-
《JavaSE-第十三章》之异常体系
前言
在你立足处深挖下去,就会有泉水涌出!别管蒙昧者们叫嚷:“下边永远是地狱!”
博客主页:KC老衲爱尼姑的博客主页
共勉:talk is cheap, show me the code
作者是爪哇岛的新手,水平很有限,如果发现错误,一定要及时告知作者哦!感谢感谢!
刷题求职神器
在下给诸位推荐一款巨好用的刷题求职神器,如果还有小伙伴没有注册该网站,可以点击下方链接直接注册,注册完后就可以立即刷题了。

传送门:牛客网
1异常
2什么是异常?
现实生活中当人的出现了一些毛病,可能就会出现发烧,感冒之类的问题。而我们写的程序也是如此,程序在执行的过程中难免出现一些奇奇怪怪的问题。因此,在java中这些在程序运行中发生的不正常的行为被称为异常。
3异常体系

Error:
- 系统级别的问题,JVM退出等
Exception:java.lang包下,被称为异常类,它表示程序本身可以处理的问题。
- RunTimeException及其子类:运行时异常,编译阶段不会拨错。(索引越界,空指针异常,算术异常)
- 除RuntimeException之外所有的异常:编译时异常,编译期间必须处理,否则程序无法通过比编译。
3.1编译时异常和运行时异常
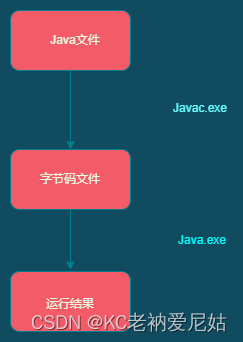
编译时异常:是在编译成class文件时必须要处理的异常,也被称为受察异常。
运行时异常:在运行字节码文件时可能出现的异常。
异常默认的处理流程
示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("程序开始"); int a = 90; int b = 0; System.out.println(a / b);//ArithmeticException System.out.println("程序结束"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
结果
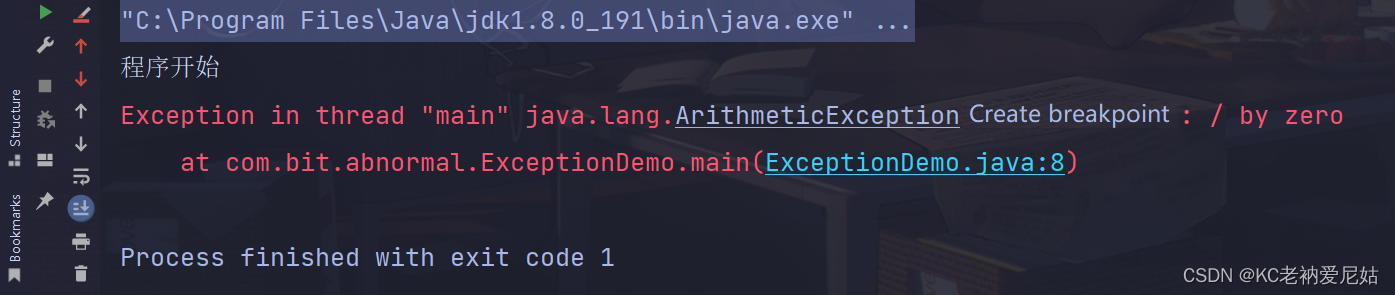
默认异常处理步骤如下
- 默认会在出现异常的代码那里自动创建一个异常对象:ArithmeticException。
- 出现异常后会抛给方法的调用者,即JVM虚拟机。
- 虚拟机接收到异常对象后,先在控制台输出异常栈的信息数据。
- 直接从出现异常处干掉此程序。
- 此时程序已经被杀死,故后续代码无法执行。
默认的处理机制会直接导致程序的死亡
异常的抛出
在编写程序时,如果程序中出现错误,此时就需要将错误的信息告知给调用者,比如:参数检测。
在Java中,可以借助throw关键字,抛出一个指定的异常对象,将错误信息告知给调用者。具体语法如下:
throw new XXXException("异常产生的原因");- 1
示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { fun(); } public static void fun(){ System.out.println("程序开始"); int a = 90; int b = 0; if (b==0){ throw new ArithmeticException("b为0"); } System.out.println(a / b);//ArithmeticException System.out.println("程序结束"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
注意 :
- throw必须写在方法体内部
- 抛出的对象必须是Exception或者Exception的子类对象
- 如果抛出的是RunTimeException或者RunTimeException的子类,则可以不用处理,直接交给JVM处理
- 如果抛出的是编译时异常,用户必须处理,否则无法通过编译。
- 异常一旦抛出,其后的的代码就不会执行。
3.4编译时异常处理
异常处理方式一:
在方法声明时参数列表后,当方法中抛出编译时异常用户不想处理该异常,此时就可以使用throws将异常给方法的调用者来处理。即自己不处理抛出调用者处理。
抛出异常的格式一: 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) throws 异常类型1,异常类型2...{ } 抛出异常的格式二:(简写) 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) throws Exception{ }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
代码示例
public static void fun() throws ParseException { String date = "2022-08-01 8:25:30"; SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); Date d = sdf.parse(date); System.out.println(d); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
异常处理方式二:
使用try-catch捕获并处理,throws对异常并没有真正处理,而是将异常报告给抛出异常方法的调用者,由调用者处理。如果真正要对异常进行处理,就需要try-catch。语法格式一: try{ //监控可能出现异常的代码 }catch(异常类型1 变量){ //异常处理1 }catch(异常类型2 变量){ //异常处理1 }finally{ // 此处代码一定会被执行到 } 语法格式二: try{ //监控可能出现异常的代码 }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace();//打印异常栈信息 }finally{ // 此处代码一定会被执行到 }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
代码示例
public class ExceptionDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("程序开始"); parseTime("2022-08-01 9:06:30"); System.out.println("程序结束"); } public static void parseTime(String date) { try { SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); Date d = sdf.parse(date); System.out.println(d); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); // 打印异常栈信息 } } } 结果 //程序开始 //Mon Aug 01 09:06:30 CST 2022 //程序结束- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
注意事项
1.如果异常之间具有父子关系,一定是子类异常在前catch,父类异常在后catch,否则语法错误:
代码示例
public class ExceptionDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3}; try { System.out.println("before"); arr = null; System.out.println(arr[4]); System.out.println("after"); } catch (Exception e) {//捕获所有异常 e.printStackTrace(); }catch (NullPointerException e){// 永远都捕获执行到 e.printStackTrace(); } } } //java: 已捕获到异常错误java.lang.NullPointerException- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2.try块内抛出异常位置之后的代码将不会被执行,如果抛出异常类型与catch时异常类型不匹配,即异常不会被成功捕获,也就不会被处理,继续往外抛,直到JVM收到后中断程序----异常是按照类型来捕获的。
finally
在写程序时,有些特定的代码,不论程序是否发生异常,都需要执行,比如程序中打开的资源:网络连接、数据库
连接、IO流等,在程序正常或者异常退出时,必须要对资源进进行回收。另外,因为异常会引发程序的跳转,可能
导致有些语句执行不到,finally就是用来解决这个问题的。
示例代码
public class Copy { public static void main(String[] args) { FileInputStream in=null; FileOutputStream out=null; try { //创建一个输入流对象 in=new FileInputStream("E:\\tet.txt"); //创建一个输出流对象 out=new FileOutputStream("E:\\tet2.txt"); byte [] bytes=new byte[1024*1024];//1M int read=0; while ((read=in.read(bytes))!=-1) { out.write(bytes,0,read); } //刷新,输出流刷新 out.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(in!=null){ try { in.close();//关闭输入流 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(out!=null){ try { out.close();//关闭输出流 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } System.out.println("如果没有抛出异常,或者异常被处理了,try-catch后的代码也会执行"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
问题:既然 fifinally 和 try-catch-fifinally 后的代码都会执行,那为什么还要有ifinally呢?
需求:实现getData方法,内部输入一个整形数字,然后将该数字返回,并再main方法中打印
代码示例
public class TestFinally { public static int getData() { Scanner sc = null; try { sc = new Scanner(System.in); int data = sc.nextInt(); return data; } catch ( InputMismatchException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { System.out.println("finally中代码"); } System.out.println("try-catch-finally之后代码"); if (null != sc) { sc.close(); } return 0; } public static void main(String[] args) { int data = getData(); System.out.println(data); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
代码示例
public class ExceptionDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { int[] array = {1,2,3}; System.out.println(array[3]); }catch (NullPointerException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("Hello World"); } }//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
异常处理方式三:
- 方法直接将异通过throws抛出去给调用者
- 调用者收到异常后直接捕获处理。
代码示例
public class ExceptionDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("程序开始"); try { parseTime("2022--08-01 09:23:60"); System.out.println("功能操作成功"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("功能操作失败"); } System.out.println("程序结束"); } public static void parseTime(String date) throws Exception { SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); Date d = sdf.parse(date); System.out.println(d); } } //12 //finally中代码 //12- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
3.5运行时异常处理
运行时异常在编译阶段是不会出错的,是在运行的时候才会出错,所以编译期间 可以不进行处理也是可以的,如果要处理可以按照上述异常处理方式三在最外层调用处集中捕获处理即可。
异常的处理流程
关于调用栈
方法之间是存在相互调用关系的, 这种调用关系我们可以用 “调用栈” 来描述. 在 JVM 中有一块内存空间称为
“虚拟机栈” 专门存储方法之间的调用关系. 当代码中出现异常的时候, 我们就可以使用 e.printStackTrace(); 的
方式查看出现异常代码的调用栈.
如果本方法中没有合适的处理异常的方式, 就会沿着调用栈向上传递
代码示例一
public class ExceptionDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { try{ fun(); }catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("Hello World"); } public static void fun(){ int [] arr ={1,2,3,4,5}; System.out.println(arr[1000]); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
代码示例二
public class ExceptionDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { fun(); System.out.println("Hello World"); } public static void fun(){ int [] arr ={1,2,3,4,5}; System.out.println(arr[1000]); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
上述程序,如果正常输入,成功接收输入后程序就返回了,try-catch-fifinally之后的代码根本就没有执行,即输入流
就没有被释放,造成资源泄漏。
注意:finally中的代码一定会执行的,一般在fifinally中进行一些资源清理的扫尾工作。
finally 执行的时机是在方法返回之前(try 或者 catch 中如果有 return 会在这个 return 之前执行 fifinally). 但是如果finally 中也存在 return 语句, 那么就会执行 fifinally 中的 return, 从而不会执行到 try 中原有的 return.
异常处理流程
- 程序先执行 try 中的代码
- 如果 try 中的代码出现异常, 就会结束 try 中的代码, 看和 catch 中的异常类型是否匹配.
- 如果找到匹配的异常类型, 就会执行 catch 中的代码
- 如果没有找到匹配的异常类型, 就会将异常向上传递到上层调用者.
- 无论是否找到匹配的异常类型, fifinally 中的代码都会被执行到(在该方法结束之前执行).
- 如果上层调用者也没有处理的了异常, 就继续向上传递.
- 一直到 main 方法也没有合适的代码处理异常, 就会交给 JVM 来进行处理, 此时程序就会异常终止.
3.6自定义异常
需求:认为年龄小于0岁,大于200岁就是一个异常。
测试类
package com.bit.abnormal; /** 需求:认为年龄小于0岁,大于200岁就是一个异常。 */ public class ExceptionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { try { checkAge2(-23); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void checkAge2(int age) { if(age < 0 || age > 200){ // 抛出去一个异常对象给调用者 // throw :在方法内部直接创建一个异常对象,并从此点抛出 // throws : 用在方法申明上的,抛出方法内部的异常 throw new ItheimaAgeIlleagalRuntimeException(age + " is illeagal!"); }else { System.out.println("年龄合法:推荐商品给其购买~~"); } } public static void checkAge(int age) throws ItheimaAgeIlleagalException { if(age < 0 || age > 200){ // 抛出去一个异常对象给调用者 // throw :在方法内部直接创建一个异常对象,并从此点抛出 // throws : 用在方法申明上的,抛出方法内部的异常 throw new ItheimaAgeIlleagalException(age + " is illeagal!"); }else { System.out.println("年龄合法:推荐商品给其购买~~"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
3.7自定义编译时异常
package com.bit.abnormal; /** 自定义的编译时异常 1、继承Exception 2、重写构造器 */ public class ItheimaAgeIlleagalException extends Exception{ public ItheimaAgeIlleagalException() { } public ItheimaAgeIlleagalException(String message) { super(message); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
3.8自定义运行时异常
package com.bit.abnormal; /** 自定义的编译时异常 1、继承RuntimeException 2、重写构造器 */ public class ItheimaAgeIlleagalRuntimeException extends RuntimeException{ public ItheimaAgeIlleagalRuntimeException() { } public ItheimaAgeIlleagalRuntimeException(String message) { super(message); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
注意事项
- 自定义异常通常会继承自 Exception 或者 RuntimeException
- 继承自 Exception 的异常默认是受查异常
- 继承自 RuntimeException 的异常默认是非受查异常

最后的话
各位看官如果觉得文章写得不错,点赞评论关注走一波!谢谢啦!。如果你想变强那么点我点我 牛客网。

-
相关阅读:
一些感悟(随笔小记)
C语言操作符深度解析(四)
柱状图:带误差棒
ref和reactive
用户端APP自动化测试_L2
MySQL34道例题
【踩坑记录】创建Go模块-从其他远程模块调用代码的教程
LeetCode 0485. 最大连续 1 的个数
Qt新手入门指南——创建一个基于Qt Widget的文本查找器(一)
图文详解MapReduce工作机制
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_60308100/article/details/126513826
