-
Spring实例化源码解析(一)
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
前言
AbstractApplicationContext类的refresh方法是spring实例化流程的开始。本章主要是介绍invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法,对其内部源码进行详细分析。接下来就来看看这句简单的代码后面具体做了什么。Spring源码版本6.0.12,代码版本不同可能代码会稍有不同,但是核心逻辑大差不差。
分析前的准备
接下来就直接从代码开始进行源码分析。源码的分析将会非常枯燥、并且常看常新。本章除了记录自己的源码学习内容,也希望能给大家带来帮助。
spring启动main方法,在调用refresh之前会register(AopConfig.class),这个是前提。
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AopConfig.class); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
AopConfig类其实可以是任意类,我只是为了加上@ComponentScan注解
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy @ComponentScan(value = {"com.qhyu.cloud.**"}) public class AopConfig { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,respecting explicit order if given.
实例化并调用所有已注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,如果给定的话,请遵守显式顺序。次方法就在AbstractApplicationContext中。
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // 核心方法 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime // (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor) if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors())是核心的方法,本以为getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法会获取到所有的BeanFactoryPostProcessors,毕竟看起来名字很像,但是打断点发现其实此处返回的List size为0。
那么接下来就直接查看invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors())方法。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
在spring的实例化过程中我们可以经常看到BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,几乎充斥着整个实例化过程。BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor也是spring框架中一个比较重要的接口。因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,所以就放一起来讲解了。
- BeanFacotryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是一个接口,用于在Spring容器实例化任何Bean之前修改BeanDefinition(Bean定义)或配置的后置处理器,它允许对BeanDefinition进行修改、添加自定义属性甚至可以完全替换beanDefinition。
关键点:
1、在spring容器加载BeanDefinition后,但在实例化Bean之前调用。
2、用于修改BeanDefinition的元数据(如类名、作用域、属性等)。
3、对所有的BeanDefinition生效,包括非延迟加载和延迟加载的bean。
4、可以通过实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口并注册为Spring容器的Bean来自定义处理逻辑。
示例:
public class CustomBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { // 在这里进行Bean定义的修改或自定义处理逻辑 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFacotryPostProcessor的子接口,用于在Spring容器实例化任何Bean之前修改Bean定义的后置处理器。与BeanFacotryPostProcessor相比,它提供了更广泛的功能,包括添加、修改和删除Bean定义。
关键点:
1、继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,扩展了修改Bean定义的功能。
2、在Spring容器加载Bean定义后,但在实例化Bean之前调用。
3、用于直接操作Bean定义的注册表,可以添加、修改和删除Bean定义。
4、可以通过实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口并注册为Spring容器的Bean来自定义处理逻辑。
示例:
public class CustomBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException { // 在这里进行Bean定义的添加、修改或删除操作 } @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { // 可以不实现该方法,或者在这里进行其他的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理逻辑 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
关系和使用区别:
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子接口,它们都用于在实例化Bean之前修改Bean定义。
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor在功能上更加强大,可以添加、修改和删除Bean定义,而BeanFactoryPostProcessor只能修改Bean定义的元数据。
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor在处理Bean定义之前,会先回调BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法,因此它们可以一起使用,但是顺序上有所区别。
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor可以直接操作Bean定义注册表,而BeanFactoryPostProcessor只能通过ConfigurableListableBeanFactory来间接操作Bean定义。
- 通常情况下,更常用的是实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,而BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor在特定需求下使用,例如需要动态地添加或修改Bean定义。
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
这里引入了一个新的类PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法的参数解释如下:
参数1:默认是DefaultListableBeanFactory,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry
参数2:一般情况下为空,除非调用Spring容器的refresh方法之前调用API手动添加了BeanFactoryPostProcessor
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily // refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use // of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is // intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered // and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be // instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext // in the wrong order. // // Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the // list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate // to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change: // https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22 // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. // 如果有的话,首先调用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors // 存放处理完毕的bfpp名称 Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 因为默认传的DefaultListableBeanFactory==beanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,所以进入if的逻辑 if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { // 也就是说这个if里面要使用的就是BeanDefinitionRegistry的特性。 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; // regular常规的意思 // regularPostProcessors记录通过硬编码方式注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的处理器 // 存放直接实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类集合,bfpp的作用是可以定制化修改bd List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // registryProcessors记录通过硬编码方式注册是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor // 存放直接实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口实现类的集合,brpp可以定制化修改bd List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 除非手动注入bfpp 否则这个for循环没有什么意义,也就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor // 此处可以作为扩展。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! // Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement // PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest. // currentRegistryProcessors记录通过配置方式注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的处理器 // 用于存放当前即将执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类 List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. // 第一次调用:首先调用实现了排序的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors // 这里这个方法多次调用返回不同的值是因为beanFactory中的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors的新增,一开始都想不明白。 // 其实最主要的就是第一次执行了invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor方法 // 真实逻辑就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法, // 这里会根据我们的AopConfig,也就是@ComponentScan注解的path来扫描我们自己的类,并且生产BeanDefiniton信息 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } // 很明显 这里是排序,先不进去看,因为此时currentRegistryProcessors只有一个ConfigurationClassPostProcessor sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 这个方法就是核心内容,我这个工程使用了AOPConfig启动类,也就是说一开始会解析这个类,包含类上的ComponentScan注解,会把路径下的东西用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner来扫描出来 // 生成beanDefinition放入BeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory),所以第二次调用的时候就可以扫描出其他的BeanFactoryPostProcessors // ConfigurationClassPostProcessor == currentRegistryProcessors invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); // 清空当前注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. // 接下来,调用实现 Ordered 的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors。 // 第二次调用:这个时候已经获取了ComponentScan注解中的路径下的BeanDefinition了。 // 所以会把我们定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor加载起来,或者第三方框架实现的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor加载 postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } // 排序,看一下排序的规则是什么?,我可以实现Ordered接口PriorityOrdered接口或者注解 sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 调用了currentRegistryProcessors中的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors--》postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法 // 因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的职责就是加载Bean的BeanDefinition,后续才好加载这个bean,至于要修改的话,交给BeanFactoryPostProcessor invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear. // 最后,调用所有其他 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 直到不再出现。 boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } else { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } /** =============下面就是处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类============= */ // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! // 获取bfpp接口实现类 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have // modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values... beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
我们今天要分析的源码就是上面这一个方法,在源码分析的时候我们还是要稍微读一读方法名称和各个单词,因为在spring中我们很多时候都可以通过方法名称来判断出要做的事情,因为源码分析打断点的时候如果一直往下看可能就出不来了。所以有的时候需要我们智能的跳过一些个方法。
beanFactory
在进入到方法之前我们先看下beanFactory,这个beanFactory我感觉可以理解为bean工厂。beanfactory是spring框架中的一个核心接口,它提供了一种机制来管理和访问程序中的对象(也称为Bean)。在spring中,对象的创建、配置和管理是由beanfactory负责的。
首先可以知道传入的是DefaultListableBeanFactory,所以说beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry是true。会进入到if逻辑中。
其次当前beanFactory中已经注册了5个beanDefinition。aopConfig就不多说了,在调用refresh方法之前手动注册的,其他四个可以先不管。
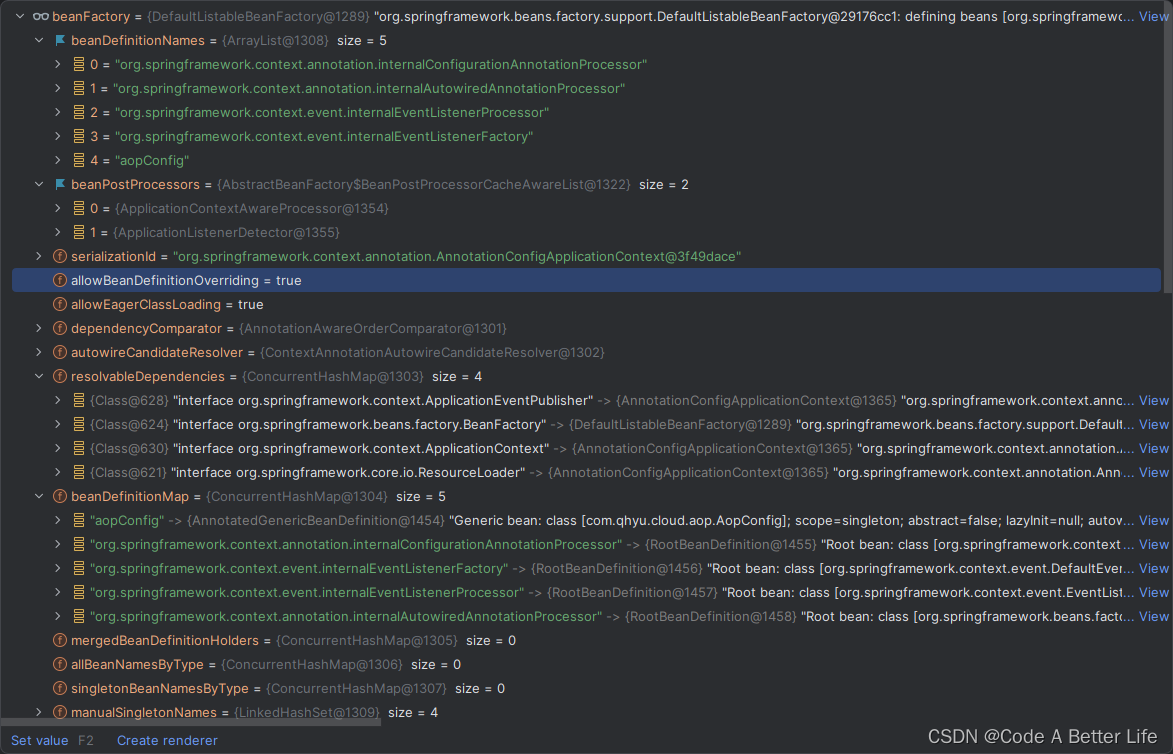
源码分析
接下来会集中拆解PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate类中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法来逐步分析源码。
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 因为默认传的DefaultListableBeanFactory==beanFactory实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,所以进入if的逻辑 if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { // 也就是说这个if里面要使用的就是BeanDefinitionRegistry的特性。或者作为参数传递固定了类型。 BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; // regular常规的意思 // regularPostProcessors记录通过硬编码方式注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的处理器 // 存放直接实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类集合,bfpp的作用是可以定制化修改bd List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // registryProcessors记录通过硬编码方式注册是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor // 存放直接实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口实现类的集合,brpp可以定制化修改bd List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
processedBeans根据是用来存放String的集合,根据processedBeans.add方法可以知道存放的是处理完成的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的名称。
regularPostProcessors存放的是BeanFacotyPostProcessor。
registryProcessors存放的是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。
接下来拆解这个for循环,beanFactoryPostProcessors参数size=0,所以当前这个for循环肯定是不会执行的。然而整个invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中只有这个for循环中有使用regularPostProcessors.add方法。所以regular相关的后续遇到了可以先跳过。
此处可以作为一个扩展点。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor可以让for循环生效。也就是手动注入beanFactoryPostProcessor,在这篇文章就不深入了。
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
// 用于存放当前即将执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类 List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();- 1
- 2
第一次调用实现了ProrityOrdered的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors逻辑,接下来将是最重要的部分了。
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } // 很明显 这里是排序,先不进去看,因为此时currentRegistryProcessors只有一个ConfigurationClassPostProcessor sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 这个方法就是核心内容,我这个工程使用了AOPConfig启动类,也就是说一开始会解析这个类,包含类上的ComponentScan注解,会把路径下的东西用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner来扫描出来 // 生成beanDefinition放入BeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory),所以第二次调用的时候就可以扫描出其他的BeanFactoryPostProcessors // ConfigurationClassPostProcessor == currentRegistryProcessors invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); // 清空当前注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors currentRegistryProcessors.clear();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
首先查看postProcessorNames会返回什么东西。

org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor 这个有点印象。可以回到开始的beanFactory的截图中找到。beanDefinitonNames中第一个记录就是这个名称。
也就是说beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType方法是从spring的beanFactory中的beanDefinitionMap中去找有没有符合类型为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的类,并且如果实现了PriorityOrdered.class就把这个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor加入到currentRegistryProcessors和processedBeans集合中。

beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)拿到的bean其实是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。
解析下来就是关键先生ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类和invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法。
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors( Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ApplicationStartup applicationStartup) { for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) { StartupStep postProcessBeanDefRegistry = applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beandef-registry.post-process") .tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString); postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); postProcessBeanDefRegistry.end(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
根据代码来看,就是执行ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,带上了registry这个参数,也就是DefaultListableBeanFacotry。
这个invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法的意思就是调用这个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,而ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法是去加载并注册我们自定义的一些被spring管理的类到spring中。在本节中不会深入的去研究这个类的具体执行逻辑,将在下一章节进行分析。
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法执行完成之后会清理currentRegistryProcessors集合。然后就开始第二次调用了。
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); currentRegistryProcessors.clear();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
其实第二次调用的这块代码和第一次调用的大差不差,主要是beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)的不同,第一次是PriorityOrdered.class。同时第二次不会处理第一次执行过的BeanFacotryPostProcessor。也就是processedBeans.contains(ppName)逻辑。

第二次调用beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false)除了第一次出现的org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor还有两个我自定义的类。
@Component public class CloudBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor , PriorityOrdered { @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("beanFactoryPostProcessor used by cloud"); } @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException { System.out.println("BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor used by cloud"); } @Override public int getOrder() { return 100; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
因为第一次调用的时候执行了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,会把我们交给spring管理的beanDefinition注册到beanFactory中,所以第二次调用这个方法的时候就会把自定义的加载起来,当然三方jar包也可能做同样的事情,比如mybatis plus。
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法还是会执行这些自定的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。执行完成之后继续清理currentRegistryProcessors集合。
接下来开始调用第三次,为什么会出现第三次,就是因为 beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)和beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class),相当于自定义的没有实现这两个接口的就在这里一次性处理完。
boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup()); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
在if方法的最后有两行代码比较重要。
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);- 1
- 2
- 3
其实重要的就是这个方法,调用BeanFacotyPostProcessors的postProcessBeanFactory方法。也就是说自定义的这些BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor会先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,待所有的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor执行完成之后再调用这些自定义的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法。因为双方存在继承关系。
至此BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor就结束了,接下来就会处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor了。
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
**postProcessorNames:**获取的是当前beanFactory中的实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的bean的名称。
**priorityOrderedPostProcessors:**很明显哈实现了PriorityOrdered的BeanFactoryPostProcessor存放在这,存放的是bean哦。
**orderedPostProcessorNames:**存放的是实现了Ordered的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,存放的是名称。
**nonOrderedPostProcessorNames:**存放的是没有实现排序的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,存放的是名称。
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
接下来就是排序和invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,分别执行这几个集合中的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法。
总结
本章主要分析了AbstractApplicationContext.refresh方法中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法,其中ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法和排序方法将在下一章进行分析和讲解,循序渐进的完成整个逻辑的讲解。
-
相关阅读:
数据化运营18 营收:如何通过交叉营销提升用户营收贡献?
Home Assistant:基于Python的智能家居开源系统详解
android 自定义View:仿QQ拖拽效果
【随想】每日两题Day.8
基于Sider-chatgpt3.5-编写一个使用springboot2.5连接elasticsearch7的demo程序,包括基本的功能,用模板方法
微信小程序componentPlaceholder解决分包后不同包组件调用报错问题
css常用属性
php操作xml字符串
如何扫码分享文件?二维码扫描预览文件的方法
【关于Linux中----文件接口、描述符、重定向、系统调用和缓冲区】
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Tanganling/article/details/132905256
