-
Mybatis 缓存原理
Mybatis 缓存原理
本文来自拉钩 java 高薪训练营,如果文章写的不好,看不懂可以找我要课程视频,不收费。v:15774135883
- 只愿在编程道路上,寻求志同道合的码友。
1 Mybatis 缓存机制
Mybatis 提供了一级、二级缓存。
- 一级缓存:线程级别的缓存,也称为
本地缓存或sqlSession级别的缓存,一级缓存是默认存在的,同一个会话中,查询两次相同的操作就会从缓存中取。 - 二级缓存:
全局范围的缓存;除了当前sqlSession能用外,其他的也可以使用。二级缓存默认也是开启的,只需要在 mapper 文件中写一个即可实现,二级缓存的实现需要 pojo 实现序列化的接口,否则会出错
搭建工程
快速搭建一个项目,以便更加深入的了解原理。
- 创建一个普通 maven 项目即可。(就不做演示了)
- 依赖中的 mysql 版本换成你们数据库对应的版本,我的是 8.0
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatisgroupId> <artifactId>mybatisartifactId> <version>3.4.5version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> <version>8.0.25version> <scope>runtimescope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junitgroupId> <artifactId>junitartifactId> <version>4.12version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4jartifactId> <version>1.2.17version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4jgroupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12artifactId> <version>1.7.7version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-redisartifactId> <version>1.0.0-beta2version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId> <artifactId>pagehelperartifactId> <version>3.7.5version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.jsqlparsergroupId> <artifactId>jsqlparserartifactId> <version>0.9.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>tk.mybatisgroupId> <artifactId>mapperartifactId> <version>3.1.2version> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
实体类
@Table(name = "user") public class User implements Serializable { @Id //对应的是注解id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //设置主键的生成策略 private Integer id; private String username; // get set 省略 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
mapper
public interface IUserMapper { //更新用户 @Update("update user set username = #{username} where id = #{id}") public void updateUser(User user); //根据id查询用户 @Options(useCache = true) @Select({"select * from user where id = #{id}"}) public User findUserById(Integer id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
配置文件 sqlMapConfig.xml
DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <typeAliases> <package name="com.lagou.pojo"/> typeAliases> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///2022_xx_mybatis"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="317311"/> dataSource> environment> environments> <mappers> <package name="com.lagou.mapper"/> mappers> configuration>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
**输出日志: **log4j.properties
### direct log messages to stdout ### log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n ### direct messages to file mylog.log ### log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender log4j.appender.file.File=c:/mylog.log log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n ### set log levels - for more verbose logging change 'info' to 'debug' ### log4j.rootLogger=debug, stdout- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
测试类:
public class CacheTest { private IUserMapper userMapper; private SqlSession sqlSession; private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; @Before public void before() throws IOException { InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml"); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); } @Test public void test1(){ // 第一次查询id为1的用户 发出sql 查询的结果,存入缓存中 User user1 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); //第⼆次查询,由于是同⼀个sqlSession,会在缓存中查询结果 //如果有,则直接从缓存中取出来,不和数据库进⾏交互 User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); System.out.println(user1==user2); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
查看控制台打印情况:

- 同样是对 user 表进⾏两次查询,只不过两次查询之间进⾏了⼀次 update 操作。
@Test public void test2() { //第⼀次查询,发出sql语句,并将查询的结果放⼊缓存中 User u1 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(u1); //第⼆步进⾏了⼀次更新操作,sqlSession.commit() User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setUsername("tom"); userMapper.updateUser(user); //第⼆次查询,由于是同⼀个sqlSession.commit(),会清空缓存信息 //则此次查询也会发出sql语句 User u2 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(u2); sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
查看控制台打印情况:

总结
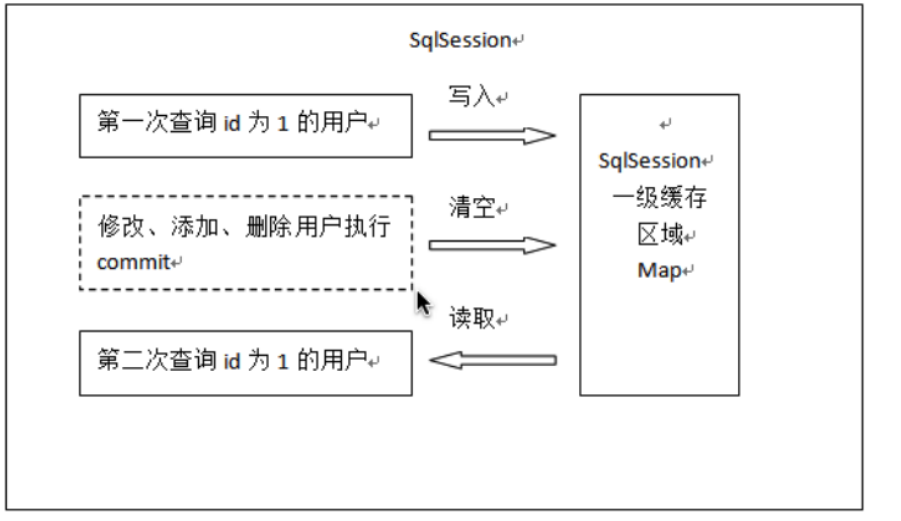
- 第⼀次发起查询⽤户 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,先去找
缓存中是否有 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,如果没有,从 数据库查询⽤户信息。得到⽤户信息,将⽤户信息存储到⼀级缓存中。 - 如果中间
sqlSession去执⾏commit操作(执⾏插⼊、更新、删除),则会清空SqlSession 中的 ⼀ 级缓存,这样做的⽬的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。 - 第⼆次发起查询⽤户 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,先去找缓存中是否有 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,缓存中有,直 接从 缓存中获取⽤户信息
一级缓存源码探究
⼀级缓存到底是什么?⼀级缓存什么时候被创建、⼀级缓存的⼯作流程是怎样的?带着如下问题来探究
- ⼤家可以这样想,上⾯我们⼀直提到⼀级缓存,那么提到⼀级缓存就绕不开 SqlSession,所以索性我们 就直接从 SqlSession,看看有没有创建缓存或者与缓存有关的属性或者⽅法

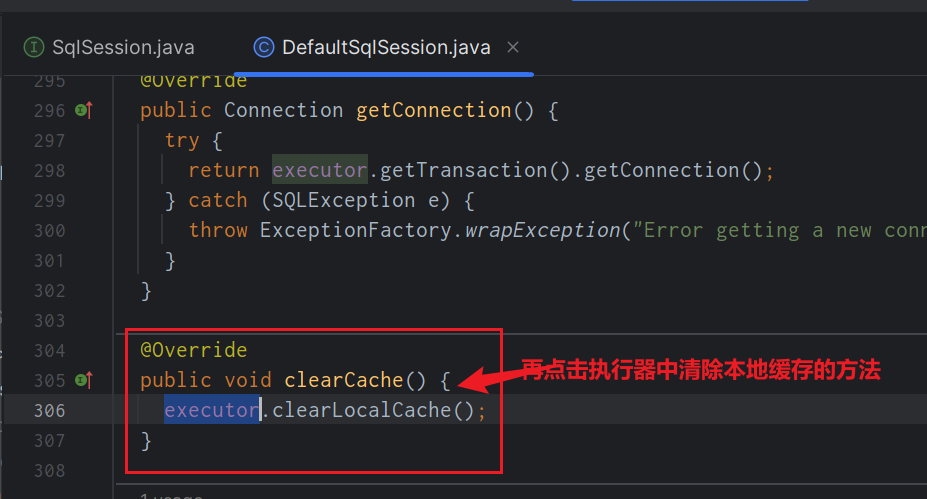
查看⼀圈,发现上述所有⽅法中,好像只有
clearCache()和缓存沾点关系,那么就直接从这个⽅法⼊⼿吧,分析源码时,我们要看它(此类)是谁,它的⽗类和⼦类分别⼜是谁,对如上关系了解了,你才会对这个类有更深的认识,分析了⼀圈,你可能会得到如下这个流程图
- 找到
clearCache()



也就是说,缓存其实就是 本地存放的⼀个 map 对象,每⼀个 SqISession 都会存放⼀个 map 对象的引⽤,那么这个 cache 是何 时创建的呢?

你觉得最有可能创建缓存的地⽅是哪⾥呢?我觉得是
Executor,为什么这么认为?因为 Executor 是 执⾏器,⽤来执⾏ SQL 请求,⽽且清除缓存的⽅法也在Executor中执⾏,所以很可能缓存的创建也很 有可 能在 Executor 中,看了⼀圈发现 Executor 中有⼀个 createCacheKey ⽅法,这个⽅法很像是创 建缓存的 ⽅法啊,跟进去看看,你发现 createCacheKey ⽅法是由 BaseExecutor 执⾏的,代码如下CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey(); //MappedStatement 的 id // id就是Sql语句的所在位置包名+类名+ SQL名称 cacheKey.update(ms.getId()); // offset 就是 0 cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset()); // limit 就是 Integer.MAXVALUE cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit()); //具体的SQL语句 cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql()); //后⾯是update 了 sql中带的参数 cacheKey.update(value); ... if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) { // issue #176 cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
创建缓存 key 会经过⼀系列的 update ⽅法,udate ⽅法由⼀个 CacheKey 这个对象来执⾏的,这个 update ⽅法最终由 updateList 的 list 来把五个值存进去,对照上⾯的代码和下⾯的图示,你应该能 理解 这五个值都是什么了?

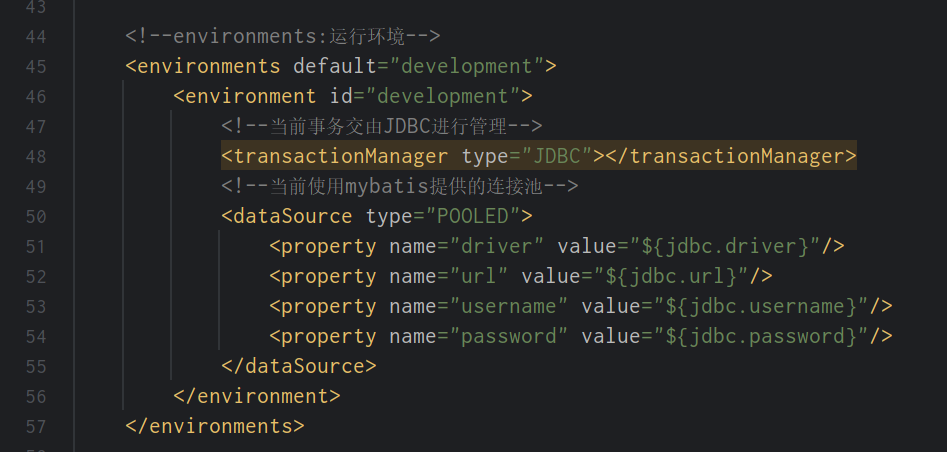
这⾥需要注意⼀下最后⼀个值,configuration.getEnvironment().getId()这是什么,这其实就是 定义在 mybatis-config.xml 中的标签,⻅如下。
那么我们回归正题,那么创建完缓存之后该⽤在何处呢?总不会凭空创建⼀个缓存不使⽤吧?绝对不会 的,经过我们对⼀级缓存的探究之后,我们发现⼀级缓存更多是⽤于查询操作,毕竟⼀级缓存也叫做查 询缓存吧,为什么叫查询缓存我们⼀会⼉说。我们先来看⼀下这个缓存到底⽤在哪了,我们跟踪到
BaseExecutor的 query ⽅法如下:
2 ⼆级缓存
⼆级缓存的原理和⼀级缓存原理⼀样,第⼀次查询,会将数据放⼊缓存中,然后第⼆次查询则会直接去 缓存中取。但是⼀级缓存是基于 sqlSession 的,⽽⼆级缓存是基于 mapper ⽂件的 namespace 的,也 就 是说多个 sqlSession 可以共享⼀个 mapper 中的⼆级缓存区域,并且如果两个 mapper 的 namespace 相 同,即使是两个 mapper,那么这两个 mapper 中执⾏ sql 查询到的数据也将存在相同的⼆级缓存区域 中
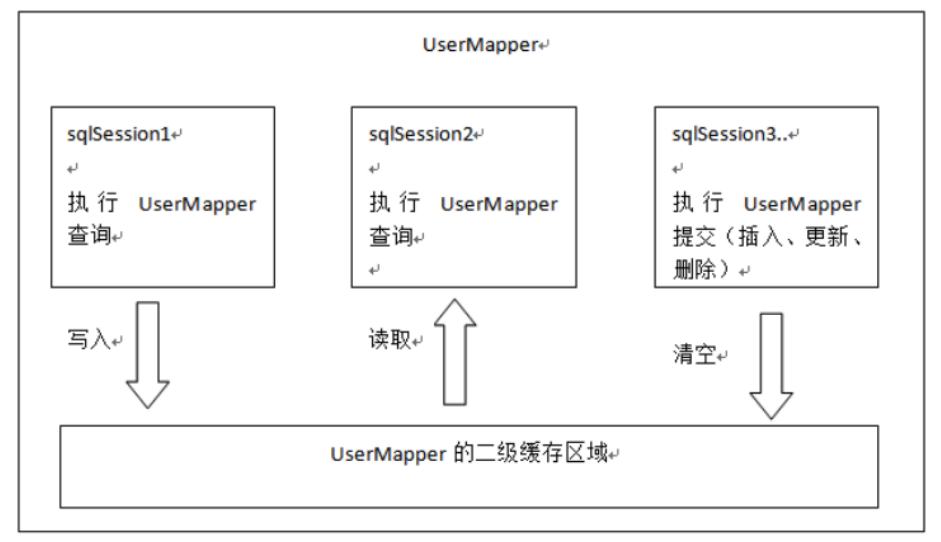
如何使⽤⼆级缓存
开启⼆级缓存 和⼀级缓存默认开启不⼀样,⼆级缓存需要我们⼿动开启 ⾸先在全局配置⽂件 sqlMapConfig.xml ⽂件中加⼊如下代码:
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> settings>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
其次在 UserMapper.xml ⽂件中开启 缓存
<cache>cache>- 1
- 2
像我们所使用的是注解开发,没有 mapper.xml 文件,可以用注解实现开启二级缓存
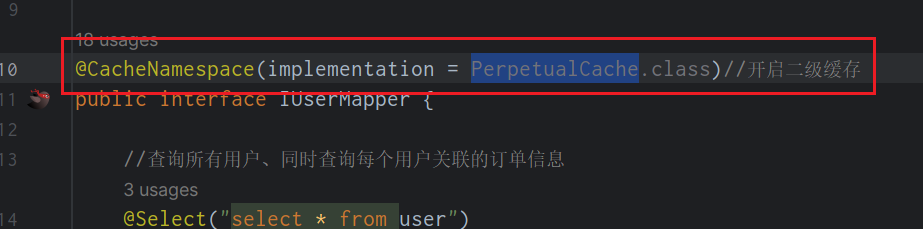
开启了⼆级缓存后,还需要将要
缓存的pojo实现Serializable接⼝,为了将缓存数据取出执⾏反序列化操作,因为⼆级缓存数据存储介质多种多样,不⼀定只存在内存中,有可能存在硬盘中,如果我们要再取 这个缓存的话,就需要反序列化了。所以 mybatis 中的pojo都去实现Serializable接⼝测试
⼀、测试⼆级缓存和 sqlSession ⽆关
@Test public void SecondLevelCache() { //根据 sqlSessionFactory 产⽣ session SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); IUserMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); IUserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); //第⼀次查询,发出sql语句,并将查询的结果放⼊缓存中 User user1 = mapper1.findUserById(1); sqlSession1.close(); //清空一级缓存 //第⼆次查询,即使sqlSession1已经关闭了,这次查询依然不发出sql语句 User user2 = mapper2.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user1 == user2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
可以看出上⾯两个不同的 sqlSession,第⼀个关闭了,第⼆次查询依然不发出 sql 查询语句
⼆、测试执⾏ commit()操作,⼆级缓存数据清空
@Test public void SecondLevelCache() { //根据 sqlSessionFactory 产⽣ session SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession3 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); IUserMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); IUserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); IUserMapper mapper3 = sqlSession3.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); //第⼀次查询,发出sql语句,并将查询的结果放⼊缓存中 User user1 = mapper1.findUserById(1); sqlSession1.close(); //清空一级缓存 User user2 = mapper2.findUserById(1); //执⾏更新操作,commit() User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setUsername("lisi"); mapper3.updateUser(user); sqlSession3.commit(); //第⼆次查询,由于上次更新操作,缓存数据已经清空(防⽌数据脏读),这⾥必须再次发出sql语 System.out.println(user1 == user2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
查看控制台情况:

useCache 和 flushCache
- userCache: 禁⽤⼆级缓存,直接从数 据 库中获取
- flushCache="true”属性,默认情况下为 true,即刷新缓存,如果改成 false 则 不 会刷新。使⽤缓存时如果⼿动修改数据库表中的查询数据会出现脏读。(一般不设置)
3 ⼆级缓存整合 redis
- 主要解决 分布式缓存
上⾯我们介绍了 mybatis ⾃带的⼆级缓存,但是这个缓存是单服务器⼯作,⽆法实现分布式缓存。 那么 什么是分布式缓存呢?假设现在有两个服务器 1 和 2,⽤户访问的时候访问了 1 服务器,查询后的缓 存就 会放在 1 服务器上,假设现在有个⽤户访问的是 2 服务器,那么他在 2 服务器上就⽆法获取刚刚那个 缓 存,如下图所示:

为了解决这个问题,就得找⼀个分布式的缓存,专⻔⽤来存储缓存数据的,这样不同的服务器要缓存数 据都往它那⾥存,取缓存数据也从它那⾥取,如下图所示
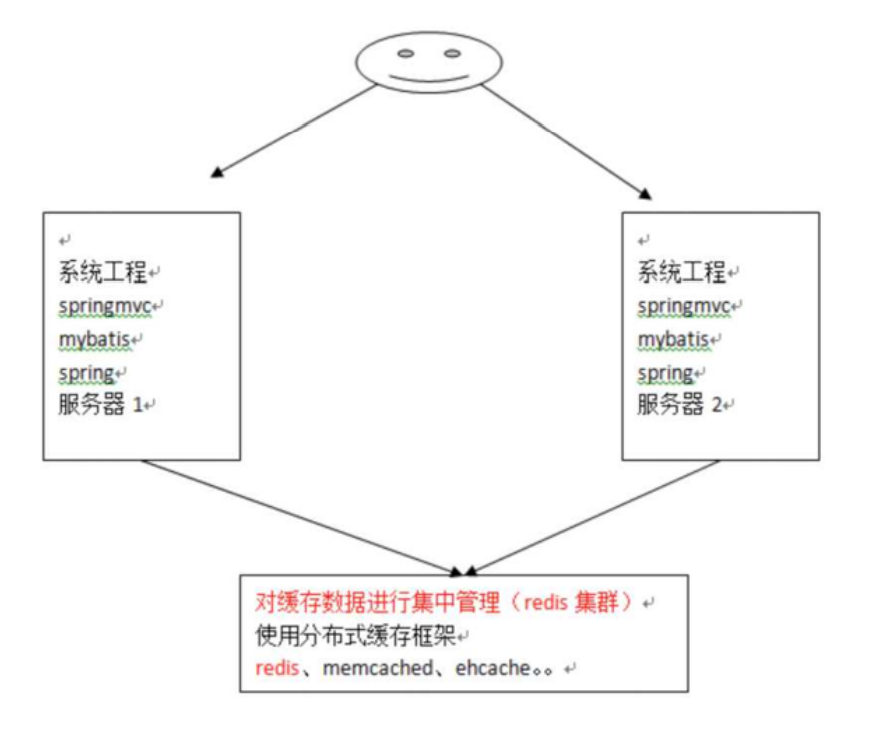
如上图所示,在⼏个不同的服务器之间,我们使⽤第三⽅缓存框架,将缓存都放在这个第三⽅框架中, 然后⽆论有多少台服务器,我们都能从缓存中获取数据。 这⾥我们介绍
mybatis与redis的整合。 刚刚提到过,mybatis提供了⼀个cache接⼝,如果要实现⾃⼰的缓存逻辑,实现cache接⼝开发即可。 mybatis 本身默认实现了⼀个,但是这个缓存的实现⽆法实现分布式缓存,所以我们要⾃⼰来实现。 redis 分布式缓存就可以,mybatis提供了⼀个针对cache接⼝的redis实现类,该类存在mybatis-redis包 中 实现添加依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-redisartifactId> <version>1.0.0-beta2version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
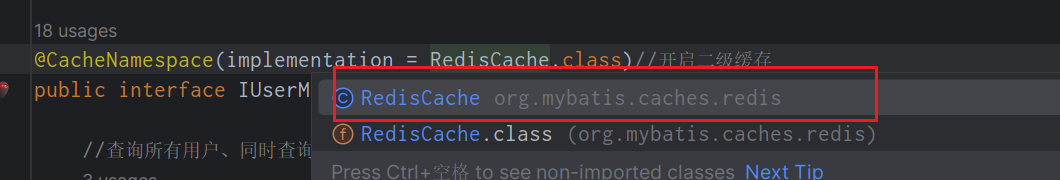
修改二级缓存实现 二级缓存
- 下面是 xml 的方式
- 但是我们文章是基于注解的方式,在 mapper 中修改
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.redis.RedisCache" />- 1
redis.properties
redis.host=localhost redis.port=6379 redis.connectionTimeout=5000 redis.password= redis.database=0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

测试:
执行一个没有清空二级缓存的操作,比如两次查询
- 可以看到 已经存储到redis中了。
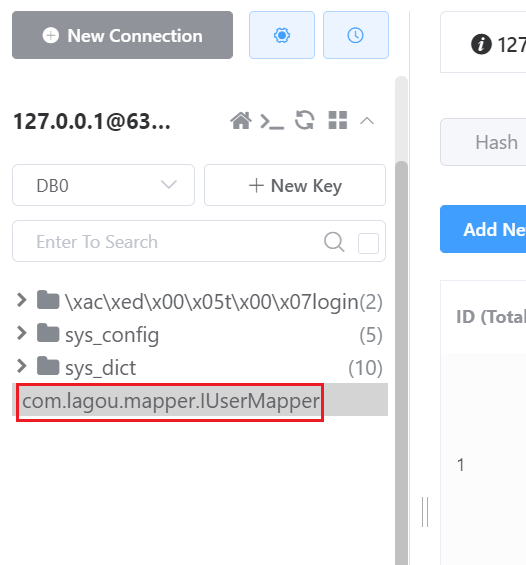

源码分析:
RedisCache和⼤家普遍实现Mybatis的缓存⽅案⼤同⼩异,⽆⾮是实现Cache接⼝,并使⽤jedis操作缓 存;不过该项⽬在设计细节上有⼀些区别;
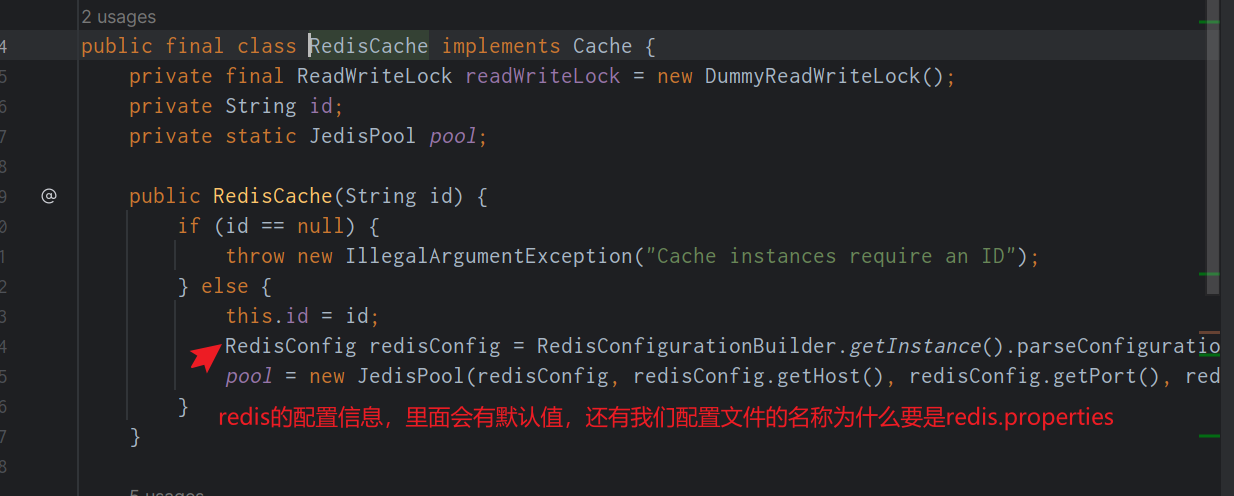
RedisCache在mybatis启动的时候,由MyBatis的CacheBuilder创建,创建的⽅式很简单,就是调⽤ RedisCache的带有String参数的构造⽅法,即RedisCache(String id);⽽在RedisCache的构造⽅法中, 调⽤了 RedisConfigu rationBuilder 来创建 RedisConfig 对象,并使⽤ RedisConfig 来创建JedisPool。 RedisConfig类继承了 JedisPoolConfig,并提供了 host,port等属性的包装,简单看⼀下RedisConfig的 属性

RedisConfig对象是由RedisConfigurationBuilder创建的,简单看下这个类的主要⽅法:
- 核⼼的⽅法就是parseConfiguration⽅法,该⽅法从classpath中读取⼀个redis.properties⽂件:

接下来看看Cache中最重要的两个⽅法:putObject和getObject,通过这两个⽅法来查看mybatis-redis 储存数据的格式:

可以很清楚的看到,mybatis-redis在存储数据的时候,是使⽤的hash结构,把cache的id作为这个hash 的key (cache的id在mybatis中就是mapper的namespace);这个mapper中的查询缓存数据作为 hash 的field,需要缓存的内容直接使⽤SerializeUtil存储,SerializeUtil和其他的序列化类差不多,负责 对象 的序列化和反序列化;**# Mybatis 缓存原理
本文来自拉钩 java 高薪训练营,如果文章写的不好,看不懂可以找我要课程视频,不收费。
- 只愿在编程道路上,寻求志同道合的码友。
1 Mybatis 缓存机制
Mybatis 提供了一级、二级缓存。
- 一级缓存:线程级别的缓存,也称为
本地缓存或sqlSession级别的缓存,一级缓存是默认存在的,同一个会话中,查询两次相同的操作就会从缓存中取。 - 二级缓存:
全局范围的缓存;除了当前sqlSession能用外,其他的也可以使用。二级缓存默认也是开启的,只需要在 mapper 文件中写一个即可实现,二级缓存的实现需要 pojo 实现序列化的接口,否则会出错
搭建工程
快速搭建一个项目,以便更加深入的了解原理。
- 创建一个普通 maven 项目即可。(就不做演示了)
- 依赖中的 mysql 版本换成你们数据库对应的版本,我的是 8.0

<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatisgroupId> <artifactId>mybatisartifactId> <version>3.4.5version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> <version>8.0.25version> <scope>runtimescope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junitgroupId> <artifactId>junitartifactId> <version>4.12version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4jartifactId> <version>1.2.17version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4jgroupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12artifactId> <version>1.7.7version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-redisartifactId> <version>1.0.0-beta2version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.pagehelpergroupId> <artifactId>pagehelperartifactId> <version>3.7.5version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.jsqlparsergroupId> <artifactId>jsqlparserartifactId> <version>0.9.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>tk.mybatisgroupId> <artifactId>mapperartifactId> <version>3.1.2version> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
实体类
@Table(name = "user") public class User implements Serializable { @Id //对应的是注解id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //设置主键的生成策略 private Integer id; private String username; // get set 省略 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
mapper
public interface IUserMapper { //更新用户 @Update("update user set username = #{username} where id = #{id}") public void updateUser(User user); //根据id查询用户 @Options(useCache = true) @Select({"select * from user where id = #{id}"}) public User findUserById(Integer id); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
配置文件 sqlMapConfig.xml
DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <typeAliases> <package name="com.lagou.pojo"/> typeAliases> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC">transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///2022_xx_mybatis"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="317311"/> dataSource> environment> environments> <mappers> <package name="com.lagou.mapper"/> mappers> configuration>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
**输出日志: **log4j.properties
### direct log messages to stdout ### log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.Target=System.out log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n ### direct messages to file mylog.log ### log4j.appender.file=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender log4j.appender.file.File=c:/mylog.log log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{ABSOLUTE} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n ### set log levels - for more verbose logging change 'info' to 'debug' ### log4j.rootLogger=debug, stdout- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
测试类:
public class CacheTest { private IUserMapper userMapper; private SqlSession sqlSession; private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; @Before public void before() throws IOException { InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml"); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream); sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); } @Test public void test1(){ // 第一次查询id为1的用户 发出sql 查询的结果,存入缓存中 User user1 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user1); //第⼆次查询,由于是同⼀个sqlSession,会在缓存中查询结果 //如果有,则直接从缓存中取出来,不和数据库进⾏交互 User user2 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user2); System.out.println(user1==user2); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
查看控制台打印情况:

- 同样是对 user 表进⾏两次查询,只不过两次查询之间进⾏了⼀次 update 操作。
@Test public void test2() { //第⼀次查询,发出sql语句,并将查询的结果放⼊缓存中 User u1 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(u1); //第⼆步进⾏了⼀次更新操作,sqlSession.commit() User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setUsername("tom"); userMapper.updateUser(user); //第⼆次查询,由于是同⼀个sqlSession.commit(),会清空缓存信息 //则此次查询也会发出sql语句 User u2 = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(u2); sqlSession.close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
查看控制台打印情况:

总结
- 第⼀次发起查询⽤户 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,先去找
缓存中是否有 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,如果没有,从 数据库查询⽤户信息。得到⽤户信息,将⽤户信息存储到⼀级缓存中。 - 如果中间
sqlSession去执⾏commit操作(执⾏插⼊、更新、删除),则会清空SqlSession 中的 ⼀ 级缓存,这样做的⽬的为了让缓存中存储的是最新的信息,避免脏读。 - 第⼆次发起查询⽤户 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,先去找缓存中是否有 id 为 1 的⽤户信息,缓存中有,直 接从 缓存中获取⽤户信息

一级缓存源码探究
⼀级缓存到底是什么?⼀级缓存什么时候被创建、⼀级缓存的⼯作流程是怎样的?带着如下问题来探究
- ⼤家可以这样想,上⾯我们⼀直提到⼀级缓存,那么提到⼀级缓存就绕不开 SqlSession,所以索性我们 就直接从 SqlSession,看看有没有创建缓存或者与缓存有关的属性或者⽅法

查看⼀圈,发现上述所有⽅法中,好像只有
clearCache()和缓存沾点关系,那么就直接从这个⽅法⼊⼿吧,分析源码时,我们要看它(此类)是谁,它的⽗类和⼦类分别⼜是谁,对如上关系了解了,你才会对这个类有更深的认识,分析了⼀圈,你可能会得到如下这个流程图
- 找到
clearCache()




也就是说,缓存其实就是 本地存放的⼀个 map 对象,每⼀个 SqISession 都会存放⼀个 map 对象的引⽤,那么这个 cache 是何 时创建的呢?

你觉得最有可能创建缓存的地⽅是哪⾥呢?我觉得是
Executor,为什么这么认为?因为 Executor 是 执⾏器,⽤来执⾏ SQL 请求,⽽且清除缓存的⽅法也在Executor中执⾏,所以很可能缓存的创建也很 有可 能在 Executor 中,看了⼀圈发现 Executor 中有⼀个 createCacheKey ⽅法,这个⽅法很像是创 建缓存的 ⽅法啊,跟进去看看,你发现 createCacheKey ⽅法是由 BaseExecutor 执⾏的,代码如下CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey(); //MappedStatement 的 id // id就是Sql语句的所在位置包名+类名+ SQL名称 cacheKey.update(ms.getId()); // offset 就是 0 cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset()); // limit 就是 Integer.MAXVALUE cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit()); //具体的SQL语句 cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql()); //后⾯是update 了 sql中带的参数 cacheKey.update(value); ... if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) { // issue #176 cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
创建缓存 key 会经过⼀系列的 update ⽅法,udate ⽅法由⼀个 CacheKey 这个对象来执⾏的,这个 update ⽅法最终由 updateList 的 list 来把五个值存进去,对照上⾯的代码和下⾯的图示,你应该能 理解 这五个值都是什么了?

这⾥需要注意⼀下最后⼀个值,configuration.getEnvironment().getId()这是什么,这其实就是 定义在 mybatis-config.xml 中的标签,⻅如下。

那么我们回归正题,那么创建完缓存之后该⽤在何处呢?总不会凭空创建⼀个缓存不使⽤吧?绝对不会 的,经过我们对⼀级缓存的探究之后,我们发现⼀级缓存更多是⽤于查询操作,毕竟⼀级缓存也叫做查 询缓存吧,为什么叫查询缓存我们⼀会⼉说。我们先来看⼀下这个缓存到底⽤在哪了,我们跟踪到
BaseExecutor的 query ⽅法如下:
2 ⼆级缓存
⼆级缓存的原理和⼀级缓存原理⼀样,第⼀次查询,会将数据放⼊缓存中,然后第⼆次查询则会直接去 缓存中取。但是⼀级缓存是基于 sqlSession 的,⽽⼆级缓存是基于 mapper ⽂件的 namespace 的,也 就 是说多个 sqlSession 可以共享⼀个 mapper 中的⼆级缓存区域,并且如果两个 mapper 的 namespace 相 同,即使是两个 mapper,那么这两个 mapper 中执⾏ sql 查询到的数据也将存在相同的⼆级缓存区域 中

如何使⽤⼆级缓存
开启⼆级缓存 和⼀级缓存默认开启不⼀样,⼆级缓存需要我们⼿动开启 ⾸先在全局配置⽂件 sqlMapConfig.xml ⽂件中加⼊如下代码:
<settings> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> settings>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
其次在 UserMapper.xml ⽂件中开启 缓存
<cache>cache>- 1
- 2
像我们所使用的是注解开发,没有 mapper.xml 文件,可以用注解实现开启二级缓存

开启了⼆级缓存后,还需要将要
缓存的pojo实现Serializable接⼝,为了将缓存数据取出执⾏反序列化操作,因为⼆级缓存数据存储介质多种多样,不⼀定只存在内存中,有可能存在硬盘中,如果我们要再取 这个缓存的话,就需要反序列化了。所以 mybatis 中的pojo都去实现Serializable接⼝测试
⼀、测试⼆级缓存和 sqlSession ⽆关
@Test public void SecondLevelCache() { //根据 sqlSessionFactory 产⽣ session SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); IUserMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); IUserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); //第⼀次查询,发出sql语句,并将查询的结果放⼊缓存中 User user1 = mapper1.findUserById(1); sqlSession1.close(); //清空一级缓存 //第⼆次查询,即使sqlSession1已经关闭了,这次查询依然不发出sql语句 User user2 = mapper2.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user1 == user2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
可以看出上⾯两个不同的 sqlSession,第⼀个关闭了,第⼆次查询依然不发出 sql 查询语句
⼆、测试执⾏ commit()操作,⼆级缓存数据清空
@Test public void SecondLevelCache() { //根据 sqlSessionFactory 产⽣ session SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); SqlSession sqlSession3 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); IUserMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); IUserMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); IUserMapper mapper3 = sqlSession3.getMapper(IUserMapper.class); //第⼀次查询,发出sql语句,并将查询的结果放⼊缓存中 User user1 = mapper1.findUserById(1); sqlSession1.close(); //清空一级缓存 User user2 = mapper2.findUserById(1); //执⾏更新操作,commit() User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setUsername("lisi"); mapper3.updateUser(user); sqlSession3.commit(); //第⼆次查询,由于上次更新操作,缓存数据已经清空(防⽌数据脏读),这⾥必须再次发出sql语 System.out.println(user1 == user2); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
查看控制台情况:

useCache 和 flushCache
- userCache: 禁⽤⼆级缓存,直接从数 据 库中获取
- flushCache="true”属性,默认情况下为 true,即刷新缓存,如果改成 false 则 不 会刷新。使⽤缓存时如果⼿动修改数据库表中的查询数据会出现脏读。(一般不设置)
3 ⼆级缓存整合 redis
- 主要解决 分布式缓存
上⾯我们介绍了 mybatis ⾃带的⼆级缓存,但是这个缓存是单服务器⼯作,⽆法实现分布式缓存。 那么 什么是分布式缓存呢?假设现在有两个服务器 1 和 2,⽤户访问的时候访问了 1 服务器,查询后的缓 存就 会放在 1 服务器上,假设现在有个⽤户访问的是 2 服务器,那么他在 2 服务器上就⽆法获取刚刚那个 缓 存,如下图所示:

为了解决这个问题,就得找⼀个分布式的缓存,专⻔⽤来存储缓存数据的,这样不同的服务器要缓存数 据都往它那⾥存,取缓存数据也从它那⾥取,如下图所示

如上图所示,在⼏个不同的服务器之间,我们使⽤第三⽅缓存框架,将缓存都放在这个第三⽅框架中, 然后⽆论有多少台服务器,我们都能从缓存中获取数据。 这⾥我们介绍
mybatis与redis的整合。 刚刚提到过,mybatis提供了⼀个cache接⼝,如果要实现⾃⼰的缓存逻辑,实现cache接⼝开发即可。 mybatis 本身默认实现了⼀个,但是这个缓存的实现⽆法实现分布式缓存,所以我们要⾃⼰来实现。 redis 分布式缓存就可以,mybatis提供了⼀个针对cache接⼝的redis实现类,该类存在mybatis-redis包 中 实现添加依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-redisartifactId> <version>1.0.0-beta2version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
修改二级缓存实现 二级缓存
- 下面是 xml 的方式
- 但是我们文章是基于注解的方式,在 mapper 中修改
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.redis.RedisCache" />- 1

redis.properties
redis.host=localhost redis.port=6379 redis.connectionTimeout=5000 redis.password= redis.database=0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

测试:
执行一个没有清空二级缓存的操作,比如两次查询
- 可以看到 已经存储到redis中了。


源码分析:
RedisCache和⼤家普遍实现Mybatis的缓存⽅案⼤同⼩异,⽆⾮是实现Cache接⼝,并使⽤jedis操作缓 存;不过该项⽬在设计细节上有⼀些区别;

RedisCache在mybatis启动的时候,由MyBatis的CacheBuilder创建,创建的⽅式很简单,就是调⽤ RedisCache的带有String参数的构造⽅法,即RedisCache(String id);⽽在RedisCache的构造⽅法中, 调⽤了 RedisConfigu rationBuilder 来创建 RedisConfig 对象,并使⽤ RedisConfig 来创建JedisPool。 RedisConfig类继承了 JedisPoolConfig,并提供了 host,port等属性的包装,简单看⼀下RedisConfig的 属性

RedisConfig对象是由RedisConfigurationBuilder创建的,简单看下这个类的主要⽅法:
- 核⼼的⽅法就是parseConfiguration⽅法,该⽅法从classpath中读取⼀个redis.properties⽂件:

接下来看看Cache中最重要的两个⽅法:putObject和getObject,通过这两个⽅法来查看mybatis-redis 储存数据的格式:

可以很清楚的看到,mybatis-redis在存储数据的时候,是使⽤的hash结构,把cache的id作为这个hash 的key (cache的id在mybatis中就是mapper的namespace);这个mapper中的查询缓存数据作为 hash 的field,需要缓存的内容直接使⽤SerializeUtil存储,SerializeUtil和其他的序列化类差不多,负责 对象 的序列化和反序列化;**
-
相关阅读:
定时任务调度(crond)
神经网络rnn是什么意思,RNN神经网络基本原理
Centos7-pgsql 11.6 安装
TiDB 中的视图功能
YOLO V1详解
Echarts案例网站(由于https://www.makeapie.com/关闭了,所以找了一些替代的)
YOLOv8改进:HIC-YOLOv8复现魔改HIC-YOLOv5,助力小目标检测(Small Object Detection)
[含lw+源码等]S2SH学生会/社团活动管理系统[包运行成功]适合计算机毕业设计前端毕设程序设计
[element] el-menu 收起展开的子菜单
element 复杂表格渲染(1)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_50975965/article/details/126163587