-
Spring声明式基于注解的缓存(2-实践篇)
一、序言
在前面 Spring声明式基于注解的缓存(1-理论篇)一节中我们大致介绍了基于注解的缓存抽象相关理论知识,包括常用注解
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict、@Caching和@CacheConfig,还有缓存相关组件CacheManager和CacheResolver的作用。这篇是实战环节,主要会包含缓存相关注解的应用。
二、使用示例
1、配置
(1) application.properties
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.password=lyl spring.redis.database=0 spring.redis.timeout=1000ms spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=50 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=1000ms spring.redis.lettuce.pool.time-between-eviction-runs=30000ms- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
(2) 基于Redis缓存的CacheManager配置
@EnableCaching @Configuration public class RedisCacheConfig { private static final String KEY_SEPERATOR = ":"; /** * 自定义CacheManager,具体配置参考{@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration} * @param redisConnectionFactory 自动配置会注入 * @return */ @Bean(name = "redisCacheManager") public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisSerializer<String> keySerializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); RedisSerializer<Object> valueSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() .serializeKeysWith(SerializationPair.fromSerializer(keySerializer)) .serializeValuesWith(SerializationPair.fromSerializer(valueSerializer)) .computePrefixWith(key -> key.concat(KEY_SEPERATOR)); return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(cacheConfig).build(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
备注:上面我们指定了
key和value的序列化器,还有缓存key的拼接策略。
2、注解运用测试用例
SpringCacheService定义了相关的缓存操作,如下:@Service @CacheConfig(cacheManager = "redisCacheManager") public class SpringCacheService { /** * key:缓存key名称,支持SPEL * value:缓存名称 * condition:满足条件可缓存才缓存结果,支持SPEL * unless:满足条件结果不缓存,支持SPEL * @param stuNo * @return */ @Cacheable(key = "#stuNo", value = "student-cache", condition = "#stuNo gt 0", unless = "#result eq null") public StudentDO getStudentByNo(int stuNo) { StudentDO student = new StudentDO(stuNo, "liuyalou"); System.out.println("模拟从数据库中读取:" + student); return student; } /** * 不指定key,默认会用{@link org.springframework.cache.interceptor.SimpleKeyGenerator} * 如果方法无参数则返回空字符串,只有一个参数则返回参数值,两个参数则返回包含两参数的SimpleKey * @param username * @param age * @return */ @Cacheable(value = "user-cache", unless = "#result eq null") public UserDO getUserByUsernameAndAge(String username, int age) { UserDO userDo = new UserDO(username, age); System.out.println("模拟从数据库中读取:" + userDo); return userDo; } @Cacheable(key = "#stuNo + '_' +#stuName", value = "student-cache", unless = "#result?.stuName eq null") public Optional<StudentDO> getStudentByNoAndName(int stuNo, String stuName) { if (stuNo <= 0) { return Optional.empty(); } StudentDO student = new StudentDO(stuNo, stuName); System.out.println("模拟从数据库中读取:" + student); return Optional.ofNullable(student); } @CacheEvict(value = "student-cache", key = "#stuNo") public void removeStudentByStudNo(int stuNo) { System.out.println("从数据库删除数据,key为" + stuNo + "的缓存将会被删"); } @CachePut(value = "student-cache", key = "#student.stuNo", condition = "#result ne null") public StudentDO updateStudent(StudentDO student) { System.out.println("数据库进行了更新,检查缓存是否一致"); return student; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
(1) 指定key条件式缓存
这里我们定义了名为
student-cache,key为1的缓存,以及是否缓存的两个条件:- 如果
stuNo小于0则不缓存。 - 如果方法执行结果不为空才缓存。
/** * key:缓存key名称,支持SPEL * value:缓存名称 * condition:满足条件可缓存才缓存结果,支持SPEL * unless:满足条件结果不缓存,支持SPEL * @param stuNo * @return */ @Cacheable(key = "#stuNo", value = "student-cache", condition = "#stuNo gt 0", unless = "#result eq null") public StudentDO getStudentByNo(int stuNo) { StudentDO student = new StudentDO(stuNo, "liuyalou"); System.out.println("模拟从数据库中读取:" + student); return student; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
@Test public void getStudentByNo() { StudentDO studentDo = springCacheService.getStudentByNo(1); System.out.println(studentDo); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
控制台输出如下,如果Redis中没有该
student-cache:1对应的值,则会执行方法体的代码。模拟从数据库中读取:StudentDO[stuName=liuyalou,stuNo=1] 程序执行结果为: StudentDO[stuName=liuyalou,stuNo=1]- 1
- 2
该方法执行后,让我们看看Redis中的key,可以看到多了
student-cache:1的缓存键值对信息。
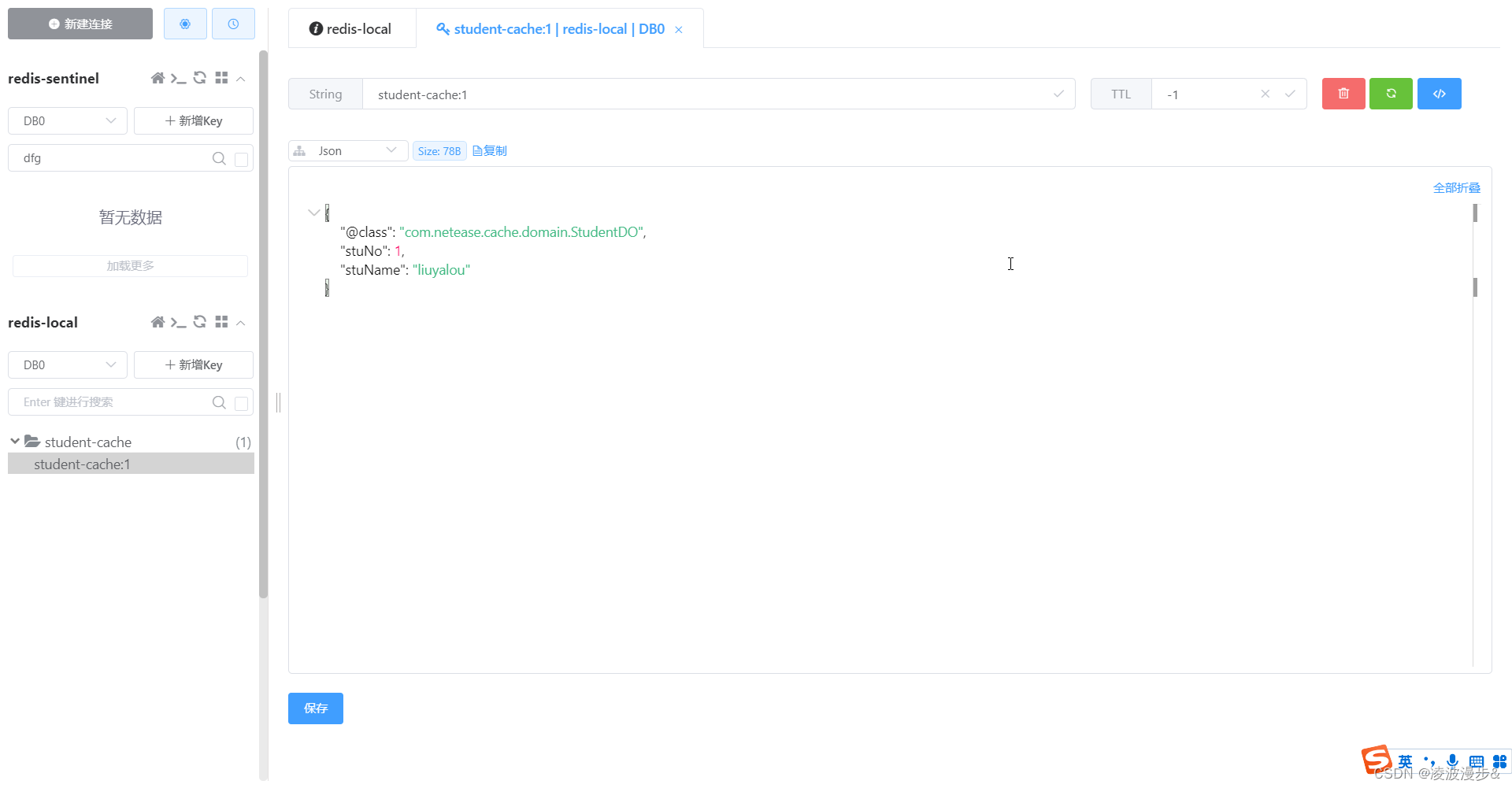
备注:当再次执行该方法时,不会执行方法体逻辑,而是从Redis中获取对应缓存key的值。
(2) 返回值为Optional类型条件式缓存
这里我们自定义了名为
student-cache,key为stuNo_stuName的缓存,方法返回参数为Optional类型。如果Optional的值为空,则方法的执行结果不会被缓存。@Cacheable(key = "#stuNo + '_' +#stuName", value = "student-cache", unless = "#result?.stuName eq null") public Optional<StudentDO> getStudentByNoAndName(int stuNo, String stuName) { if (stuNo <= 0) { return Optional.empty(); } StudentDO student = new StudentDO(stuNo, stuName); System.out.println("模拟从数据库中读取:" + student); return Optional.ofNullable(student); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
@Test public void getStudentByNoAndName() { Optional<StudentDO> studentDo = springCacheService.getStudentByNoAndName(1, "Nick"); System.out.println("程序执行结果为: " + studentDo.orElse(null)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
备注:
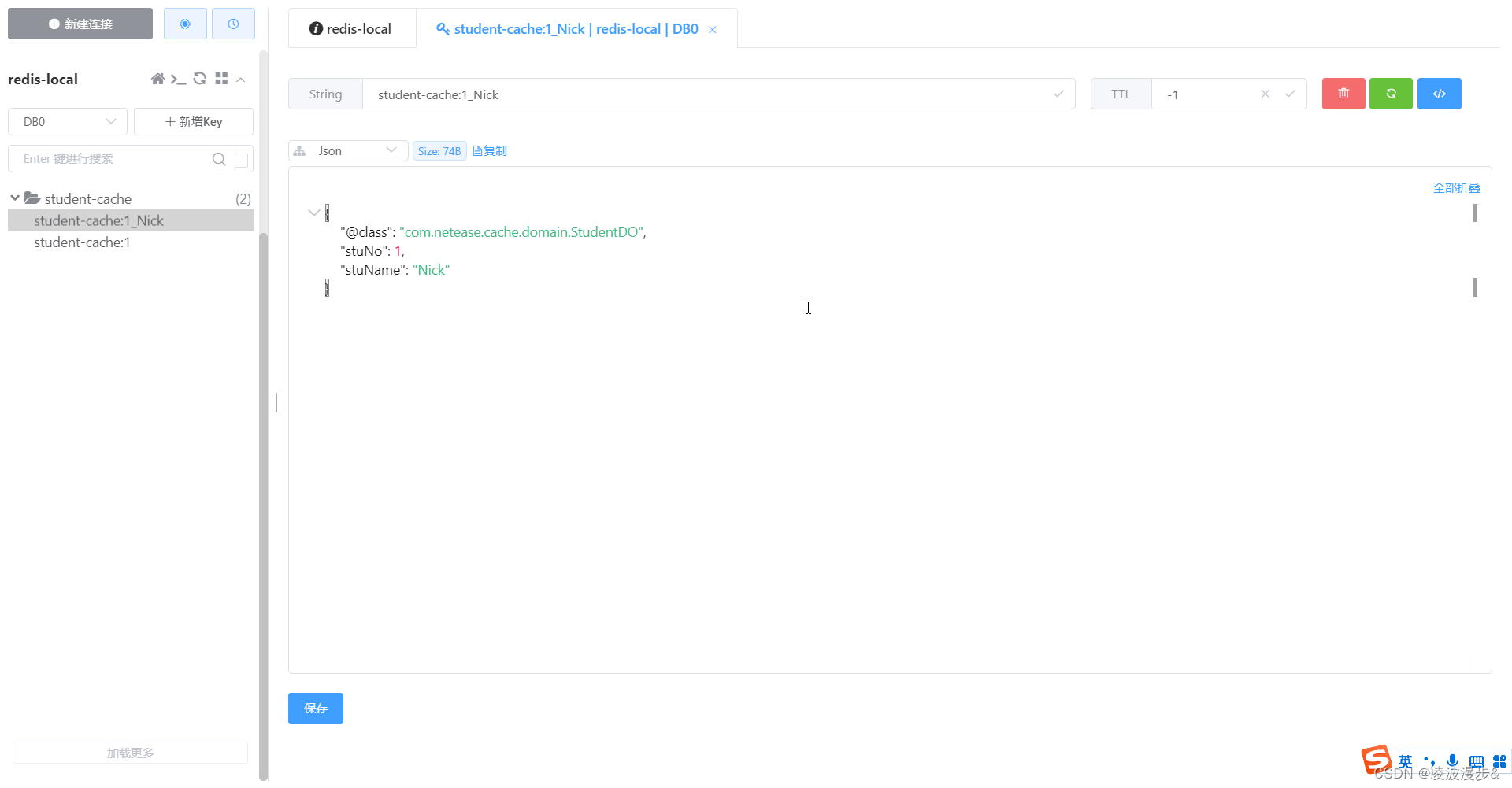
#result指向的不是Optional实例,而是Student实例,因为Optional中的值可能为null,这里我们用了安全导航操作符?。控制台输出:
模拟从数据库中读取:StudentDO[stuName=Nick,stuNo=1] 程序执行结果为: StudentDO[stuName=Nick,stuNo=1]- 1
- 2
让我们再看下Redis中的key情况:
(3) 不指定key条件式缓存
下面的方法我们没有指定
key属性,key的生成会用默认的key生成器SimpleKeyGenerator来生成。@Cacheable(value = "user-cache", unless = "#result eq null") public UserDO getUserByUsernameAndAge(String username, int age) { UserDO userDo = new UserDO(username, age); System.out.println("模拟从数据库中读取:" + userDo); return userDo; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
@Test public void getUserByUsernameAndAge() { UserDO userDo = springCacheService.getUserByUsernameAndAge("liuyalou", 23); System.out.println("程序执行结果为: " + userDo); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
方法执行完后,让我们看看Redis中的key情况:
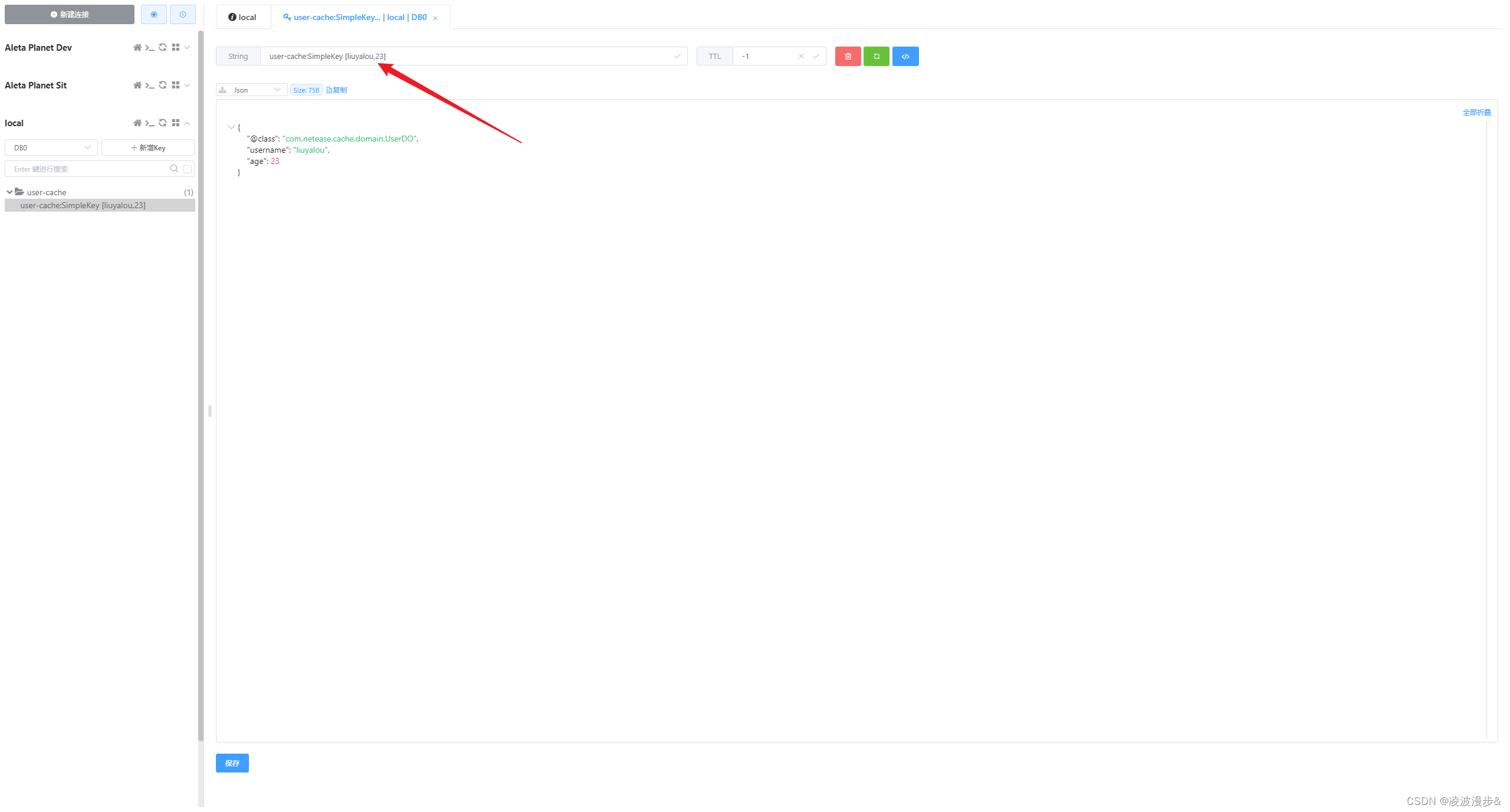
备注:可以看到
SimpleKeyGernerator生成的key名是根据对象属性来生成的。(4) 指定key删除缓存
这个注解我们用来根据指定缓存key来清除缓存。
@CacheEvict(value = "student-cache", key = "#stuNo") public void removeStudentByStudNo(int stuNo) { System.out.println("从数据库删除数据,key为" + stuNo + "的缓存将会被删"); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
@Test public void getStudentByNo() { StudentDO studentDo = springCacheService.getStudentByNo(1); System.out.println("程序执行结果为: " + studentDo); } @Test public void removeStudentByStudNo() { springCacheService.removeStudentByStudNo(1); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
我们先执行
getStudentByNo测试用例,再执行removeStudentByStudNo,控制台输出如下:模拟从数据库中读取:StudentDO[stuName=liuyalou,stuNo=1] 程序执行结果为: StudentDO[stuName=liuyalou,stuNo=1]- 1
- 2
从数据库删除数据,key为1的缓存将会被删- 1
备注:执行完后可以看到Redis中的key会被删除。
(5) 指定key更新缓存
接下来我们根据指定key更新缓存,这里我们也指定了缓存条件,只有当缓存结果不为空时才缓存。
@CachePut(value = "student-cache", key = "#student.stuNo", unless = "#result eq null”) public StudentDO updateStudent(StudentDO student) { System.out.println("数据库进行了更新,检查缓存是否一致"); return student; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
@Test public void updateStudent() { StudentDO oldStudent = springCacheService.getStudentByNo(1); System.out.println("原缓存内容为:" + oldStudent); springCacheService.updateStudent(new StudentDO(1, "Evy")); StudentDO newStudent = springCacheService.getStudentByNo(1); System.out.println("更新后缓存内容为:" + newStudent); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
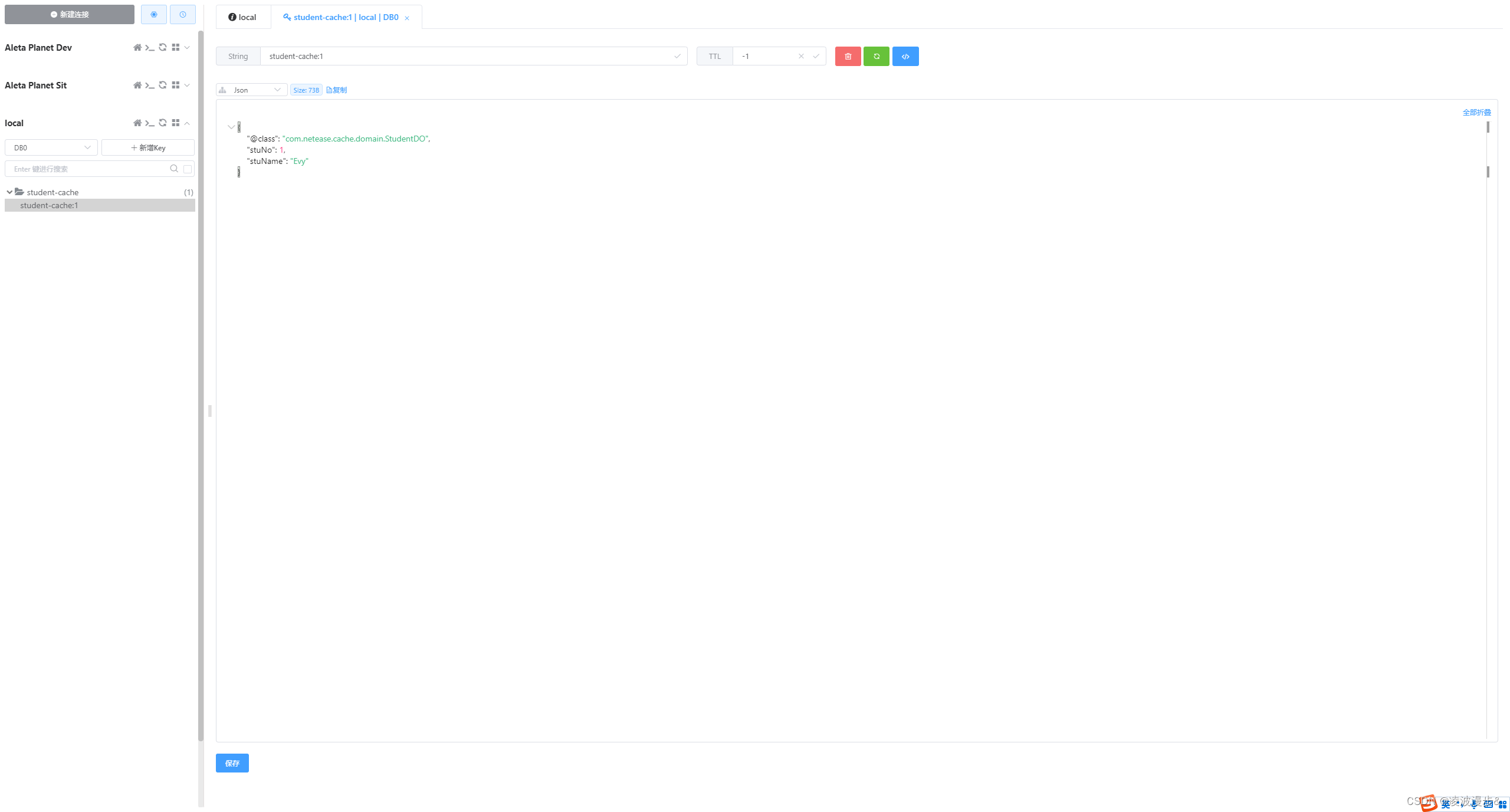
控制台输出为:
原缓存内容为:StudentDO[stuName=Evy,stuNo=1] 数据库进行了更新,检查缓存是否一致 更新后缓存内容为:StudentDO[stuName=Evy,stuNo=1]- 1
- 2
- 3
最终Redis中的key信息如下:
三、结语
总得来说,声明式缓存抽象和声明式事务一样,使用起来都比较简单。更多的细节描述可以参考:Spring缓存抽象官方文档。
有同学可能会发现,Spring提供的这些注解不支持过期时间的设置,官方文档也有一些解释,如下:
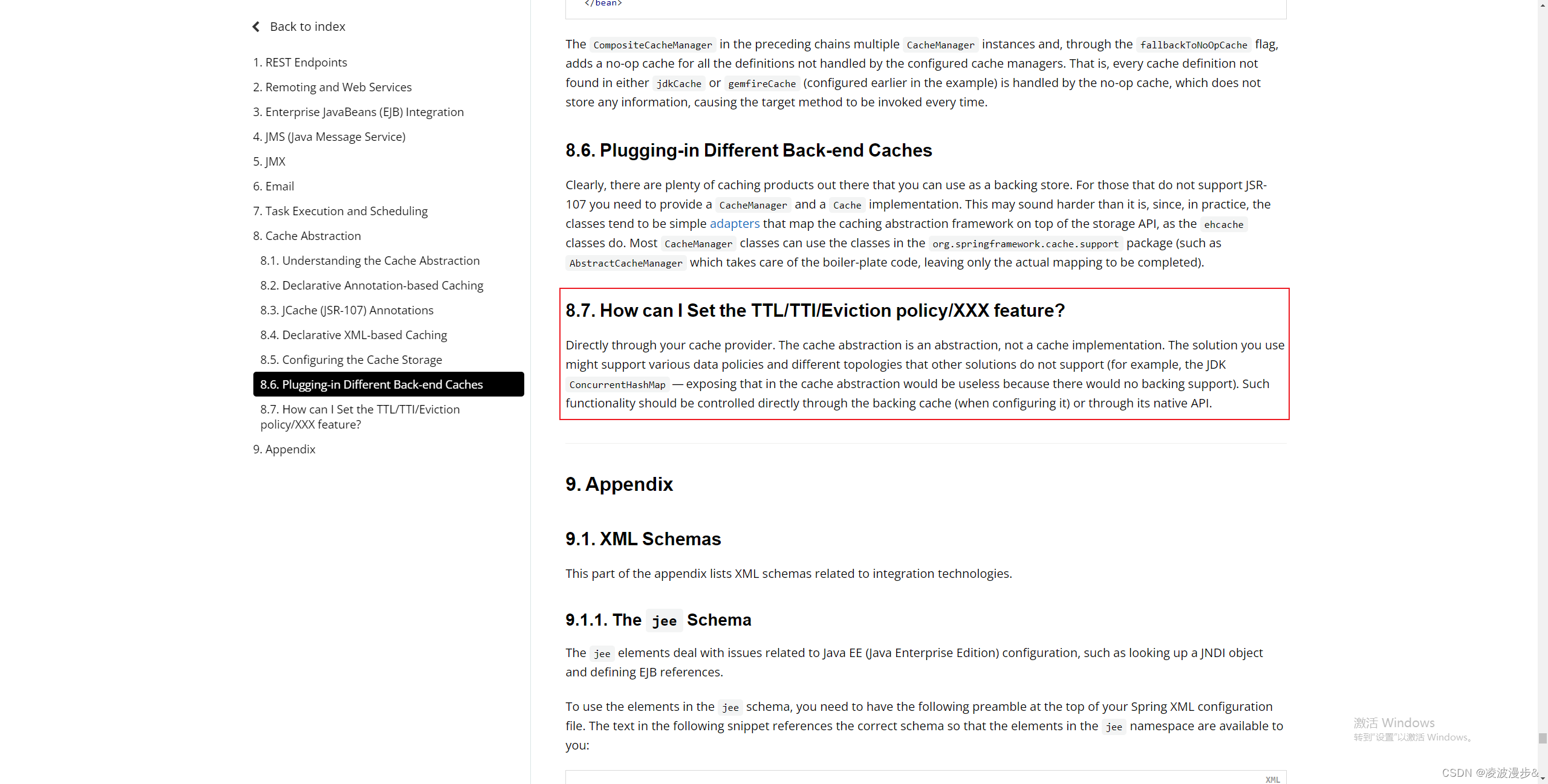
官方提供的建议是通过缓存提供器来实现,其实就是我们可以通过自定义CacheManager来实现。缓存抽象只是一种逻辑抽象,而不是具体的缓存实现,具体怎么写缓存,缓存写到哪里应该由缓存管理器来实现。下一节我们会通过自定义
CacheResolver、RedisCacheManager、以及相关Cache注解来实现带过期时间的缓存实现。
-
相关阅读:
(高阶)Redis 7 第12讲 数据双写一致性 经验篇
git常用操作汇总
IntelliJ IDEA安装CloudToolkit自动部署工具
thinkphp6 入门(4)--数据库操作 增删改查
冒号等于(:=)在Python语言中是什么意思?
FFmpeg合并音视频文件操作备忘(mac版)
Java JDK安装与配置
rk3399 9.0驱动添加Powser按键
生态系统服务——水源涵养水源涵养分布
C&C++动态内存管理
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/lingbomanbu_lyl/article/details/126450406