-
Spring Boot实现web.xml功能
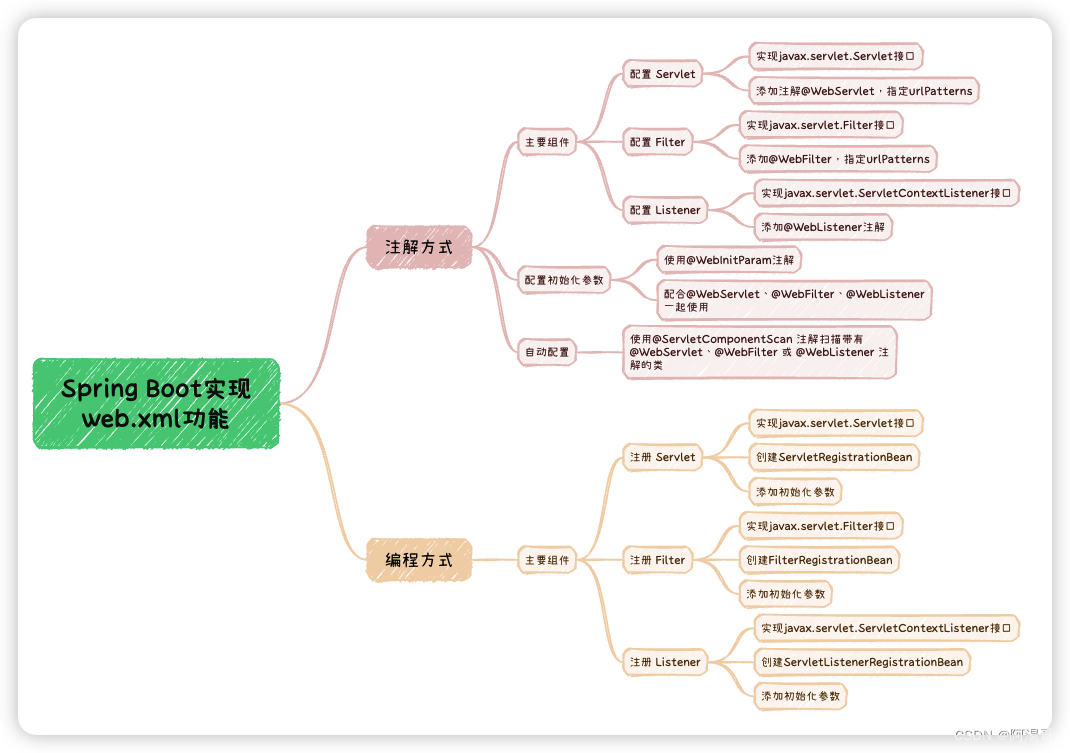
在Spring Boot中,不再需要使用传统的
web.xml文件来配置web应用的功能,Spring Boot支持通过注解和基于代码两种方式来实现web.xml的功能。本文主要介绍这两种方法的实现。1. 基于注解实现
在 Spring Boot 中,不再需要使用传统的
web.xml文件来配置 Web 应用的功能。Spring Boot 使用基于注解的配置和自动配置来简化 Web 应用的开发和部署。以下是一些常见的
web.xml配置及其在 Spring Boot 中的替代方案:-
配置 Servlet:
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以通过创建一个类并继承
javax.servlet.Servlet接口来定义 Servlet。然后,使用@WebServlet注解将其标记为 Servlet,并指定 URL 映射。
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以通过创建一个类并继承
-
配置 Filter:
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以通过创建一个类并实现
javax.servlet.Filter接口来定义 Filter。然后,使用@WebFilter注解将其标记为 Filter,并指定 URL 模式。
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以通过创建一个类并实现
-
配置 Listener:
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以通过创建一个类并实现
javax.servlet.ServletContextListener接口来定义 Listener。然后,使用@WebListener注解将其标记为 Listener。
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以通过创建一个类并实现
-
配置初始化参数:
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以使用
@ServletComponentScan注解扫描带有@WebServlet、@WebFilter或@WebListener注解的类,并使用@WebInitParam注解来指定初始化参数。
- 在 Spring Boot 中,可以使用
总的来说,Spring Boot 鼓励使用基于注解的方式来配置和管理 Web 应用的功能,以简化开发和减少配置文件的使用。通过使用注解,可以在类级别上直接标记 Servlet、Filter 和 Listener,并以更直观的方式指定它们的配置和映射。
1.1 组件注册
以下是一个示例,展示了如何在 Spring Boot 中使用注解来配置 Servlet、Filter 和 Listener:
- 创建一个 Servlet:
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/hello") public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { resp.getWriter().println("Hello, World!"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 创建一个 Filter:
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter; import javax.servlet.*; import java.io.IOException; @WebFilter(urlPatterns = "/hello") public class HelloFilter implements Filter { @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { System.out.println("Before HelloServlet"); chain.doFilter(request, response); System.out.println("After HelloServlet"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 创建一个 Listener:
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; @WebListener public class HelloListener implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) { System.out.println("Web application initialized"); } @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) { System.out.println("Web application destroyed"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
在上述示例中,我们使用了
@WebServlet、@WebFilter和@WebListener注解来标记 Servlet、Filter 和 Listener。通过urlPatterns属性,我们指定了 Servlet 和 Filter 的 URL 映射。请注意,为了使注解生效,还需要在启动类上添加
@ServletComponentScan注解,以扫描并加载带有注解的 Servlet、Filter 和 Listener:import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan; @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class YourApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(YourApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
这样,你就可以在 Spring Boot 中使用注解来配置和管理 Servlet、Filter 和 Listener,而不再需要使用传统的
web.xml文件。1.2 @WebInitParam注解
使用
@WebInitParam注解可以在 Servlet、Filter 或 Listener 上指定初始化参数。下面是一个示例,展示了如何使用@WebInitParam来设置初始化参数:- 创建一个 Servlet 并设置初始化参数:
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; @WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/hello", initParams = { @WebInitParam(name = "message", value = "Hello, World!"), @WebInitParam(name = "count", value = "5") }) public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException { String message = getInitParameter("message"); int count = Integer.parseInt(getInitParameter("count")); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { resp.getWriter().println(message); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
在上述示例中,我们使用
@WebServlet注解为 Servlet 指定了两个初始化参数:message和count。可以使用getInitParameter()方法在 Servlet 中获取这些初始化参数的值。- 在启动类上添加
@ServletComponentScan注解:
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan; @SpringBootApplication @ServletComponentScan public class YourApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(YourApplication.class, args); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 运行应用并访问
/hello路径,将输出初始化参数指定的消息多次:
Hello, World! Hello, World! Hello, World! Hello, World! Hello, World!- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
通过使用
@WebInitParam注解,并在对应的 Servlet、Filter 或 Listener 上指定初始化参数,你可以方便地设置和获取这些初始化参数的值。这样,你就可以在应用程序中使用这些参数来进行相应的逻辑处理。2. 基于编码实现
2.1 Servlet & Filter
除了使用注解的方式,还有一种方式可以在 Spring Boot 中实现
web.xml的功能,即通过编写一个ServletRegistrationBean或FilterRegistrationBean的 Bean 来注册 Servlet 或 Filter。以下是使用
ServletRegistrationBean注册 Servlet 的示例:import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class ServletConfig { @Bean public ServletRegistrationBean<HelloServlet> helloServletRegistrationBean() { ServletRegistrationBean<HelloServlet> registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(new HelloServlet(), "/hello"); registrationBean.addInitParameter("message", "Hello, World!"); registrationBean.addInitParameter("count", "5"); return registrationBean; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
在上述示例中,我们创建了一个
ServletRegistrationBean的 Bean,并将自定义的HelloServlet类设置为 Servlet。然后,使用addInitParameter方法指定初始化参数的名称和值。类似地,你可以使用
FilterRegistrationBean注册 Filter。以下是一个使用FilterRegistrationBean注册 Filter 的示例:import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class FilterConfig { @Bean public FilterRegistrationBean<HelloFilter> helloFilterRegistrationBean() { FilterRegistrationBean<HelloFilter> registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(new HelloFilter()); registrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/hello"); return registrationBean; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
在上述示例中,我们创建了一个
FilterRegistrationBean的 Bean,并将自定义的HelloFilter类设置为 Filter。然后,使用addUrlPatterns方法指定要过滤的 URL 模式。通过使用
ServletRegistrationBean和FilterRegistrationBean,你可以在 Spring Boot 中以编程方式注册 Servlet 和 Filter,并设置相应的初始化参数和 URL 模式。需要注意的是,如果你的 Servlet 或 Filter 类是通过
@Component或@Bean注解进行注入的,Spring Boot 会自动将其作为 Servlet 或 Filter 进行注册。如果你的 Servlet 或 Filter 类不是由 Spring 管理的 Bean,你可以使用ServletRegistrationBean或FilterRegistrationBean手动注册。2.2 Listener
以下是一个示例代码,展示了如何使用
ListenerRegistrationBean来注册一个Listener:import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletListenerRegistrationBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class MyListenerConfig { @Bean public ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener> myListenerRegistrationBean() { ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener> registrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<>(new MyListener()); return registrationBean; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
在上面的示例中,我们通过创建一个
ServletListenerRegistrationBean的实例来注册一个MyListener。这里不需要指定URL映射,因为Listener不是通过URL访问的。类似于
ServletRegistrationBean和FilterRegistrationBean,ListenerRegistrationBean也提供了一些可配置的选项,例如顺序、初始化参数等。可以根据具体的需求进行配置。通过使用
ListenerRegistrationBean,我们可以方便地在Spring应用程序中注册和配置Listener,而无需依赖于web.xml文件。3. 总结
通过上述介绍我们了解到,在Spring Boot应用中,我们可以通过注解和编程两种方式实现web.xml的功能,包括如何创建及注册Servlet、Filter以及Listener等。至于具体采用哪种方式,大家可以根据自己的喜好自行选择。
-
-
相关阅读:
C语言入门log02
哈夫曼树实现哈夫曼编码(C++)
java计算机毕业设计基于安卓Android的禁毒宣传APP(源码+系统+mysql数据库+Lw文档)
Word控件Spire.Doc 【图像形状】教程(6): 如何在 C#、VB.NET 的 Word 文档中插入形状和形状组
8255 boot介绍及bring up实战分享
图像在神经网络中的预处理与后处理的原理和作用(最详细版本)
计算机毕业设计ssm房屋租赁管理系统d97n3系统+程序+源码+lw+远程部署
Tauri+Rust+Vue 跨平台桌面应用简明教程(1)环境创建+系统事件+自定义菜单
大数据必学Java基础(五):第一段程序
基于SpringBoot构造超简易QQ邮件服务发送(分离-图解-新手)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ttyy1112/article/details/132988996
