-
《30天吃掉那只 TensorFlow2.0》 3-3 高阶API示范
3-3 高阶API示范

下面的范例使用TensorFlow的高阶API实现线性回归模型和DNN二分类模型。
TensorFlow的高阶API主要为tf.keras.models提供的模型的类接口。
使用Keras接口有以下3种方式构建模型:使用Sequential按层顺序构建模型,使用函数式API构建任意结构模型,继承Model基类构建自定义模型。
此处分别演示使用Sequential按层顺序构建模型以及继承Model基类构建自定义模型。
这里还是一开始定义一个打印时间分割线的函数
import tensorflow as tf #打印时间分割线 @tf.function def printbar(): today_ts = tf.timestamp()%(24*60*60) hour = tf.cast(today_ts//3600+8,tf.int32)%tf.constant(24) minite = tf.cast((today_ts%3600)//60,tf.int32) second = tf.cast(tf.floor(today_ts%60),tf.int32) def timeformat(m): if tf.strings.length(tf.strings.format("{}",m))==1: return(tf.strings.format("0{}",m)) else: return(tf.strings.format("{}",m)) timestring = tf.strings.join([timeformat(hour),timeformat(minite), timeformat(second)],separator = ":") tf.print("=========="*8+timestring)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
一,线性回归模型
此范例我们使用Sequential按层顺序构建模型,并使用内置model.fit方法训练模型【面向新手】。
1,准备数据
首先我们得先准备数据,我们可以用tensorflow来生成随机数,由于我们是线性回归,我们就可以利用矩阵乘法生成,并且加入一些正态扰动即可
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import models,layers,losses,metrics,optimizers #样本数量 n = 400 # 生成测试用数据集 X = tf.random.uniform([n,2],minval=-10,maxval=10) w0 = tf.constant([[2.0],[-3.0]]) b0 = tf.constant([[3.0]]) Y = X@w0 + b0 + tf.random.normal([n,1],mean = 0.0,stddev= 2.0) # @表示矩阵乘法,增加正态扰动- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
# 数据可视化 %matplotlib inline %config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg' plt.figure(figsize = (12,5)) ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.scatter(X[:,0],Y[:,0], c = "b") plt.xlabel("x1") plt.ylabel("y",rotation = 0) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.scatter(X[:,1],Y[:,0], c = "g") plt.xlabel("x2") plt.ylabel("y",rotation = 0) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16

2,定义模型
这里的定义模型,我们可以用tf.keras的高阶API,简单就可以定义完成,只需要通过add
tf.keras.backend.clear_session() model = models.Sequential() model.add(layers.Dense(1,input_shape =(2,))) model.summary()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Model: "sequential" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= dense (Dense) (None, 1) 3 ================================================================= Total params: 3 Trainable params: 3 Non-trainable params: 0- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
3,训练模型
这里可以直接用fit方法训练,不需要写过多的东西
### 使用fit方法进行训练 model.compile(optimizer="adam",loss="mse",metrics=["mae"]) model.fit(X,Y,batch_size = 10,epochs = 200) tf.print("w = ",model.layers[0].kernel) tf.print("b = ",model.layers[0].bias)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
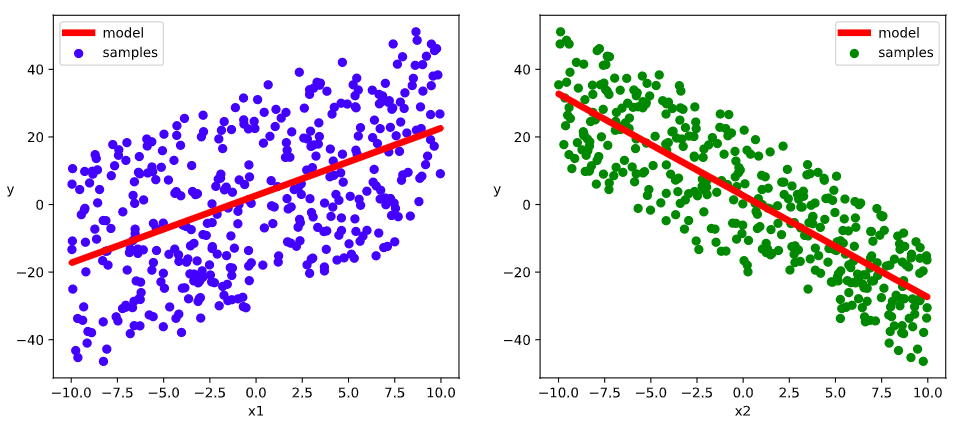
Epoch 197/200 400/400 [==============================] - 0s 190us/sample - loss: 4.3977 - mae: 1.7129 Epoch 198/200 400/400 [==============================] - 0s 172us/sample - loss: 4.3918 - mae: 1.7117 Epoch 199/200 400/400 [==============================] - 0s 134us/sample - loss: 4.3861 - mae: 1.7106 Epoch 200/200 400/400 [==============================] - 0s 166us/sample - loss: 4.3786 - mae: 1.7092 w = [[1.99339032] [-3.00866461]] b = [2.67018795]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
# 结果可视化 %matplotlib inline %config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg' w,b = model.variables plt.figure(figsize = (12,5)) ax1 = plt.subplot(121) ax1.scatter(X[:,0],Y[:,0], c = "b",label = "samples") ax1.plot(X[:,0],w[0]*X[:,0]+b[0],"-r",linewidth = 5.0,label = "model") ax1.legend() plt.xlabel("x1") plt.ylabel("y",rotation = 0) ax2 = plt.subplot(122) ax2.scatter(X[:,1],Y[:,0], c = "g",label = "samples") ax2.plot(X[:,1],w[1]*X[:,1]+b[0],"-r",linewidth = 5.0,label = "model") ax2.legend() plt.xlabel("x2") plt.ylabel("y",rotation = 0) plt.show()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
二,DNN二分类模型
此范例我们使用继承Model基类构建自定义模型,并构建自定义训练循环【面向专家】
1,准备数据
这里和前面有些类似,首先我们利用tensorflow的random函数来得到我们的数据
-
生成正样本, 小圆环分布
-
生成负样本, 大圆环分布
生成后也可以可视化,对数据的分布有一个更好的理解
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import layers,losses,metrics,optimizers %matplotlib inline %config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg' #正负样本数量 n_positive,n_negative = 2000,2000 #生成正样本, 小圆环分布 r_p = 5.0 + tf.random.truncated_normal([n_positive,1],0.0,1.0) theta_p = tf.random.uniform([n_positive,1],0.0,2*np.pi) Xp = tf.concat([r_p*tf.cos(theta_p),r_p*tf.sin(theta_p)],axis = 1) Yp = tf.ones_like(r_p) #生成负样本, 大圆环分布 r_n = 8.0 + tf.random.truncated_normal([n_negative,1],0.0,1.0) theta_n = tf.random.uniform([n_negative,1],0.0,2*np.pi) Xn = tf.concat([r_n*tf.cos(theta_n),r_n*tf.sin(theta_n)],axis = 1) Yn = tf.zeros_like(r_n) #汇总样本 X = tf.concat([Xp,Xn],axis = 0) Y = tf.concat([Yp,Yn],axis = 0) #样本洗牌 data = tf.concat([X,Y],axis = 1) data = tf.random.shuffle(data) X = data[:,:2] Y = data[:,2:] #可视化 plt.figure(figsize = (6,6)) plt.scatter(Xp[:,0].numpy(),Xp[:,1].numpy(),c = "r") plt.scatter(Xn[:,0].numpy(),Xn[:,1].numpy(),c = "g") plt.legend(["positive","negative"]);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40

这里还是构建数据管道
ds_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X[0:n*3//4,:],Y[0:n*3//4,:])) \ .shuffle(buffer_size = 1000).batch(20) \ .prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE) \ .cache() ds_valid = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((X[n*3//4:,:],Y[n*3//4:,:])) \ .batch(20) \ .prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE) \ .cache()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
2,定义模型
这里的定义模型是和中阶API的一样的,定义正向传播和模型的结构
tf.keras.backend.clear_session() class DNNModel(models.Model): def __init__(self): super(DNNModel, self).__init__() def build(self,input_shape): self.dense1 = layers.Dense(4,activation = "relu",name = "dense1") self.dense2 = layers.Dense(8,activation = "relu",name = "dense2") self.dense3 = layers.Dense(1,activation = "sigmoid",name = "dense3") super(DNNModel,self).build(input_shape) # 正向传播 @tf.function(input_signature=[tf.TensorSpec(shape = [None,2], dtype = tf.float32)]) def call(self,x): x = self.dense1(x) x = self.dense2(x) y = self.dense3(x) return y model = DNNModel() model.build(input_shape =(None,2)) model.summary()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
Model: "dnn_model" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= dense1 (Dense) multiple 12 _________________________________________________________________ dense2 (Dense) multiple 40 _________________________________________________________________ dense3 (Dense) multiple 9 ================================================================= Total params: 61 Trainable params: 61 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
3,训练模型
### 自定义训练循环 optimizer = optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.01) loss_func = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy() train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss') train_metric = tf.keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy(name='train_accuracy') valid_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='valid_loss') valid_metric = tf.keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy(name='valid_accuracy') @tf.function def train_step(model, features, labels): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: predictions = model(features) loss = loss_func(labels, predictions) grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables)) train_loss.update_state(loss) train_metric.update_state(labels, predictions) @tf.function def valid_step(model, features, labels): predictions = model(features) batch_loss = loss_func(labels, predictions) valid_loss.update_state(batch_loss) valid_metric.update_state(labels, predictions) def train_model(model,ds_train,ds_valid,epochs): for epoch in tf.range(1,epochs+1): for features, labels in ds_train: train_step(model,features,labels) for features, labels in ds_valid: valid_step(model,features,labels) logs = 'Epoch={},Loss:{},Accuracy:{},Valid Loss:{},Valid Accuracy:{}' if epoch%100 ==0: printbar() tf.print(tf.strings.format(logs, (epoch,train_loss.result(),train_metric.result(),valid_loss.result(),valid_metric.result()))) train_loss.reset_states() valid_loss.reset_states() train_metric.reset_states() valid_metric.reset_states() train_model(model,ds_train,ds_valid,1000)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
================================================================================17:35:02 Epoch=100,Loss:0.194088802,Accuracy:0.923064,Valid Loss:0.215538561,Valid Accuracy:0.904368 ================================================================================17:35:22 Epoch=200,Loss:0.151239693,Accuracy:0.93768847,Valid Loss:0.181166962,Valid Accuracy:0.920664132 ================================================================================17:35:43 Epoch=300,Loss:0.134556711,Accuracy:0.944247484,Valid Loss:0.171530813,Valid Accuracy:0.926396072 ================================================================================17:36:04 Epoch=400,Loss:0.125722557,Accuracy:0.949172914,Valid Loss:0.16731061,Valid Accuracy:0.929318547 ================================================================================17:36:24 Epoch=500,Loss:0.120216407,Accuracy:0.952525079,Valid Loss:0.164817035,Valid Accuracy:0.931044817 ================================================================================17:36:44 Epoch=600,Loss:0.116434008,Accuracy:0.954830289,Valid Loss:0.163089141,Valid Accuracy:0.932202339 ================================================================================17:37:05 Epoch=700,Loss:0.113658346,Accuracy:0.956433,Valid Loss:0.161804497,Valid Accuracy:0.933092058 ================================================================================17:37:25 Epoch=800,Loss:0.111522928,Accuracy:0.957467675,Valid Loss:0.160796657,Valid Accuracy:0.93379426 ================================================================================17:37:46 Epoch=900,Loss:0.109816991,Accuracy:0.958205402,Valid Loss:0.159987748,Valid Accuracy:0.934343576 ================================================================================17:38:06 Epoch=1000,Loss:0.10841465,Accuracy:0.958805501,Valid Loss:0.159325734,Valid Accuracy:0.934785843- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
# 结果可视化 fig, (ax1,ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize = (12,5)) ax1.scatter(Xp[:,0].numpy(),Xp[:,1].numpy(),c = "r") ax1.scatter(Xn[:,0].numpy(),Xn[:,1].numpy(),c = "g") ax1.legend(["positive","negative"]); ax1.set_title("y_true"); Xp_pred = tf.boolean_mask(X,tf.squeeze(model(X)>=0.5),axis = 0) Xn_pred = tf.boolean_mask(X,tf.squeeze(model(X)<0.5),axis = 0) ax2.scatter(Xp_pred[:,0].numpy(),Xp_pred[:,1].numpy(),c = "r") ax2.scatter(Xn_pred[:,0].numpy(),Xn_pred[:,1].numpy(),c = "g") ax2.legend(["positive","negative"]); ax2.set_title("y_pred");- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14

-
相关阅读:
如何在SpringBoot中集成MyBatis?
Windows 同时安装 MySQL5 和 MySQL8 版本
01. 课程简介
web网页设计期末课程大作业——HTML+CSS+JavaScript美食餐饮文化主题网站设计与实现
docker-compose 部署rabbitmq 15672打不开
RS笔记:深度推荐模型之Wide&Deep [2016.6 谷歌]
Go开始:Go基本元素介绍
低市值Pow赛道解析,探寻百倍潜力项目
Coursera自然语言处理专项课程04:Natural Language Processing with Attention Models笔记 Week02
生产环境安装、配置、管理PostgreSQL数据库集群
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45508265/article/details/126582485
