-
栈和队列(栈和队列的实现、两个队列实现栈、两个栈实现一个队列等经典例题)


꧁ 大家好,我是 兔7 ,一位努力学习C++的博主~ ꧂
☙ 如果文章知识点有错误的地方,请指正!和大家一起学习,一起进步❧
🚀 如有不懂,可以随时向我提问,我会全力讲解~💬
🔥 如果感觉博主的文章还不错的话,希望大家关注、点赞、收藏三连支持一下博主哦~!👀
🔥 你们的支持是我创作的动力!⛅
🧸 我相信现在的努力的艰辛,都是为以后的美好最好的见证!⭐
🧸 人的心态决定姿态!⭐
🚀 本文章CSDN首发!✍
目录
0. 前言
此博客为博主以后复习的资料,所以大家放心学习,总结的很全面,每段代码都给大家发了出来,大家如果有疑问可以尝试去调试。
大家一定要认真看图,图里的文字都是精华,好多的细节都在图中展示、写出来了,所以大家一定要仔细哦~
感谢大家对我的支持,感谢大家的喜欢, 兔7 祝大家在学习的路上一路顺利,生活的路上顺心顺意~!
1. 栈
1.1 栈的概念及结构
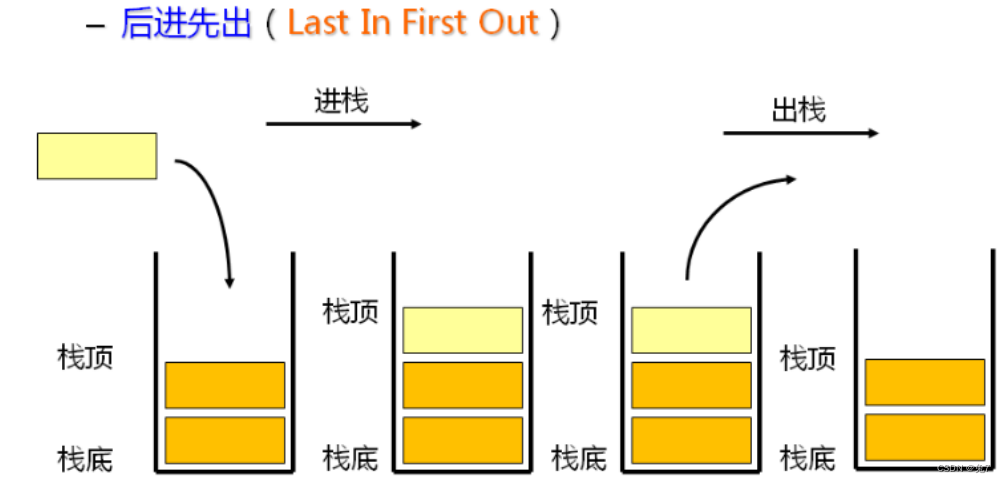
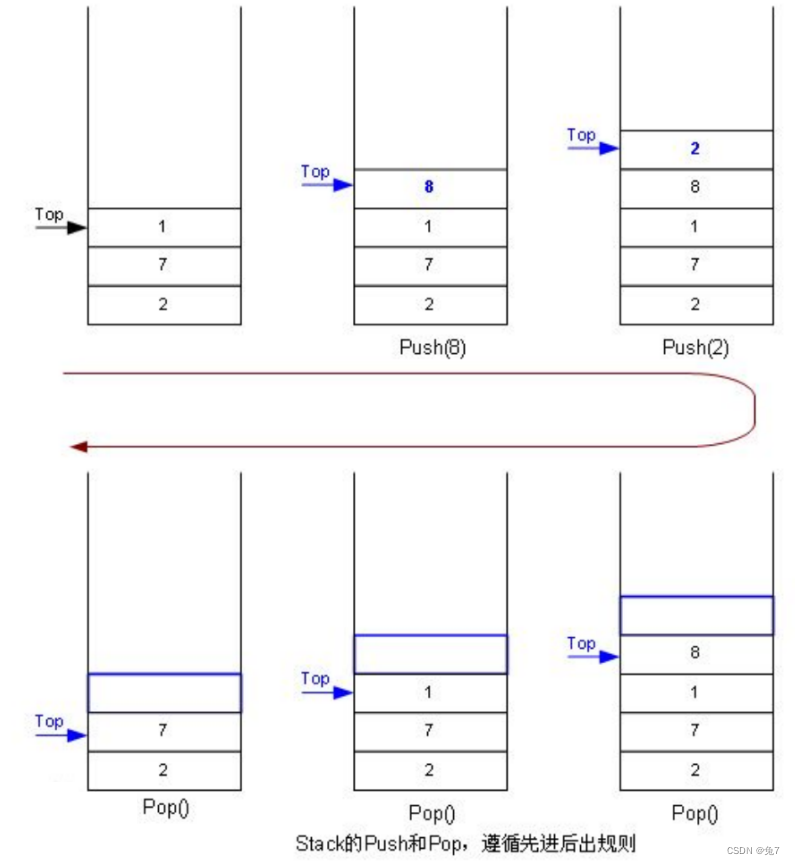
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
1.2 栈的实现
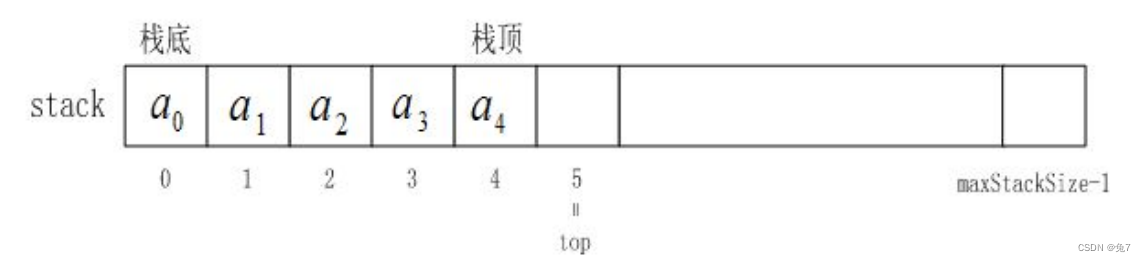
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。
Stack.h
- #pragma once
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int STDataType;
- typedef struct Stack
- {
- STDataType* a;
- int top;
- int capacity;
- }Stack;
- void StackInit(Stack* ps);
- void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
- void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x);
- void StackPop(Stack* ps);
- STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
- bool IsEmpty(Stack* ps);
- int Size(Stack* ps);
Stack.c
- #include "Stack.h"
- void StackInit(Stack* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
- ps->top = 0;
- ps->capacity = 4;
- }
- void StackDestroy(Stack* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->a);
- ps->a = NULL;
- ps->top = 0;
- ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- bool IsEmpty(Stack* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType x)
- {
- assert(ps);
- if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
- {
- int newcapacity = ps->capacity * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("StackPush error");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->a = tmp;
- ps->capacity = newcapacity;
- }
- ps->a[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- void StackPop(Stack* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!IsEmpty(ps));
- ps->top--;
- }
- STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(IsEmpty(ps));
- return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
- }
- int Size(Stack* ps)
- {
- return ps->top;
- }
- void Print(Stack* ps)
- {
- assert(ps);
- int top = ps->top - 1;
- while (top >= 0)
- {
- printf("%d ", ps->a[top--]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
2. 队列
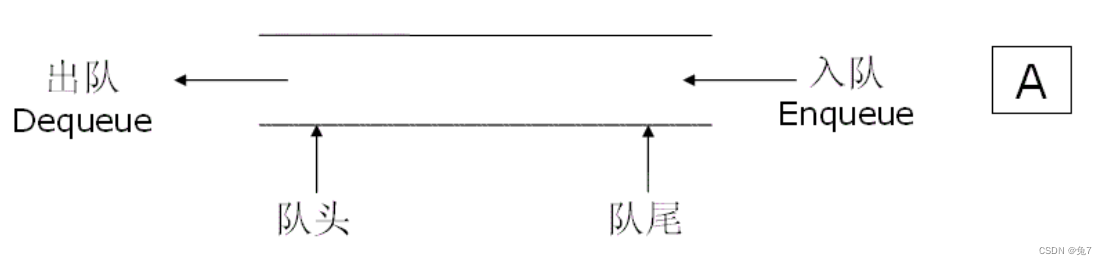
2.1 队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
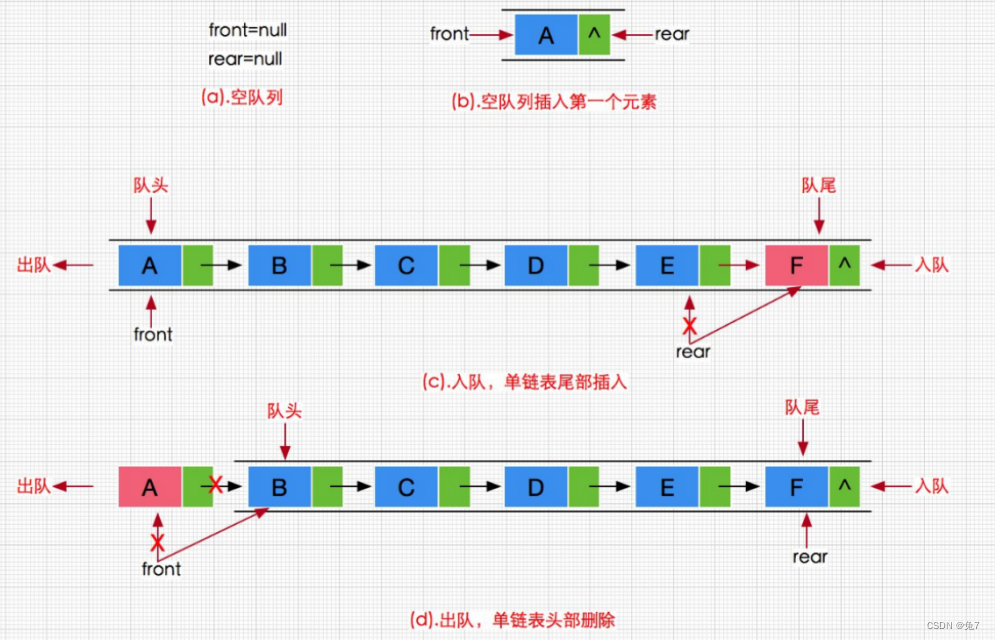
2.2队列的实现
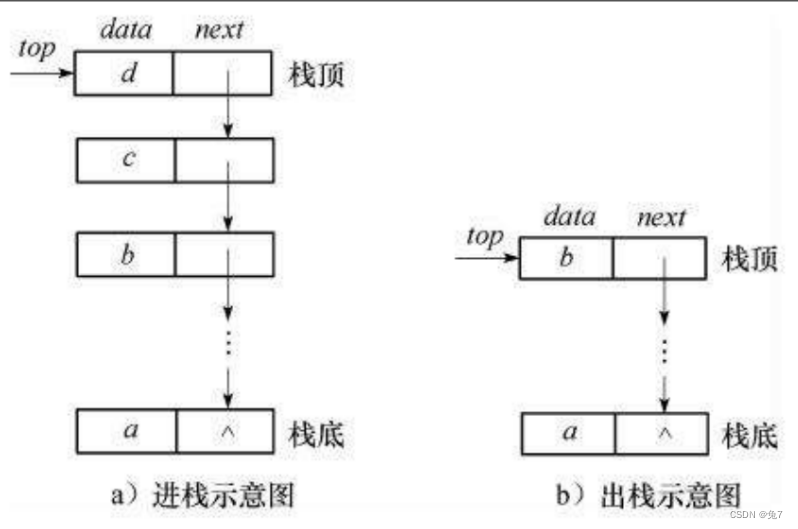
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
Queue.h
- #pragma once
- #include
- #include
- #include
- typedef int QDataType;
- typedef struct QueueNode
- {
- struct QueueNode* next;
- QDataType data;
- }QueueNode;
- typedef struct Queue
- {
- QueueNode* head;
- QueueNode* tail;
- }Queue;
- void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
- void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
- void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
- void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
- QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
- QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
- int Size(Queue* pq);
- int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
- void Print(Queue* pq);
Queue.c
- #include "Queue.h"
- void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
- }
- void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
- while (cur)
- {
- QueueNode* del = cur;
- cur = cur->next;
- free(del);
- }
- pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
- }
- void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
- {
- assert(pq);
- QueueNode* newNode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
- if (newNode == NULL)
- {
- perror("QueuePush error");
- exit(-1);
- }
- newNode->data = x;
- newNode->next = NULL;
- if (pq->tail == NULL)
- {
- pq->head = pq->tail = newNode;
- }
- else
- {
- pq->tail->next = newNode;
- pq->tail = newNode;
- }
- }
- void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- if (pq->head->next == NULL)
- {
- free(pq->head);
- pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
- }
- else
- {
- QueueNode* del = pq->head;
- pq->head = del->next;;
- free(del);
- }
- }
- QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- return pq->head->data;
- }
- QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- return pq->tail->data;
- }
- int Size(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- int n = 0;
- QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
- while (cur)
- {
- n++;
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- return n;
- }
- int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
- {
- assert(pq);
- return (pq->head == pq->tail) && (pq->head == NULL) && (pq->tail == NULL);
- }
- void Print(Queue* pq)
- {
- QueueNode* cur = pq->head;
- while (cur)
- {
- printf("%d ", cur->data);
- cur = cur->next;
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型 时可以就会使用循环队列。环形队列可以使用数组实现,也可以使用循环链表实现。
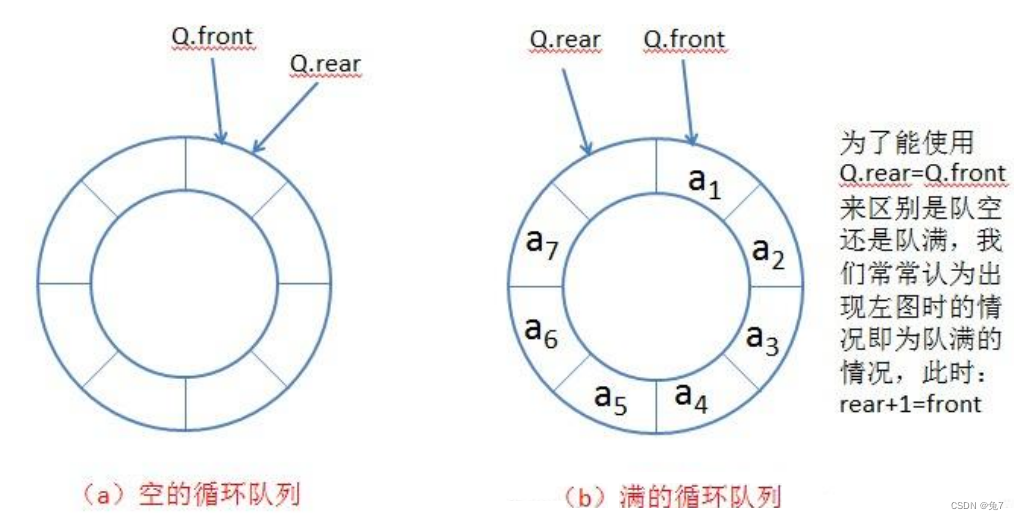
3. 栈和队列面试题
先找左括号,找到左括号入栈。如果有左括号,再找到右括号就将左括号出栈。如果是右括号的一种,栈顶的是左括号的另外一种,那么就有问题。
- class Solution {
- public:
- bool isValid(string s) {
- stack<char> st;
- for(auto ch : s)
- {
- if(ch == '{' || ch == '[' || ch == '(')
- {
- st.push(ch);
- }
- else
- {
- if(st.empty())
- {
- return false;
- }
- if((ch == '}' && st.top() == '{')
- || (ch == ']' && st.top() == '[')
- || (ch == ')' && st.top() == '('))
- {
- st.pop();
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- }
- return st.empty();
- }
- };
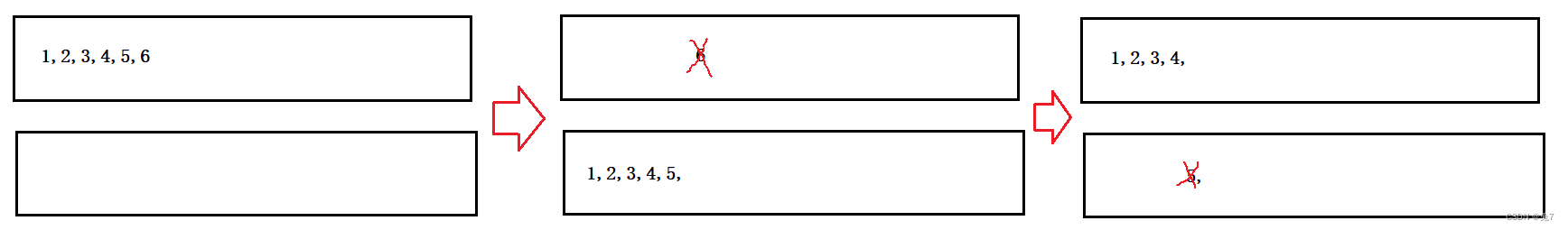
以此类推,当pop的时候将除了最后一个数据从队列里出队列,进入另一个队列中,然后出队列,这就用队列实现了栈的功能。
具体代码实现如下:
- class MyStack {
- public:
- MyStack() {
- }
- void push(int x) {
- if(q1.empty())
- q2.push(x);
- else
- q1.push(x);
- }
- int pop() {
- // 让q1是空,q2不是空
- if(q2.empty())
- {
- queue<int> tmp = q1;
- q1 = q2;
- q2 = tmp;
- }
- while(q2.size() > 1)
- {
- q1.push(q2.front());
- q2.pop();
- }
- int del = q2.front();
- q2.pop();
- return del;
- }
- int top() {
- if(q1.empty())
- return q2.back();
- else
- return q1.back();
- }
- bool empty() {
- return q1.empty() && q2.empty();
- }
- private:
- queue<int> q1;
- queue<int> q2;
- };
- /**
- * Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
- * MyStack* obj = new MyStack();
- * obj->push(x);
- * int param_2 = obj->pop();
- * int param_3 = obj->top();
- * bool param_4 = obj->empty();
- */
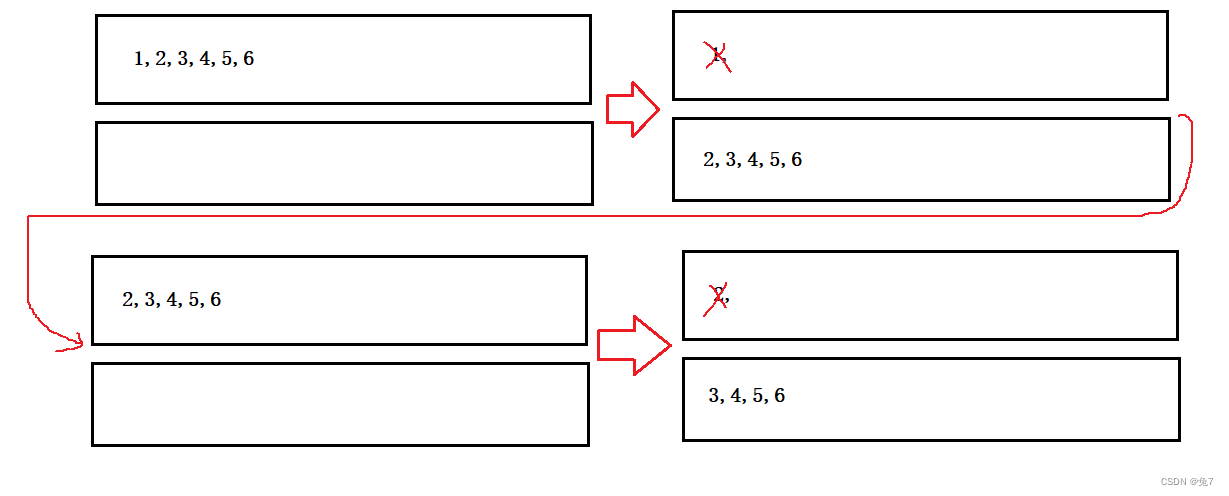
这里上面的是用来出队列的,下面的是用来入队列的,上面的出栈到最后一个,然后将最后一个pop掉,然后再从入队列的入到出队列的中,如此往复就用栈实现了队列。
具体代码实现如下:
- class MyQueue {
- public:
- MyQueue() {
- }
- void push(int x) {
- s1.push(x);
- }
- int pop() {
- while(s1.size() > 1)
- {
- s2.push(s1.top());
- s1.pop();
- }
- int tmp = s1.top();
- s1.pop();
- while(s2.size())
- {
- s1.push(s2.top());
- s2.pop();
- }
- return tmp;
- }
- int peek() {
- while(s1.size())
- {
- s2.push(s1.top());
- s1.pop();
- }
- int tmp = s2.top();
- while(s2.size())
- {
- s1.push(s2.top());
- s2.pop();
- }
- return tmp;
- }
- bool empty() {
- return s1.empty() && s1.empty();
- }
- private:
- stack<int> s1;
- stack<int> s2;
- };
- /**
- * Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
- * MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
- * obj->push(x);
- * int param_2 = obj->pop();
- * int param_3 = obj->peek();
- * bool param_4 = obj->empty();
- */
我这里设置的循环队列是通过数组来实现的,通过多开一个空间,来进行判断队列的空和满,也就是数组的头和尾是一个位置就是空,尾的下一个位置是头就是满,当然这里需要通过取模来完成,其中有一些细节需要完善,然后push的时候就是头到下一个位置,pop的时候就是尾巴向前走一个位置。
具体的实现看下面的代码,当然这里的代码是我写的思路,当然也会有其它思路。
- class MyCircularQueue {
- public:
- MyCircularQueue(int k) {
- n = k;
- a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (k + 1));
- head = tail = 0;
- }
- bool enQueue(int value) {
- if(isFull())
- return false;
- a[tail] = value;
- tail++;
- if(tail >= n)
- tail %= (n+1);
- return true;
- }
- bool deQueue() {
- if(isEmpty())
- return false;
- head++;
- if(head >= n)
- head %= (n+1);
- return true;
- }
- int Front() {
- if(head == tail)
- return -1;
- return a[head];
- }
- int Rear() {
- if(head == tail)
- return -1;
- int T = tail - 1;
- if(T < 0)
- T = n;
- return a[T];
- }
- bool isEmpty() {
- return head == tail;
- }
- bool isFull() {
- return head == (tail+1)%(n+1);
- }
- private:
- int* a;
- int n;//个数
- int head;
- int tail;
- };
- /**
- * Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
- * MyCircularQueue* obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
- * bool param_1 = obj->enQueue(value);
- * bool param_2 = obj->deQueue();
- * int param_3 = obj->Front();
- * int param_4 = obj->Rear();
- * bool param_5 = obj->isEmpty();
- * bool param_6 = obj->isFull();
- */
如上就是 栈和队列 的所有知识,如果大家喜欢看此文章并且有收获,可以支持下 兔7 ,给 兔7 三连加关注,你的关注是对我最大的鼓励,也是我的创作动力~!
再次感谢大家观看,感谢大家支持!
-
相关阅读:
文档在线预览word、pdf、excel文件转html以实现文档在线预览
KMP算法详解(Python&Java代码)
mysql 存储引擎
redis no-appendfsync-on-rewrite
【第2章 Node.js基础】2.7 Node.js 的流(一) 可读流
文章组合生成-免费文章组合生成软件
给 「大模型初学者」 的 LLaMA 3 核心技术剖析
【无标题】
JAVA学习-基础部分【1】
3.21 小红书薯条改版了,都改了些什么呢?【玩赚小红书】
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_69725192/article/details/126449709
