-
【实战】SpringBoot对接外部API并一步一步性能调优
需求分析:
本平台对接某某平台的接口,保证接口的稳定性和安全性
实战:
首先我们初始化一个Demo,SpringBoot初始化教程略,初始化后的效果如下:

1.引入依赖:[这里我们使用 commons-httpclient 3]<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-httpclient/commons-httpclient --> <dependency> <groupId>commons-httpclient</groupId> <artifactId>commons-httpclient</artifactId> <version>3.1</version> </dependency> <!-- 使用goole的json转化工具 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId> <artifactId>gson</artifactId> <version>2.8.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2.编写工具类(HttpClientUtils):
Get请求:
根据需求,这里我们需要两个参数,一个是token,一个是url参数 + url地址,权限验证采用的是Bearer Tokenpublic static String sendGet(String urlParam, String token) { // 1.创建httpClient实例对象 HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient(); // 设置httpClient连接主机服务器超时时间:15000毫秒 httpClient.getHttpConnectionManager().getParams().setConnectionTimeout(15000); // 2.创建GetMothod实例对象 GetMethod getMethod = new GetMethod(urlParam); // 3.设置post请求超时时间、请求头 getMethod.getParams().setParameter(HttpMethodParams.SO_TIMEOUT, 60000); getMethod.addRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { Header header = new Header("Authorization", "Bearer " + token); getMethod.addRequestHeader(header); } try { // 4.执行getMethod,调用http接口 httpClient.executeMethod(getMethod); // 5.读取内容[流的形式读取] InputStream is = getMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 采用线程安全的StringBuffer StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); String str= ""; while((str = br.readLine()) != null){ res.append(str); } return res.toString(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6.释放连接 getMethod.releaseConnection(); } return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
Post请求:
根据需求,这里我们需要三个参数,一个是token,一个是url参数 + url地址,还有一个是请求体,权限验证采用的是Bearer Tokenpublic static String sendPost(String urlParam, Map<String, Object> jsonMap, String token) { // 1.创建httpClient实例对象 HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient(); // 设置httpClient连接主机服务器超时时间:15000毫秒 httpClient.getHttpConnectionManager().getParams().setConnectionTimeout(15000); // 2.创建PostMethod实例对象 PostMethod postMethod = new PostMethod(urlParam); // 设置post请求超时时间、请求头 postMethod.getParams().setParameter(HttpMethodParams.SO_TIMEOUT, 60000); postMethod.addRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8"); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { Header header = new Header("Authorization", "Bearer " + token); postMethod.addRequestHeader(header); } // 3.设置请求体 Gson gson = new Gson(); String jsonStr = gson.toJson(jsonMap); postMethod.setRequestBody(jsonStr); try { // 4.执行postMethod,调用http接口 httpClient.executeMethod(postMethod); // 5.读取内容[流的形式读取] InputStream is = postMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 采用线程安全的StringBuffer StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); String str= ""; while((str = br.readLine()) != null){ res.append(str); } return res.toString(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 7.释放连接 postMethod.releaseConnection(); } return null; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
Main方法测试:
// 1.调用获取token接口 String baseUrl = "http://*****/"; String url = baseUrl + "/****/token"; Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>(); jsonMap.put("username", "***"); jsonMap.put("password", "***"); String res = sendPost(url, jsonMap, null); log.info("获得的请求结果:{}", res);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
获得的请求结果: {"message":"success","status":1,"data":{"token":"eyJh****"}}- 1
- 2
我们请求得到JSON字符串后,使用GSON来解析JSON,提取有用的信息,如token
// 2.解析JSON,得到token Gson gson = new Gson(); // 克服泛型类型擦除问题 // 具体查阅https://zditect.com/main-advanced/java/gson-json-to-map.html Type mapType = new TypeToken<HashMap<String, Object>>(){}.getType(); HashMap<String, Object> resMap = gson.fromJson(res, mapType); log.info("请求结果解析:{}", resMap); LinkedTreeMap data = (LinkedTreeMap) resMap.get("data"); String token = (String) data.get("token"); log.info("token为:{}", token);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
获取得到token后我们开始使用,模拟一次Get请求:
url = baseUrl + "******"; log.info("获得的请求结果:{}", sendGet(url, token)); 获得的请求结果: {"message":"success","status":1,"data":{****}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
完整工具类,方便大家拿来直接使用:
HttpClientUtils.javapackage com.example.demo; import com.google.gson.Gson; import com.google.gson.internal.LinkedTreeMap; import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.Header; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.GetMethod; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.PostMethod; import org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpMethodParams; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.lang.reflect.Type; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @author xh * @Date 2022/9/14 */ @Slf4j public class HttpClientUtils { public static String sendPost(String urlParam, Map<String, Object> jsonMap, String token) { // 1.创建httpClient实例对象 HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient(); // 设置httpClient连接主机服务器超时时间:15000毫秒 httpClient.getHttpConnectionManager().getParams().setConnectionTimeout(15000); // 2.创建PostMethod实例对象 PostMethod postMethod = new PostMethod(urlParam); // 设置post请求超时时间、请求头 postMethod.getParams().setParameter(HttpMethodParams.SO_TIMEOUT, 60000); postMethod.addRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf-8"); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { Header header = new Header("Authorization", "Bearer " + token); postMethod.addRequestHeader(header); } // 3.设置请求体 Gson gson = new Gson(); String jsonStr = gson.toJson(jsonMap); postMethod.setRequestBody(jsonStr); try { // 4.执行postMethod,调用http接口 httpClient.executeMethod(postMethod); // 5.读取内容[流的形式读取] InputStream is = postMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 采用线程安全的StringBuffer StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); String str= ""; while((str = br.readLine()) != null){ res.append(str); } return res.toString(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 7.释放连接 postMethod.releaseConnection(); } return null; } public static String sendGet(String urlParam, String token) { // 1.创建httpClient实例对象 HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient(); // 设置httpClient连接主机服务器超时时间:15000毫秒 httpClient.getHttpConnectionManager().getParams().setConnectionTimeout(15000); // 2.创建GetMothod实例对象 GetMethod getMethod = new GetMethod(urlParam); // 3.设置post请求超时时间、请求头 getMethod.getParams().setParameter(HttpMethodParams.SO_TIMEOUT, 60000); getMethod.addRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { Header header = new Header("Authorization", "Bearer " + token); getMethod.addRequestHeader(header); } try { // 4.执行getMethod,调用http接口 httpClient.executeMethod(getMethod); // 5.读取内容[流的形式读取] InputStream is = getMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 采用线程安全的StringBuffer StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer(); String str= ""; while((str = br.readLine()) != null){ res.append(str); } return res.toString(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 6.释放连接 getMethod.releaseConnection(); } return null; } public static void main(String[] args) { // 1.调用获取token接口 String baseUrl = "http://****"; String url = baseUrl + "/*****"; Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>(); jsonMap.put("username", "****"); jsonMap.put("password", "*****"); String res = sendPost(url, jsonMap, null); log.info("获得的请求结果:{}", res); // 2.解析JSON,得到token Gson gson = new Gson(); // 克服泛型类型擦除问题 // 具体查阅https://zditect.com/main-advanced/java/gson-json-to-map.html Type mapType = new TypeToken<HashMap<String, Object>>(){}.getType(); HashMap<String, Object> resMap = gson.fromJson(res, mapType); log.info("请求结果解析:{}", resMap); LinkedTreeMap data = (LinkedTreeMap) resMap.get("data"); String token = (String) data.get("token"); log.info("token为:{}", token); // 3.模拟Get请求 // TODO 需要使用URL编码 url = baseUrl + "****"; log.info("获得的请求结果:{}", sendGet(url, token)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
为前端提供接口并测试:
首先我们统一返回风格:
Result.javapackage com.example.demo; import lombok.Data; import java.io.Serializable; /** * @author xh * @Date 2022/9/14 */ @Data public class Result<T> implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * 编码:0表示成功,其他值表示失败 */ private int code = 0; /** * 消息内容 */ private String msg = "success"; /** * 响应数据 */ private T data; public Result<T> ok(T data) { this.setData(data); return this; } public Result<T> error(String msg) { this.code = 500; this.msg = msg; return this; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
新建ApiController:
首先我们将公共变量做一个提取:public static String TOKEN = ""; public static final String BASE_URL = "http://****"; public static final String USERNAME = "****"; public static final String PASSWORD = "****"; // 静态代码块 static { // 1.调用获取token接口 String url = BASE_URL + "/****"; Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>(); jsonMap.put("username", USERNAME); jsonMap.put("password", PASSWORD); String res = sendPost(url, jsonMap, null); // 2.解析JSON,得到token Gson gson = new Gson(); Type mapType = new TypeToken<HashMap<String, Object>>(){}.getType(); HashMap<String, Object> resMap = gson.fromJson(res, mapType); LinkedTreeMap data = (LinkedTreeMap) resMap.get("data"); TOKEN = (String) data.get("token"); log.info("token获取成功:{}", TOKEN); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
模拟Get请求:
/** * Get请求 * 请求地址:http://localhost:8080/identity/getDetail_get?handle=xxx * @return */ @GetMapping("/getDetail_get") public Result<String> getDataGet(@RequestParam String handle) { log.info("开始发起Get请求, token为:{}", TOKEN); Assert.notNull(handle); String url = BASE_URL + "/xxx=" + handle; try { String res = sendGet(url, TOKEN); return new Result<String>().ok(res); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return new Result<String>().error("请求失败!"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
模拟Post请求:
/** * 模拟POST请求 * 请求地址:http://localhost:8080/identity/getDetail_post */ @PostMapping("/getDetail_post") public Result<String> getDataPost(@RequestBody HashMap<String, Object> requestBody) { String url = BASE_URL + "/****"; try { String res = sendPost(url, requestBody, TOKEN);; return new Result<String>().ok(res); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return new Result<String>().error("请求失败!"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
整体代码:
package com.example.demo; import com.google.gson.Gson; import com.google.gson.internal.LinkedTreeMap; import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.lang.reflect.Type; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import static com.example.demo.HttpClientUtils.sendGet; import static com.example.demo.HttpClientUtils.sendPost; /** * @author xh * @Date 2022/9/14 */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/identity/") @Slf4j public class ApiController { public static String TOKEN = ""; public static final String BASE_URL = "http://*****"; public static final String USERNAME = "****"; public static final String PASSWORD = "****"; // 静态代码块 static { // 1.调用获取token接口 String url = BASE_URL + "/identity/token"; Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>(); jsonMap.put("username", USERNAME); jsonMap.put("password", PASSWORD); String res = sendPost(url, jsonMap, null); // 2.解析JSON,得到token Gson gson = new Gson(); Type mapType = new TypeToken<HashMap<String, Object>>(){}.getType(); HashMap<String, Object> resMap = gson.fromJson(res, mapType); LinkedTreeMap data = (LinkedTreeMap) resMap.get("data"); TOKEN = (String) data.get("token"); log.info("token获取成功:{}", TOKEN); } /** * Get请求 * 请求地址:http://localhost:8080/identity/getDetail_get?handle=**** * @return */ @GetMapping("/getDetail_get") public Result<String> getDataGet(@RequestParam String handle) { log.info("开始发起Get请求, token为:{}", TOKEN); Assert.notNull(handle); String url = BASE_URL + "/****" + handle; try { String res = sendGet(url, TOKEN); return new Result<String>().ok(res); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return new Result<String>().error("请求失败!"); } } /** * 模拟POST请求 * 请求地址:http://localhost:8080/identity/getDetail_post */ @PostMapping("/getDetail_post") public Result<String> getDataPost(@RequestBody HashMap<String, Object> requestBody) { String url = BASE_URL + "/****"; try { String res = sendPost(url, requestBody, TOKEN);; return new Result<String>().ok(res); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return new Result<String>().error("请求失败!"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
优化:
模拟场景:在尽可能的
不破坏源代码的情况下,不喜勿喷
优化一:属性通过配置文件读取
新建application.yml文件api: baseUrl: http://***** username: **** password: ****- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
新建配置文件读取类:
ApiConfig.javapackage com.example.demo; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * @author xh * @Date 2022/9/14 */ @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "api") @Data public class ApiConfig { /** * API地址 */ private String baseUrl; /** * 代理用户名 */ private String username; /** * 代理密码 */ private String password; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
ApiController进行微调:
@Autowired ApiConfig apiConfig; public static String TOKEN = ""; public static String BASE_URL = ""; public static String USERNAME = ""; public static String PASSWORD = ""; @PostConstruct private void getBaseInfo() { BASE_URL = apiConfig.getBaseUrl(); USERNAME = apiConfig.getUsername(); PASSWORD = apiConfig.getPassword(); } private String getToken() { if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(TOKEN)) { return TOKEN; } // 1.调用获取token接口 String url = BASE_URL + "/***/token"; Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>(); jsonMap.put("username", USERNAME); jsonMap.put("password", PASSWORD); String res = sendPost(url, jsonMap, null); // 2.解析JSON,得到token Gson gson = new Gson(); Type mapType = new TypeToken<HashMap<String, Object>>(){}.getType(); HashMap<String, Object> resMap = gson.fromJson(res, mapType); LinkedTreeMap data = (LinkedTreeMap) resMap.get("data"); TOKEN = (String) data.get("token"); log.info("token获取成功:{}", TOKEN); return TOKEN; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
由于Token会存在过期时间,所以我们这里引用Redis
1.引入依赖:<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2.在application.yml添加redis配置:
spring: # redis 配置 redis: # 地址 host: xxxxx # 端口,默认为xxx port: xxxx # 数据库索引(db0,db1,db2...不同业务可以放在不同数据库中) database: 0 # 密码 password: 'xxxx'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2.注入RedisTemplate,并优化
@Autowired RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; private String getToken() { ValueOperations<String, String> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); // 0.查询Redis if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(operations.get("token"))) { return operations.get("token"); } // 1.调用获取token接口 String url = BASE_URL + "/***/token"; Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>(); jsonMap.put("username", USERNAME); jsonMap.put("password", PASSWORD); String res = sendPost(url, jsonMap, null); // 2.解析JSON,得到token Gson gson = new Gson(); Type mapType = new TypeToken<HashMap<String, Object>>(){}.getType(); HashMap<String, Object> resMap = gson.fromJson(res, mapType); LinkedTreeMap data = (LinkedTreeMap) resMap.get("data"); String token = (String) data.get("token"); // 设置TOKEN 6小时过期 operations.set("token", token, 6, TimeUnit.HOURS); log.info("token获取成功:{}", token); return token; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
进一步优化,场景:如果有大量请求同时访问一个正好过期的缓存数据,可能会出现缓存击穿,所以我们的解决方案是添加
分布式锁1.加入依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.redissongroupId> <artifactId>redissonartifactId> <version>3.11.0version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
2.创建RedissionConfig.java 配置RedissionClient
package com.example.demo; import org.redisson.Redisson; import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient; import org.redisson.config.Config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * @author xh * @Date 2022/9/14 */ @Component public class RedissionConfig { /** * 所有对redisson的使用都是通过RedissonClient对象 */ @Bean(destroyMethod="shutdown") public RedissonClient redisson() { //创建配置 Config config = new Config(); //可以用"rediss://"来启用SSL连接,useSingleServer表示单例模式 config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://xxxx:xxxx").setDatabase(0).setPassword("xxxx"); //根据config创建出RedissonClient实例 return Redisson.create(config); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
3.注入并编写读锁、写锁:
@Autowired RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; @Autowired RedissonClient redisson; private String getToken() { // 0.查询Redis String token = readToken(); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(token)) { return token; } // 1.调用获取token接口 String url = BASE_URL + "/xxx/token"; Map<String, Object> jsonMap = new HashMap<>(); jsonMap.put("username", USERNAME); jsonMap.put("password", PASSWORD); String res = sendPost(url, jsonMap, null); // 2.解析JSON,得到token Gson gson = new Gson(); Type mapType = new TypeToken<HashMap<String, Object>>(){}.getType(); HashMap<String, Object> resMap = gson.fromJson(res, mapType); LinkedTreeMap data = (LinkedTreeMap) resMap.get("data"); token = (String) data.get("token"); // 设置TOKEN Assert.isTrue(setToken(token)); log.info("token获取成功:{}", token); return token; } private String readToken() { RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("token-lock"); RLock rLock = lock.readLock(); String token = ""; try { //加读锁 rLock.lock(); token = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("token"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { rLock.unlock(); } return token; } private boolean setToken(String token) { RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("token-lock"); RLock rLock = lock.writeLock(); try { // 改数据加写锁,读数据加读锁 rLock.lock(); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("token", token, 6, TimeUnit.HOURS); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { rLock.unlock(); } return true; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
使用JMeter测试:
再次优化:
互联网系统经常会遇到高并发大流量的请求,在突发情况下(如秒杀、抢购),瞬间大流量会直接把系统打垮,为了防止出现这种情况最常见的解决方案之一就是限流,当请求达到一定的并发数或速率,就进行等待、排队、降级、拒绝服务等。
基于Guava工具类【令牌桶算法】,借助自定义注解+AOP实现接口限流
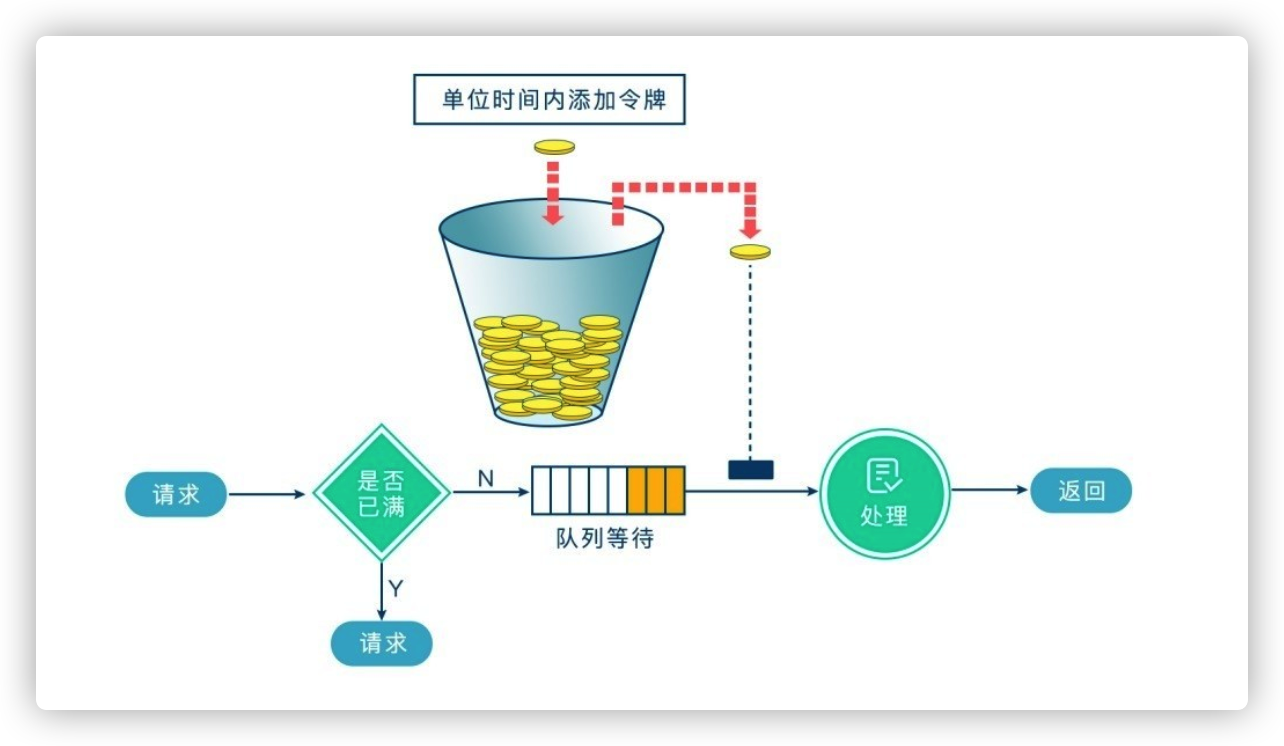
令牌桶算法的原理也比较简单:系统会维护一个令牌(token)桶,以一个恒定的速度往桶里放入令牌(token),这时如果有请求进来想要被处理,则需要先从桶里获取一个令牌(token),当桶里没有令牌(token)可取时,则该请求将被拒绝服务。令牌桶算法通过控制桶的容量、发放令牌的速率,来达到对请求的限制。单机模式模拟:
1.添加依赖:
<!-- Guava: 限流工具类RateLimiter --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>30.1-jre</version> </dependency> <!-- 加入AOP依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2.自定义限流注解:
Limit.javapackage com.example.demo; import java.lang.annotation.*; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; /** * @author xh * @Date 2022/9/15 */ @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) @Documented public @interface Limit { /** * 资源的key,唯一 * 作用:不同的接口,不同的流量控制 */ String key() default ""; /** * 最多的访问限制次数 */ double permitsPerSecond () ; /** * 获取令牌最大等待时间 */ long timeout(); /** * 获取令牌最大等待时间,单位(例:分钟/秒/毫秒) 默认:毫秒 */ TimeUnit timeunit() default TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS; /** * 得不到令牌的提示语 */ String msg() default "系统繁忙,请稍后再试."; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
3.使用AOP切面拦截限流注解
package com.example.demo; import com.google.common.collect.Maps; import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder; import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * @author xh * @Date 2022/9/15 */ @Slf4j @Aspect @Component public class LimitAop { /** * 不同的接口,不同的流量控制 * map的key为 Limiter.key */ private final Map<String, RateLimiter> limitMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap(); @Around("@annotation(com.example.demo.Limit)") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{ MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); //拿limit的注解 Limit limit = method.getAnnotation(Limit.class); if (limit != null) { //key作用:不同的接口,不同的流量控制 String key=limit.key(); RateLimiter rateLimiter = null; //验证缓存是否有命中key if (!limitMap.containsKey(key)) { // 创建令牌桶 rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(limit.permitsPerSecond()); limitMap.put(key, rateLimiter); log.info("新建了令牌桶={},容量={}",key,limit.permitsPerSecond()); } rateLimiter = limitMap.get(key); // 拿令牌 boolean acquire = rateLimiter.tryAcquire(limit.timeout(), limit.timeunit()); // 拿不到命令,直接返回异常提示 if (!acquire) { log.debug("令牌桶={},获取令牌失败",key); this.responseFail(limit.msg()); return null; } } return joinPoint.proceed(); } /** * 直接向前端抛出异常 * @param msg 提示信息 */ private void responseFail(String msg) { HttpServletResponse resp=((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getResponse(); resp.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8"); resp.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8"); PrintWriter writer = null; try { writer = resp.getWriter(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } writer.write(new Result<String>().error(msg).toString()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
4.给需要限流的接口加上注解
/** * Get请求 * @return */ @GetMapping("/getDetail_get") @Limit(key = "limit1", permitsPerSecond = 1, timeout = 1000, timeunit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, msg = "当前排队人数较多,请稍后再试!") public Result<String> getDataGet(@RequestParam String handle) { log.info("开始发起Get请求, token为:{}", getToken()); Assert.notNull(handle); String url = BASE_URL + "/****" + handle; try { String res = sendGet(url, getToken()); return new Result<String>().ok(res); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return new Result<String>().error("请求失败!"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
多次请求时:

-
相关阅读:
golang有序map
大数据十大关键词,涵盖政策、理念、安全、技术等要素,快来了解!
Pinia不就是Vuex5?
SpringMVC的请求与响应和参数传递
模仿 mapstruct 实现一个微服务编排框架(上)
轻量级SQLite可视化工具Sqliteviz
大白话云IDE产品初体验测评(运行一个.py python文件)
图像处理技术的综合应用——提取篮球
莫能菌素人血清白蛋白纳米粒Monensin-HSA|合成路线
挑战52天背完小猪佩奇(第02天)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51517236/article/details/126855104
