-
C++实践2:在c++20中为spdlog与fmt装配source_location
本文简介
首先介绍了source_location是什么,为什么要使用source_location
然后介绍了fmt是什么,同时着重介绍了fmt如何搭配source_location去使用
最后介绍了spdlog,这是本文介绍的打印日志的最终解决方案。一. source_location简介
简介:是
cpp20的新特性,替换掉了原有的宏定义式打印函数名称,源文件路径和源文件行数。
链接:https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/utility/source_location
具体说明:使用日志时,假如想打印出调用log函数所在的外层函数时,当下常见方法是宏定义。比如下面例子的__FILE_NAME__
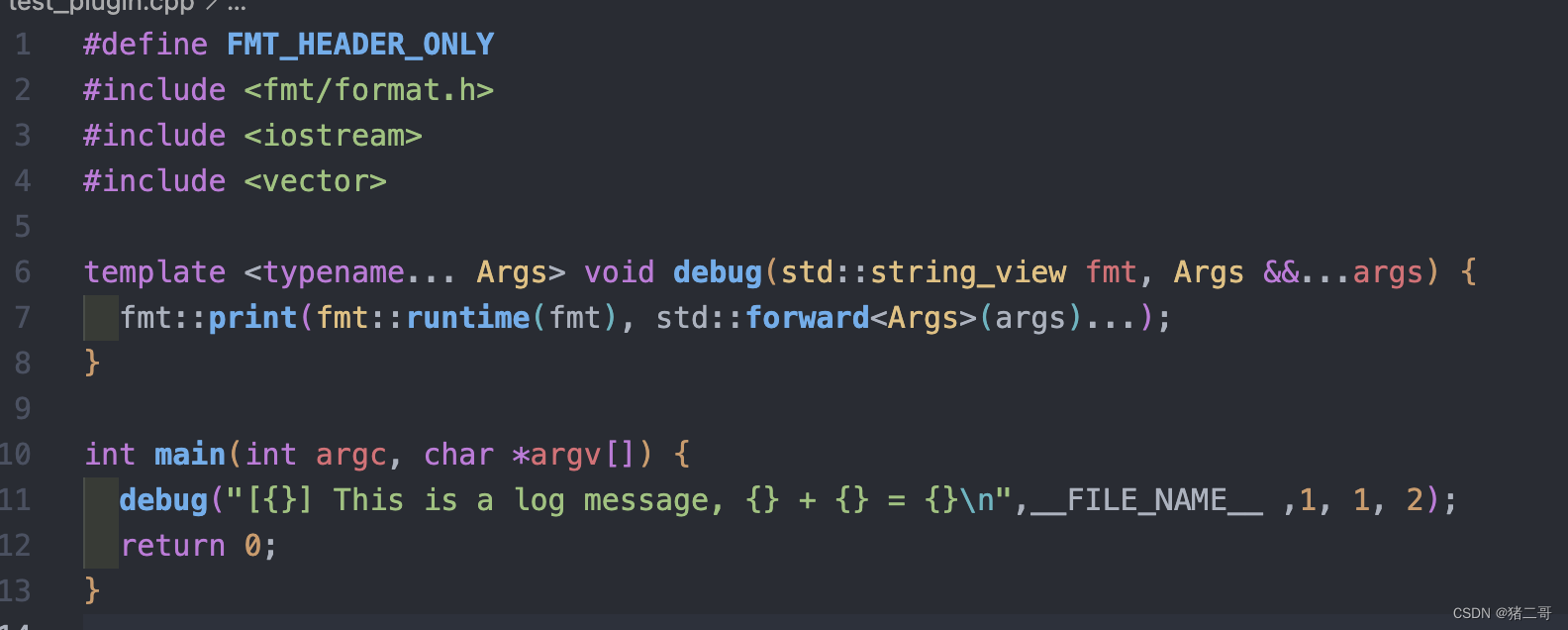

宏定义弊端:- 宏定义总是要写在最外层的发起调用的函数处,即call site。
- 宏定义的值依赖于编译器实现(虽然基本都实现)。
- 若要进行自定义日志级别输出,需要对宏定义封装,即在宏内实现相关功能。相比于常见的函数式编程,宏定义编程要考虑到宏本身文本替换可能引发的bug,需要较繁琐的操作。
source_location: 从语言规范层面明确了这些常用值。对上述例子进行改写:


二. FMT使用source_location说明
FMT简介
说明:一种格式化打印输出的方式。
- 在使用体验上,替换掉了
printf主导的%s/%d等格式化输出符号和cout等流系列的<<,而是使用{}替代,熟悉python的应该都有使用过fmt。但是fmt依旧支持类型检查,输出长度控制等,例子:
fmt::print(fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::beige), "" "┌{0:-^{2}}┐\n" "│{1: ^{2}}|\n" "└{0:-^{2}}┘\n", "","hello world",20 );- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
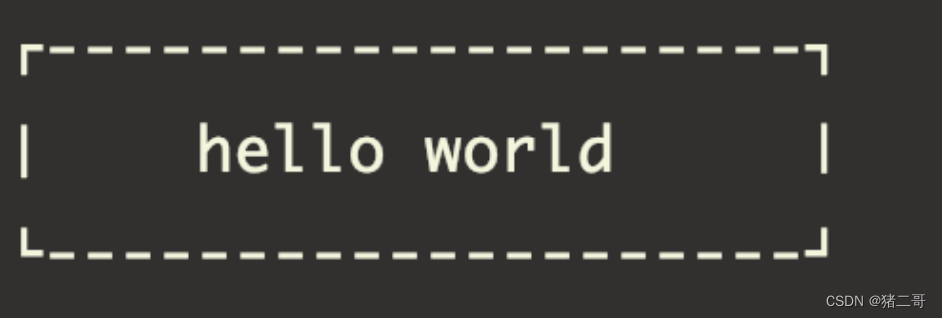
- 性能:它的速度比printf系列函数平均快出35%,有时候甚至更多(对于浮点数,std::format甚至比snprintf快出10倍以上。
分类:当前有两种fmt,一种是cpp20支持的std::formt,另一种是fmtlib::fmt。fmtlib功能更为全面,std::format当前有些阉割。
FMT使用source_location例子
见上面改写后的例子。
解释为什么引入FmtWithLocation类:要着重注意,debug()函数的最后一个参数必须为模板参数包,这是显然的。而我们又不希望每次都在调用debug()函数时手动提供上source_location,即要把source_location作为默认参数。在函数形参中,默认参数需要从后往前去挨个提供初始值,但是模版参数包又必须在最后的位置,因此,我们给引入FmtWithLocation类, 不提供默认参数,通过类构造的形式,将source_location插入到函数参数中来。参考:stackover的解释
source_location依旧要在log函数调用链的顶层处赋值: 和宏定义一样,依旧要在打印log日志时,提供上source_location。
支持更多定制化的功能:和宏定义不同,现在我们的source_location是一个有着明确类型的结构体,我们可以自由的拼装,自由的修改,而不需要string s = __FILE_NAME__这种操作。
cpp20及以上版本使用fmt必须要注意constexpr限制:下面详细讨论FMT使用source_location要注意cpp版本
cpp17及其以下:根据官方文档正常使用即可,没有限制常量属性
cpp20及cpp23: 新增了consteval的编译器模板检查,要求提供给构造函数的fmt参数必须是constexpr,即编译期的常量,下图展示了源码部分的限制。参考:讨论和 解决方案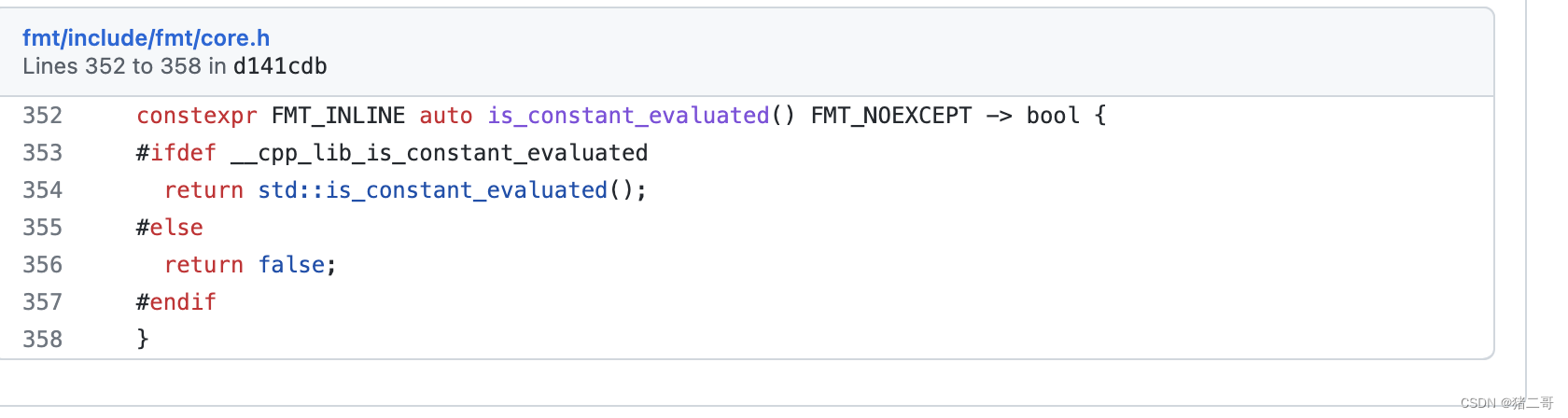
cpp20版本解决方案:如例子所述和上述讨论,如果需要解除常量限制,就使用fmt::runtime。如果要保持常量表达式的特性,可以参考:这里三. 最终解决方案:spdlog
spdlog简介
链接:github
说明:spdlog 是一个快速的 C++ 日志库,header only的第三方库,兼容 C++11。
特性:
非常快
只包含头文件
无需依赖第三方库
支持跨平台 - Linux / Windows on 32/64 bits
支持多线程
可对日志文件进行循环输出
可每日生成日志文件
支持控制台日志输出
可选的异步日志
支持日志输出级别
可自定义日志格式结合fmt
spdlog借助fmt使用格式化输出,header only模式下,在include spdlog时,需要定义
#define FMT_HEADER_ONLY自带source_loc类处理source_location
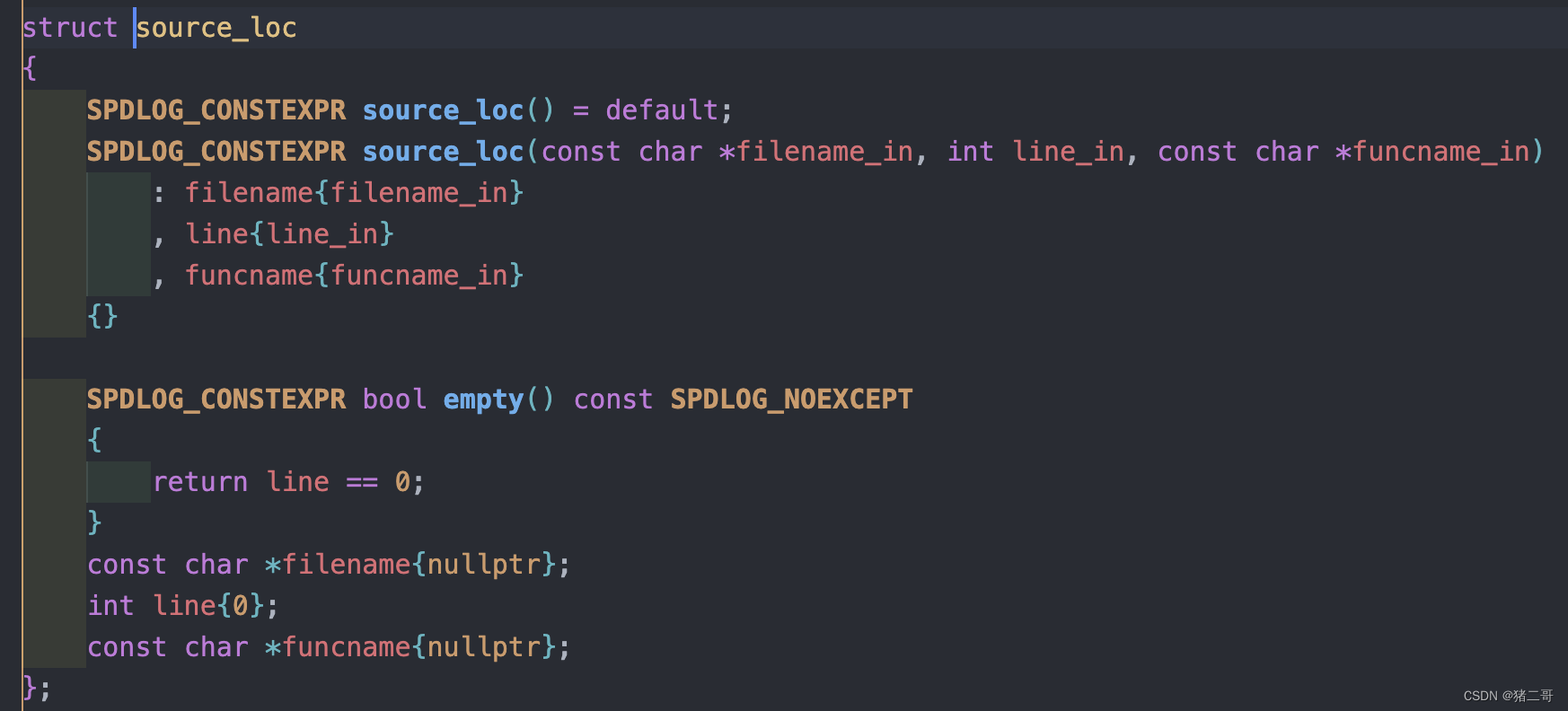
如何使用该类:如上,当按顺序提供filename,line和funcname后,就可以使用%#等格式说明符打印了
但是我们需要手动给spdlog提供source_location,即再封装一层。当前不支持自动获取,作者的解释。为spdlog的source_loc提供source_location
cpp17版本及以下,参考:
cpp20及其以上版本,参考:
log.h#define FMT_HEADER_ONLY #include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include static constexpr size_t MAX_FILE_SIZE = 1024 * 1024 * 100; // 100Mb static constexpr size_t MAX_FILE_COUNT = 10; static constexpr std::string_view BASE_FILE_NAME = "../logs/running.log"; using source_location = std::experimental::source_location; void InitBeforeStart(int level); [[nodiscard]] constexpr auto get_log_source_location(const source_location &location) { return spdlog::source_loc{location.file_name(), static_cast<std::int32_t>(location.line()), location.function_name()}; } struct format_with_location { std::string_view value; spdlog::source_loc loc; template <typename String> format_with_location(const String &s, const source_location &location = source_location::current()) : value{s}, loc{get_log_source_location(location)} {} }; template <typename... Args> void warn(format_with_location fmt_, Args &&...args) { // !cpp20 above should warp fmt_.value with fmt::runtime spdlog::default_logger_raw()->log(fmt_.loc, spdlog::level::warn, fmt::runtime(fmt_.value), std::forward<Args>(args)...); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
log.cpp
#include "log.h" void InitBeforeStart(int level) { std::shared_ptr<spdlog::logger> main_logger = nullptr; std::vector<spdlog::sink_ptr> sinks; sinks.push_back(std::make_shared<spdlog::sinks::stdout_color_sink_mt>()); sinks.push_back(std::make_shared<spdlog::sinks::rotating_file_sink_mt>( std::string(BASE_FILE_NAME), MAX_FILE_SIZE, MAX_FILE_COUNT)); sinks[0]->set_pattern("[%Y-%m-%d %T.%e][%^%-8l%$][%-20s:%#] %v"); sinks[1]->set_pattern("[%Y-%m-%d %T.%e][%-8l][%-20s:%#] %v"); main_logger = std::make_shared<spdlog::logger>("xxx", begin(sinks), end(sinks)); main_logger->flush_on(spdlog::level::err); spdlog::flush_every(std::chrono::seconds(1)); /* set default */ spdlog::set_default_logger(main_logger); main_logger->set_level(static_cast<spdlog::level::level_enum>(level)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
main.cpp
#include "log.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { warn(" This is a log message, {} + {} = {}\n", 1, 1, 2); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
最终效果

-
相关阅读:
Windows11下清理Docker Desktop与wsl的C盘空间占用
搭建内网穿透服务
flink学习之sql-client之踩坑记录
linux环境下Nginx下载配置,及vue项目前端部署教程
力扣:138. 随机链表的复制(Python3)
聊聊Go里面的闭包
大模型的实践应用7-阿里的多版本通义千问Qwen大模型的快速应用与部署
Linux——孤儿进程|进程的优先级 用top命令去修改优先级 其他概念 环境变量 PATH 获取环境变量
【bug】vxe-table编辑列表中使用vue-treeselect,防止卡顿,默认插槽用div导致单击树下拉框不展现,完美解决
npm 清缓存
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42254068/article/details/126566982
