-
YOLOv5结合GradCAM热力图可视化
一、修改
model/yolo.py文件中的Detect类中的forward函数如下- logits_ = [] # 修改---1
- logits = x[i][..., 5:] # 修改---2
- logits_.append(logits.view(bs, -1, self.no - 5)) # 修改---3
- return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), torch.cat(logits_, 1), x) # 修改---4

二、在
model文件夹中,添加yolov5_object_detector.py文件:- import numpy as np
- import torch
- from models.experimental import attempt_load
- from utils.general import xywh2xyxy
- from utils.datasets import letterbox
- import cv2
- import time
- import torchvision
- import torch.nn as nn
- from utils.metrics import box_iou
- class YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self,
- model_weight,
- device,
- img_size,
- names=None,
- mode='eval',
- confidence=0.45,
- iou_thresh=0.45,
- agnostic_nms=False):
- super(YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector, self).__init__()
- self.device = device
- self.model = None
- self.img_size = img_size
- self.mode = mode
- self.confidence = confidence
- self.iou_thresh = iou_thresh
- self.agnostic = agnostic_nms
- self.model = attempt_load(model_weight, map_location=device, inplace=False, fuse=False)
- self.model.requires_grad_(True)
- self.model.to(device)
- if self.mode == 'train':
- self.model.train()
- else:
- self.model.eval()
- # fetch the names
- if names is None:
- self.names = ['your dataset classname']
- else:
- self.names = names
- # preventing cold start
- img = torch.zeros((1, 3, *self.img_size), device=device)
- self.model(img)
- @staticmethod
- def non_max_suppression(prediction, logits, conf_thres=0.3, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False,
- multi_label=False, labels=(), max_det=300):
- """Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference and logits results
- Returns:
- list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls] and pruned input logits (n, number-classes)
- """
- nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 # number of classes
- xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
- # Checks
- assert 0 <= conf_thres <= 1, f'Invalid Confidence threshold {conf_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
- assert 0 <= iou_thres <= 1, f'Invalid IoU {iou_thres}, valid values are between 0.0 and 1.0'
- # Settings
- min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
- max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
- time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
- redundant = True # require redundant detections
- multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
- merge = False # use merge-NMS
- t = time.time()
- output = [torch.zeros((0, 6), device=prediction.device)] * prediction.shape[0]
- logits_output = [torch.zeros((0, nc), device=logits.device)] * logits.shape[0]
- # logits_output = [torch.zeros((0, 80), device=logits.device)] * logits.shape[0]
- for xi, (x, log_) in enumerate(zip(prediction, logits)): # image index, image inference
- # Apply constraints
- # x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
- x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
- log_ = log_[xc[xi]]
- # Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
- if labels and len(labels[xi]):
- l = labels[xi]
- v = torch.zeros((len(l), nc + 5), device=x.device)
- v[:, :4] = l[:, 1:5] # box
- v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
- v[range(len(l)), l[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
- x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
- # If none remain process next image
- if not x.shape[0]:
- continue
- # Compute conf
- x[:, 5:] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
- # Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
- box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
- # Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
- if multi_label:
- i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
- x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
- else: # best class only
- conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
- x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
- log_ = log_[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
- # Filter by class
- if classes is not None:
- x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
- # Check shape
- n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
- if not n: # no boxes
- continue
- elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
- x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
- # Batched NMS
- c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
- boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
- i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
- if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
- i = i[:max_det]
- if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
- # update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
- iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
- weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
- x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
- if redundant:
- i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
- output[xi] = x[i]
- logits_output[xi] = log_[i]
- assert log_[i].shape[0] == x[i].shape[0]
- if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
- print(f'WARNING: NMS time limit {time_limit}s exceeded')
- break # time limit exceeded
- return output, logits_output
- @staticmethod
- def yolo_resize(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True):
- return letterbox(img, new_shape=new_shape, color=color, auto=auto, scaleFill=scaleFill, scaleup=scaleup)
- def forward(self, img):
- prediction, logits, _ = self.model(img, augment=False)
- prediction, logits = self.non_max_suppression(prediction, logits, self.confidence, self.iou_thresh,
- classes=None,
- agnostic=self.agnostic)
- self.boxes, self.class_names, self.classes, self.confidences = [[[] for _ in range(img.shape[0])] for _ in
- range(4)]
- for i, det in enumerate(prediction): # detections per image
- if len(det):
- for *xyxy, conf, cls in det:
- # 返回整数
- bbox = [int(b) for b in xyxy]
- self.boxes[i].append(bbox)
- self.confidences[i].append(round(conf.item(), 2))
- cls = int(cls.item())
- self.classes[i].append(cls)
- if self.names is not None:
- self.class_names[i].append(self.names[cls])
- else:
- self.class_names[i].append(cls)
- return [self.boxes, self.classes, self.class_names, self.confidences], logits
- def preprocessing(self, img):
- if len(img.shape) != 4:
- img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
- im0 = img.astype(np.uint8)
- img = np.array([self.yolo_resize(im, new_shape=self.img_size)[0] for im in im0])
- img = img.transpose((0, 3, 1, 2))
- img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
- img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device)
- img = img / 255.0
- return img
三、在
model文件夹中,添加gradcam.py文件:- import time
- import torch
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- def find_yolo_layer(model, layer_name):
- """Find yolov5 layer to calculate GradCAM and GradCAM++
- Args:
- model: yolov5 model.
- layer_name (str): the name of layer with its hierarchical information.
- Return:
- target_layer: found layer
- """
- hierarchy = layer_name.split('_')
- target_layer = model.model._modules[hierarchy[0]]
- for h in hierarchy[1:]:
- target_layer = target_layer._modules[h]
- return target_layer
- class YOLOV5GradCAM:
- # 初始化,得到target_layer层
- def __init__(self, model, layer_name, img_size=(640, 640)):
- self.model = model
- self.gradients = dict()
- self.activations = dict()
- def backward_hook(module, grad_input, grad_output):
- self.gradients['value'] = grad_output[0]
- return None
- def forward_hook(module, input, output):
- self.activations['value'] = output
- return None
- target_layer = find_yolo_layer(self.model, layer_name)
- # 获取forward过程中每层的输入和输出,用于对比hook是不是正确记录
- target_layer.register_forward_hook(forward_hook)
- target_layer.register_full_backward_hook(backward_hook)
- device = 'cuda' if next(self.model.model.parameters()).is_cuda else 'cpu'
- self.model(torch.zeros(1, 3, *img_size, device=device))
- def forward(self, input_img, class_idx=True):
- """
- Args:
- input_img: input image with shape of (1, 3, H, W)
- Return:
- mask: saliency map of the same spatial dimension with input
- logit: model output
- preds: The object predictions
- """
- saliency_maps = []
- b, c, h, w = input_img.size()
- preds, logits = self.model(input_img)
- for logit, cls, cls_name in zip(logits[0], preds[1][0], preds[2][0]):
- if class_idx:
- score = logit[cls]
- else:
- score = logit.max()
- self.model.zero_grad()
- tic = time.time()
- # 获取梯度
- score.backward(retain_graph=True)
- print(f"[INFO] {cls_name}, model-backward took: ", round(time.time() - tic, 4), 'seconds')
- gradients = self.gradients['value']
- activations = self.activations['value']
- b, k, u, v = gradients.size()
- alpha = gradients.view(b, k, -1).mean(2)
- weights = alpha.view(b, k, 1, 1)
- saliency_map = (weights * activations).sum(1, keepdim=True)
- saliency_map = F.relu(saliency_map)
- saliency_map = F.interpolate(saliency_map, size=(h, w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
- saliency_map_min, saliency_map_max = saliency_map.min(), saliency_map.max()
- saliency_map = (saliency_map - saliency_map_min).div(saliency_map_max - saliency_map_min).data
- saliency_maps.append(saliency_map)
- return saliency_maps, logits, preds
- def __call__(self, input_img):
- return self.forward(input_img)
- class YOLOV5GradCAMPP(YOLOV5GradCAM):
- def __init__(self, model, layer_name, img_size=(640, 640)):
- super(YOLOV5GradCAMPP, self).__init__(model, layer_name, img_size)
- def forward(self, input_img, class_idx=True):
- saliency_maps = []
- b, c, h, w = input_img.size()
- tic = time.time()
- preds, logits = self.model(input_img)
- print("[INFO] model-forward took: ", round(time.time() - tic, 4), 'seconds')
- for logit, cls, cls_name in zip(logits[0], preds[1][0], preds[2][0]):
- if class_idx:
- score = logit[cls]
- else:
- score = logit.max()
- self.model.zero_grad()
- tic = time.time()
- # 获取梯度
- score.backward(retain_graph=True)
- print(f"[INFO] {cls_name}, model-backward took: ", round(time.time() - tic, 4), 'seconds')
- gradients = self.gradients['value'] # dS/dA
- activations = self.activations['value'] # A
- b, k, u, v = gradients.size()
- alpha_num = gradients.pow(2)
- alpha_denom = gradients.pow(2).mul(2) + \
- activations.mul(gradients.pow(3)).view(b, k, u * v).sum(-1, keepdim=True).view(b, k, 1, 1)
- # torch.where(condition, x, y) condition是条件,满足条件就返回x,不满足就返回y
- alpha_denom = torch.where(alpha_denom != 0.0, alpha_denom, torch.ones_like(alpha_denom))
- alpha = alpha_num.div(alpha_denom + 1e-7)
- positive_gradients = F.relu(score.exp() * gradients) # ReLU(dY/dA) == ReLU(exp(S)*dS/dA))
- weights = (alpha * positive_gradients).view(b, k, u * v).sum(-1).view(b, k, 1, 1)
- saliency_map = (weights * activations).sum(1, keepdim=True)
- saliency_map = F.relu(saliency_map)
- saliency_map = F.interpolate(saliency_map, size=(h, w), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
- saliency_map_min, saliency_map_max = saliency_map.min(), saliency_map.max()
- saliency_map = (saliency_map - saliency_map_min).div(saliency_map_max - saliency_map_min).data
- saliency_maps.append(saliency_map)
- return saliency_maps, logits, preds
四、在根目录下新建
main_gradcam.py文件 :- import os
- import random
- import time
- import argparse
- import numpy as np
- from models.gradcam import YOLOV5GradCAM, YOLOV5GradCAMPP
- from models.yolov5_object_detector import YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector
- import cv2
- # 数据集类别名
- names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
- 'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
- 'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
- 'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
- 'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
- 'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
- 'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
- 'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
- 'hair drier', 'toothbrush'] # class names
- # yolov5s网络中的三个detect层
- target_layers = ['model_17_cv3_act', 'model_20_cv3_act', 'model_23_cv3_act']
- # Arguments
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
- parser.add_argument('--model-path', type=str, default="weights/yolov5s.pt", help='Path to the model')
- parser.add_argument('--img-path', type=str, default='data/images', help='input image path')
- parser.add_argument('--output-dir', type=str, default='outputs/', help='output dir')
- parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=640, help="input image size")
- parser.add_argument('--target-layer', type=str, default='model_17_cv3_act',
- help='The layer hierarchical address to which gradcam will applied,'
- ' the names should be separated by underline')
- parser.add_argument('--method', type=str, default='gradcam', help='gradcam method')
- parser.add_argument('--device', type=str, default='cpu', help='cuda or cpu')
- parser.add_argument('--no_text_box', action='store_true',
- help='do not show label and box on the heatmap')
- args = parser.parse_args()
- def get_res_img(bbox, mask, res_img):
- mask = mask.squeeze(0).mul(255).add_(0.5).clamp_(0, 255).permute(1, 2, 0).detach().cpu().numpy().astype(
- np.uint8)
- heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(mask, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
- # n_heatmat = (Box.fill_outer_box(heatmap, bbox) / 255).astype(np.float32)
- n_heatmat = (heatmap / 255).astype(np.float32)
- res_img = res_img / 255
- res_img = cv2.add(res_img, n_heatmat)
- res_img = (res_img / res_img.max())
- return res_img, n_heatmat
- def plot_one_box(x, img, color=None, label=None, line_thickness=3):
- # this is a bug in cv2. It does not put box on a converted image from torch unless it's buffered and read again!
- cv2.imwrite('temp.jpg', (img * 255).astype(np.uint8))
- img = cv2.imread('temp.jpg')
- # Plots one bounding box on image img
- tl = line_thickness or round(0.002 * (img.shape[0] + img.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness
- color = color or [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)]
- c1, c2 = (int(x[0]), int(x[1])), (int(x[2]), int(x[3]))
- cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
- if label:
- tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness
- t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0]
- outside = c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3 >= 0 # label fits outside box up
- c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3 if outside else c1[1] + t_size[1] + 3
- outsize_right = c2[0] - img.shape[:2][1] > 0 # label fits outside box right
- c1 = c1[0] - (c2[0] - img.shape[:2][1]) if outsize_right else c1[0], c1[1]
- c2 = c2[0] - (c2[0] - img.shape[:2][1]) if outsize_right else c2[0], c2[1]
- cv2.rectangle(img, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
- cv2.putText(img, label, (c1[0], c1[1] - 2 if outside else c2[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf,
- lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
- return img
- # 检测单个图片
- def main(img_path):
- colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in names]
- device = args.device
- input_size = (args.img_size, args.img_size)
- # 读入图片
- img = cv2.imread(img_path) # 读取图像格式:BGR
- print('[INFO] Loading the model')
- # 实例化YOLOv5模型,得到检测结果
- model = YOLOV5TorchObjectDetector(args.model_path, device, img_size=input_size, names=names)
- # img[..., ::-1]: BGR --> RGB
- # (480, 640, 3) --> (1, 3, 480, 640)
- torch_img = model.preprocessing(img[..., ::-1])
- tic = time.time()
- # 遍历三层检测层
- for target_layer in target_layers:
- # 获取grad-cam方法
- if args.method == 'gradcam':
- saliency_method = YOLOV5GradCAM(model=model, layer_name=target_layer, img_size=input_size)
- elif args.method == 'gradcampp':
- saliency_method = YOLOV5GradCAMPP(model=model, layer_name=target_layer, img_size=input_size)
- masks, logits, [boxes, _, class_names, conf] = saliency_method(torch_img) # 得到预测结果
- result = torch_img.squeeze(0).mul(255).add_(0.5).clamp_(0, 255).permute(1, 2, 0).detach().cpu().numpy()
- result = result[..., ::-1] # convert to bgr
- # 保存设置
- imgae_name = os.path.basename(img_path) # 获取图片名
- save_path = f'{args.output_dir}{imgae_name[:-4]}/{args.method}'
- if not os.path.exists(save_path):
- os.makedirs(save_path)
- print(f'[INFO] Saving the final image at {save_path}')
- # 遍历每张图片中的每个目标
- for i, mask in enumerate(masks):
- # 遍历图片中的每个目标
- res_img = result.copy()
- # 获取目标的位置和类别信息
- bbox, cls_name = boxes[0][i], class_names[0][i]
- label = f'{cls_name} {conf[0][i]}' # 类别+置信分数
- # 获取目标的热力图
- res_img, heat_map = get_res_img(bbox, mask, res_img)
- res_img = plot_one_box(bbox, res_img, label=label, color=colors[int(names.index(cls_name))],
- line_thickness=3)
- # 缩放到原图片大小
- res_img = cv2.resize(res_img, dsize=(img.shape[:-1][::-1]))
- output_path = f'{save_path}/{target_layer[6:8]}_{i}.jpg'
- cv2.imwrite(output_path, res_img)
- print(f'{target_layer[6:8]}_{i}.jpg done!!')
- print(f'Total time : {round(time.time() - tic, 4)} s')
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- # 图片路径为文件夹
- if os.path.isdir(args.img_path):
- img_list = os.listdir(args.img_path)
- print(img_list)
- for item in img_list:
- # 依次获取文件夹中的图片名,组合成图片的路径
- main(os.path.join(args.img_path, item))
- # 单个图片
- else:
- main(args.img_path)
五、使用介绍
1、更改
main_gradcam.py文件中的类别2、更改model-path和img-path路径
3、运行
main_gradcam.py文件,结果如下
4、如果不想要显示坐标框,可以将
main_gradcam.py文件中的下面这段代码注释掉
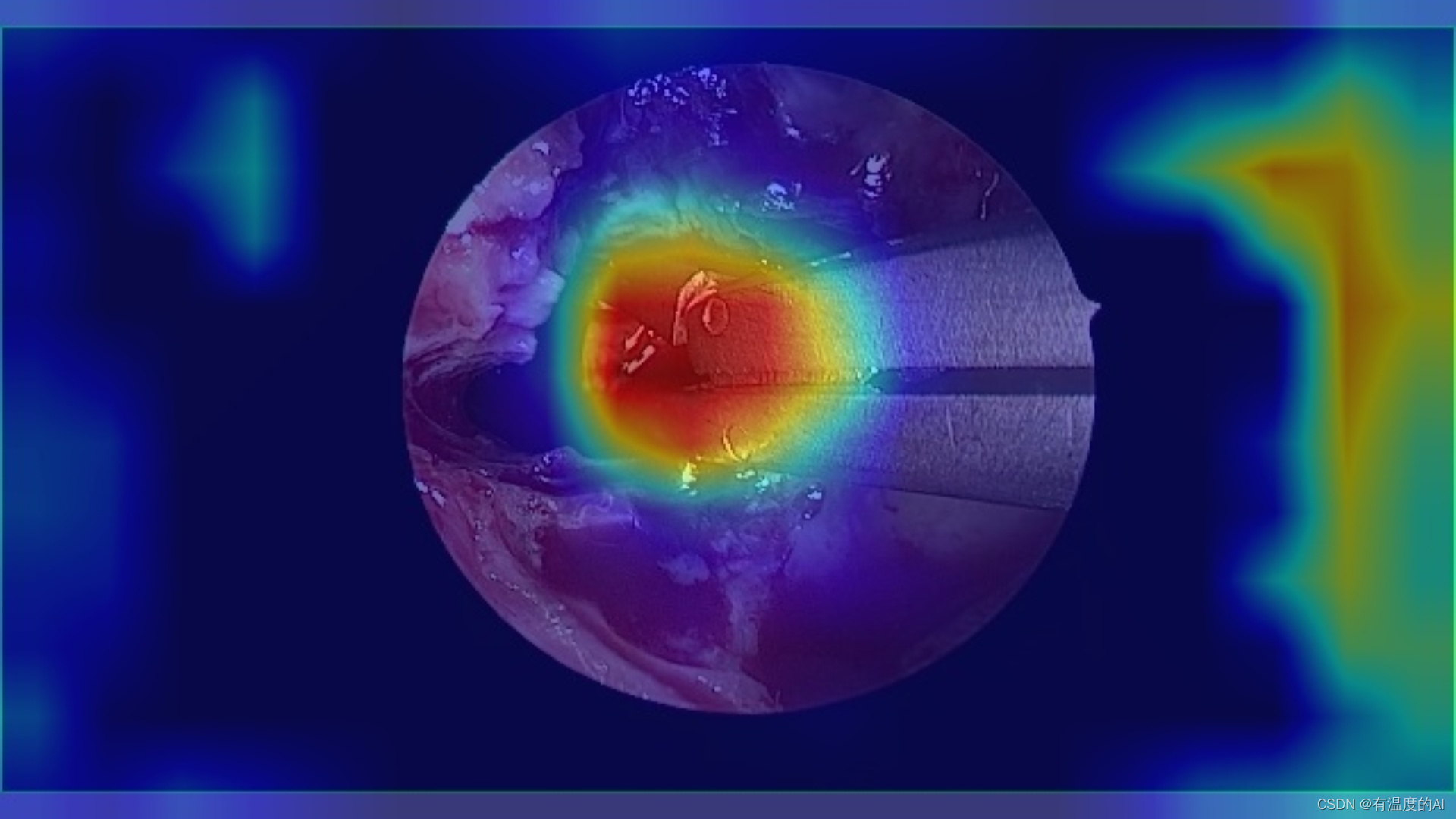
Appendix
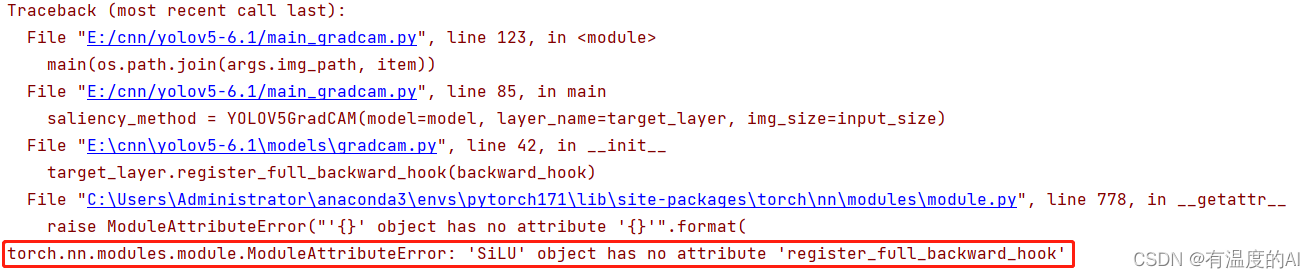
如果以上报错,即为torch版本不对,升级为1.8.0以上就可
也可以将gradcam.py文件中的register_full_backward_hook换成register_backward_hook

reference
-
相关阅读:
3D 沙盒游戏之避障踩坑和实现之旅
Linux之xinetd安装及实践
深度剖析 Vue3 如何通过虚拟DOM更新页面
用HTML+CSS做一个漂亮简单的个人网页——动漫网页【火影忍者】1个页面
轻松玩转树莓派Pico之四、Ubuntu下在线debug环境搭建
数据量太大了,数据分批处理
【JAVA数据结构系列】12_泛型
软件工程详细知识点复习(上)
算法练习13——H 指数
[管理与领导-102]:经营与管理的关系:攻守关系;武将文官关系;开疆拓土与守护城池的关系;战斗与练兵的关系;水涨船高,水落船低的关系。
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_56247038/article/details/126677066

 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43799388/article/details/126207632?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43799388/article/details/126207632?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502