-
SpringMVC
SpringMVC
1.简介
MVC是一种软件架构的思想,将软件按照模型、视图、控制器来划分
- M:Model,模型层,指工程中的JavaBean,作用是处理数据
- JavaBean分为两类:
一类称为实体类Bean:专门存储业务数据的,如 Student、User 等
一类称为业务处理 Bean:指 Service 或 Dao 对象,专门用于处理业务逻辑和数据访问。
- JavaBean分为两类:
- V:View,视图层,指工程中的html或jsp等页面,作用是与用户进行交互,展示数据
- C:Controller,控制层,指工程中的servlet,作用是接收请求和响应浏览器
MVC的工作流程: 用户通过视图层发送请求到服务器,在服务器中请求被Controller接收Controller调用相应的Model层处理请求,处理完毕将结果返回到Controller,Controller再根据请求处理的结果找到相应的View视图,渲染数据后最终响应给浏览器
2.入门案例
2.1创建maven工程
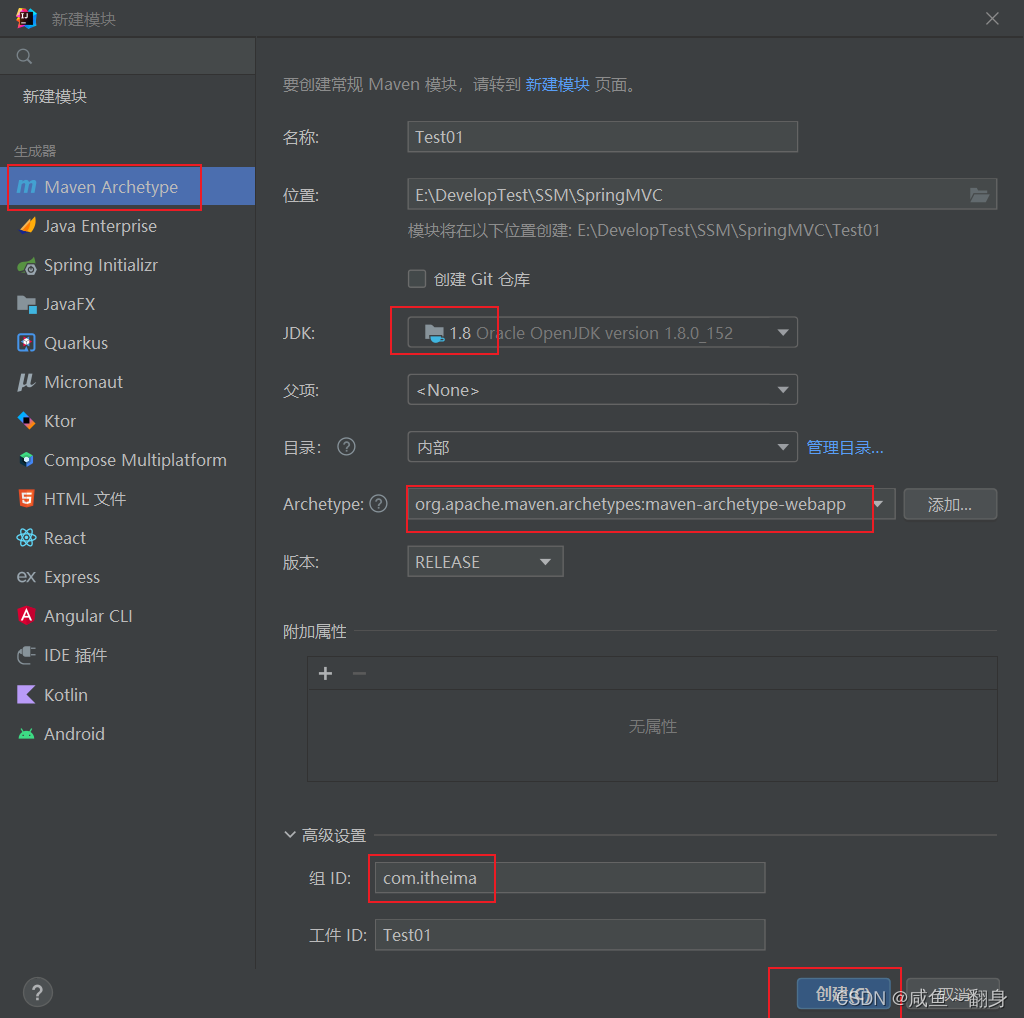
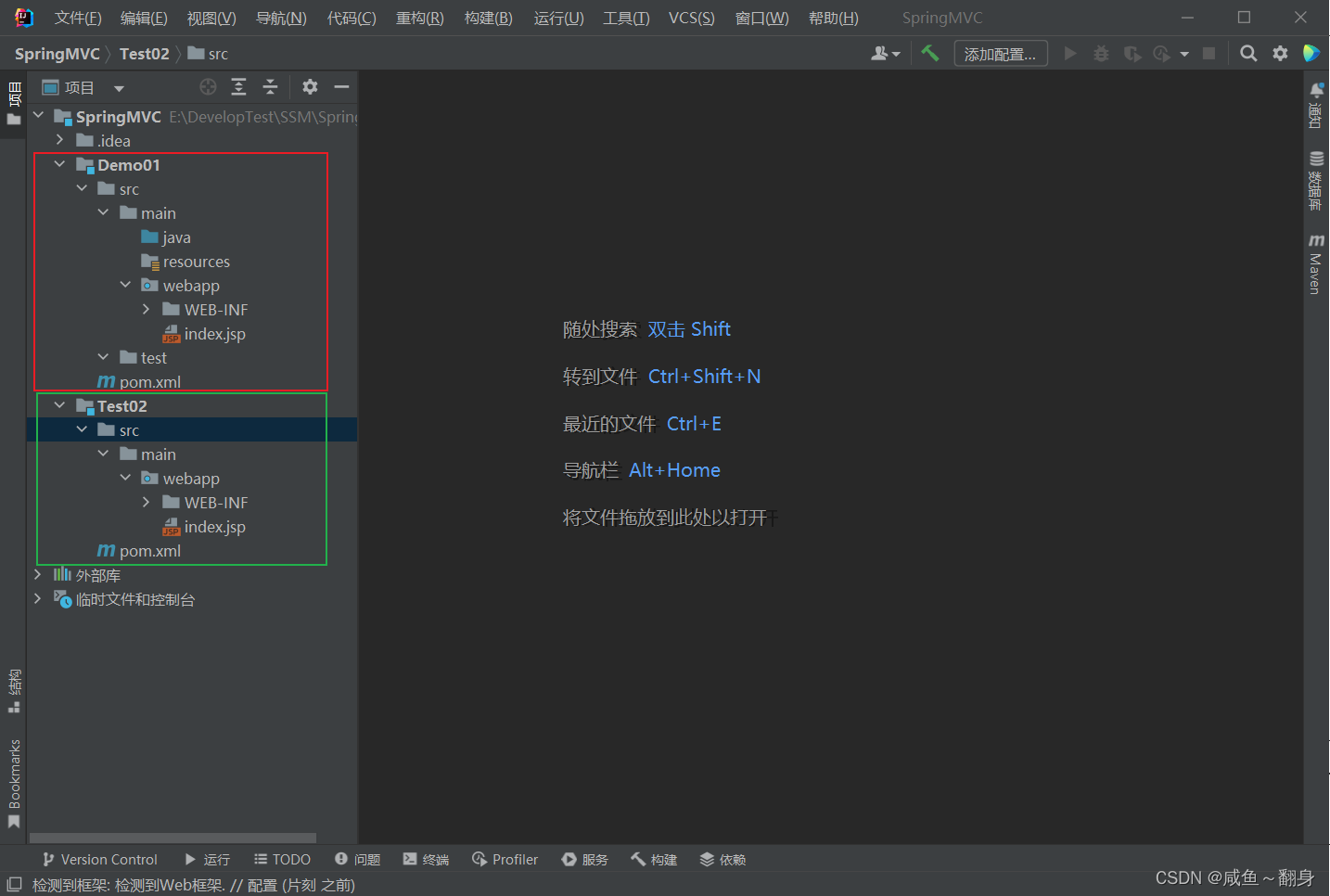
2.2引入依赖(pom.xml)
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId> <version>5.3.1version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logbackgroupId> <artifactId>logback-classicartifactId> <version>1.2.3version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servletgroupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId> <version>3.1.0version> <scope>providedscope> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleafgroupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5artifactId> <version>3.0.12.RELEASEversion> dependency> dependencies>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
2.3配置web.xml
2.3.1默认配置方式
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class> servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name> <url-pattern>/url-pattern> servlet-mapping> web-app>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24

2.3.2扩展配置方式
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xmlparam-value> init-param> <load-on-startup>1load-on-startup> servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name> <url-pattern>/url-pattern> servlet-mapping> web-app>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38

将SpringMVC配置文件放到指定的配置文件中方便管理2.4创建请求控制器
由于前端控制器对浏览器发送的请求进行了统一的处理,但是具体的请求有不同的处理过程,因此需要 创建处理具体请求的类,即请求控制器 请求控制器中每一个处理请求的方法成为控制器方法 因为SpringMVC的控制器由一个POJO(普通的Java类)担任,因此需要通过@Controller注解将其标识 为一个控制层组件,交给Spring的IoC容器管理,此时SpringMVC才能够识别控制器的存在- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
package com.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/8 19:16 */ @Controller public class HelloController { }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
2.5创建SpringMVC的配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima.controller"/> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver"> <property name="order" value="1"/> <property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/> <property name="templateEngine"> <bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine"> <property name="templateResolver"> <bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".html"/> <property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/> <property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" /> bean> property> bean> property> bean> beans>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
2.6配置Tomcat

2.7测试

- 实现对主页的访问
package com.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/8 19:16 */ @Controller public class HelloController { // @RequestMapping注解:处理请求和控制器方法之间的映射关系 // @RequestMapping注解的value属性可以通过请求地址匹配请求,/表示的当前工程的上下文路径 // localhost:8080/springMVC/ @RequestMapping("/") public String index() { //设置逻辑视图名称 return "test"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 通过超链接跳转到指定页面
- 在主页中设置超链接
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>首页title> head> <body> <h1>index.htmlh1> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试SpringMVCa> <a href="/hello">测试绝对路径a> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 在请求控制中创建处理请求的方法
package com.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/8 19:16 */ @Controller public class HelloController { // @RequestMapping注解:处理请求和控制器方法之间的映射关系 // @RequestMapping注解的value属性可以通过请求地址匹配请求,/表示的当前工程的上下文路径 // localhost:8080/springMVC/ @RequestMapping("/") public String index() { //设置逻辑视图名称 return "test"; } @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return "ok"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
2.8总结
浏览器发送请求,若请求地址符合前端控制器的url-pattern,该请求就会被前端控制器DispatcherServlet处理。前端控制器会读取SpringMVC的核心配置文件,通过扫描组件找到控制器,将请求地址和控制器中@RequestMapping注解的value属性值进行匹配,若匹配成功,该注解所标识的控制器方法就是处理请求的方法。处理请求的方法需要返回一个字符串类型的视图名称,该视图名称会被视图解析器解析,加上前缀和后缀组成视图的路径,通过Thymeleaf对视图进行渲染,最终转发到视图所对应页面
3.@RequestMapping注解
3.1功能
- @RequestMapping注解的作用:就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系
- SpringMVC接收到指定的请求,就会来找到在映射关系中对应的控制器方法处理这个请求
3.2位置
- @RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息
- @RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求的请求路径的具体信息
package com.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/8 19:16 */ @Controller @RequestMapping("/Test") public class HelloController { // @RequestMapping注解:处理请求和控制器方法之间的映射关系 // @RequestMapping注解的value属性可以通过请求地址匹配请求,/表示的当前工程的上下文路径 // localhost:8080/springMVC/ @RequestMapping("/") public String index() { //设置逻辑视图名称 return "test"; } //此时请求映射所映射的请求的请求路径为:/Test/hello @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return "ok"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
3.3value属性
- @RequestMapping注解的value属性通过请求的请求地址匹配请求映射
- @RequestMapping注解的vlaue属性是一个字符串类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求,
- @RequestMapping注解的value属性值必须设置,至少通过请求地址匹配请求映射
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>首页title> head> <body> <h1>index.htmlh1> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试SpringMVCa> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/Test/hello}">测试SpringMVC(当控制类配置上了@RequestMapping("/Test") )点这个a> <p>p> <a href="/hello">测试绝对路径a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/success1}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/success2}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/success3}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性a> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
package com.itheima.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/8 19:16 */ @Controller //@RequestMapping("/Test") public class HelloController { // @RequestMapping注解:处理请求和控制器方法之间的映射关系 // @RequestMapping注解的value属性可以通过请求地址匹配请求,/表示的当前工程的上下文路径 // localhost:8080/springMVC/ @RequestMapping("/") public String index() { //设置逻辑视图名称 return "test"; } //此时请求映射所映射的请求的请求路径为:/Test/hello @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello() { return "ok"; } @RequestMapping(value = {"/success1", "/success2", "/success3"}) public String success() { return "success"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
3.4method属性
- @RequestMapping注解的method属性通过请求的请求方式(get或post)匹配请求映射
- @RequestMapping注解的method属性是一个RequestMethod类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多种请求方式的请求
- 若当前请求的请求地址满足请求映射的value属性,但是请求方式不满足method属性,则浏览器报错
405:Request method ‘xxx’ not supported
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>首页title> head> <body> <h1>index.htmlh1> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/hello}">测试SpringMVCa> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/Test/hello}">测试SpringMVC(当控制类配置上了@RequestMapping("/Test") )点这个a> <p>p> <a href="/hello">测试绝对路径a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/success1}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/success2}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/success3}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/success}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的method属性a> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
@RequestMapping(value = "success",method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST}) public String method(){ return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
注意:
1、对于处理指定请求方式的控制器方法,SpringMVC中提供了@RequestMapping的派生注解
处理get请求的映射–>@GetMapping
处理post请求的映射–>@PostMapping
处理put请求的映射–>@PutMapping
处理delete请求的映射–>@DeleteMapping
2、常用的请求方式有get,post,put,delete
但是目前浏览器只支持get和post,若在form表单提交时,为method设置了其他请求方式的字符
串(put或delete),则按照默认的请求方式get处理
若要发送put和delete请求,则需要通过spring提供的过滤器HiddenHttpMethodFilter,在
RESTful部分会讲到3.5params属性
- @RequestMapping注解的params属性通过请求的请求参数匹配请求映射,即浏览器发送的请求的请求参数必须满足params属性的参数
- @RequestMapping注解的params属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求参数和请求映射的匹配关系
- “param”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求参数中必须携带param请求参数
- “!param”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求参数中必须不能携带param请求参数
- “param=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求参数中必须携带param请求参数且param=value
- “param!=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求参数中可以不携带param请求参数若携带则param!=value
@RequestMapping(value = "/params",params = {"username","password=123456"}) public String params(){ return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
<p>p> <a th:href="@{/params?username=admin&password=123456}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的params属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/params(username='admin',password=123456)}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的params属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/params(username='admin',password=456)}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的params属性a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/params(username='admin')}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的params属性a>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
注意:
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足params属性,此时
页面回报错400:Parameter conditions “username, password!=123456” not met for actual
request parameters: username={admin}, password={123456}3.6headers属性
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求头信
息和请求映射的匹配关系
“header”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息
“!header”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息
“header=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value
“header!=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求可以不携带header请求头信息,若携带则header!=value
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面
显示404错误,即资源未找到@RequestMapping(value = "/params",params = {"username","password=123456"},headers ={"referer"}) public String params(){ return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
3.7SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径
1.?:表示任意的单个字符(不包括??前是路径,?后是请求参数)
2.* :表示任意的0个或多个字符
3.** :表示任意层数的任意目录
注意:在使用3时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式@RequestMapping("/a?a/test/ant") public String ant1(){ return "success"; } @RequestMapping("/a*a/test/ant") public String ant2(){ return "success"; } @RequestMapping("/**/test/ant") public String ant3(){ return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
<p>p> <a th:href="@{/aaa/test/ant}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的ant风格路径a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/asa/test/ant}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的ant风格路径a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/aa/test/ant}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的ant风格路径a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/asssssa/test/ant}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的ant风格路径a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/a/b/c/test/ant}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的ant风格路径a> <p>p> <a th:href="@{/test/ant}" th:method="get">测试@RequestMapping的ant风格路径a>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
3.8SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符
原始方式:/deleteUser?id=1
rest方式:/user/delete/1SpringMVC路径中的占位符常用于RESTful风格中,当请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符{xxx}表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参
@RequestMapping("/a/fu/{username}/{id}") public String fu(@PathVariable("username") String username,@PathVariable("id") Integer id){ System.out.println("id: " + id); System.out.println("username: " + username); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
<p>p> <a th:href="@{/a/fu/admin/1}">测试@RequestMapping支持路径中的占位符a>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4.SpringMVC获取请求参数
4.1通过ServletAPI获取
将HttpServletRequest作为控制器方法的形参,此时HttpServletRequest类型的参数表示封装了当前请求的请求报文的对象
<form th:action="@{/ServletAPI}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br> 密码:<input type="text" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="登录"><br> form>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
@RequestMapping("/ServletAPI") public String ServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request) { String username = request.getParameter("username"); String password = request.getParameter("password"); System.out.println("username: " + username + ",password: " + password); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4.2通过控制器方法的形参获取请求参数
在控制器方法的形参位置,设置和请求参数同名的形参,当浏览器发送请求,匹配到请求映射时,在DispatcherServlet中就会将请求参数赋值给相应的形参
<form th:action="@{/param}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br> 密码:<input type="text" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="登录"><br> form>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
@RequestMapping("/param") public String getParam(String username, Integer password) { System.out.println("username: " + username + ",password: " + password); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
注意:
若请求所传输的请求参数中有多个同名的请求参数,此时可以在控制器方法的形参中设置字符串
数组或者字符串类型的形参接收此请求参数
若使用字符串数组类型的形参,此参数的数组中包含了每一个数据若使用字符串类型的形参,此参数的值为每个数据中间使用逗号拼接的结果4.3@RequestParam
@RequestParam是将请求参数和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@RequestParam注解一共有三个属性:
value:指定为形参赋值的请求参数的参数名
required:设置是否必须传输此请求参数,默认值为true
若设置为true时,则当前请求必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输该请求参数,且没有设置defaultValue属性,则页面报错400:Required String parameter ‘xxx’ is not present;
若设置为false,则当前请求不是必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输,则注解所标识的形参的值为null
defaultValue:不管required属性值为true或false,当value所指定的请求参数没有传输或传输的值为""时,则使用默认值为形参赋值4.4@RequestHeader
@RequestHeader是将请求头信息和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@RequestHeader注解一共有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,用法同@RequestParam<form th:action="@{/param/Request}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="name"><br> 密码:<input type="text" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="登录"><br> form>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
@RequestMapping("/param/Request") public String getParamByRequest( @RequestParam(value = "name",required = true,defaultValue = "坂本龙一") String username, Integer password, @RequestHeader(value = "referer",required = true,defaultValue = "不知道来源") String referer ) { System.out.println("referer: " + referer); System.out.println("username: " + username + ",password: " + password); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
4.5@CookieValue
@CookieValue是将cookie数据和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@CookieValue注解一共有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,用法同@RequestParam4.6通过POJO获取请求参数
可以在控制器方法的形参位置设置一个实体类类型的形参,此时若浏览器传输的请求参数的参数名和实体类中的属性名一致,那么请求参数就会为此属性赋值
<form th:action="@{/param/POJO}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br> 密码:<input type="text" name="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="登录"><br> form>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
@RequestMapping("/param/POJO") public String getParamByPOJO(User user) { System.out.println(user); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
4.7解决获取请求参数的乱码问题
解决获取请求参数的乱码问题,可以使用SpringMVC提供的编码过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter,但是必须在web.xml中进行注册
<filter> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encodingparam-name> <param-value>UTF-8param-value> init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceEncodingparam-name> <param-value>trueparam-value> init-param> filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name> <url-pattern>/*url-pattern> filter-mapping>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
注:
SpringMVC中处理编码的过滤器一定要配置到其他过滤器之前,否则无效5.域对象共享数据
5.1使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/servletAPI") public String testServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request) { request.setAttribute("testScope", "你好,servletAPI"); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
test.html
<a th:href="@{/servletAPI}">测试使用servletAPI向域对象中共享数据a>- 1
- 2
- 3
success.html
<p th:text="${testScope}">p>- 1
- 2
5.2使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView") public ModelAndView testModelAndView(){ /* * ModelAndView有model和view的功能 * model主要用于向请求域共享数据 * view主要用于设置视图,实现页面跳转 * */ ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); //向请求域共享数据 mav.addObject("testScope2", "你好,ModelAndView"); //设置视图,实现页面跳转 mav.setViewName("success"); return mav; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
test.html
<a th:href="@{/modelAndView}">测试使用ModelAndView向域对象中共享数据a>- 1
- 2
success.html
<p th:text="${testScope2}"></p>- 1
- 2
5.3使用Model向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/model") public String testModel(Model model) { model.addAttribute("testScope3","你好,Model"); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
test.html
<a th:href="@{/model}">测试使用Model向域对象中共享数据a>- 1
- 2
success.html
<p th:text="${testScope3}">p>- 1
- 2
5.4使用map向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/map") public String testMap(Map<String, Object> map) { map.put("testScope4", "你好,map"); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
test.html
<a th:href="@{/map}">测试使用map向域对象中共享数据a>- 1
- 2
success.html
<p th:text="${testScope4}"></p>- 1
5.5使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/modelMap") public String testModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){ modelMap.addAttribute("testScope5","你好,ModelMap!"); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
test.html
<a th:href="@{/modelMap}">测试使用ModelMap向域对象中共享数据a>- 1
- 2
success.html
<p th:text="${testScope5}">p>- 1
- 2
5.6Model,ModelMap,Map的关系
Model、ModelMap、Map类型的参数其实本质上都是 BindingAwareModelMap 类型的
public interface Model{} public class ModelMap extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> {} public class ExtendedModelMap extends ModelMap implements Model {} public class BindingAwareModelMap extends ExtendedModelMap {}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
5.7向session域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/session") public String testSession(HttpSession httpSession) { httpSession.setAttribute("scope1", "你好,session"); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
test.html
<a th:href="@{/session}">测试向session对象中共享数据a>- 1
sccess.html
<p th:text="${session.scope1}">p>- 1
- 2
5.8向application域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/application") public String testApplication(HttpSession httpSession) { ServletContext servletContext = httpSession.getServletContext(); servletContext.setAttribute("scope2","你好,application"); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
test.html
<a th:href="@{/application}">测试向application对象中共享数据a>- 1
- 2
sccess.html
<p th:text="${application.scope2}">p>- 1
- 2
6.SpringMVC的视图
SpringMVC中的视图是View接口,视图的作用渲染数据,将模型Model中的数据展示给用户
SpringMVC视图的种类很多,默认有转发视图和重定向视图
当工程引入jstl的依赖,转发视图会自动转换为JstlView
若使用的视图技术为Thymeleaf,在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置了Thymeleaf的视图解析器,由此视图解析器解析之后所得到的是ThymeleafView6.1ThymeleafView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,视图名称拼接视图前缀和视图后缀所得到的最终路径,会通过转发的方式实现跳转
@RequestMapping("/thymeleafView") public String testThymeleafView(){ return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
<a th:href="@{/thymeleafView}">测试ThymeleafView视图a>- 1
6.2转发视图
SpringMVC中默认的转发视图是InternalResourceView
SpringMVC中创建转发视图的情况:当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"forward:"为前缀时,创建InternalResourceView视图,此时的视
图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"forward:“去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过转发的方式实现跳转
例如"forward:/”,“forward:/employee”@RequestMapping("/internalResourceView") public String testInternalResourceView(){ return "forward:/thymeleafView"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
<a th:href="@{/internalResourceView}">测试internalResourceView转发视图a>- 1
6.3重定向视图
SpringMVC中默认的重定向视图是RedirectView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"redirect:"为前缀时,创建RedirectView视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"redirect:“去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过重定向的方式实现跳转
例如"redirect:/”,“redirect:/employee”@RequestMapping("/redirectView") public String testRedirectView(){ return "redirect:/thymeleafView"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
<a th:href="@{/redirectView}">测试redirectView重定向视图a>- 1
- 2
注:
重定向视图在解析时,会先将redirect:前缀去掉,然后会判断剩余部分是否以/开头,若是则会自
动拼接上下文路径6.4视图控制器view-controller
当控制器方法中,仅仅用来实现页面跳转,即只需要设置视图名称时,可以将处理器方法使用viewcontroller标签进行表示(在springmvc.xml中配置)
<mvc:annotation-driven/> <mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="test">mvc:view-controller>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
注:
当SpringMVC中设置任何一个view-controller时,其他控制器中的请求映射将全部失效,此时需要在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中设置开启mvc注解驱动的标签:7.RESTFUL
7.1简介
REST:Representational State Transfer,表现层资源状态转移。
7.2RESTful的实现
具体说,就是 HTTP 协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。
它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源。
REST 风格提倡 URL 地址使用统一的风格设计,从前到后各个单词使用斜杠分开,不使用问号键值对方式携带请求参数,而是将要发送给服务器的数据作为 URL 地址的一部分,以保证整体风格的一致性。

7.3HiddenHttpMethodFilter
由于浏览器只支持发送get和post方式的请求,那么该如何发送put和delete请求呢?
SpringMVC 提供了 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 帮助我们将 POST 请求转换为 DELETE 或 PUT 请求
HiddenHttpMethodFilter 处理put和delete请求的条件:
a>当前请求的请求方式必须为post
b>当前请求必须传输请求参数_method
满足以上条件,HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器就会将当前请求的请求方式转换为请求参数_method的值,因此请求参数_method的值才是最终的请求方式在web.xml中注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter
注:<filter> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilterclass> filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name> <url-pattern>/*url-pattern> filter-mapping>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
目前为止,SpringMVC中提供了两个过滤器:CharacterEncodingFilter和HiddenHttpMethodFilter
在web.xml中注册时,必须先注册CharacterEncodingFilter,再注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter
原因:
在 CharacterEncodingFilter 中通过request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法设置字
符集的
request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法要求前面不能有任何获取请求参数的操作
而 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 恰恰有一个获取请求方式的操作:String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);7.4例子
index.html
<a th:href="@{/user}">测试查询所有用户信息a> <hr> <a th:href="@{/user/1}">测试根据id查询用户信息a> <hr> <form th:action="@{/user}" method="post"> <input type="submit" value="添加用户信息"> form> <hr> <form th:action="@{/user}" method="post"> <input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put">inpu> <input type="submit" value="修改用户信息"> form> <hr> <form th:action="@{/user/1}" method="post"> <input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">inpu> <input type="submit" value="删除用户信息"> form>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
@RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String testInquire() { System.out.println("查询所有用户信息--/user--get"); return "success"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String testUserById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { System.out.println("根据id查询用户信息--/user/" + id+ "--get"); return "success"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.POST) public String testInsertUser() { System.out.println("添加用户信息--/user--post"); return "success"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.PUT) public String testUpdateUser() { System.out.println("修改用户信息--/user--put"); return "success"; } @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) public String testDeleteUser(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) { System.out.println("删除用户信息--/user/" + id + "--delete"); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
8.RESTFUL案例
8.1准备工作
8.2功能清单
8.3具体功能:访问首页
8.4具体功能:查询所有员工数据
8.5具体功能:删除
8.6具体功能:跳转到添加数据页面
8.7具体功能:执行保存
8.8具体功能:跳转到更新数据页面
8.9具体功能:执行更新
9.SpringMVC处理ajax请求
10.文件上传和下载
10.1文件下载
- ResponseEntity应用于控制器方法的返回值类型,该控制器方法的返回值就是响应到浏览器的响应报文
- 使用ResponseEntity实现下载文件功能
@RequestMapping("/testDown") public ResponseEntity<byte[]> testResponseEntity(HttpSession session) throws IOException { //获取ServletContext对象 ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); //获取服务器中文件的真实路径 // String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath(""); 获取的当前项目的文件路径 // String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("/img/1.jpg"); //当不知道文件之间用什么分割符时,用以下的方法 String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("img"); realPath = realPath + File.separator + "1.jpg"; //创建输入流 InputStream is = new FileInputStream(realPath); //创建字节数组 is.available()获取输入流文件所对应字节数 byte[] bytes = new byte[is.available()]; //将流读到字节数组中 is.read(bytes); //创建HttpHeaders对象设置响应头信息 MultiValueMap<String, String> headers = new HttpHeaders(); //设置要下载方式以及下载文件的名字 headers.add("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=1.jpg"); //设置响应状态码 HttpStatus statusCode = HttpStatus.OK; //创建ResponseEntity对象 ResponseEntity<byte[]> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity<>(bytes, headers, statusCode); //关闭输入流 is.close(); return responseEntity; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
index.html
<a th:href="@{/testDown}">下载图片a>- 1
- 2
- 3

10.2文件上传
index.html
<form th:action="@{/testUp}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 头像:<input type="file" name="photo"><br> <input type="submit" value="上传"> form>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
springmvc.xml
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> bean>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
pom.xml
<dependency> <groupId>commons-fileuploadgroupId> <artifactId>commons-fileuploadartifactId> <version>1.3.1version> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
@RequestMapping("/testUp") public String testFile(MultipartFile photo,HttpSession session) throws IOException { //获取上传前的文件的文件名 String fileName= photo.getOriginalFilename(); //处理文件重名问题 String hzName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf(".")); fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + hzName; //获取ServletContext对象 ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext(); //获取当前工程下photo目录的真实路径 String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("photo"); //创建realPath对应的File对象 File file = new File(realPath); //判断file所对应的目录是否存在 if (!file.exists()){ file.mkdirs(); } String finalPath = realPath + File.separator + fileName; //上传文件 photo.transferTo(new File(finalPath)); return "success"; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
11.拦截器
11.1拦截器的配置SpringMVC中的拦截器用于拦截控制器方法的执行
- SpringMVC中的拦截器用于拦截控制器方法的执行
- SpringMVC中的拦截器需要实HandlerInterceptor
package com.itheima.intercept; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/17 16:27 */ //ctrl+o 重写接口中的方法 public class testIntercept implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("拦截器方法1:preHandle"); return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("拦截器方法2:postHandle"); } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("拦截器方法3:afterCompletion"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- SpringMVC的拦截器必须在SpringMVC的配置文件中进行配置:
<bean id="testIntercept" class="com.itheima.intercept.testIntercept" >bean> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/*"/> <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/abc"/> <ref bean="testIntercept">ref> mvc:interceptor> mvc:interceptors>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
11.2拦截器的三个抽象方法
SpringMVC中的拦截器有三个抽象方法:
- preHandle:控制器方法执行之前执行preHandle(),其boolean类型的返回值表示是否拦截或放行,返回true为放行,即调用控制器方法;返回false表示拦截,即不调用控制器方法
- postHandle:控制器方法执行之后执行postHandle()
- afterCompletion:处理完视图和模型数据,渲染视图完毕之后执行afterCompletion()
11.3多个拦截器的执行顺序
- ①若每个拦截器的preHandle()都返回true
此时多个拦截器的执行顺序和拦截器在SpringMVC的配置文件的配置顺序有关:
preHandle()会按照配置的顺序执行,而postHandle()和afterCompletion()会按照配置的反序执行 - ②若某个拦截器的preHandle()返回了false
preHandle()返回false和它之前的拦截器的preHandle()都会执行,postHandle()都不执行,返回false的拦截器之前的拦截器的afterCompletion()会执行
12.异常处理器
12.1基于配置的异常处理
- SpringMVC提供了一个处理控制器方法执行过程中所出现的异常的接口:HandlerExceptionResolver
- HandlerExceptionResolver接口的实现类有:DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver和
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver - SpringMVC提供了自定义的异常处理器SimpleMappingExceptionResolver,使用方式:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver"> <property name="exceptionMappings"> <props> <prop key="java.lang.ArithmeticException">errorprop> props> property> <property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex">property> bean>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
12.2基于注解的异常处理
//@ControllerAdvice将当前类标识为异常处理组件 @ControllerAdvice public class ExceptionController { //@ExceptionHandler用于设置所标识方法处理的异常 @ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class) //ex表示当前请求处理中出现的异常对象 public String handleArithmeticException(Exception ex, Model model){ model.addAttribute("ex11", ex); return "error"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
13.注解配置SpringMVC
13.1创建初始化类,代替web.xml
在Servlet3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,
如果找到的话就用它来配置Servlet容器。 Spring提供了这个接口的实现,名为
SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个类反过来又会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配
置的任务交给它们来完成。Spring3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基础实现,名为
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,当我们的类扩展了
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer并将其部署到Servlet3.0容器的时候,容器会自
动发现它,并用它来配置Servlet上下文。package com.itheima.config; import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter; import org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter; import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer; import javax.servlet.Filter; /** * @description:代替web.xml * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/18 14:12 */ public class Web extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override //设置一个配置类,代替spring的配置文件 protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class[]{SpringConfig.class}; } @Override //设置一个配置类,代替SpringMVC的配置文件 protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class[]{SpringMVCConfig.class}; } @Override //设置SpringMVC的前端控制器DispatcherServlet的url-pattern protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[]{"/"}; } @Override //添加过滤器 //配置SpringMVC的编码过滤器 //设置处理请求方式的过滤器 protected Filter[] getServletFilters() { CharacterEncodingFilter encodingFilter = new CharacterEncodingFilter(); encodingFilter.setEncoding("UTF-8"); encodingFilter.setForceRequestEncoding(true); HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter(); return new Filter[]{encodingFilter, hiddenHttpMethodFilter}; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
13.2创建SpringConfig配置类,代替spring的配置文件
package com.itheima.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/18 14:17 */ //代替Spring的配置文件 //将当前类表示为配置类 @Configuration public class SpringConfig { //ssm整合后,spring的配置信息写在此类中 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
13.3创建SpringMVCConfig配置类,代替SpringMVC的配置文件
package com.itheima.config; import com.itheima.interceptor.FirstInterceptor; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.*; import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver; import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine; import org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver; import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode; import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ITemplateResolver; import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver; import java.util.List; import java.util.Properties; /** * @description: * @author: Lenovo * @time: 2022/9/18 14:17 */ //代替SpringMVC的配置文件 //将当前类表示为配置类 @Configuration //扫描组件 @ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller") //开启MVC的注解驱动 @EnableWebMvc public class SpringMVCConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { //使用默认的servlet处理静态资源 @Override public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) { configurer.enable(); } //配置文件上传解析器 @Bean //@Bean注解可以将表示的方法的返回值作为bean进行管理 public CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver() { return new CommonsMultipartResolver(); } //配置拦截器 /* @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { FirstInterceptor firstInterceptor = new FirstInterceptor(); registry.addInterceptor((HandlerInterceptor) firstInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**"); }*/ //配置视图控制 @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index"); } //配置异常映射 @Override public void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) { SimpleMappingExceptionResolver exceptionResolver = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver(); Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.setProperty("java.lang.ArithmeticException", "error"); //设置异常映射 exceptionResolver.setExceptionMappings(prop); //设置共享异常信息的键 exceptionResolver.setExceptionAttribute("ex"); resolvers.add(exceptionResolver); } //配置生成模板解析器 @Bean public ITemplateResolver templateResolver() { WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext(); // ServletContextTemplateResolver需要一个ServletContext作为构造参数,可通过WebApplicationContext 的方法获得 ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new ServletContextTemplateResolver(webApplicationContext.getServletContext()); templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/"); templateResolver.setSuffix(".html"); templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML); return templateResolver; } //生成模板引擎并为模板引擎注入模板解析器 @Bean public SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine(ITemplateResolver templateResolver) { SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine(); templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver); return templateEngine; } //生成视图解析器并为解析器注入模板引擎 @Bean public ViewResolver viewResolver(SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine) { ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver(); viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(templateEngine); return viewResolver; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
14.SpringMVC执行流程
14.1SpringMVC常用组件
- DispatcherServlet:前端控制器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:统一处理请求和响应,整个流程控制的中心,由它调用其它组件处理用户的请求 - HandlerMapping:处理器映射器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:根据请求的url、method等信息查找Handler,即控制器方法 - Handler:处理器,需要工程师开发
作用:在DispatcherServlet的控制下Handler对具体的用户请求进行处理 - HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:通过HandlerAdapter对处理器(控制器方法)进行执行 - ViewResolver:视图解析器,不需要工程师开发,由框架提供
作用:进行视图解析,得到相应的视图,例如:ThymeleafView、InternalResourceView、
RedirectView - View:视图
作用:将模型数据通过页面展示给用户
14.2DispatcherServlet初始化过程
DispatcherServlet 本质上是一个 Servlet,所以天然的遵循 Servlet 的生命周期。所以宏观上是 Servlet生命周期来进行调度。
14.3DispatcherServlet调用组件处理请求
14.4SpringMVC的执行流程
- 用户向服务器发送请求,请求被SpringMVC 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet捕获。
- DispatcherServlet对请求URL进行解析,得到请求资源标识符(URI),判断请求URI对应的映射:
a) 不存在
- 再判断是否配置了mvc:default-servlet-handler
- 如果没配置,则控制台报映射查找不到,客户端展示404错误
b) 存在则执行下面的流程
- 根据该URI,调用HandlerMapping获得该Handler配置的所有相关的对象(包括Handler对象以及
Handler对象对应的拦截器),最后以HandlerExecutionChain执行链对象的形式返回。 - DispatcherServlet 根据获得的Handler,选择一个合适的HandlerAdapter。
- 如果成功获得HandlerAdapter,此时将开始执行拦截器的preHandler(…)方法【正向】
- 提取Request中的模型数据,填充Handler入参,开始执行Handler(Controller)方法,处理请求。
在填充Handler的入参过程中,根据你的配置,Spring将帮你做一些额外的工作:
a) HttpMessageConveter: 将请求消息(如Json、xml等数据)转换成一个对象,将对象转换为指定
的响应信息
b) 数据转换:对请求消息进行数据转换。如String转换成Integer、Double等
c) 数据格式化:对请求消息进行数据格式化。 如将字符串转换成格式化数字或格式化日期等
d) 数据验证: 验证数据的有效性(长度、格式等),验证结果存储到BindingResult或Error中 - Handler执行完成后,向DispatcherServlet 返回一个ModelAndView对象。
- 此时将开始执行拦截器的postHandle(…)方法【逆向】。
- 根据返回的ModelAndView(此时会判断是否存在异常:如果存在异常,则执行
HandlerExceptionResolver进行异常处理)选择一个适合的ViewResolver进行视图解析,根据Model
和View,来渲染视图。 - 渲染视图完毕执行拦截器的afterCompletion(…)方法【逆向】。
- 将渲染结果返回给客户端。
- M:Model,模型层,指工程中的JavaBean,作用是处理数据
-
相关阅读:
【WSL】单机大模型前的基础环境配置
cell-var-from-loop
Docker覆盖网络--初步了解
DDRx寻址原理
Usenix Security 2022 FIXREVERTER A Realistic Bug Injection Methodology for
DL Homework 3
Redis缓存的高并发问题
走进Elasticsearch
操作系统(OS) 基础知识
JavaScript Promise 的真正工作原理
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47700419/article/details/126768468
