-
【LeetCode】刷题模版/套路合集(持续更新)
数据结构
业务类型题
Top K问题
资料来源:甜姨力扣题解
使用场景 -> 方法 -> 类型题
求前K大 / 前K小 / 第K大 / 第K小
- O(N):用
快排变形最最最高效解决TopK问题 - O(NlogK):大根堆(前K小) / 小根堆(前K大)
- O(NlogK):二叉搜索树
- O(N):对于数据范围有限的情况,可以直接计数排序 O(N) 解决
🟢🟠🔴 类型题
🟠 347. 前K个高频元素
🟢 剑指offer 40. 最小的K个数
🟠 215.数组中的第K个最大元素1. 方法一:快速搜索(快排变形)
求前K大 / 前K小 / 第K大 / 第K小,不需要对整个数组进行O(NlogN)排序,可以通过快排切分直接O(N)找到第K大的数(如求中位数就可以用本方法找到第mid大的数)
根据快排切分的性质,它左边的K-1个数都小于等于它,因此它以及它左边的树就是我们要找的前K小的数。
class Solution { public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) { if(k == 0 || arr.length == 0) { return new int[0]; } // 最后一个参数传入我们要找的下标(第k小的数下标是k-1) return quickSearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, k - 1); } private int[] quickSearch(int[] nums, int lo, int hi, int k){ // 每快排一次,得到的j就是左边都小于它,右边都大于它。什么时候j==k了,说明找到前k个了 int j = partition(nums, lo, hi); if(j == k) { return Arrays.copyOf(nums, j + 1); } return j > k? quickSearch(nums, lo, j - 1, k) : quickSearch(nums, j + 1, hi, k); } private int partition(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) { int v = nums[lo]; int i = lo, j = hi + 1; while(true) { // 从lo+1到hi,对应数值如果小于v,往后走(到从前往后第一个大于等于v的停下来) while(++i <= hi && nums[i] < v); // 从hi到lo,对应数值如果大于v,往前走(到从后往前第一个小于等于v的停下来) while(--j >= lo && nums[j] > v); if(i >= j) break; // 如果i < j,交换i和j的位置,继续排 if(i < j) { int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; } } // 交换被比较数和j的位置 nums[lo] = nums[j]; nums[j] = v; // 此时返回的j,左边所有的数都比它小,右边的所有数都比它大 return j; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { // 统计每个数字出现的次数 Map<Integer, Integer> counterMap = IntStream.of(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e, e -> 1, Integer::sum)); // 构造Pair数组,Pair.num 表示数值,Pair.freq 表示数字出现的次数 Pair[] pairs = IntStream.of(nums).distinct().boxed().map(num -> new Pair(num, counterMap.get(num))).toArray(Pair[]::new); // 使用快排变形 O(N) 获取Pair数组中频次最大的 k 个元素(第 4 个参数是下标,因此是 k - 1)。 Pair[] topKPairs = quickSelect(pairs, 0, pairs.length - 1, k - 1); // 构造返回结果 int[] res = new int[k]; int idx = 0; for (Pair pair: topKPairs) { res[idx++] = pair.num; } return res; } private Pair[] quickSelect(Pair[] pairs, int lo, int hi, int idx) { } private int partition(Pair[] pairs, int lo, int hi) { } } class Pair { int num; int freq; public Pair(int num, int freq) { this.num = num; this.freq = freq; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
时间复杂度分析:
第一次切分要遍历整个数组N,(假设一直对半切分)下一次切分遍历数组(0, k-1)。
看作每次调用partition遍历的元素数目都是上一次遍历的1/2,平均时间复杂度N + N/2 + N/4 + … + N/N = 2N ⇒O(N)2. 大根堆 (前K小) / 小根堆(前K大) O(NlogK)
保持堆的大小为K,然后遍历数组中的数字,遍历的时候做如下判断:
- 若目前堆的大小小于K,将当前数字放入堆中
- 否则判断当前数字与大根堆堆顶元素的大小关系,如果当前数字比大根堆堆顶还大(或等于),这个数直接跳过;
反之,如果当前数字比大根堆堆顶小,先poll掉堆顶,再将该数字放入堆中
class Solution { public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) { if(k == 0 || arr.length == 0) { return new int[0]; } // 默认时小根堆,实现大根堆要重写一下比较器 Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v2 - v1); for(int num : arr) { if(pq.size() < k) { pq.offer(num); } else if (num < pq.peek()) { // 你不够小就出来,下一个来 pq.poll(); pq.offer(num); } } // 返回堆中的元素 ... } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { // 统计每个数字出现的次数 Map<Integer, Integer> counter = IntStream.of(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e, e -> 1, Integer::sum)); // 定义小根堆,根据数字频率从小到大排序 Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> counter.get(v1) - counter.get(v2)); // 遍历数组,维护一个大小为k的小根堆 // 不足k个直接将当前数字加入到堆中,否则判断堆中的最小次数是否小于当前数字的出现次数, // 如果是,拉出堆顶,加入该数字 counter.forEach((num, cnt) -> { if(pq.size() < k){ pq.offer(num); } else if(counter.get(pq.peek()) < cnt) { pq.poll(); pq.offer(num); } }); // 构造返回结果 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
总结:
用Java里的优先队列 PriorityQueue的构造器,- 构造小根堆/大根堆
小根堆前K大,构造器从小到大,PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a - b),
大根堆前K小,构造器从大到小,PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a)。
🌟 对于347.这种比较频率的,先用hashmap计数,PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> map.get(a) - map.get(b))
【小根K大,前减后】 - 两个判断:
a. 如果不足k个,往里加;
b. 如果大于小根堆堆顶,拉出堆顶,把自己放进去。(你不够大就我来)
3. 二叉搜索树 O(NlogK)
二叉搜索树(TreeMap)
做法其实和小根堆差不多,
因为有重复的数字,所以用的是TreeMap而不是TreeSet。TreeMap的key是数字,value是该数字的个数。
我们遍历数组中的数字,维护一个数字总个数为k的TreeMap,每遍历一个元素:
1. 若当前map中数字的个数小于K,则将map中当前数字对应的个数+1
2. 否则,判断当前数字与map中最大数字的大小关系:
若当前数字小于map中的最大数字,则将map中当前数字对应的个数+1,并将map中最大数字对应的个数-1
若当前数字大于等于map中的最大数字,就直接跳过该数字;在内部会对Key进行排序,这种Map就是SortedMap。注意到SortedMap是接口,它的实现类是TreeMap。- 1
class Solution { public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) { if(k == 0 || arr.length == 0) { return new int[0]; } // TreeMap的key是数字,value是该数字的个数 // cnt表示当前map总共存了多少个数字 TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(); int cnt = 0; for(int num : arr) { // 1. 遍历数组,若当前map中的数字个数小于k,则map中当前数字对应个数+1 if(cnt < k) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); cnt++; continue; } // 2. 否则,取出map中最大的key(最大的数字),判断当前数字与map中最大数字的大小关系 // 若当前数字小于map中的最大数字,则将map中当前数字对应的个数+1,并将map中最大数字对应的个数-1 Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = map.lastEntry(); if(entry.getKey() > num) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); if(entry.getValue() == 1) { map.pollLastEntry(); } else { map.put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue() - 1); } } } // 取出map中的数 int[] res = new int[k]; int idx = 0; for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { int freq = entry.getValue(); while (freq-- > 0) { res[idx++] = entry.getKey(); } } return res; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
4. 计数排序(桶排序)
- 统计出现次数
- 用一个freqList[i]记录出现次数为i的所有数字,最后获得freqList里后k个元素
class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { // 统计每个数字出现的次数 Map<Integer, Integer> counterMap = IntStream.of(nums).boxed().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e, e -> 1, Integer::sum)); // 一个数字最多出现 nums.length 次,因此定义一个长度为 nums.length + 1 的数组,freqList[i] 中存储出现次数为 i 的所有数字。 List<Integer>[] freqList = new List[nums.length + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < freqList.length; i++) { freqList[i] = new ArrayList<>(); } counterMap.forEach((num, freq) -> { freqList[freq].add(num); }); // 按照出现频次,从大到小遍历频次数组,构造返回结果。 int[] res = new int[k]; int idx = 0; for (int freq = freqList.length - 1; freq > 0; freq--) { for (int num: freqList[freq]) { res[idx++] = num; if (idx == k) { return res; } } } return res; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
class Solution { public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) { if (k == 0 || arr.length == 0) { return new int[0]; } // 统计每个数字出现的次数 int[] counter = new int[10001]; for (int num: arr) { counter[num]++; } // 根据counter数组从头找出k个数作为返回结果 int[] res = new int[k]; int idx = 0; for (int num = 0; num < counter.length; num++) { while (counter[num]-- > 0 && idx < k) { res[idx++] = num; } if (idx == k) { break; } } return res; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
代码模版
十大排序
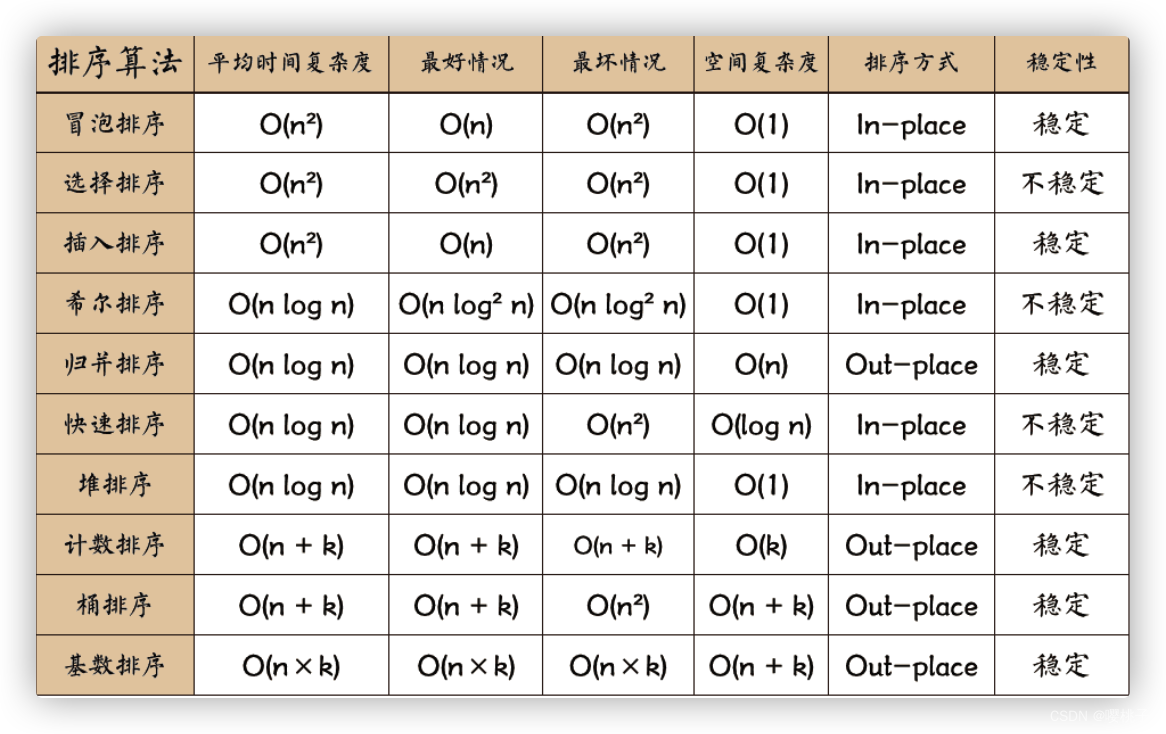
图片来源:程序员吴师兄题解
1. 快速排序(快排)
public void quickSort(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) { if(lo >= hi) return; int x = nums[lo + hi >> 1]; int i = lo + 1, j = hi - 1; while(i < j) { while(nums[++i] < x); // 找到从前往后第一个大于等于x的 while(nums[--j] > x); // 找到从后往前第一个小于等于x的 if(i < j) swap(nums, i, j); // 如果 i < j,把小的换到前面,大的换到后面 } // 此时j左边的所有数都小于等于nums[j],右边的所有数都大于等于nums[j] quickSort(nums, lo, j); // 左边继续排 quickSort(nums, j+1, hi); // 右边继续排 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
快排变形-快速搜索(返回前K小/大,返回排序后位于第K位的)
写法一:
private int[] quickSearch(int[] nums, int lo, int hi, int k){ // 每快排一次,得到的j就是左边都小于它,右边都大于它。什么时候j==k了,说明找到前k个了 int j = partition(nums, lo, hi); if(j == k) { return Arrays.copyOf(nums, j + 1); } return j > k? quickSearch(nums, lo, j - 1, k) : quickSearch(nums, j + 1, hi, k); } private int partition(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) { int v = nums[lo]; int i = lo, j = hi + 1; while(true) { // 从lo+1到hi,对应数值如果小于v,往后走(到从前往后第一个大于等于v的停下来) while(++i <= hi && nums[i] < v); // 从hi到lo,对应数值如果大于v,往前走(到从后往前第一个小于等于v的停下来) while(--j >= lo && nums[j] > v); if(i >= j) break; // 如果i < j,交换i和j的位置,继续排 if(i < j) { int tmp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = tmp; } } // 交换被比较数和j的位置 nums[lo] = nums[j]; nums[j] = v; // 此时返回的j,左边所有的数都比它小,右边的所有数都比它大 return j; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
写法二:
import java.util.Random; public class Solution { private static Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { int len = nums.length; int target = len - k; int left = 0; int right = len - 1; while (true) { int index = partition(nums, left, right); if (index < target) { left = index + 1; } else if (index > target) { right = index - 1; } else { return nums[index]; } } } // 在区间 nums[left..right] 区间执行 partition 操作 private int partition(int[] nums, int left, int right) { // 在区间随机选择一个元素作为标定点 if (right > left) { int randomIndex = left + 1 + random.nextInt(right - left); swap(nums, left, randomIndex); } int pivot = nums[left]; int j = left; for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; i++) { if (nums[i] < pivot) { j++; swap(nums, j, i); } } swap(nums, left, j); return j; } private void swap(int[] nums, int index1, int index2) { int temp = nums[index1]; nums[index1] = nums[index2]; nums[index2] = temp; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
写法一:《算法四》
写法二:liweiwei题解优雅的代码形式
用HashMap统计数组中每个数组出现的次数(一行代码)
Map<Integer, Integer> counter = IntStream.of(nums).boxed.collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e, e-> 1, Integer :: sum));- 1
- 2
- O(N):用
-
相关阅读:
Taro进阶
C语言从头学26——函数说明符
通过动态IP解决网络数据采集问题
x264、x265、OpenH264 简要对比
【开发心得】架构企业OA平台只需3步
兄弟兄弟,在git中的使用.gitignore忽略不想要提交的文件,了解一下呗
汉字转拼音
Leetcode 805. 数组的均值分割
关于数据库连接池和线程,记录几个问题
python:基础知识
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/CherryChenieth/article/details/126720436
