-
【数据结构入门_链表】 Leetcode 141. 环形链表
原题连接:Leetcode 141.Linked List Cycle
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail’s next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return
trueif there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, returnfalse.Example 1:
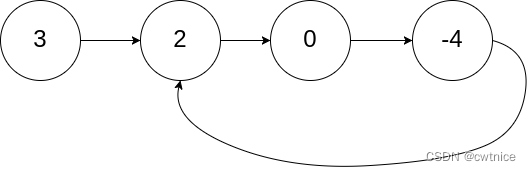
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 Output: true Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).- 1
- 2
- 3
Example 2:
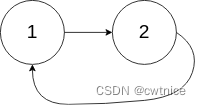
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0 Output: true Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.- 1
- 2
- 3
Example 3:

Input: head = [1], pos = -1 Output: false Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.- 1
- 2
- 3
Constraints:
- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
- pos is -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Follow up : Can you solve it using O(1) memory?
方法一:哈希表
思路:
遍历一遍链表,将遍历到的 结点 存入链表中,如果重复就返回true
注意 : 哈希表中一定要存结点而不是结点的值。因为链表中不同结点的值可能相同,但他们不是同一个结点c++代码:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { if(!head || !head->next) return false; unordered_set<ListNode*> st; while(head != nullptr){ if(st.count(head)) return true; st.insert(head); head = head->next; } return false; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),需要遍历一遍链表
- 空间复杂度:O(n),哈希表最多存整个链表的元素
方法二:快慢指针
思路:
Floyd 判圈算法,也龟兔赛跑算法:
设置快慢两个指针,慢的一次移动一位,快的一次移动两位,如果存在环,那么快的指针一定会从后面追上慢的指针c++代码:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode* head) { if (!head || !head->next) { return false; } // 注意此处fast的起点 ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head->next; while (slow != fast) { // 如果有指针先到NULL说明无环 if (!fast || !fast->next) { return false; } // 慢指针移动一位 快指针移动两位 slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } return true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),不存在环的时候,指针一共会移n次(两个指针各自移动n/2,快指针到达终点);存在环的时候,每一轮移动后,快慢指针的距离将减小一。而初始距离为环的长度,因此至多移动 n 轮。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),两个指针
-
相关阅读:
gitlab克隆本地切换p分支
力扣第24题 两两交换链表中的节点 c++精讲 。
Mybatis-SQL分析组件
lampiao靶场
遇到这3种职场变化,趁早为自己打算
计算程序运行时间:计算或者不计算sleep()的两种情况perf_counter()和process_time()
单链表的介绍和内存布局 [数据结构][Java]
聊聊Spring中最常用的11个扩展点
iOS代码混淆-从入门到放弃
JavaScript 函数
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/cwtnice/article/details/125516717
