类:
1)配置文件的格式:
键=值 键=值
2)注意:键值对之间不需要有空格,值不需要用引号括起来。默认的类型是String
3)Properties的常见方法:
- load:加载配置文件的键值对到Properties对象
- list:将数据显示到指定设备/流对象
- getProperty(Key):根据键获取值
- setProperty(Key,Value):设置键值对到Properties对象
- store:将Properties中的键值对存储到配置文件中,在idea中,保存信息到配置文件,如果含有中文,会存储为unicode码
应用案例1:使用Properties类完成对mysql.properties 的读取
package li.io.properties_; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.util.Properties; public class Properties02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //使用Properties类来读取 mysql.properties 文件 // 1.创建Properties对象 Properties properties = new Properties(); // 2.加载指定的配置文件 properties.load(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties")); // 3.将 k-v 显示到控制台 properties.list(System.out); // 4.根据key获取对应的值 String user = properties.getProperty("user"); String pwd = properties.getProperty("pwd"); System.out.println("用户名=" + user); System.out.println("密码=" + pwd); } }

应用案例2:使用Properties类添加 key-value 到新文件 mysql2.properties 中,并修改某个 key-value
package li.io.properties_; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Properties; public class Properties03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //使用Properties类添加 key-value 到新文件 mysql2.properties 中 //创建对象 Properties properties = new Properties(); //创建 //如果该文件没有key,就是创建 //如果该文件有key,就是修改/替换 /** * Properties类的父类就是 Hashtable ,底层就是 Hashtable的核心方法 * public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { * // Make sure the value is not null * if (value == null) { * throw new NullPointerException(); * } * * // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable. * Entry tab[] = table; * int hash = key.hashCode(); * int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; * @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") * Entry entry = (Entry)tab[index]; * for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) { * if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) { * V old = entry.value;//如果key存在,就替换 * entry.value = value; * return old; * } * } * * addEntry(hash, key, value, index);//如果是新的key,就添加新 key * return null; * } */ properties.setProperty("charset", "utf-8"); properties.setProperty("user", "汤姆");//注意:保存的是中文的Unicode码值 properties.setProperty("pwd", "abcd123"); properties.setProperty("pwd", "1111");//替换 //将k-v存储到文件中即可 properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\mysql2.properties"), null);//第二个参数是添加注释 System.out.println("保存配置文件成功~"); } }

查询发现 \u6C64\u59C6 对应的中文就是 汤姆

5.IO习题
5.1Homework01
(1)判断d盘下是否有文件夹mytemp,如果没有就创建mytemp
(2)在d:\mytemp目录下,创建文件hello.txt
(3)如果hello.txt已经存在,就提示该文件已经存在,就不要重复创建了
(4)并在hello.txt文件中写入内容"hello,world".
package li.io.homework; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class HomeWork01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "d:\\mytemp\\hello.txt"; String dictionaryPath = "d:\\mytemp"; //创建对象 File file = new File(dictionaryPath);//目录 File file2 = new File(filePath);//文件 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; if (!file.exists()) {//如果目录不存在 if (file.mkdir()) {//创建目录 System.out.println("创建目录mytemp成功~"); } } else { System.out.println("目录mytemp已存在"); } if (file2.exists()) { System.out.println("hello.txt文件已存在"); //如果文件存在,就写入数据 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath); fileOutputStream.write("hello,world".getBytes()); System.out.println("已写入数据~"); } else { if (file2.createNewFile()) { System.out.println("创建hello.txt文件成功~"); //如果文件存在,就写入数据 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath); fileOutputStream.write("hello,world".getBytes()); System.out.println("已写入数据~"); } } //关闭流 fileOutputStream.close(); } }


5.2Homework02
编程题:要求:使用BufferedReader读取一个文本文件,为每行加上行号,再连同内容一并输出到屏幕上。
package li.io.homework; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; public class HomeWork02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "d:\\story.txt"; String line = ""; int i = 0;//行号 //创建对象 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); //读取 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println((++i) + "\t" + line); } //关闭流 br.close(); } }

要求2:如果将文本的编码改为GBK,怎么将其输出到控制台上而不使其乱码?
使用转换流,FileInputStream-->InputStreamReader(指定编码)-->BufferedReader
package li.io.homework; import java.io.*; public class HomeWork02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "d:\\story.txt"; String line = ""; int i = 0;//行号 //创建对象 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath),"GBK"));//使用转换流,选择编码为“GBK” //读取 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {//循环读取 System.out.println((++i) + "\t" + line); } //关闭流 br.close(); } }
5.3Homework03
编程题:
-
要编写一个dog.properties
name=tom age=5 color=red -
编写Dog类(name,age,color)创建一个dog对象,读取dog.properties 用相应的内容完成初始化,并输出
-
将创建的Dog对象,序列化到 文件 dog.dat文件
-
再反序列化dog对象
package li.io.homework; import java.io.*; import java.util.Properties; public class HomeWork03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { //1.编写dog.properties //创建Properties对象 Properties properties = new Properties(); //在properties对象中添加k-v properties.setProperty("name", "tom"); properties.setProperty("age", "5"); properties.setProperty("color", "red"); //将properties对象的k-v存储到文件中 properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\dog.properties"), null); //2.读取dog.properties完成Dog对象 的初始化 int age = Integer.parseInt(properties.getProperty("age")); Dog dog = new Dog(properties.getProperty("name"), age, properties.getProperty("color")); System.out.println(dog); //3.将创建的Dog对象,序列化到 dog.dat文件 String filePath = "d:\\dog.dat"; ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath)); oos.writeObject(dog); //关闭流 oos.close(); System.out.println("Dog序列化完成"); //4.反序列化dog对象 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath)); Dog dog1 = (Dog) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(dog1); //关闭流 ois.close(); System.out.println("反序列化完成"); } } //序列化的类要实现Serializable接口 class Dog implements Serializable { private String name; private int age; private String red; public Dog(String name, int age, String red) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.red = red; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", red='" + red + '\'' + '}'; } }

