-
Ribbon学习笔记一

使用Ribbon,主要就是RestTemplate的使用。
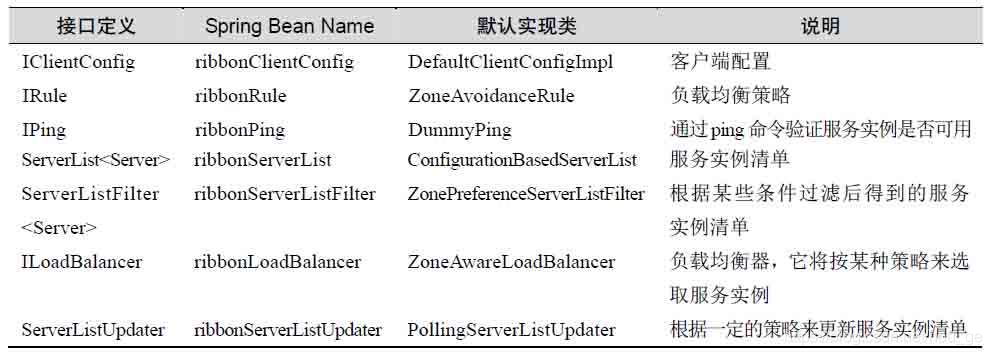
IClientConfig是Ribbon客户端的配置,我们可以通过它配置Ribbon相关的内容。IRule是负载均衡策略接口,也就是说,具体的负载均衡是通过它来提供算法的。IPing接口能判断服务实例是否可用。服务实例存在上线、下线和故障等多种可能,通过IPing接口能判定服务实例是否可用。ServerList是从Eureka服务端拉取服务实例清单,其中包含注册过的服务实例(包括可用的和不可用的)。ServerListFilter是服务实例过滤清单,一般过滤条件包含这么几种:实例是否可用、负载是否过大、服务版本选择等,通过这些过滤条件就可以选中合适的实例了。ILoadBalancer负载均衡器,它通过IRule接口提供的算法来选取服务实例;ServerListUpdater属于服务实例列表更新。
public interface ServiceInstanceChooser { //这个方法的参数serviceId指代的是微服务的ID,也就是实例的配置项spring.application.name,通过它根据一定的策略能返回一个具体的微服务实例 ServiceInstance choose(String serviceId); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser { <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException; <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException; URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
因为LoadBalancerClient接口扩展了ServiceInstanceChooser接口,所以拥有了choose(String serviceId)方法。
- execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest request):根据serviceId找到具体的服务实例执行请求。
- execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance,LoadBalancerRequest request):根据serviceId和serviceInstance(服务实例)执行请求。
- URI reconstructURI(ServiceInstance instance, URI original):根据当前给出的URI重构可用的URL。
RibbonLoadBalancerClient
第一个execute()方法
@Override public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { return execute(serviceId, request, null); } public <T> T execute(String serviceId, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request, Object hint) throws IOException { //获取负责均衡器 ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(serviceId); //根据负载均衡器获取具体的服务实例 Server server = getServer(loadBalancer, hint); if (server == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId); } //包装成RibbonServer 对象 RibbonServer ribbonServer = new RibbonServer(serviceId, server, isSecure(server, serviceId), serverIntrospector(serviceId).getMetadata(server)); //调用另外一个execute()方法执行 return execute(serviceId, ribbonServer, request); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
getLoadBalancer()方法
protected ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String serviceId) { return this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancer(serviceId); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
//SpringClientFactory.java public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String name) { return getInstance(name, ILoadBalancer.class); } @Override public <C> C getInstance(String name, Class<C> type) { C instance = super.getInstance(name, type); if (instance != null) { return instance; } IClientConfig config = getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class); return instantiateWithConfig(getContext(name), type, config); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
//NamedContextFactory.java public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name); if (BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context, type).length > 0) { return context.getBean(type); } return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
getServer()方法
这里获取具体微服务实例的方法是getServer,使用的是负载均衡器(ILoadBalancer)的chooseServer方法,而非LoadBalancerClient所定义的choose方法。
protected Server getServer(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, Object hint) { if (loadBalancer == null) { return null; } // Use 'default' on a null hint, or just pass it on? return loadBalancer.chooseServer(hint != null ? hint : "default"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
静态内部类RibbonServer
public static class RibbonServer implements ServiceInstance { private final String serviceId; private final Server server; private final boolean secure; private Map<String, String> metadata; public RibbonServer(String serviceId, Server server) { this(serviceId, server, false, Collections.emptyMap()); } public RibbonServer(String serviceId, Server server, boolean secure, Map<String, String> metadata) { this.serviceId = serviceId; this.server = server; this.secure = secure; this.metadata = metadata; } //省略getter or setter方法 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
第二个execute()方法
@Override public <T> T execute(String serviceId, ServiceInstance serviceInstance, LoadBalancerRequest<T> request) throws IOException { Server server = null; if (serviceInstance instanceof RibbonServer) { server = ((RibbonServer) serviceInstance).getServer(); } if (server == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("No instances available for " + serviceId); } //创建分析记录器 RibbonLoadBalancerContext context = this.clientFactory .getLoadBalancerContext(serviceId); RibbonStatsRecorder statsRecorder = new RibbonStatsRecorder(context, server); try { //将请求发送到具体的服务实例上 T returnVal = request.apply(serviceInstance); //记录请求结果,用来统计分析这次请求,对服务器的情况做一定的分析 statsRecorder.recordStats(returnVal); return returnVal; } // catch IOException and rethrow so RestTemplate behaves correctly catch (IOException ex) { statsRecorder.recordStats(ex); throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { statsRecorder.recordStats(ex); ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex); } return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器
Ribbon中提供了拦截器LoadBalancerInterceptor,对标注@LoadBalanced注解的RestTemplate进行拦截,然后植入LoadBalancerClient的逻辑。
public class LoadBalancerInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor { //负载均衡器 private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer; //创建LoadBalancerRequest的工厂类 private LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory; //构造函数 public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) { this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer; this.requestFactory = requestFactory; } public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) { // for backwards compatibility this(loadBalancer, new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancer)); } //拦截器方法 @Override public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body, final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException { final URI originalUri = request.getURI(); String serviceName = originalUri.getHost(); Assert.state(serviceName != null, "Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri); //调用负载均衡器的execute()方法 return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, this.requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration配置类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class) @ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class) public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration { //维护被@LoadBalanced标注的对象 @LoadBalanced @Autowired(required = false) private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList(); @Autowired(required = false) private List<LoadBalancerRequestTransformer> transformers = Collections.emptyList(); @Bean public SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializerDeprecated( final ObjectProvider<List<RestTemplateCustomizer>> restTemplateCustomizers) { return () -> restTemplateCustomizers.ifAvailable(customizers -> { for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) { for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) { customizer.customize(restTemplate); } } }); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public LoadBalancerRequestFactory loadBalancerRequestFactory( LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient) { return new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancerClient, this.transformers); } @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate") static class LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig { //创建LoadBalancerInterceptor对象,这样就存在了拦截器,用于拦截相应的被标注了@LoadBalanced的RestTemplate对象。 @Bean public LoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor( LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) { return new LoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, requestFactory); } //创建RestTemplateCustomizer对象,并且将拦截器设置到已有的拦截列表中,这样LoadBalancerInterceptor对象就可以拦截RestTemplate对象了。 @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer( final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) { return restTemplate -> { List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>( restTemplate.getInterceptors()); list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor); restTemplate.setInterceptors(list); }; } } /** * Auto configuration for retry mechanism. */ @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass(RetryTemplate.class) public static class RetryAutoConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public LoadBalancedRetryFactory loadBalancedRetryFactory() { return new LoadBalancedRetryFactory() { }; } } /** * Auto configuration for retry intercepting mechanism. */ @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass(RetryTemplate.class) public static class RetryInterceptorAutoConfiguration { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor( LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient, LoadBalancerRetryProperties properties, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory, LoadBalancedRetryFactory loadBalancedRetryFactory) { return new RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, properties, requestFactory, loadBalancedRetryFactory); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer( final RetryLoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) { return restTemplate -> { List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>( restTemplate.getInterceptors()); list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor); restTemplate.setInterceptors(list); }; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
负载均衡器
在前面的execute()方法中,通过getLoadBalancer()方法获取到了负载均衡器,即ILoadBalancer实现类的对象。
protected ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String serviceId) { return this.clientFactory.getLoadBalancer(serviceId); }- 1
- 2
- 3
ILoadBalancer 接口
用于选择具体实例。
public interface ILoadBalancer { //新增服务实例集合 public void addServers(List<Server> newServers); //选择服务实例 public Server chooseServer(Object key); //标记服务实例下线 public void markServerDown(Server server); //获取服务实例集合,已标记弃用 @Deprecated public List<Server> getServerList(boolean availableOnly); //获取正常可用的服务实例集合 public List<Server> getReachableServers(); //获取全部的服务实例集合 public List<Server> getAllServers(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15

选择实例 chooseServer()方法
主要用来选择服务实例,底层是通过IRule实现类的choose()方法选择服务实例。在该类中,默认使用的IRule实现类是RoundRobinRule,默认采用的是轮询策略。
//BaseLoadBalancer.java //返回服务实例的ID public String choose(Object key) { if (rule == null) { return null; } else { try { Server svr = rule.choose(key); return ((svr == null) ? null : svr.getId()); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server", name, e); return null; } } } //返回服务实例 public Server chooseServer(Object key) { //获取计数器 if (counter == null) { counter = createCounter(); } //计数器+1 counter.increment(); if (rule == null) { return null; } else { try { //根据路由策略,选择符合要求的服务实例 return rule.choose(key); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e); return null; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer类实现chooseServer()方法,该方法实现主要增加了根据负载阈值和故障阈值筛选Zone可用列表的逻辑。
//ZoneAwareLoadBalancer.java @Override public Server chooseServer(Object key) { //如果不存在Zone的概念,且获取的Zone的数量小于等于1,则只需父类的chooseServer()方法 if (!ENABLED.get() || getLoadBalancerStats().getAvailableZones().size() <= 1) { logger.debug("Zone aware logic disabled or there is only one zone"); return super.chooseServer(key); } Server server = null; try { //获取负载均衡器的统计数据 LoadBalancerStats lbStats = getLoadBalancerStats(); //获取当前负载均衡器中所有Zone的快照,用于负载均衡器算法 Map<String, ZoneSnapshot> zoneSnapshot = ZoneAvoidanceRule.createSnapshot(lbStats); logger.debug("Zone snapshots: {}", zoneSnapshot); //安装一定比例的阈值(默认20%)进行过滤,筛除掉负载最高的Zone if (triggeringLoad == null) { triggeringLoad = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty( "ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".triggeringLoadPerServerThreshold", 0.2d); } //按照故障率筛选Zone列表 if (triggeringBlackoutPercentage == null) { triggeringBlackoutPercentage = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty( "ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".avoidZoneWithBlackoutPercetage", 0.99999d); } //根据负载阈值和故障阈值,筛选可用的Zone列表 Set<String> availableZones = ZoneAvoidanceRule.getAvailableZones(zoneSnapshot, triggeringLoad.get(), triggeringBlackoutPercentage.get()); logger.debug("Available zones: {}", availableZones); //如果存在可用Zone,则筛选除zone,然后再使用BaseLoadBalancer 负载均衡器的chooseServer()方法,筛选出对应的服务实例。 if (availableZones != null && availableZones.size() < zoneSnapshot.keySet().size()) { String zone = ZoneAvoidanceRule.randomChooseZone(zoneSnapshot, availableZones); logger.debug("Zone chosen: {}", zone); if (zone != null) { BaseLoadBalancer zoneLoadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(zone); server = zoneLoadBalancer.chooseServer(key); } } } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Error choosing server using zone aware logic for load balancer={}", name, e); } if (server != null) { return server; } else { logger.debug("Zone avoidance logic is not invoked."); return super.chooseServer(key); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 判断是否启用了Zone的功能,如果没有Zone或者是Zone的数量只有1个,就采用BaseLoadBalancer的chooseServer方法来选择具体的服务,结束流程。
- 按照负载阈值来排除Zone,排除最高负载20%的Zone。
- 按照故障率阈值来排除Zone,排除故障率大于99.999%的Zone。
- 如果以上步骤都存在可用Zone,就采用随机算法获取Zone,选中Zone后,再通过负载均衡器(zoneLoadBalancer)的chooseServer方法选择服务。
- 如果Zone选择失败,就采用BaseLoadBalancer的chooseServer来选择服务实例。
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer作为默认负载均衡器的加载方式
在Spring Boot自动配置的情况下,会默认使用ZoneAwareLoadBalancer作为负载均衡器,创建该对象的过程可以看到org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClientConfiguration的源码。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @EnableConfigurationProperties @Import({ HttpClientConfiguration.class, OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class, RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class }) public class RibbonClientConfiguration { /** * Ribbon client default connect timeout. */ public static final int DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 1000; /** * Ribbon client default read timeout. */ public static final int DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT = 1000; /** * Ribbon client default Gzip Payload flag. */ public static final boolean DEFAULT_GZIP_PAYLOAD = true; @RibbonClientName private String name = "client"; // TODO: maybe re-instate autowired load balancers: identified by name they could be // associated with ribbon clients @Autowired private PropertiesFactory propertiesFactory; @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public IClientConfig ribbonClientConfig() { DefaultClientConfigImpl config = new DefaultClientConfigImpl(); config.loadProperties(this.name); config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout, DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT); config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout, DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT); config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.GZipPayload, DEFAULT_GZIP_PAYLOAD); return config; } //默认的负载均衡策略,ZoneAvoidanceRule @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public IRule ribbonRule(IClientConfig config) { if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IRule.class, name)) { return this.propertiesFactory.get(IRule.class, config, name); } ZoneAvoidanceRule rule = new ZoneAvoidanceRule(); rule.initWithNiwsConfig(config); return rule; } //验证服务器是否可用的IPing实现为DummyPing @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public IPing ribbonPing(IClientConfig config) { if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IPing.class, name)) { return this.propertiesFactory.get(IPing.class, config, name); } return new DummyPing(); } //服务实例清单 ConfigurationBasedServerList @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config) { if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, name)) { return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, name); } ConfigurationBasedServerList serverList = new ConfigurationBasedServerList(); serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config); return serverList; } //服务实例清单更新器,根据一定策略更新服务实例清单。PollingServerListUpdater @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ServerListUpdater ribbonServerListUpdater(IClientConfig config) { return new PollingServerListUpdater(config); } //负载均衡器,默认ZoneAwareLoadBalancer @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config, ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter, IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) { if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) { return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name); } return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList, serverListFilter, serverListUpdater); } //服务实例清单过滤器,ZonePreferenceServerListFilter @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public ServerListFilter<Server> ribbonServerListFilter(IClientConfig config) { if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerListFilter.class, name)) { return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerListFilter.class, config, name); } ZonePreferenceServerListFilter filter = new ZonePreferenceServerListFilter(); filter.initWithNiwsConfig(config); return filter; } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public RibbonLoadBalancerContext ribbonLoadBalancerContext(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, IClientConfig config, RetryHandler retryHandler) { return new RibbonLoadBalancerContext(loadBalancer, config, retryHandler); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public RetryHandler retryHandler(IClientConfig config) { return new DefaultLoadBalancerRetryHandler(config); } @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector() { return new DefaultServerIntrospector(); } @PostConstruct public void preprocess() { setRibbonProperty(name, DeploymentContextBasedVipAddresses.key(), name); } static class OverrideRestClient extends RestClient { private IClientConfig config; private ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector; protected OverrideRestClient(IClientConfig config, ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector) { super(); this.config = config; this.serverIntrospector = serverIntrospector; initWithNiwsConfig(this.config); } @Override public URI reconstructURIWithServer(Server server, URI original) { URI uri = updateToSecureConnectionIfNeeded(original, this.config, this.serverIntrospector, server); return super.reconstructURIWithServer(server, uri); } @Override protected Client apacheHttpClientSpecificInitialization() { ApacheHttpClient4 apache = (ApacheHttpClient4) super.apacheHttpClientSpecificInitialization(); apache.getClientHandler().getHttpClient().getParams().setParameter( ClientPNames.COOKIE_POLICY, CookiePolicy.IGNORE_COOKIES); return apache; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
负载均衡策略
前面我们知道在负载均衡器中,选择服务的时候,实际上是由负载均衡策略负责的。


RoundRobinRule
RoundRobinRule提供了轮询策略,实际中使用最多的负载均衡策略。
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { //如果负载均衡器为空,则直接返回 if (lb == null) { log.warn("no load balancer"); return null; } Server server = null; //循环次数计数 int count = 0; //当服务实例为null,且循环次数小于10次时 while (server == null && count++ < 10) { //通过负载均衡器,获取可用服务实例清单 List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers(); //获取全部服务实例清单 List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers(); //可用和全部服务实例的个数 int upCount = reachableServers.size(); int serverCount = allServers.size(); if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) { log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb); return null; } //轮询策略,下一个需要获取到的服务实例的序号 int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount); server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex); //如果获取的服务实例为null,则线程让步,继续下一次的循环 if (server == null) { /* Transient. */ Thread.yield(); continue; } //服务实例可用(已经启动完成),则直接返回 if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) { return (server); } // 如果服务实例不可用,则重置为null,进入下一次循环 server = null; } //如果循环超过10次,还没有获取到可用服务实例,则退出 if (count >= 10) { log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: " + lb); } return server; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
程序将生成一个线程安全的整数,然后加1并取模来确定一个下标(index)以获取服务。
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) { for (;;) { int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get(); int next = (current + 1) % modulo; if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next)) return next; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
RetryRule
RetryRule主要是增加了重试机制,获取服务实例的逻辑还是通过其他负载均衡策略(在RetryRule中为子策略)完成。
//默认子策略,即实际用来选取服务实例的策略,默认是轮询 IRule subRule = new RoundRobinRule(); //最大尝试时间戳 500毫秒 long maxRetryMillis = 500; public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { //请求时间,即进入该方法的时间 long requestTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //截止时间,即重试的截止时间点(当前时间+maxRetryMillis ) long deadline = requestTime + maxRetryMillis; Server answer = null; //子策略获取服务实例 answer = subRule.choose(key); //如果获取服务实例为null 或不可用,且当前时间没有超过截止时间 if (((answer == null) || (!answer.isAlive())) && (System.currentTimeMillis() < deadline)) { //设置线程终止时间 InterruptTask task = new InterruptTask(deadline - System.currentTimeMillis()); //在线程终止前(包括获取到可用服务实例),不停尝试获取服务实例 while (!Thread.interrupted()) { answer = subRule.choose(key); if (((answer == null) || (!answer.isAlive())) && (System.currentTimeMillis() < deadline)) { /* pause and retry hoping it's transient */ Thread.yield(); } else {//表示获取到了可用服务实例 break; } } //退出线程任务 task.cancel(); } //如果通过重试,还是没有获取到可用服务实例,则返回null if ((answer == null) || (!answer.isAlive())) { return null; } else { return answer; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
public class InterruptTask extends TimerTask { static Timer timer = new Timer("InterruptTimer", true); protected Thread target = null; public InterruptTask(long millis) { target = Thread.currentThread(); timer.schedule(this, millis); } /* Auto-scheduling constructor */ public InterruptTask(Thread target, long millis) { this.target = target; timer.schedule(this, millis); } public boolean cancel() { try { /* This shouldn't throw exceptions, but... */ return super.cancel(); } catch (Exception e) { return false; } } public void run() { if ((target != null) && (target.isAlive())) { target.interrupt(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
WeightedResponseTimeRule
按响应时间权重加权轮询(WeightedResponseTimeRule),是通过一个后台线程来统计分析各个服务的响应时间。该类是轮询策略RoundRobinRule的一个实现类。
首先是内部类ServerWeight,用来维护每个服务实例的权重。该类就一个maintainWeights()方法,具体实现如下:
class ServerWeight { public void maintainWeights() { //获取负载均衡器 ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer(); if (lb == null) { return; } //如果被其他线程更占用,则放弃本次计算 if (!serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) { return; } try { logger.info("Weight adjusting job started"); //获取负载均衡器的统计分析类LoadBalancerStats AbstractLoadBalancer nlb = (AbstractLoadBalancer) lb; LoadBalancerStats stats = nlb.getLoadBalancerStats(); if (stats == null) { // no statistics, nothing to do return; } //总平均响应时间 double totalResponseTime = 0; // 变量所有的服务实例,计算总平均响应时间 for (Server server : nlb.getAllServers()) { // 获取服务实例状态对象 ServerStats ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server); //累计平均响应时间 totalResponseTime += ss.getResponseTimeAvg(); } // 计算服务实例权重值 Double weightSoFar = 0.0; //保存服务实例清单各个实例的权重值 List<Double> finalWeights = new ArrayList<Double>(); //遍历 for (Server server : nlb.getAllServers()) { // 获取服务实例状态对象 ServerStats ss = stats.getSingleServerStat(server); //服务实例的权重值:weightSoFar + 总平均响应时间totalResponseTime - 当前服务实例的响应时间。因此,当前服务实例响应时间越长,权重会越小 double weight = totalResponseTime - ss.getResponseTimeAvg(); weightSoFar += weight; finalWeights.add(weightSoFar); } //设置权重值到变量中,ListaccumulatedWeights = new ArrayList setWeights(finalWeights); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Error calculating server weights", e); } finally { //并发判断,执行完后,设置false,运行其他线程继续使用 serverWeightAssignmentInProgress.set(false); } } }(); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
初始化方法initialize(),主要用来初始化服务实例清单中的权重值,通过定时任务DynamicServerWeightTask定期刷新,最终还是通过内部类ServerWeight 实现。
void initialize(ILoadBalancer lb) { if (serverWeightTimer != null) { serverWeightTimer.cancel(); } //创建计算权重的线程,并定期执行,默认周期为30s。 serverWeightTimer = new Timer("NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-" + name, true); serverWeightTimer.schedule(new DynamicServerWeightTask(), 0, serverWeightTaskTimerInterval); // 初始化时执行一次,因为serverWeightTimer定时器没有延时直接执行,所以该调用或定期任务的第一次调用可能只会执行其中一个 ServerWeight sw = new ServerWeight(); sw.maintainWeights(); //关闭定时器任务 Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(new Runnable() { public void run() { logger .info("Stopping NFLoadBalancer-serverWeightTimer-" + name); serverWeightTimer.cancel(); } })); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
class DynamicServerWeightTask extends TimerTask { public void run() { ServerWeight serverWeight = new ServerWeight(); try { serverWeight.maintainWeights(); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Error running DynamicServerWeightTask for {}", name, e); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
最后,还是choose()方法:
@edu.umd.cs.findbugs.annotations.SuppressWarnings(value = "RCN_REDUNDANT_NULLCHECK_OF_NULL_VALUE") @Override public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { if (lb == null) {//如果负载均衡器为null,则直接返回 return null; } Server server = null; //循环,获取服务实例 while (server == null) { // 获取最新的服务实例清单的权重集合 List<Double> currentWeights = accumulatedWeights; if (Thread.interrupted()) {//线程终止,直接返回 return null; } //全部服务实例清单 List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers(); int serverCount = allList.size(); //服务实例清单为null,则直接返回null if (serverCount == 0) { return null; } int serverIndex = 0; // 获取最大的权重值,默认0 double maxTotalWeight = currentWeights.size() == 0 ? 0 : currentWeights.get(currentWeights.size() - 1); // 如果权重集合没有被初始化或权重集合和当前服务实例数量不匹配,则选用父类的策略选择服务实例 if (maxTotalWeight < 0.001d || serverCount != currentWeights.size()) { server = super.choose(getLoadBalancer(), key); if(server == null) { return server; } } else { // 尝试一个随机数 double randomWeight = random.nextDouble() * maxTotalWeight; // pick the server index based on the randomIndex int n = 0; //循环获取符合要求的服务实例序号 for (Double d : currentWeights) { if (d >= randomWeight) { serverIndex = n; break; } else { n++; } } //根据服务序号,获取服务实例 server = allList.get(serverIndex); } if (server == null) { /* Transient. */ Thread.yield(); continue; } if (server.isAlive()) { return (server); } // Next. server = null; } return server; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
ZoneAvoidanceRule
ZoneAvoidanceRule是一种先过滤后执行的策略。
ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule类包含了一个RoundRobinRule 负载均衡策略。
public class ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule { RoundRobinRule roundRobinRule = new RoundRobinRule(); @Override public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) { roundRobinRule = new RoundRobinRule(); } @Override public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb) { super.setLoadBalancer(lb); roundRobinRule.setLoadBalancer(lb); } @Override public Server choose(Object key) { if (roundRobinRule != null) { return roundRobinRule.choose(key); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "This class has not been initialized with the RoundRobinRule class"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
PredicateBasedRule 主要增加了过滤逻辑
public abstract class PredicateBasedRule extends ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule { public abstract AbstractServerPredicate getPredicate(); @Override public Server choose(Object key) { ILoadBalancer lb = getLoadBalancer(); Optional<Server> server = getPredicate().chooseRoundRobinAfterFiltering(lb.getAllServers(), key); if (server.isPresent()) { return server.get(); } else { return null; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
ZoneAvoidanceRule类主要增加了选择Zone的相关逻辑。其中,首先创建了两个过滤断言(Predicate),一个是Zone断言(ZoneAvoidancePredicate),另一个是可用性断言(AvailabilityPredicate),然后它们组合起来形成组合过滤断言(CompositePredicate)。ZoneAvoidancePredicate的作用是找到那些性能较差的Zone,然后将其排除在外,随机选择性能较好的Zone。AvailabilityPredicate的作用是确定服务是否被熔断或者负载过大,超过临界值,如果没有这样的情况则返回该服务。CompositePredicate的作用是组合ZoneAvoidancePredicate和AvailabilityPredicate,先使用ZoneAvoidancePredicate进行过滤,然后再使用AvailabilityPredicate进行过滤,这样就能得到性能较高的可用服务了
-
相关阅读:
R语言使用colSums函数和is.na函数统计dataframe数据中每个数据列中包含的缺失值的个数
【Visual Leak Detector】配置项 ForceIncludeModules
PRCV 2023 - Day2
gopacket reassembly源码分析
关于 Spring Boot 自动装配你知道多少?
宽字节注入
spring 注解练习
纳米/荧光/磷脂/荧光探针/聚合物/化合物/磁性纳米粒子修饰AIE微球相关研究
OSPF —— LSA-3
C#中的as和is
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/hou_ge/article/details/112035281
