-
[C++]unordered系列关联式容器
一、unordered系列关联式容器
在C++98中,STL提供了底层为红黑树结构的一系列关联式容器,在查询时效率可达到logN,即最差情况下需要比较红黑树的高度次,当树中的节点非常多时,查询效率也不理想。最好的查询是,进行很少的比较次数就能够将元素找到,因此在C++11中,STL又提供了4个unordered系列的关联式容器,这四个容器与红黑树结构的关联式容器使用方式基本类似,只是其底层结构不同
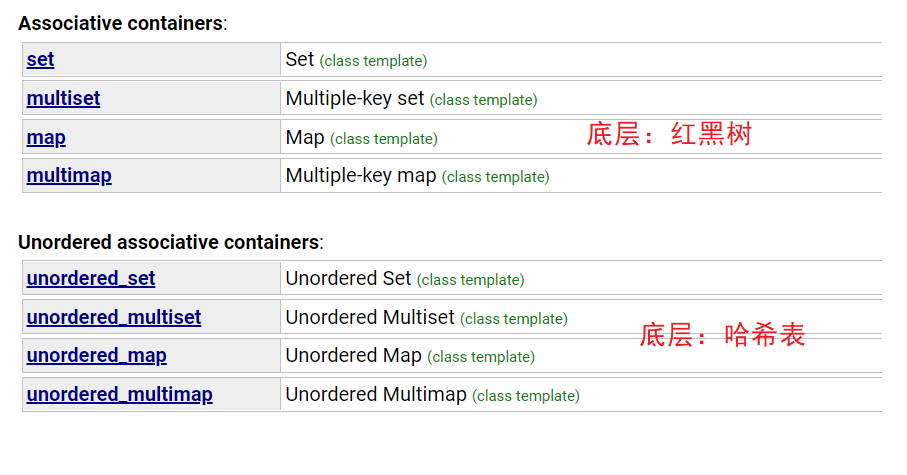
两者区别:- unordered系列是不按key排序,命名体现了(无序的)
- unordered系列是单向迭代器
- 头文件是unordered_xxx
二、unordered_set
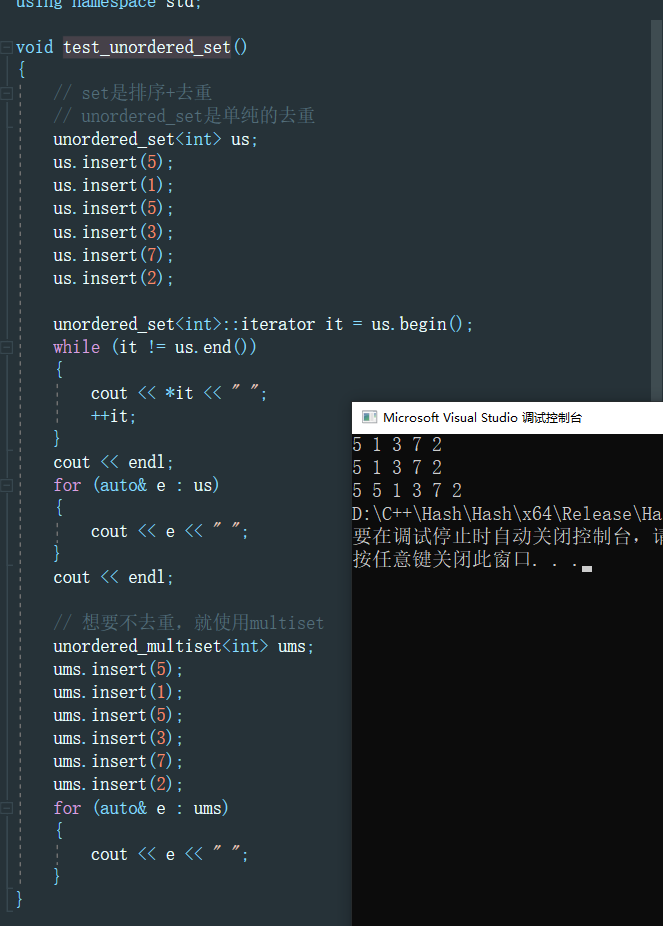
unordered_set的功能演示,与之前使用的set很类似
void test_unordered_set() { // set是排序+去重 // unordered_set是单纯的去重 unordered_set<int> us; us.insert(5); us.insert(1); us.insert(5); us.insert(3); us.insert(7); us.insert(2); unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin(); while (it != us.end()) { cout << *it << " "; ++it; } cout << endl; for (auto& e : us) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl; // 想要不去重,就使用multiset unordered_multiset<int> ums; ums.insert(5); ums.insert(1); ums.insert(5); ums.insert(3); ums.insert(7); ums.insert(2); for (auto& e : ums) { cout << e << " "; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
unordered系列效率略胜set和map,尽量使用unordered系列
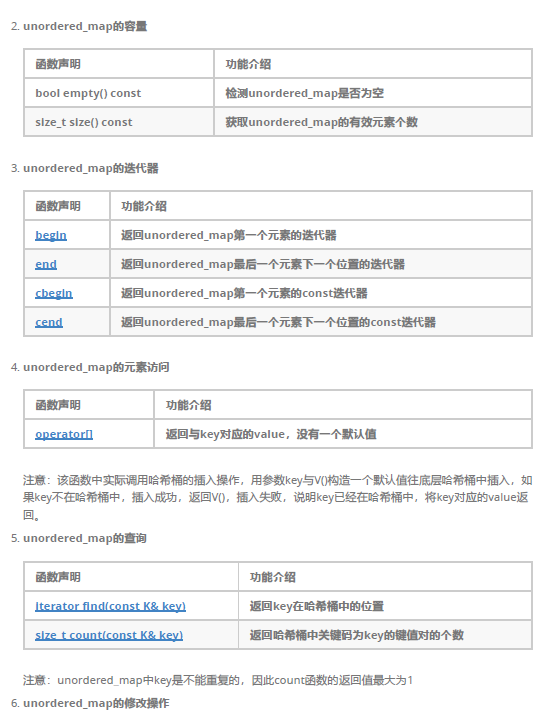
三、unordered_map


四、经典OJ题
4.1 重复n次的元素

思路1: 使用unordered_map,统计second的次数,然后遍历,如果second的次数为N次,就说明重复了N次,就输出他 思路2: 排序,中间位置的值就是答案- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
class Solution { public: int repeatedNTimes(vector<int>& nums) { unordered_map<int, int> um; for (auto e : nums) { um[e]++; } size_t N = nums.size() / 2; for (auto e : um) { if (e.second == N) { return e.first; } } return 0; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
4.2 两个数组的交集 I

思路1: 放到两个set中去,然后遍历s1,若s1某个元素在s2中出现过即为交集 这里要用set,因为要去重,不然就会出现重复的结果- 1
- 2
- 3
class Solution { public: vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { unordered_set<int> us1; unordered_set<int> us2; for (auto e : nums1) { us1.insert(e); } for (auto e : nums2) { us2.insert(e); } vector<int> ans; // 遍历s1,如果s1的值在s2中出现过,就是交集 for (auto e : us1) { if (us2.find(e) != us2.end()) // 找到 { ans.push_back(e); } } return ans; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
思路2: 1. 谁小谁++ 2. 相等就是交集,同时++ 3. 有1个结束就结束了- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
class Solution { public: vector<int> intersection(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { set<int> s1; set<int> s2; for (auto e : nums1) { s1.insert(e); } for (auto e : nums2) { s2.insert(e); } auto it1 = s1.begin(); auto it2 = s2.begin(); vector<int> ans; while (it1 != s1.end() && it2 != s2.end()) { if (*it1 < *it2) { it1++; } else if (*it1 > *it2) { it2++; } else { ans.push_back(*it1); it1++; it2++; } } return ans; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
4.3 两个数组的交集 II
思路: 这次是不需要去重,这次·在上题基础上还要进行删除掉元素- 1
- 2
class Solution { public: vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) { // 分别放入两个set中 unordered_multiset<int> us1; unordered_multiset<int> us2; for (auto e : nums1) { us1.insert(e); } for (auto e : nums2) { us2.insert(e); } vector<int> ans; int n = nums1.size(); for (auto e : us2) { if (us1.find(e) != us1.end()) { ans.push_back(e); // 注意这里删除的us1 us1.erase(us1.find(e)); // 这里删除的必须是us1.find(e),如果写us1.erase(e)就会把所有的e删除掉,而不是只删除掉一个 } } return ans; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
4.4 存在重复元素
思路: 使用map,统计每一个元素出现的次数,若second为0表示没有重复过- 1
- 2
class Solution { public: bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) { unordered_map<int, int> um; for (auto e : nums) { um[e]++; } for (auto e : um) { if (e.second != 1) { return true; } } return false; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
-
相关阅读:
Redis远程连接&设置密码登录
linux 系统资源命令
Idea借助Maven插件生成项目骨架archetype
matlab simulink仿真
IDEA中 GIT基础操作
NLP 项目:维基百科文章爬虫和分类 - 语料库阅读器
快上车,LLM专列:想要的资源统统给你准备好了
JAVA_JDBC
Python 中-m 模块的妙用
如何通过ADB命令的方式关闭华为系手机的emui系统更新升级?解决:error: no devices/emulators found
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51304981/article/details/126492569