-
JAVA图书管理练习
0.前言
1.在学习了面向对象,接口继承等语法后,综合使用这些语法完成一个简单的图书管理小练习.
2.在写代码之前,我们首先要把各种类抽象出来,图书管理会有多个类,比如书类,放书的书架类,操作书籍的类,用户类
1.书类(BOOK)
1.1 Book
先创建一个包,里面存放书类和书架类,

BOOK类包含五个成员变量并且添加构造方法等其他成员方法,当我们实例化对象后,一本书就会有这五个属性和成员方法.public class Book { private String name; //书名 private String author; //作者 private int price; //价格 private String type; //类型 private Boolean isBorrowed=false; //是否借出 public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public Boolean getBorrowed() { return isBorrowed; } public void setBorrowed(Boolean borrowed) { isBorrowed = borrowed; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + ", price=" + price + ", type='" + type + '\'' + ", isBorrowed=" + (isBorrowed?"true":"false") + '}'; } public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; this.type = type; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
1.2 BookList
书架用来存放实例化后的书对象,里面包含了两个成员变量,一个是记录存放书籍数量的UsedSize,另外一个是创建的Book类数组,用来存放书对象.
//BookList Book[] books=new Book[10]; int UsedSize; //已借出书籍的数量- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
public class BookList { private Book[] books=new Book[10]; private int UsedSize; //已借出书籍的数量 public BookList(){ this.books[0]=new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",119,"小说"); this.books[1]=new Book("鸟哥的 Linux 私房菜","鸟哥",118,"小说"); this.books[2]=new Book("剑指 Offer","何海涛",65,"小说"); this.UsedSize=3; } //放书 public void setBooks(int pos,Book book) { books[pos]=book; } public int getUsedSize() { return UsedSize; } public void setUsedSize(int UsedSize) { this.UsedSize = UsedSize; } public Book getbook(int pos){ return books[pos]; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
2. User类
2.1 user类
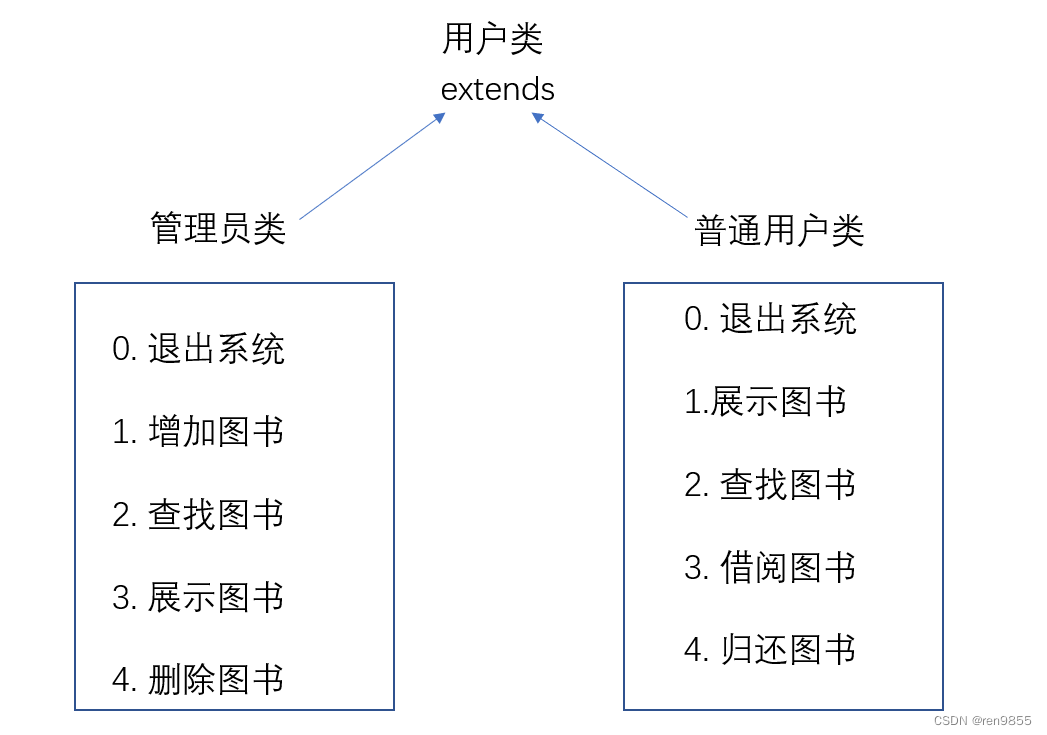
我们把用户分为管理员和普通用户,分别对应不同的功能
User类
public abstract class User { protected String name; public abstract int menu(); protected Ioperation[] ioperations; public User(String name) { this.name = name; } public void dowork(int choice, BookList bookList){ this.ioperations[choice].work(bookList); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
2.2 AdminUser类
public class AdminUser extends User { public AdminUser(String name) { super(name); this.ioperations =new Ioperation[]{ new ExitOperation(), new AddOperation(), new FindOperation(), new DisplayOperation(), new DelOperation() }; } public int menu() { System.out.println("============================="); System.out.println("Hello " + name + ", 欢迎使用图书管理系统!"); System.out.println("0. 退出系统"); System.out.println("1. 增加图书"); System.out.println("2. 查找图书"); System.out.println("3. 展示图书"); System.out.println("4. 删除图书"); System.out.println("============================="); System.out.println("请输入要选择的选项:"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = sc.nextInt(); return choice; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
2.3 NormalUser类
public class NormUser extends User{ public int menu() { System.out.println("============================="); System.out.println("Hello " + name + ", 欢迎使用图书管理系统!"); System.out.println("0. 退出系统"); System.out.println("1. 展示图书"); System.out.println("2. 查找图书"); System.out.println("3. 借阅图书"); System.out.println("4. 归还图书"); System.out.println("============================="); System.out.println("请输入要选择的选项:"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = sc.nextInt(); return choice; } public NormUser(String name){ super(name); this.ioperations=new Ioperation[]{ new ExitOperation(), new DisplayOperation(), new FindOperation(), new BorrowOperation(), new ReturnOperation() }; } } `- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
3.Operation类
public interface Ioperation { void work(BookList bookList); }- 1
- 2
- 3
3.1 添加图书
public class AddOperation implements Ioperation { public void work(BookList bookList){ System.out.println("添加图书"); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入书名:"); String name=sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入作者:"); String author=sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入价格:"); int price=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入书的类型:"); String type=sc.nextLine(); Book book=new Book(name,author,price,type); int pos= bookList.getUsedSize(); bookList.setBooks(pos,book); bookList.setUsedSize(pos+1); System.out.println("图书添加完成"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
3.2 删除图书
public class DelOperation implements Ioperation{ @Override public void work(BookList booklist) { System.out.println("删除图书"); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入要删除的图书:"); String name=sc.nextLine(); for (int i = 0; i < booklist.getUsedSize(); i++) { if(name.equals(booklist.getbook(i).getName())){ while(booklist.getUsedSize()-i-1!=0){ booklist.setBooks(i,booklist.getbook(i+1)); i++; } booklist.setUsedSize(booklist.getUsedSize()-1); System.out.println("删除成功"); return; } } System.out.println("删除失败,没有这本书"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
3.3 查找图书
public class FindOperation implements Ioperation{ @Override public void work(BookList booklist) { System.out.println("查找图书"); System.out.println("请输入要查找的图书:"); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); String name=sc.nextLine(); for (int i = 0; i < booklist.getUsedSize(); i++) { Book book=booklist.getbook(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ System.out.println("找到了"); System.out.println(book); return; } } System.out.println("没有找到"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
3.4 展示图书
public class DisplayOperation implements Ioperation { @Override public void work(BookList booklist) { System.out.println("展示图书"); for (int i = 0; i < booklist.getUsedSize(); i++) { Book book=booklist.getbook(i); System.out.println(book); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3.5 退出系统
public class ExitOperation implements Ioperation { @Override public void work(BookList booklist) { System.out.println("退出系统"); System.exit(0); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
3.6 借阅图书
public class BorrowOperation implements Ioperation { @Override public void work(BookList booklist) { System.out.println("借阅图书"); System.out.println("请输入要借阅的图书:"); Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); String name=sc.nextLine(); int i; for(i = 0; i < booklist.getUsedSize(); i++) { Book book=booklist.getbook(i); if(book.getName().equals(name) && !book.getBorrowed()){ System.out.println("借阅成功"); booklist.getbook(i).setBorrowed(true); return; } System.out.println("借阅失败,该书已经被借阅"); return; } System.out.println("没有找到这本书"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
3.7 归还图书
public class ReturnOperation implements Ioperation { @Override public void work(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("归还图书"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入归还书籍的名称"); String name = sc.next(); for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUsedSize(); i++) { if (name.equals(bookList.getbook(i).getName())) { if (bookList.getbook(i).getBorrowed()) { System.out.println("归还成功"); bookList.getbook(i).setBorrowed(false); return; } else { System.out.println("该书未被借阅"); return; } } } System.out.println("没有该书或者书名错误"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
-
相关阅读:
【vue3】消息的订阅与发布
高数:第三章:一元函数积分学
记一次 JDK SPI 配置不生效的问题 → 这么简单都不会,还是回家养猪吧
音频抗丢包以及暴力重传实现抗丢包80%
Vue 自定义指令绑定的处理函数中传递参数
动态内存管理
【广州华锐互动】VR虚拟现实技术应用于新兵作战体验的优势
金蝶EAS本地WebService发布
webpack
JAVA基础——day04
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/ren9855/article/details/127929715
