-
Java-String的用法
Java-String的用法
文章目录
1.介绍
String类定义时,首字母大写,String本身也是一个类本类,在Java中是一种比较特殊的类。
2.实例化String的两种方法
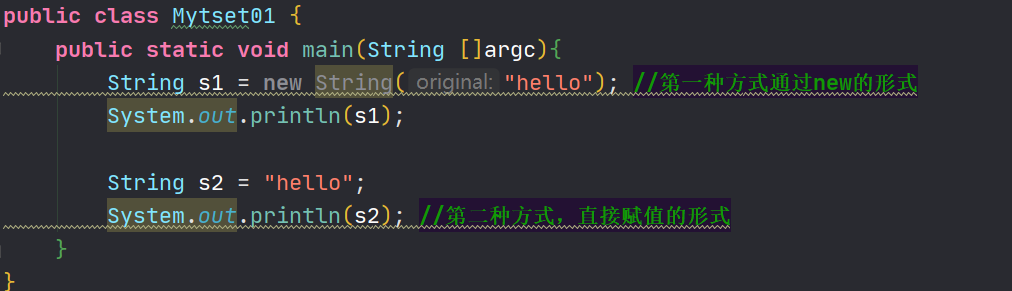
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1 = new String("hello"); //第一种方式通过new的形式 System.out.println(s1); String s2 = "hello"; System.out.println(s2); //第二种方式,直接赋值的形式 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
 两者的具体区别后面详解
两者的具体区别后面详解3.String内容的比较
通常我们用
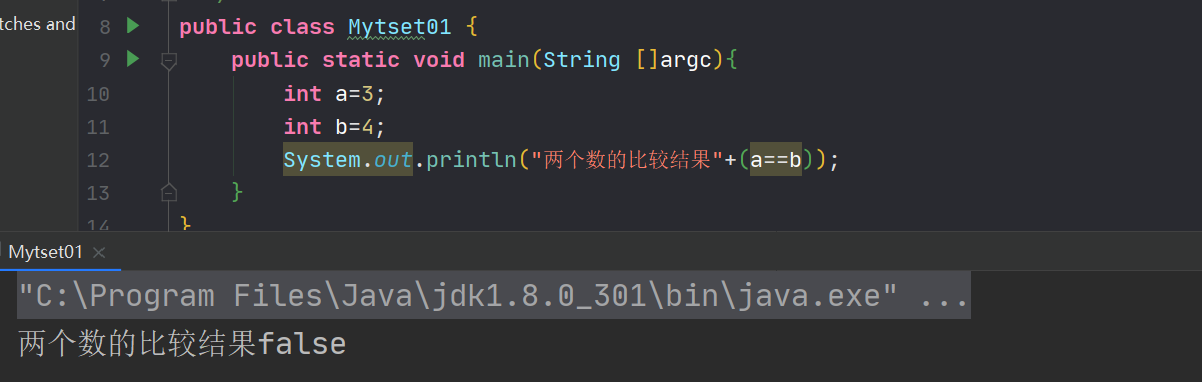
==来对基本的数据类型进行比较,如public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ int a=3; int b=4; System.out.println("两个数的比较结果"+(a==b)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
3.1使用“==”进行基本数据类型的比较
3.2String中使用“==”比较字符串的内容
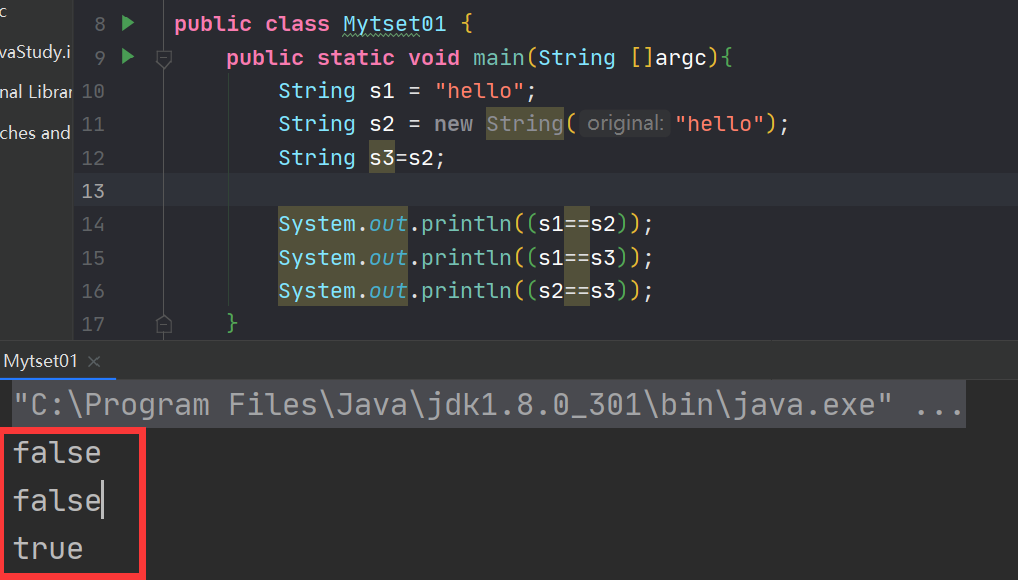 虽然String的内容是一样的,但是比较结果却有差异,给出以下解释
虽然String的内容是一样的,但是比较结果却有差异,给出以下解释
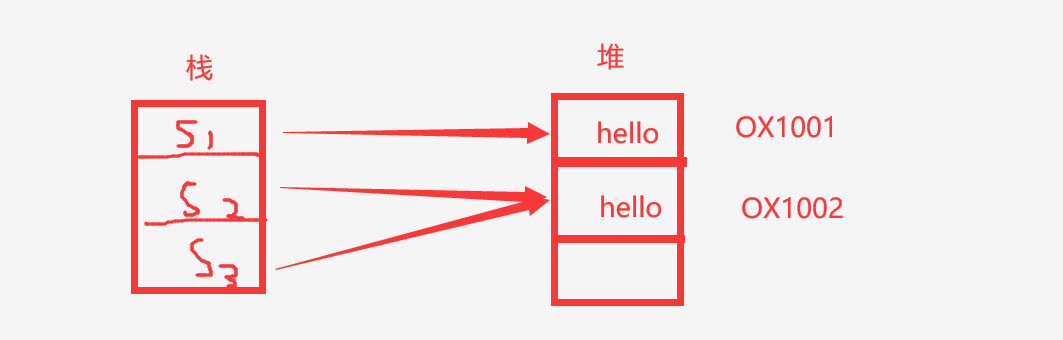
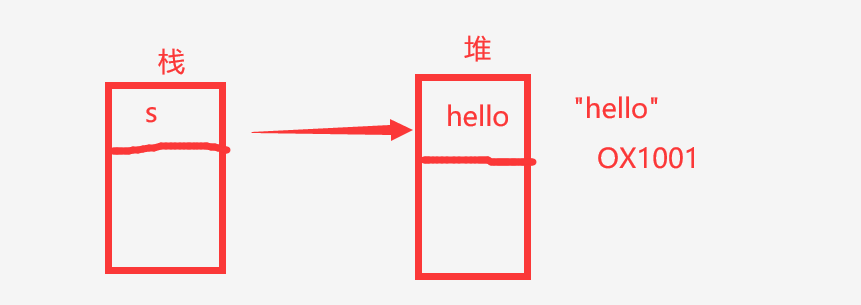
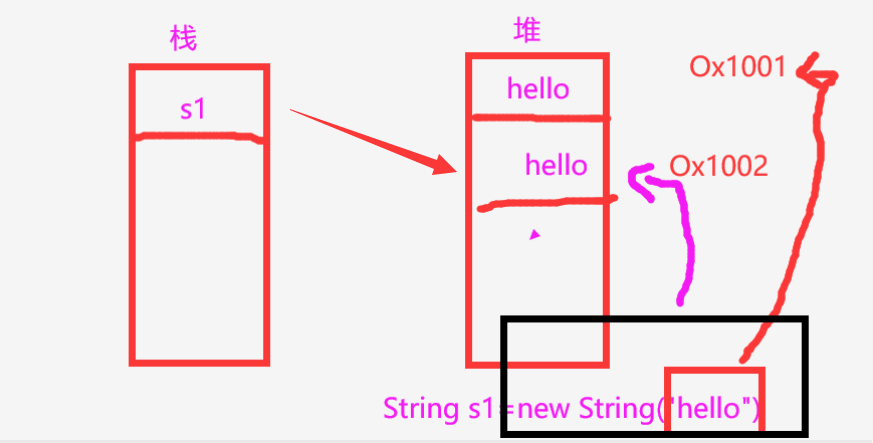
我们都知道栈空间存放着堆空间的引用地址,通过栈空间的对象名可以找得到相应堆空间的内容
s1指向堆空间内容"hello"
s2因为是new的一块空间,虽然内容相同,但是在堆空间还会开辟一块地址存放着hello
s2同时把引用的地址交给了s3,此时s2和s3指向了同一个堆空间的地址,因为s2把引用的地址交给了s3
如图所示
总结:==通常进行基本数据类型的比较- 在String中的
==进行地址的比较
3.3使用equals方法进行String内容的比较
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = new String("hello"); System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
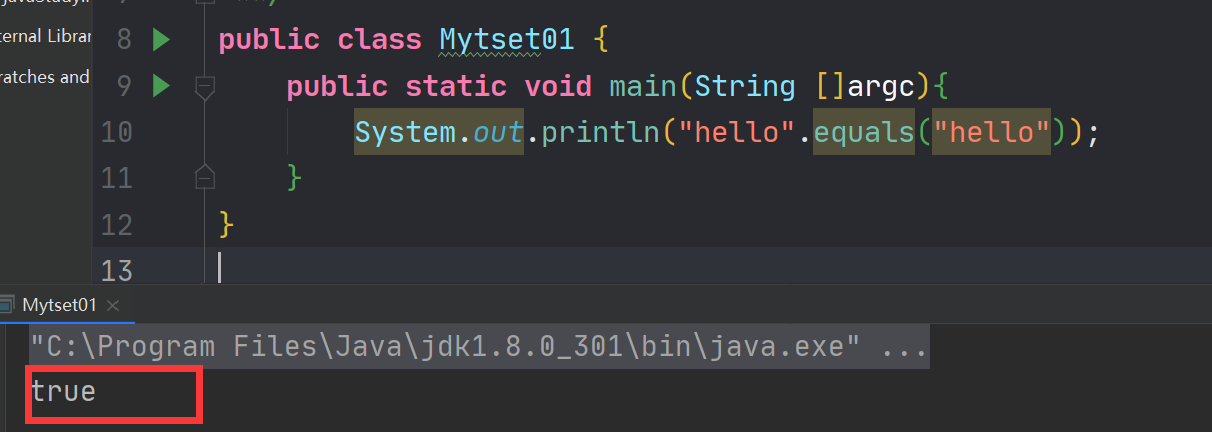
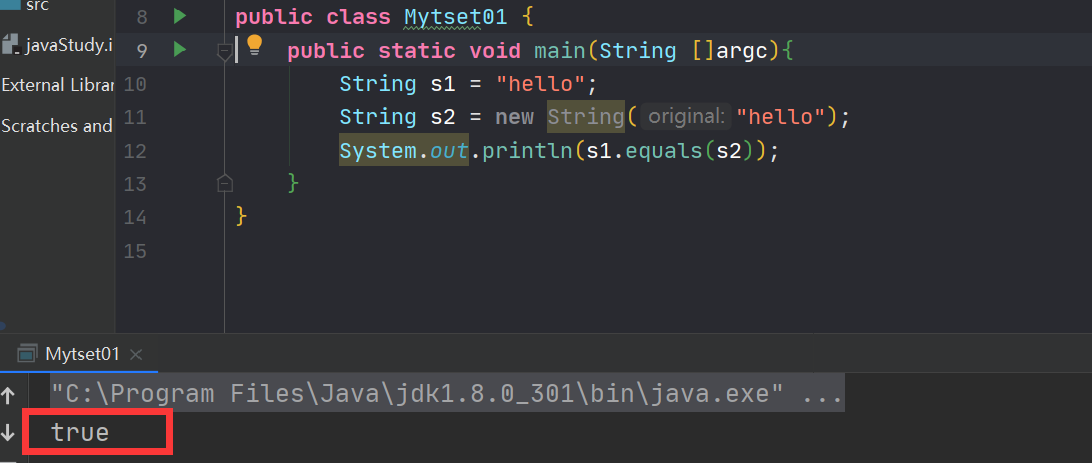 equals方法就是进行内容的比较此处返回true
equals方法就是进行内容的比较此处返回true4.String两种实例化的方式的区别
4.1直接赋值的方式
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1 = new String("hello"); //第一种方式通过new的形式 System.out.println(s1); String s2 = "hello"; System.out.println(s2); //第二种方式,直接赋值的形式 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
首先明白一个字符串其实就是一个String匿名对象,而匿名对象只能被一次实例化,匿名对象其实就是已经开辟了堆空间并可以直接使用的对象。
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ System.out.println("hello".equals("hello")); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
直接赋值的方式,其实就是把匿名对象的堆空间的地址的使用权交给了实例化对象,该对象保存着堆空间的引用地址。
如果一个字符串已经被一个名称应用,以后再有相同的字符串声明时,就不会再重新开辟空间,而继续使用已经开辟好的堆内存。
演示:public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "hello"; String s3 = "hello"; String s4 = "hello"; System.out.println((s1==s2)); System.out.println((s1==s3)); System.out.println((s1==s4)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
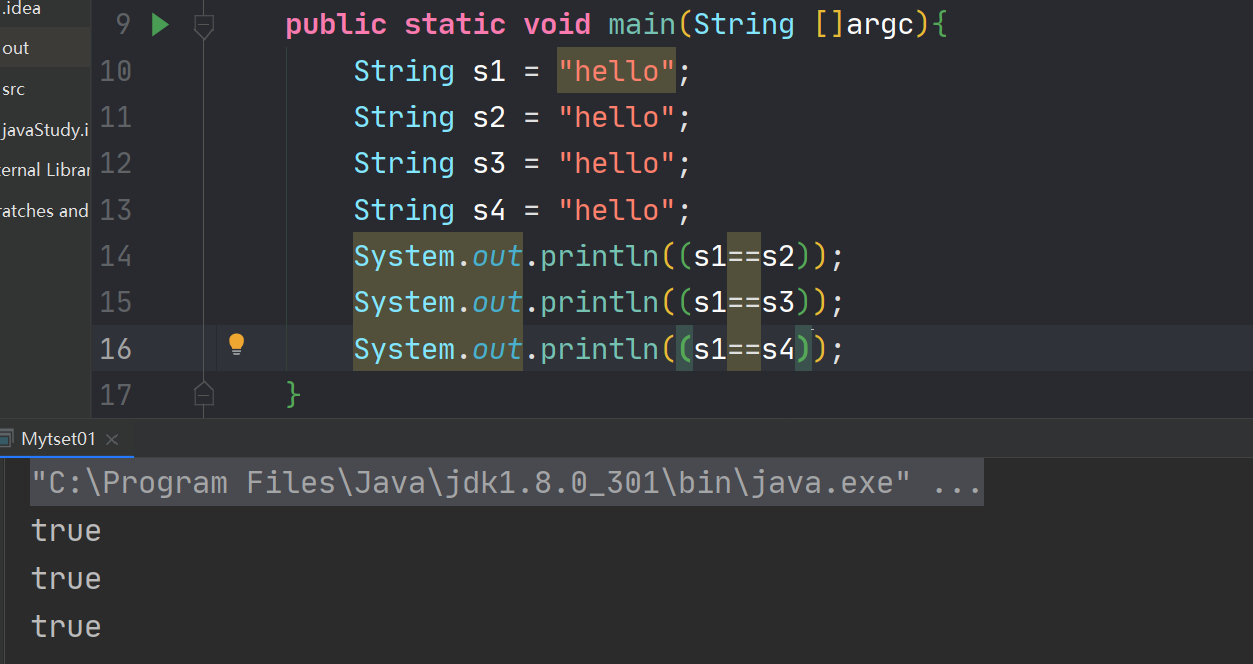
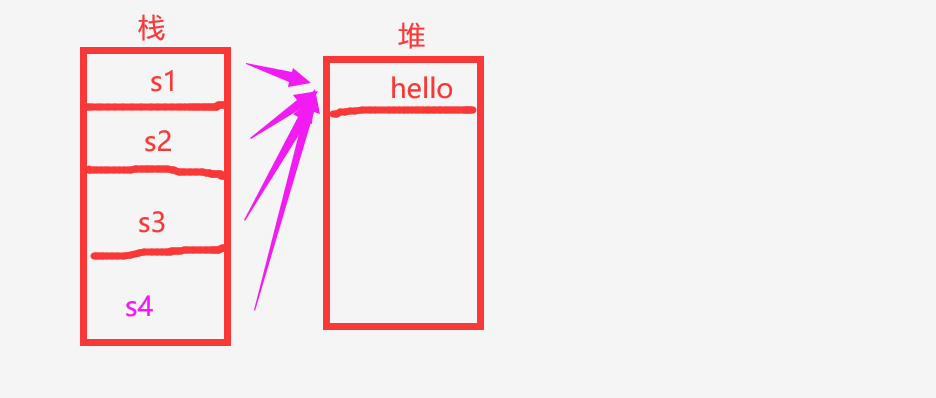
也就是说s1,s2,s3,s4共同指向同一个堆内存的地址
记住当String使用直接赋值的方式之后,只要以后再引用字符串的相关内容,就不会在开辟新的堆空间的内存了
如图所示:
4.2new的方式
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1 = new String("hello"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
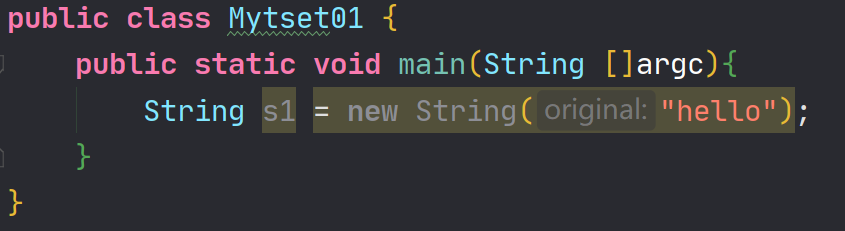 解释:
解释:
一个字符串就是一个匿名对象,如果使用new关键字,不管任何会重新开辟一个新的空间出来,但真正使用的只是一个new关键字开辟出来的堆空间,另一个匿名对象开辟出来的堆空间就浪费了,就是垃圾空间了。
如图所示:
5.字符串的内容不可变
字符串一旦声明则不可以改变
5.1修改字符串的内容
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hello"; s1=s1+"java"; System.out.println("s1="+s1); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
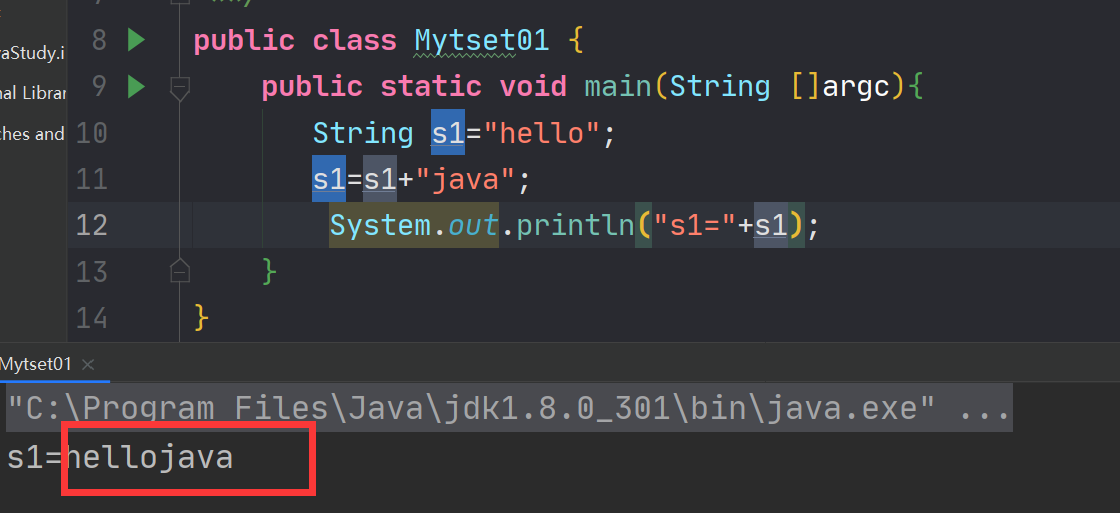
看似好像改变了,其实没有变
如图所示:
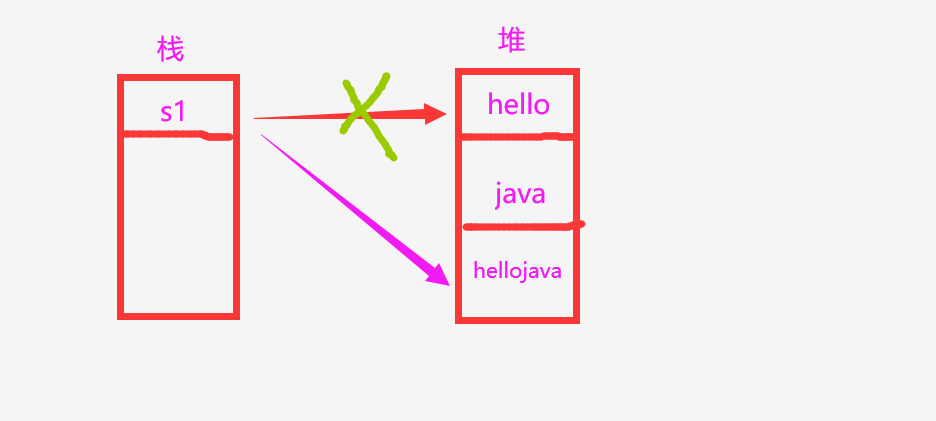
其实只是改变了堆内存地址的指向,通过内存地址的断开-连接变化完成的,而本身字符串的内容没有改变。6.String类中常用的方法
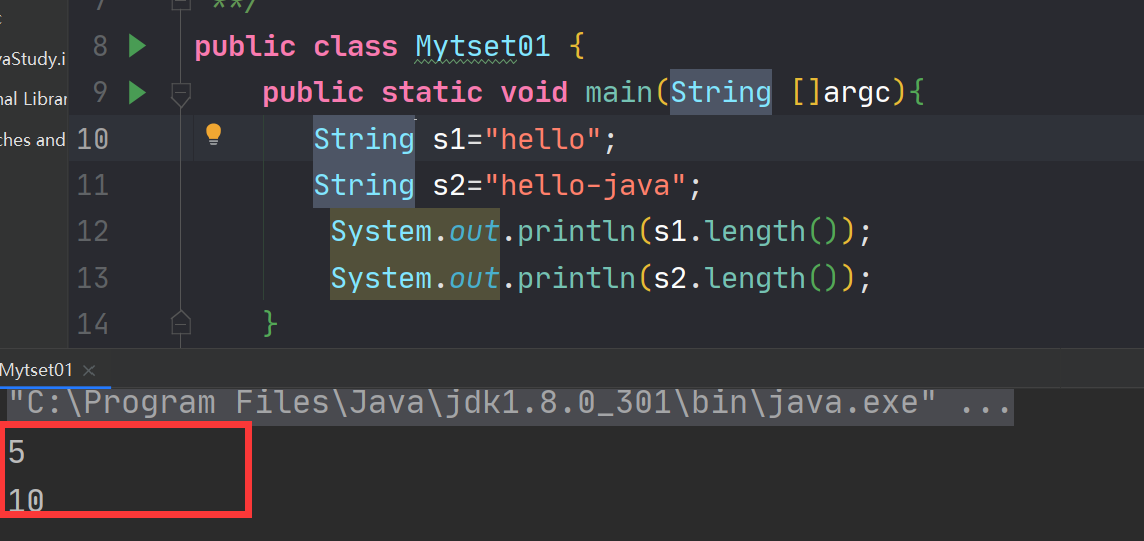
6.1取得一个字符串的长度
在String中使用length()方法取得字符串长度
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hello"; String s2="hello-java"; System.out.println(s1.length()); System.out.println(s2.length()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
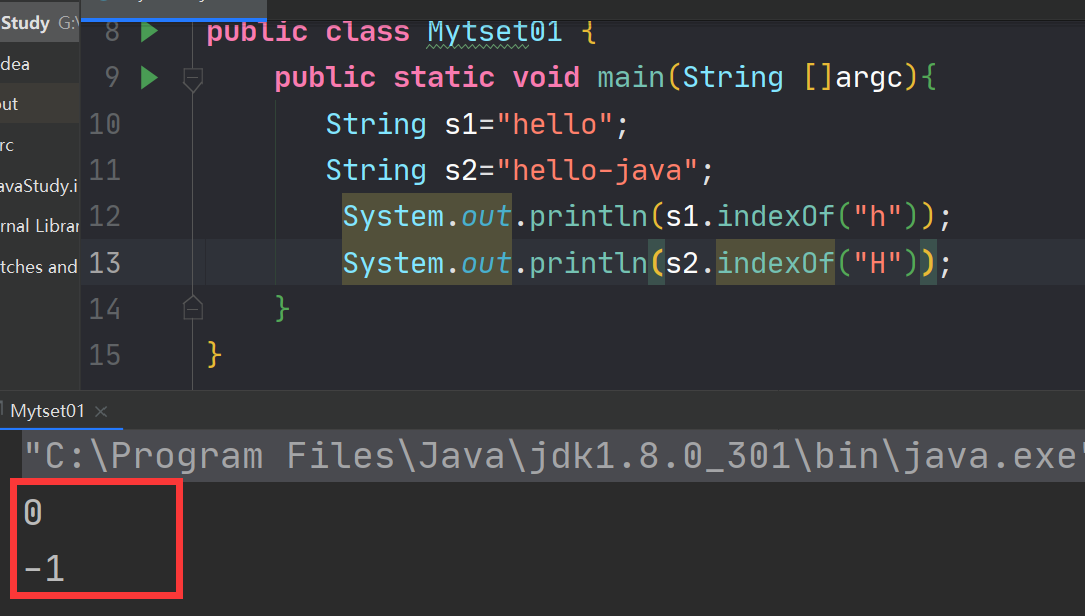
6.2判断一个字符串是否存在
在String中使用indexof()方法,可以返回指定的字符串的位置,如果不存在就返回-1
注意:java字符串位置从0开始public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hello"; String s2="hello-java"; System.out.println(s1.indexOf("h")); System.out.println(s2.indexOf("H")); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
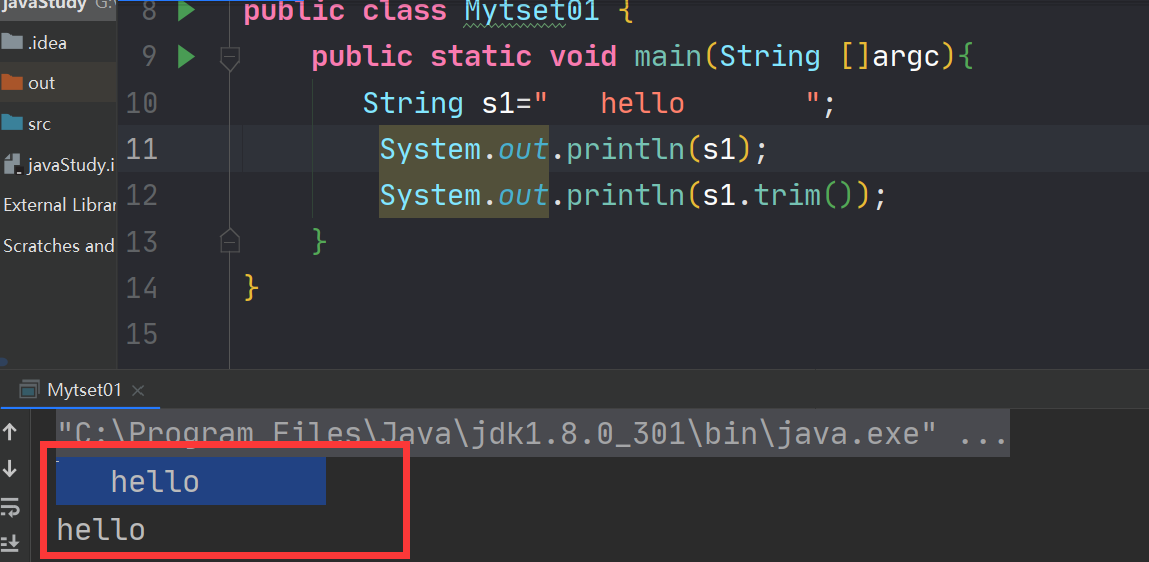
6.3去掉左右空格
可以使用trim()方法去除字符串的左右空格
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1=" hello "; System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s1.trim()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
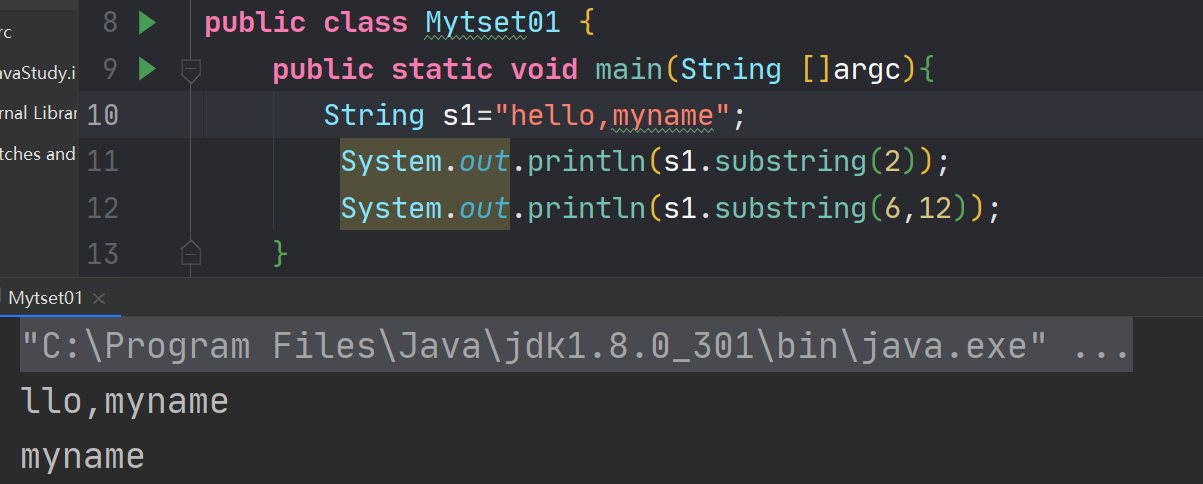
6.4字符串的截取
在String中提供了两个substring()方法,一个从指定位置截取到字符串的末尾,另一个是截取指定范围的内容。
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hello,myname"; System.out.println(s1.substring(2)); System.out.println(s1.substring(6,12)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
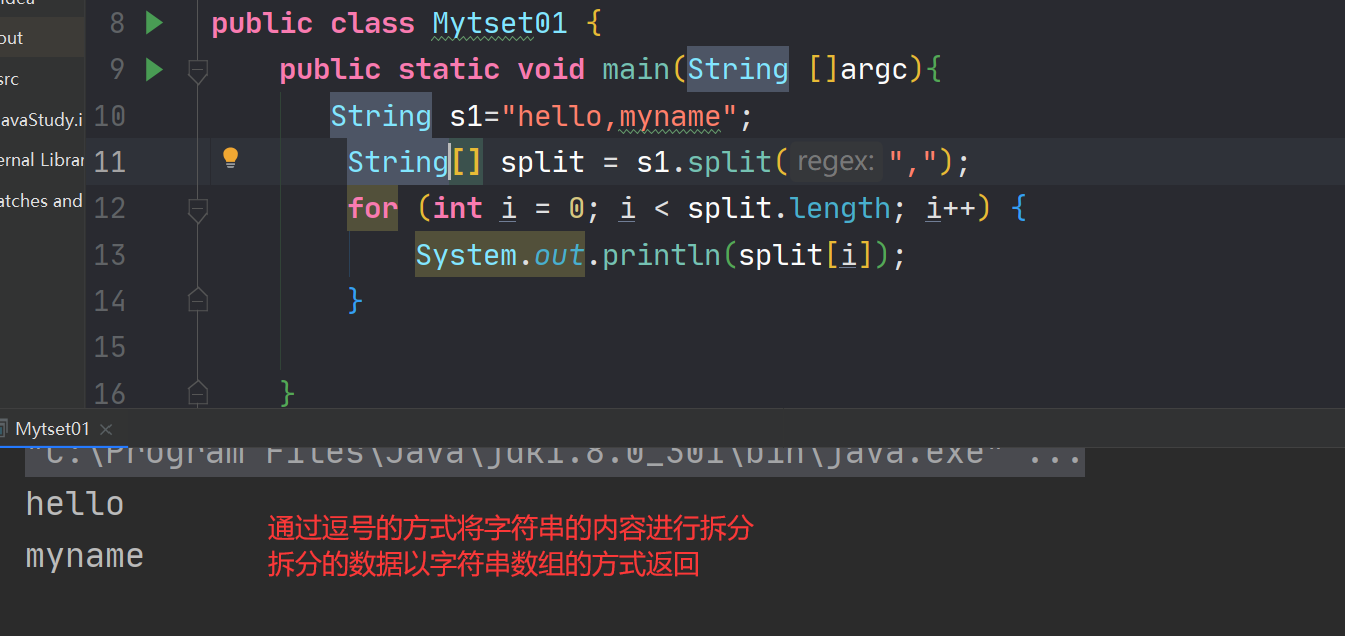
6.5按照指定的字符串拆分字符串
在String中通过split()方法可以将字符串进行拆分的操作,拆分的数据通过字符串数组的形式返回。
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hello,myname"; String[] split = s1.split(","); for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) { System.out.println(split[i]); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
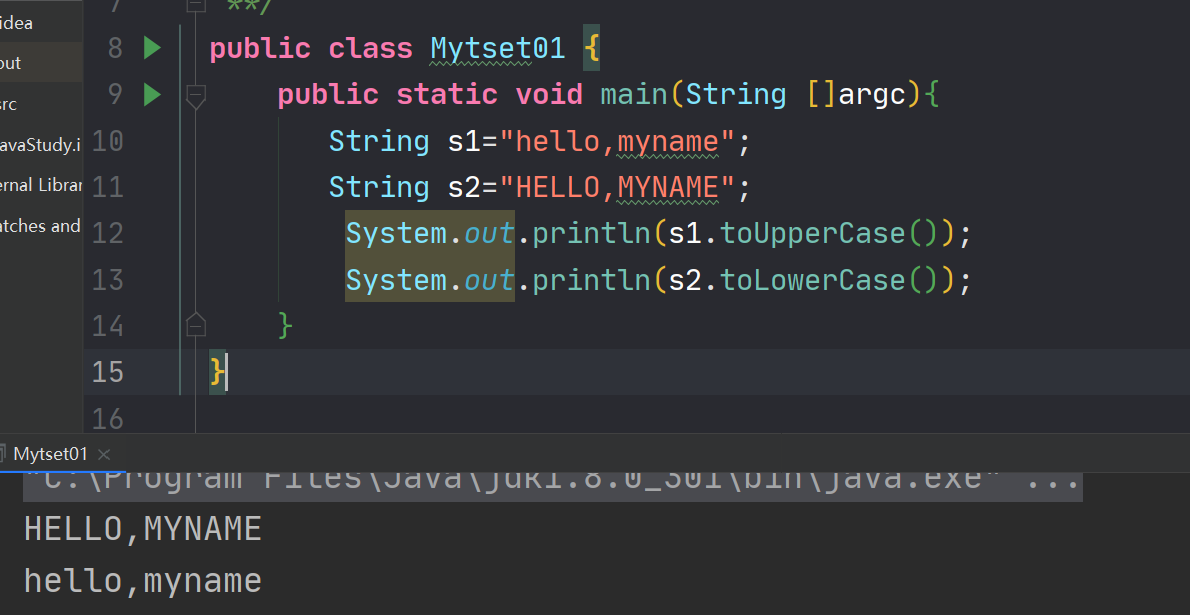
6.6字符串的大小写转换
在String中,通过toUpperCase()和toLowCase()两个方法完成字符串的大小写的转换操作。
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hello,myname"; String s2="HELLO,MYNAME"; System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase()); System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase()); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
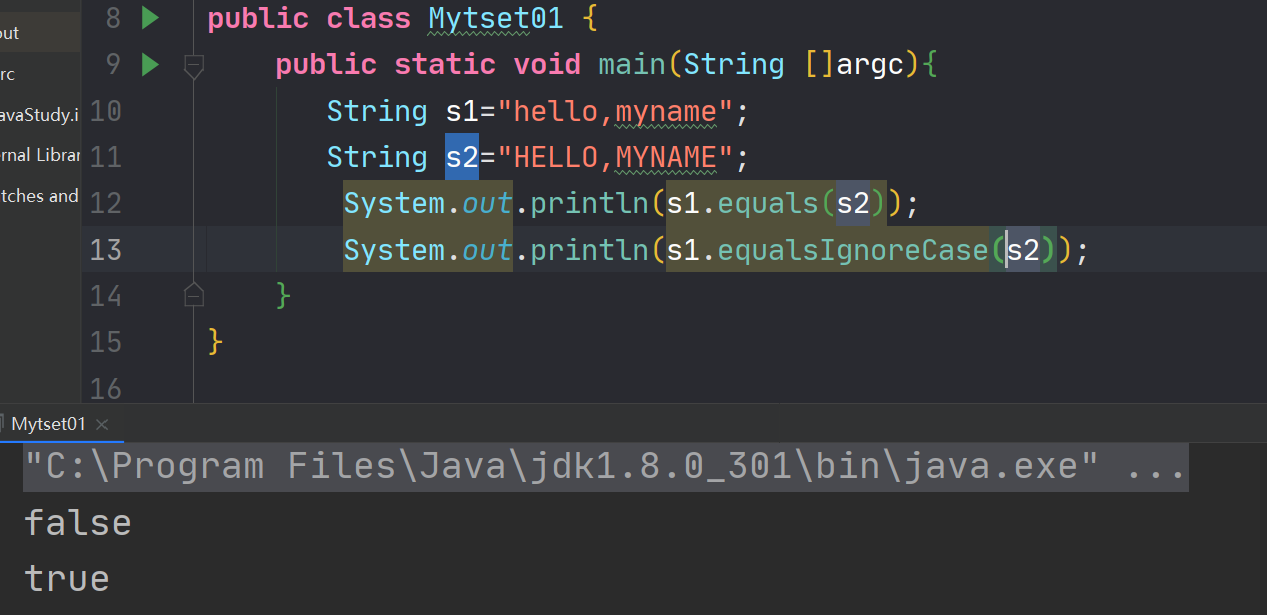
6.7不区分大小写的字符串的比较
在String中,通过equalsIgnoreCase()方法进行比较。
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hello,myname"; String s2="HELLO,MYNAME"; System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
6.8将一个指定的字符串替换成其他的字符串
在String中,通过replaceAll()方法可以将字符串的指定内容进行替换。
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1="hhaabbddxx"; System.out.println(s1.replace("b","B")); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
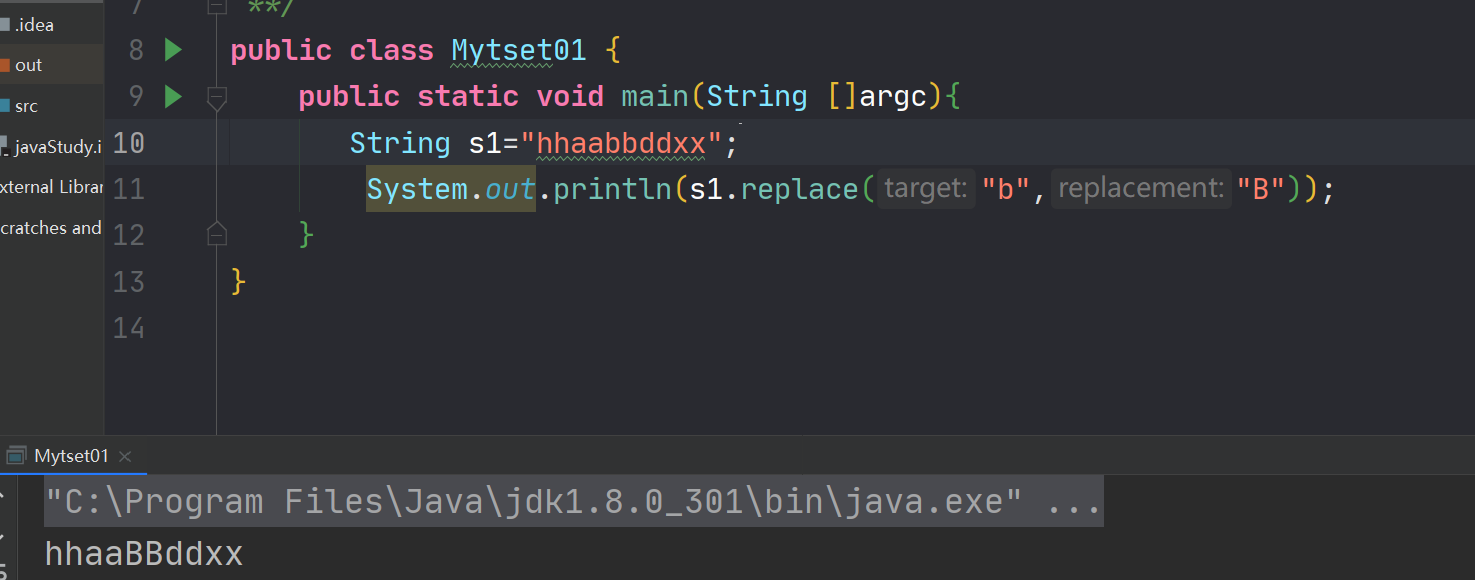
7.引用传递基本应用
7.1对象引用传递
案例一
class Demo{ int temp=30; } public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ Demo demo=new Demo(); demo.temp=59; System.out.println(demo.temp); fun(demo); System.out.println(demo.temp); } public static void fun(Demo d){ d.temp=1000; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
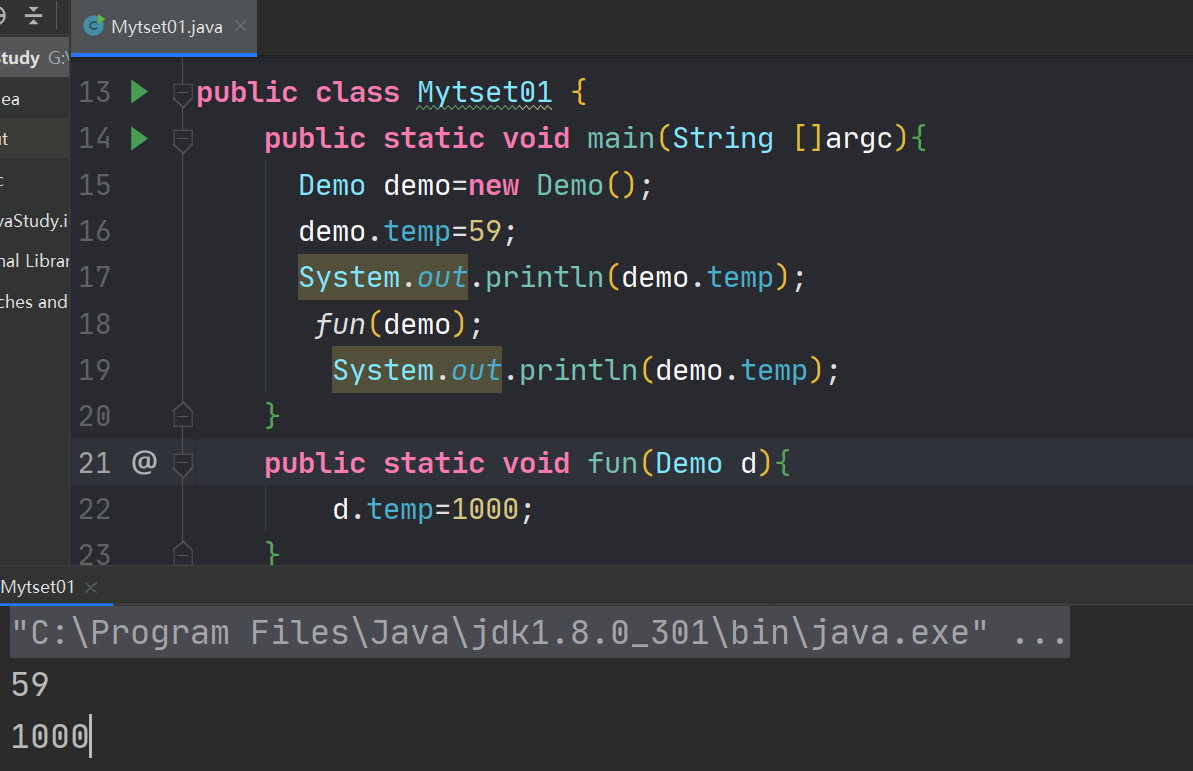
分析:
new demo()的时候开辟了堆内存,里面存放着Demo类的属性temp=30,随后将demo.temp=50,随后调用函数,因为d是局部变量,50地址的引用交给了demo和d,共同指向temp=50的内存地址,当函数调用完,局部变量就消失了,也就是断开了指向1000的连接。案例二
public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ String s1 = "hello"; System.out.println(s1); fun(s1); System.out.println(s1); } public static void fun(String f){ f="me"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
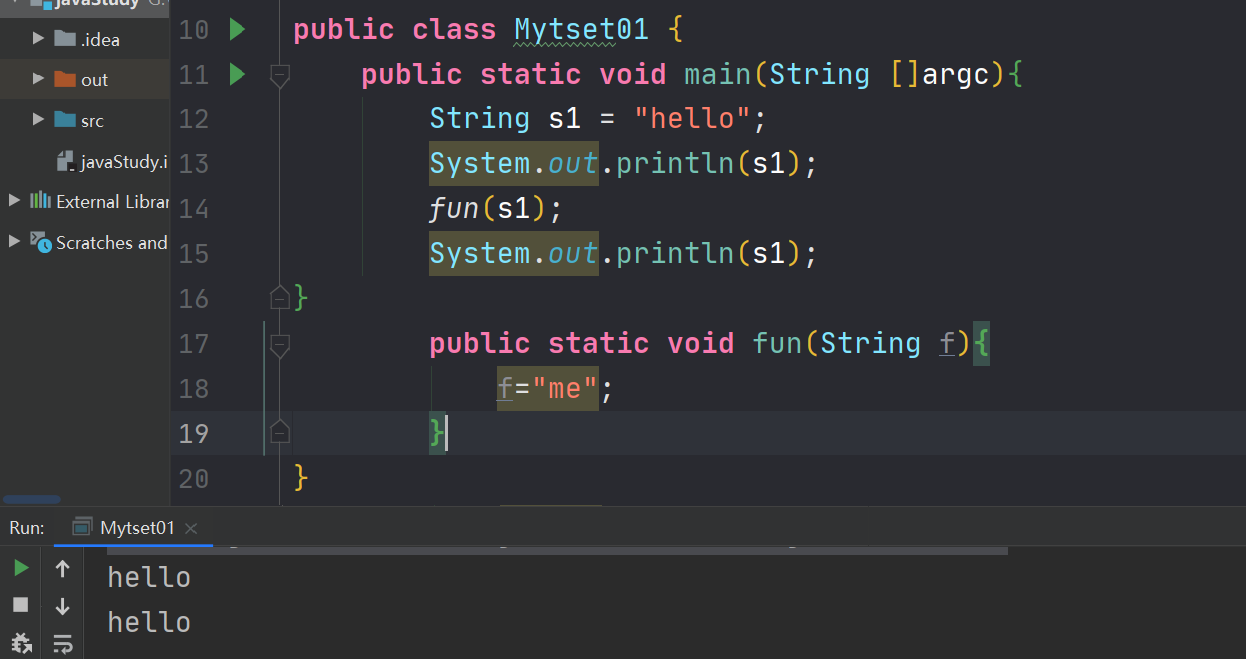 请自行分析
请自行分析
案例三class Demo{ String temp = "hello"; } public class Mytset01 { public static void main(String []argc){ Demo demo=new Demo(); demo.temp = "wold"; System.out.println(demo.temp); fun(demo); System.out.println(demo); } public static void fun(Demo d){ d.temp="me"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
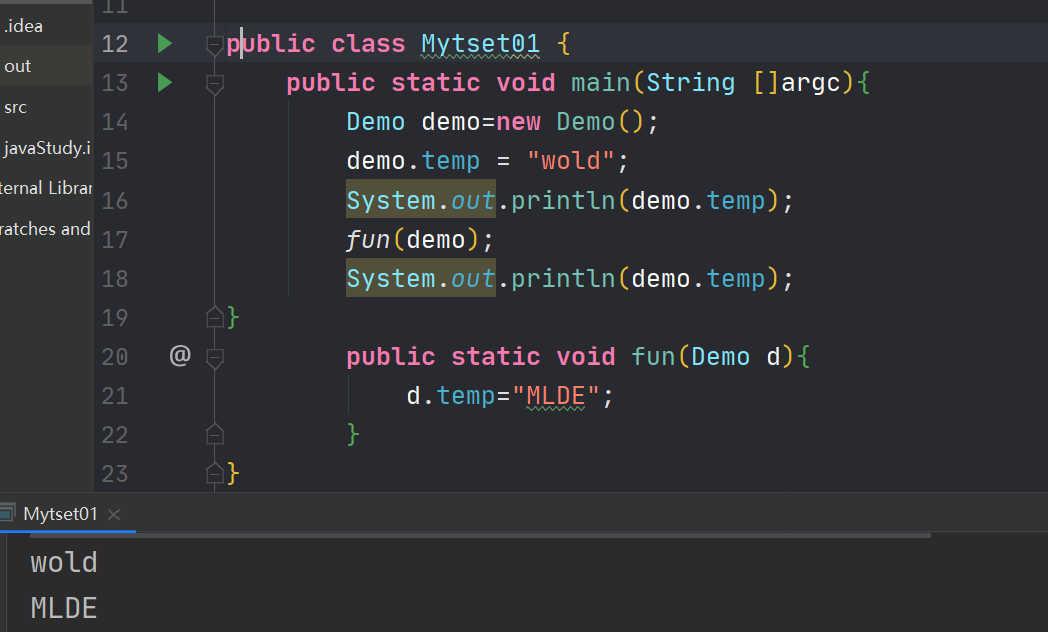
分析和第一个案例一样,因为String是作为一个Demo类的属性存在,操作时更改了类中的属性内容,所以改变了。
-
相关阅读:
484-红黑树
如何配置Header Editor
ApplicationContext接口解读
《C和指针》读书笔记(第十四章 预处理器)
YoloV5|V7改进策略:全新特征融合模块AFPN,更换YoloV5|V7的Neck
黑磷量子点/无机荧光量子点/石墨烯量子点水凝胶/量子点/纳米水凝胶荧光探针的研究制备
pytest中的pytest.ini
面试官:谈谈 Go GC 算法
Java系列 | 如何讲自己的JAR包上传至阿里云maven私有仓库【云效制品仓库】
【蓝桥杯Web】第十三届蓝桥杯(Web 应用开发)第一次线上模拟赛
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52166656/article/details/126714098