-
RabbitMQ入门
1. 异步通讯简述
好处:
- 吞吐量提升:无需等待订阅者处理完成,响应更快速
- 故障隔离:服务没有直接调用,不存在级联失败问题
- 调用间没有阻塞,不会造成无效的资源占用
- 耦合度极低,每个服务都可以灵活插拔,可替换
- 流量削峰:不管发布事件的流量波动多大,都由Broker接收,订阅者可以按照自己的速度去处理事件
缺点:
- 架构复杂了,业务没有明显的流程线,不好管理
- 需要依赖于Broker的可靠、安全、性能
2. 常见的消息模型
SpringAMQP是基于RabbitMQ封装的一套模板,并且还利用SpringBoot对其实现了自动装配,使用起来非常方便。
提供了三个功能:
- 自动声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系
- 基于注解的监听器模式,异步接收消息
- 封装了RabbitTemplate工具,用于发送消息
2.1 SimpleQueue
在pom.xml中添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqpartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2.1.1消息发送
首先配置MQ得地址,在application.yml中配置
spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.150.101 # 主机名 port: 5672 # 端口 virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机 username: itcast # 用户名 password: 123321 # 密码- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
编写生产者的代码,生产消息
package cn.itcast.mq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class SpringRabbitListener { @RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(String msg) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息:【" + msg + "】"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
编写消费者的代码,消费消息
public class SpringRabbitListener { @RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(String msg) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息:【" + msg + "】"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.2 工作队列
简单来说就是让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息。
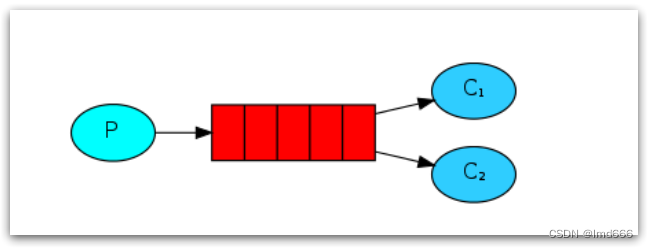
当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会远远大于消息的消费速度。长此以往,消息就会堆积越来越多,无法及时处理。此时就可以使用work 模型,多个消费者共同处理消息处理,速度就能大大提高了。
与简单队列类似,只不过多了个消费者绑定到队列上。代码省略。
2.3 Fanout(广播队列)
生产者产生消息发送给交换机,交换机决定把消息发送给哪个队列。
广播模式下,交换机会发送给所有绑定它的队列,此处注意,每一条消息都会发给所有绑定了该交换机的队列,即一条消息会被发给多个队列import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding; import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class FanoutConfig { /** * 声明交换机 * @return Fanout类型交换机 */ @Bean public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){ return new FanoutExchange("it.fanout"); } /** * 第1个队列 */ @Bean public Queue fanoutQueue1(){ return new Queue("fanout.queue1"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanoutExchange); } /** * 第2个队列 */ @Bean public Queue fanoutQueue2(){ return new Queue("fanout.queue2"); } /** * 绑定队列和交换机 */ @Bean public Binding bindingQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanoutExchange); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
消息生产和消费与之前一致。
路由与广播的区别是,交换机不是无脑发送信息给队列,而是需要对 ‘暗号’ 只有暗号对了队列才会接收到消息。
主题与路由的区别是,主题是支持通配符,而路由是一个写死的密码。 -
相关阅读:
DRL经典文献阅读(二):确定性策略梯度(DPG+DDPG)【附代码】
解决AndroidStudio Gradle只有testDebugUnitTest
抓包工具 Charles 使用手册
【C++笔记】多态的原理、单继承和多继承关系的虚函数表、 override 和 final、抽象类、重载、覆盖(重写)、隐藏(重定义)的对比
Spring更简单的使用方法
HBase中的数据表是如何用CHAT进行分区的?
Metabase学习教程:视图-5
结构体(1)
Java Annotation Processor注解处理器如何Debug
【力扣刷题】只出现一次的数字
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lmd666/article/details/133754847
