-
数据分析-numpy2
numpy
统计函数
- 求平均值mean()
m1=np.arange(20).reshape((4,5) #默认求数组所有元素的平均值) m1.mean() #axis=0列从上往下 m1.mean(axis=0) #axis=1行从左往右 m1.mean(axis=1)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 中位数np.median
ar1=np.array([1,3,5,6,8]) np.median(ar1)- 1
- 2
- 标准差ndarray.std
定义:总体各单位标准值与其平均数离差平方的算术平均数的平方根
ar1=np.array([1,3,5,6,8]) np.std(ar1) 按步骤计算标准差 import math math.sqrt(np.sum(((ar1-np.mean(ar1))**2)/a.size))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 方差ndarray.var()
ar1=np.array([1,3,5,6,8]) ar1.var- 1
- 2
- 最大 ndarray.max()和最小ndarray.min()
最大: m1.max() m1.max(axis=0)#axis=0列从上往下 m1.max(axis=1)#axis=1行从左往右 最小: m1.min() 求和: m1.sum()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 加权平均数

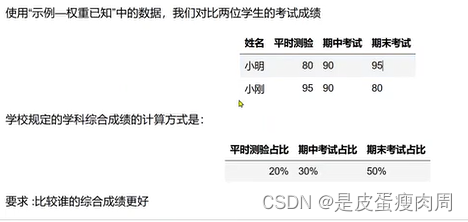
xiaoming=np.array([80,90,95]) xiaogang=np.array([95,90,80]) #权重 weights=np.array([0.2,0.3,0.5]) #加权平均值 np.average(xiaoming,weights=weights) np.average(xiaogang,weights=weights)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
变异系数:当需要比较两组数据大小的时候,如果两组数据的测量尺度相差太大,或者数据量纲的不同,直接使用标准差来进行表示比较不合适,此时应该消除尺度和量纲的影响,而变异系数可以做到这一点,它是原始数据标准差与原始数据平均数的比

#股票信息 stat_info=np.array([ [110.93,16.46,0.2376,0.0573], [-0.13,31.01,0.1188,0.0836], [8.94,26.67,0.0565,0.0676], [17.24,19.53,0.1512,0.0433], [43.86,-10.14,0.097,0.0421], [-15.34,-13.04,0.0902,0.0732], [-20.82,-23.37,0.0582,0.1091] ]) #先计算7年的期望值(平均值) stat_mean=np.mean(stat_info,axis=0) #计算7年的标准差 stat_std=np.std(stat_info,axis=0) #变异系数=原始数据标准差/原始数据平均数 stat_std/stat_mean- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
数据类型
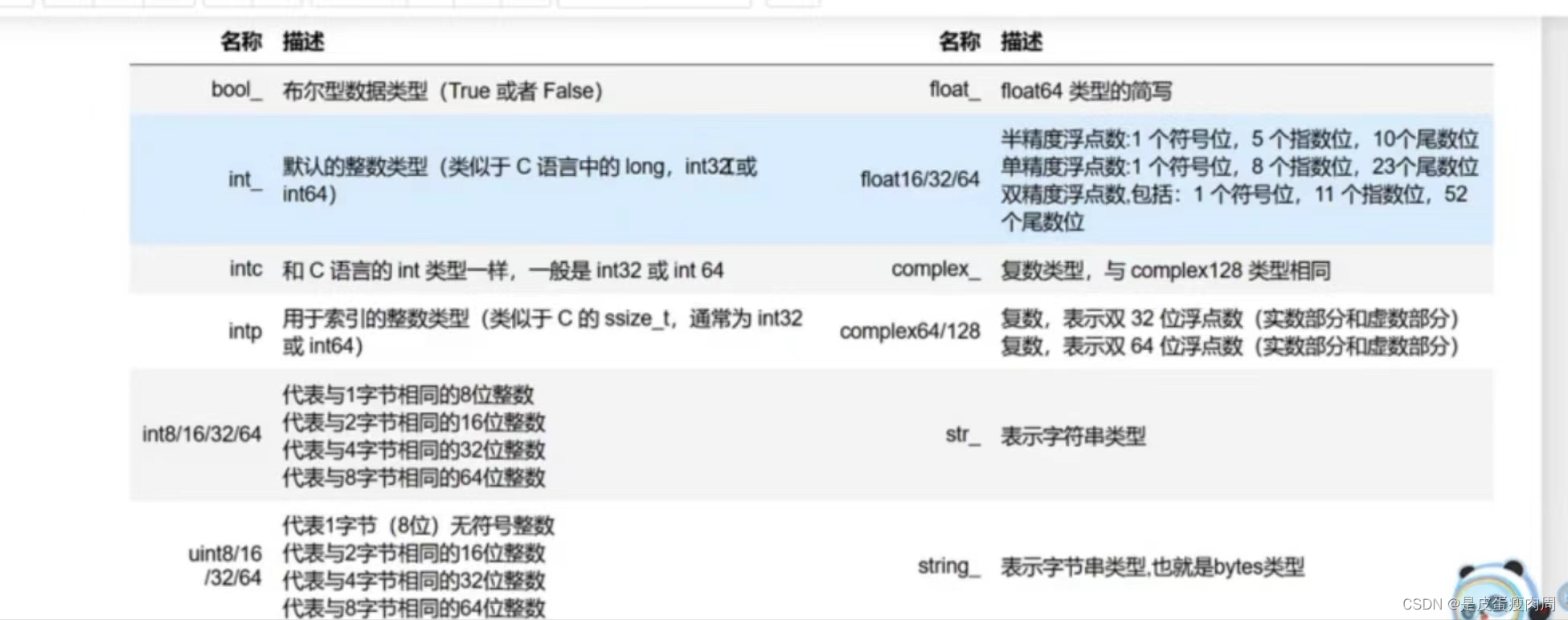
将数组类型存储为浮点型 a=np.array([1,2,3,4],dtype=np.float64)- 1
- 2
- 定义结构化数据
随机函数
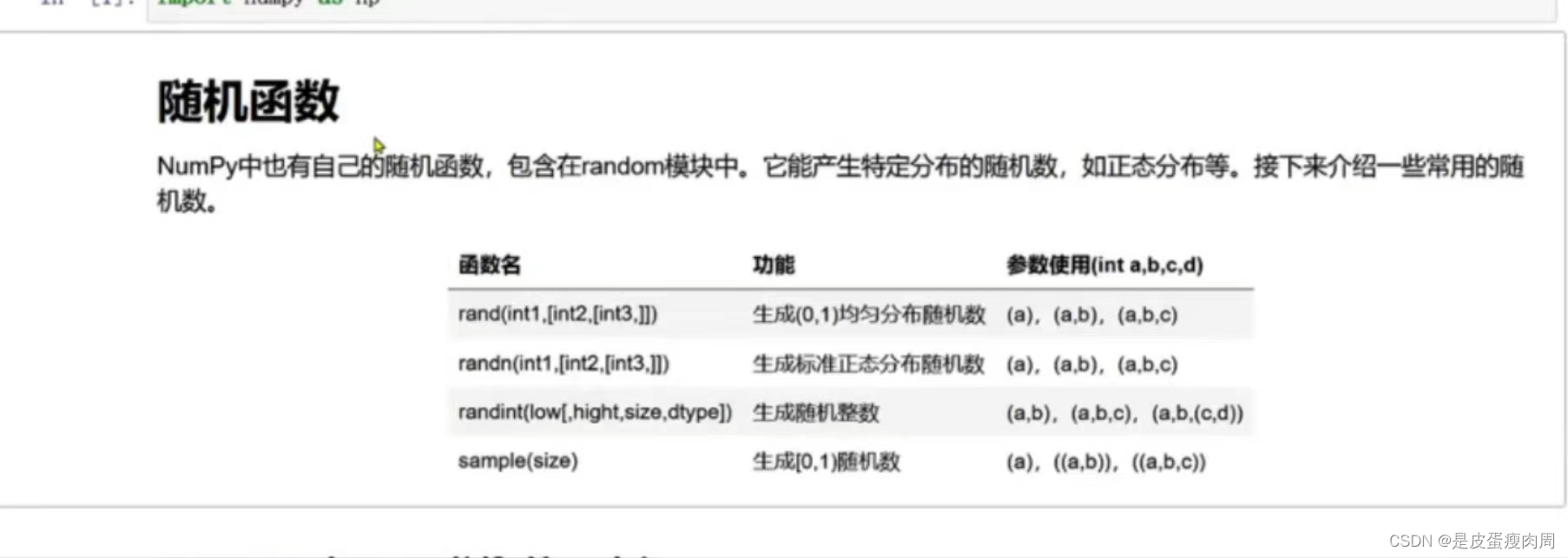
- numpy.random.rand(d0,d1,…,dn)
rand函数根据给定维度生成(0,1)之间的数据,包含0,不包含1 dn表示每个维度 返回值为指定维度的array
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt a=np.random.rand(10000) print(a) plt.hist(a)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4

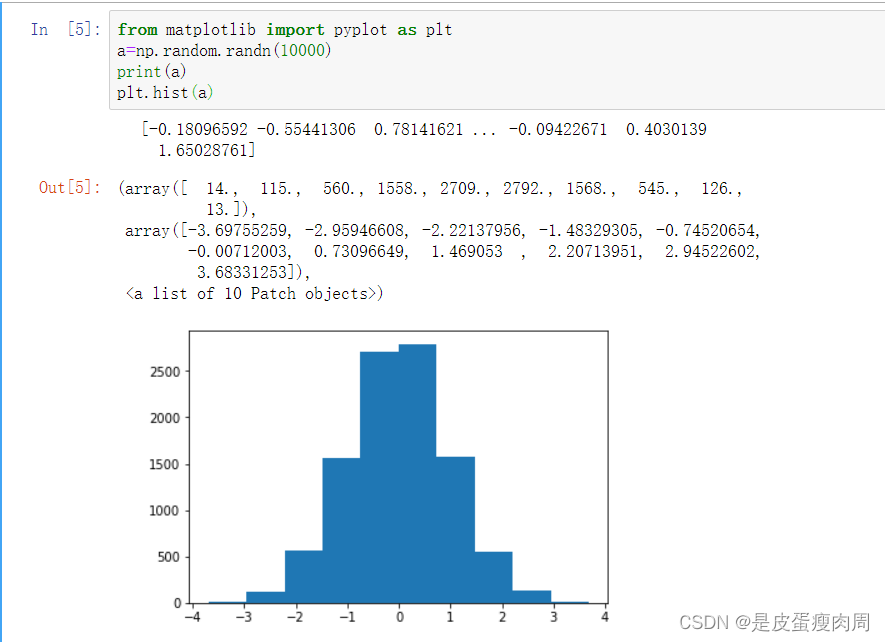
- numpy.random.randn(d0,d1,…,dn)
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt a=np.random.randn(10000) print(a) plt.hist(a)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- numpy.random.randint()
numpy.random.randint(low,high=None,size=None,dtype=‘1’)
返回随机整数,范围区间在[low,high),包含low,不包含high
参数:low为最小值,high为最大值,size为数组维度大小,dtype为数据类型
high没有填写时,默认生成随机数的范围是[0,low)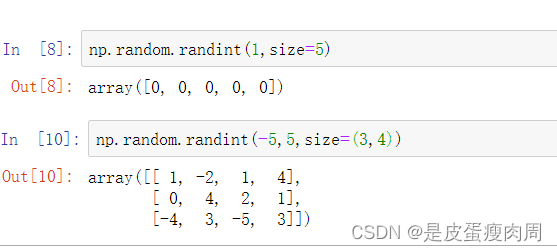
- numpy.random.sample(size=None)
返回半开区间的随机浮点数[0.0,1.0]
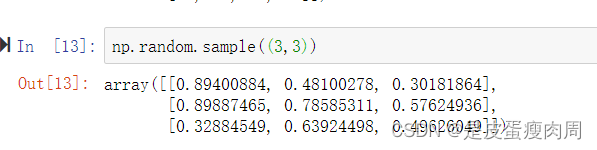
- 随机种子np.random.seed()
使用相同seed()值,则每次生成的随机数都相同,使得随机数可以预测
但是,只在调用的时候seed()一下并不能使生成的随机数相同,需要每次都调用seed()一下,表示种子相同,从而随机数相同

- 正态分布numpy.random.normal

数组的其他函数
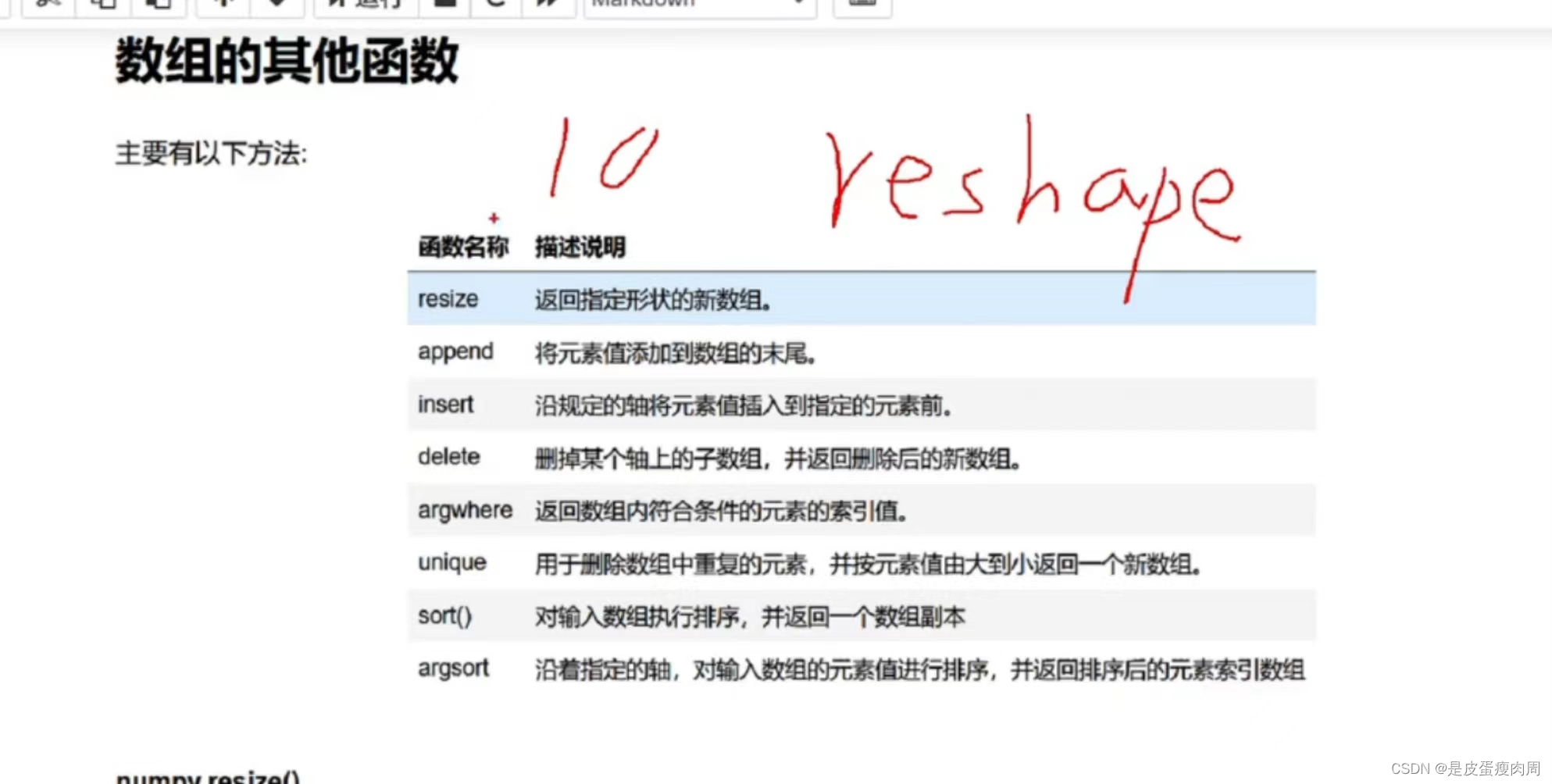
- numpy.resize()
numpy.resize()返回指定形状的新数组
numpy.resize(arr,shape)和ndarray.resize(shape,refcheck=False)区别:
numpy.resize(arr,shape),有返回值,返回复制内容。如果维度不够,会使用原数组数据补齐。
ndarray.resize(shape,refcheck=False),修改原数组,不会返回数据,如果维度不够,会使用0补齐a=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) print('数组a:',a) print('a数组形状:',a.shape) b=np.resize(a,(3,3)) a.resize((3,3),refcheck=False)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
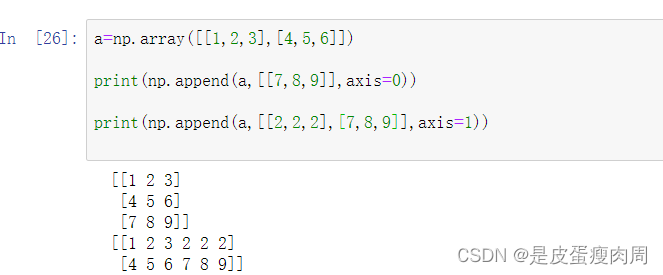
- numpy.append(arr,values,axis=None)
a=np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) print(np.append(a,[[7,8,9]],axis=0)) print(np.append(a,[[2,2,2],[7,8,9]],axis=1))- 1
- 2
- 3
- numpy.insert(arr,obj,value,axis)
arr:要输入的数组
obj:表示引值,在该索引值之前插入values值
values:要插入的值
axis:指定的轴。如果未提供,则输入数组会被展开为一维数组a=np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]]) #不提供按照数组展开 print(np.insert(a,3,[11,12])) #沿轴0垂直方向 print(np.insert(a,1,[11],axis=0) #沿轴1水平方向 print(np.insert(a,1,11,axis=1))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7

- numpy.delete(arr,obj,axis)
arr:要输入的数组
obj:整数或者整数数组,表示要被删除数组元素或者子数组
axis:沿着哪条轴删除子数组
注意:不提供axis参数,则输入数组被展开为一维数组a=np.arange(12).reshape(3,4) #a数组 print(a) #不提供axis参数情况 print(np.delete(a,5)) #删除第2列 print(np.delete(a,1,axis=1)) a=np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]) #删除多行 print(np.delete(a,[1,2,3,4]))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- numpy.argwhere()
返回数组中非0元素的索引,若是多维数组则返回行,列索引组成的索引坐标
x=np.arange(6).reshape(2,3) print(x) #返回所有大于1 的索引 y=np.argwhere(x>1) print(y,y.shape)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
-
相关阅读:
【老生谈算法】matlab实现巴特沃斯IIR滤波器程序设计源码
[Pandas] Pandas数据结构
K8S知识点(六)
Java 基于微信小程序的快递柜小程序
PLC 学习day01 了解PLC 的组成和知识。
如何使UI自动化项目成功?
ORM框架SQLAlchemy
MVP模式根模块
7.10飞书一面面经
(229)Verilog HDL:与运算
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_66610130/article/details/126690755
