-
【数据结构--排序】堆排序

💐 🌸 🌷 🍀 🌹 🌻 🌺 🍁 🍃 🍂 🌿 🍄🍝 🍛 🍤
📃个人主页 :阿然成长日记 👈点击可跳转
📆 个人专栏: 🔹数据结构与算法🔹C语言进阶
🚩 不能则学,不知则问,耻于问人,决无长进
🍭 🍯 🍎 🍏 🍊 🍋 🍒 🍇 🍉 🍓 🍑 🍈 🍌 🍐 🍍
堆排序
一、🌱排降序
口诀:排降序,建小堆
1.思路:
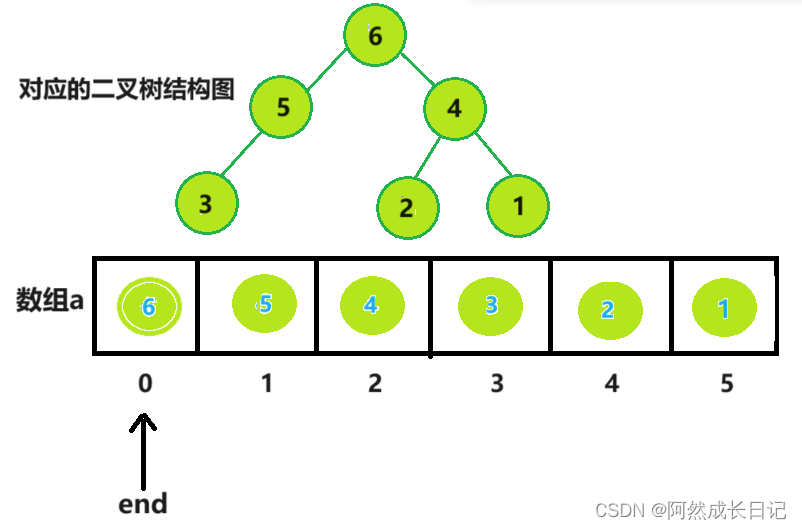
(1)首先使用从下到上的方法建立小堆;如下图
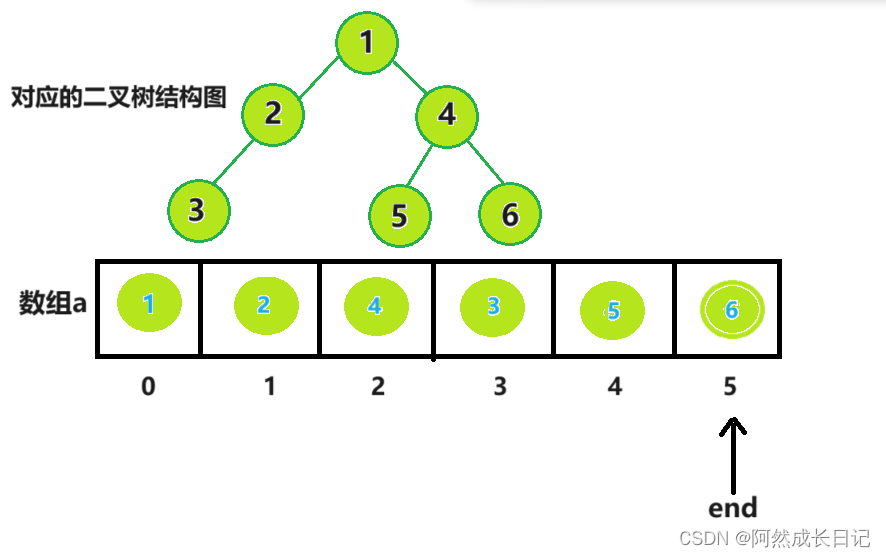
(2)堆顶与最后一个节点交换,由于是小堆,堆顶是最小值。交换后,就选出了
最小值并将其放到数组的组后位置,
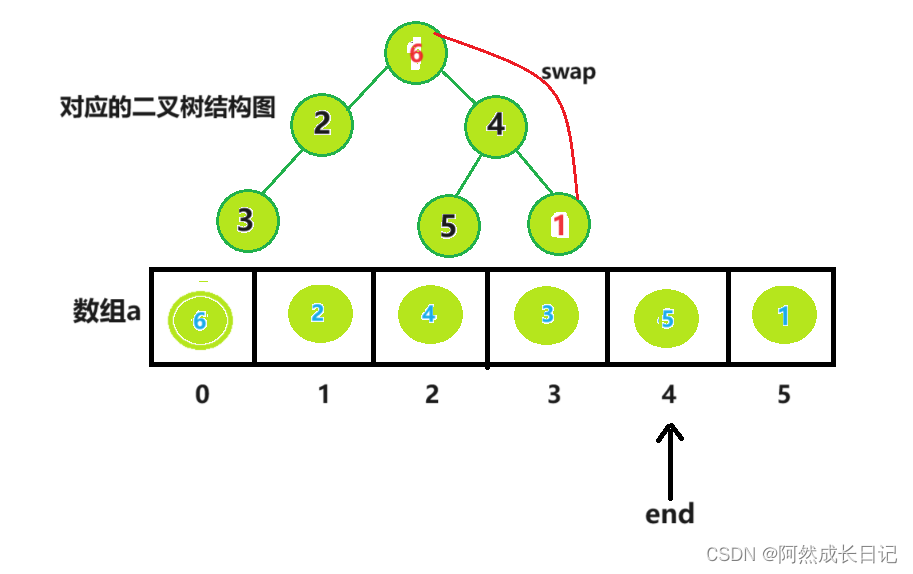
(3).将堆的长度减1【end–】(数组长度减1)。
(4).在对剩下的堆进行基于小堆的向下调整,从而将第二小的数调整到了堆顶。
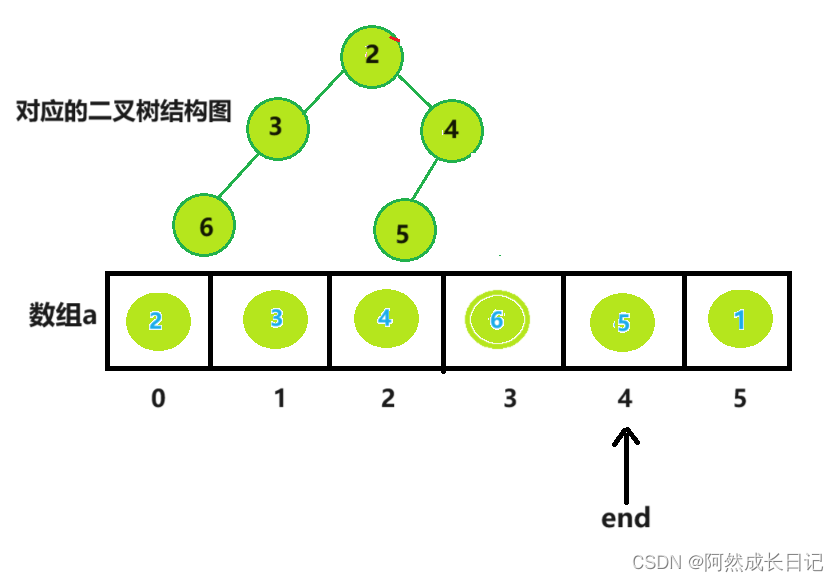
重复步骤2.3.4,end一直减到0;
4.最后,这个原本存储小堆的数组,就变成了一个从小到大的降序数组。
2.代码实现:
1.交换
//交换 void Swap(int* a, int* b) { int tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.修改AdjustDown(a, end, 0);为调小堆
基于小堆的向下调整 ```c void AdjustDownxiao(int* a, int n, int parent) { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //一直交换到数的最后,也就是数组的最后一个位置 while (child < n) { if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child]) { child++; } if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); // 继续往下调整 parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { return; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
3.排降序
void HeapSortDES(int* a, int n) { //建立小堆 for (int i = (n-1-1)/2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDownxiao(a, n, i); } int end = n - 1; while (end > 0) { Swap(&a[0], &a[end]); //每次调整从根0到end,end每次会减1。 AdjustDownxiao(a, end, 0); --end; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
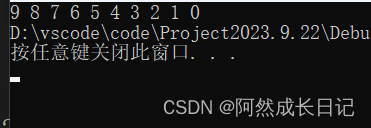
3.测试结果
4.总代码
//交换 void Swap(int* a, int* b) { int tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp; } //基于小堆的向下调整 void AdjustDownxiao(int* a, int n, int parent) { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //一直交换到数的最后,也就是数组的最后一个位置 while (child < n) { if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child]) { child++; } if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); // 继续往下调整 parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { return; } } } //降序 void HeapSortDES(int* a, int n) { //建立小堆 for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDownxiao(a, n, i); } int end = n - 1; while (end > 0) { Swap(&a[0], &a[end]); //每次调整从根0到end,end每次会减1。 AdjustDownxiao(a, end, 0); end--; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
二、🌸排升序
口诀:排升序,建大堆
意思是:想要将数组的顺序变成一个升序的,那么可以建立一个大堆存在数组中,在对堆进行调整。即可将数组变成一个升序数组。
1.思路:
首先使用从下到上的方法建立大堆;
1.堆顶与最后一个节点交换,由于是大堆,堆顶是最大值。交换后,就选出了最大值并将其放到数组的组后位置,
2.并将堆的长度减1(数组长度减1)。
3.在对剩下的堆进行基于大堆的向下调整,从而将第二大的数调整到了堆顶。
4.最后,这个原本存储大堆的数组,就变成了一个从小到大的升序数组。2.代码实现:
1.交换
//交换 void Swap(int* a, int* b) { int tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.基于大堆的向下调整
//基于大堆的向下调整 void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent) { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //一直交换到数的最后,也就是数组的最后一个位置 while (child < n) { if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] > a[child]) { child++; } if (a[child] > a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); // 继续往下调整 parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { return; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
3.排升序
//排升序 void HeapSortASC(int* a, int n) { //建立大堆 for (int i = (n-1-1)/2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDown(a, n, i); } int end = n - 1; while (end > 0) { swap(&a[0], &a[end]); //每次调整从根0到end,end每次会减1。 AdjustDown(a, end, 0); end--; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
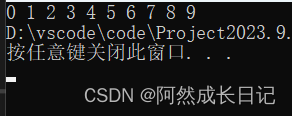
3.测试结果:
4.总代码
//交换 void Swap(int* a, int* b) { int tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp; } void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent) { int child = parent * 2 + 1; //一直交换到数的最后,也就是数组的最后一个位置 while (child < n) { if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] > a[child]) { child++; } if (a[child] > a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); // 继续往下调整 parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { return; } } } //升序 void HeapSortASC(int* a, int n) { //建立小堆 for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--) { AdjustDown(a, n, i); } int end = n - 1; while (end > 0) { Swap(&a[0], &a[end]); //每次调整从根0到end,end每次会减1。 AdjustDown(a, end, 0); end--; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
三、堆排序的时间复杂度
堆排序分两步:1.建堆(使用时间复杂度更低的向下调整建堆)2.排序
向下调整建堆的时间复杂度为O(n);
n-1次删除操作的时间复杂度为O(nlogn);
所以总操作时间复杂度为O(nlogn) -
相关阅读:
课程31:API请求日志脱敏处理
【重识云原生】第四章云网络4.7.4节vhost-user方案——virtio的DPDK卸载方案
wy的leetcode刷题记录_Day32
软件评测师之校验码
C语言操作符详解
基于SSM的汽车销售管理系统
使用VS Code 搭建 platformio 平台
【开源】JAVA+Vue.js实现APK检测管理系统
AI DevOps | ChatGPT 与研发效能、效率提升(中)
uniapp小程序v-for提示“不支持循环数据”
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/luhaoran814/article/details/133211070