-
【打卡】【sysfs相关API详解】21天学习挑战赛—RK3399平台开发入门到精通-Day21
活动地址:CSDN21天学习挑战赛
学习的最大理由是想摆脱平庸,早一天就多一份人生的精彩;迟一天就多一天平庸的困扰。各位小伙伴,如果您:
想系统/深入学习某技术知识点…
一个人摸索学习很难坚持,想组团高效学习…
想写博客但无从下手,急需写作干货注入能量…
热爱写作,愿意让自己成为更好的人…device_register
kernel/drivers/base/core.c
int device_register(struct device *dev) { device_initialize(dev); return device_add(dev); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(device_register); void device_initialize(struct device *dev) { dev->kobj.kset = devices_kset; kobject_init(&dev->kobj, &device_ktype); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->dma_pools); mutex_init(&dev->mutex); lockdep_set_novalidate_class(&dev->mutex); spin_lock_init(&dev->devres_lock); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->devres_head); device_pm_init(dev); set_dev_node(dev, -1); #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->msi_list); #endif } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(device_initialize);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
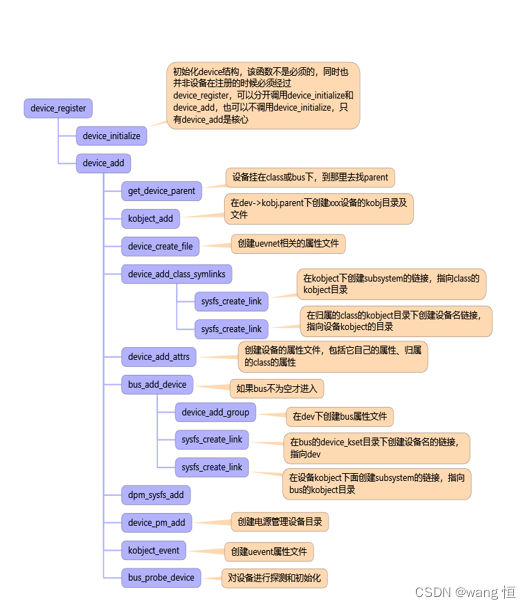
通过以上可以看到device_register的作用:设备主要的初始化都是在/sys/devices/***/下创建一个自己设备名字的目录,如pci0000:00,然后再里面创建对应设备的属性文件接口,如下图:

同时它也会创建一个subsystem的链接,指向bus或者class,表示它归属的类型,挂在bus下面意味着它是由某个bus管控,如果挂载class下面,这只是一个视角问题,其实质也是表示它具备着某些共同属性,管理操作属性上的一致。

然后再/sys/bus或者/sys/class下面就没有必要再去创建同样的东西,因为它们都是重复的,直接创建一个链接指向device,意味着从它们的目录去看,可以看到bus或者class都管理着什么设备。

driver_register
kernel/drivers/base/driver.c
/** * driver_register - register driver with bus * @drv: driver to register * * We pass off most of the work to the bus_add_driver() call, * since most of the things we have to do deal with the bus * structures. */ int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv) { int ret; struct device_driver *other; BUG_ON(!drv->bus->p); if ((drv->bus->probe && drv->probe) || (drv->bus->remove && drv->remove) || (drv->bus->shutdown && drv->shutdown)) printk(KERN_WARNING "Driver '%s' needs updating - please use " "bus_type methods\n", drv->name); other = driver_find(drv->name, drv->bus); if (other) { printk(KERN_ERR "Error: Driver '%s' is already registered, " "aborting...\n", drv->name); return -EBUSY; } ret = bus_add_driver(drv); if (ret) return ret; ret = driver_add_groups(drv, drv->groups); if (ret) { bus_remove_driver(drv); return ret; } kobject_uevent(&drv->p->kobj, KOBJ_ADD); return ret; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(driver_register);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42

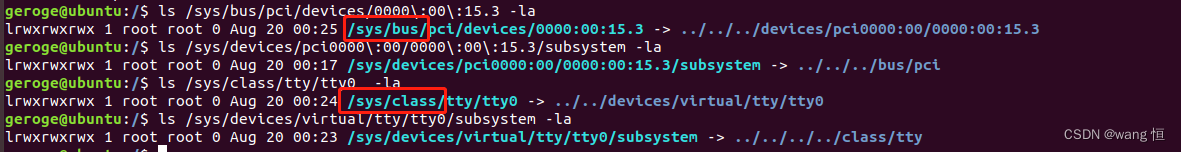
可以看到,对于driver_register它主要实在/sys/bus/xxx/drivers目录下创建自己名字的目录,然后在里面初始化驱动属性文件。
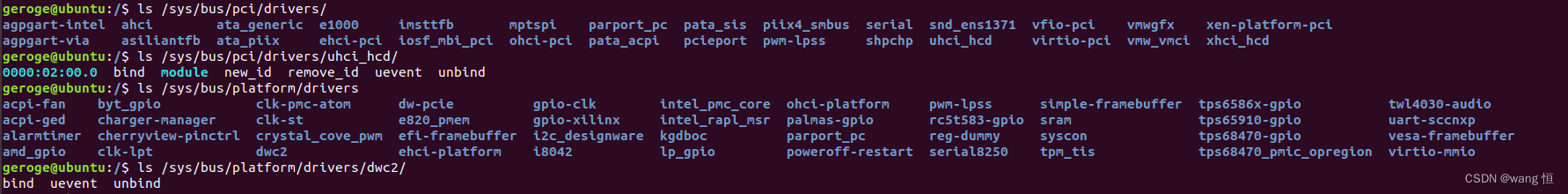
同时创建链接指向module,表示该驱动是由哪个内核模块提供功能,同样module也反指向驱动,表示它提供的是什么样的驱动能力,当然只有驱动模块才会有指向驱动的链接。


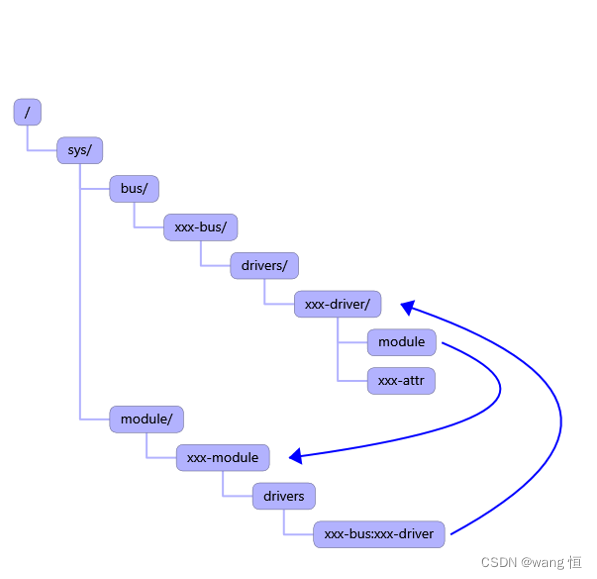
以上关于bus,device,driver的各自register以及各自的加载流程及机制,在sysfs中的展示都讲完,那么关于挂载在bus上的devices和drivers是如何在合适的时机进行设备驱动probe的呢?继续看!设备驱动probe的时机
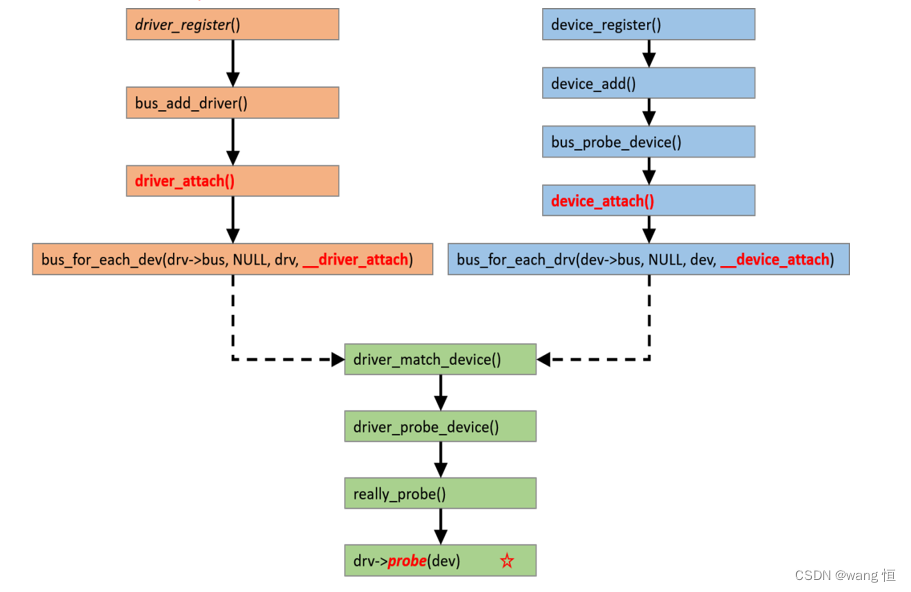
kernel/drivers/base/base.hstatic inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev) { return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
前面是否还有疑问关于driver_register从哪里调用,有过相关概念和基础的可能大致能推出从驱动里调用,那么关于bus,devices和drivers的关系,因为driver是针对特定的硬件的,它是用来操作具体的硬件的,因此需要在特定的硬件驱动程序里去调用,这里跟随这前面platform_bus_init(里面实现了bus_register和device_register)的脚步继续platform_driver_register的注册分析:
kernel/include/linux/platform_device.h
/* * use a macro to avoid include chaining to get THIS_MODULE */ #define platform_driver_register(drv) \ __platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE) extern int __platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *, struct module *);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
kernel/drivers/base/platform.c
/** * __platform_driver_register - register a driver for platform-level devices * @drv: platform driver structure * @owner: owning module/driver */ int __platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv, struct module *owner) { drv->driver.owner = owner; drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type; drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe; drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove; drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown; return driver_register(&drv->driver); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__platform_driver_register);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
至此,platform的bus,devices和driver都注册完成,来看看它的match场景:
kernel/drivers/base/platform.c/** * platform_match - bind platform device to platform driver. * @dev: device. * @drv: driver. * * Platform device IDs are assumed to be encoded like this: * "", where is a short description of the type of * device, like "pci" or "floppy", and is the enumerated * instance of the device, like '0' or '42'. Driver IDs are simply * " ". So, extract the from the platform_device structure, * and compare it against the name of the driver. Return whether they match * or not. */ - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
根据上述,可以得出以下匹配规则:
- 若要一个平台驱动支持多个不同名字的平台设备,利用id_table[]的name进行区分;
- 若要一个平台驱动支持多个同名字的平台设备,根据平台设备的name进行区分;
- 利用总线上的match来匹配,若无match函数,则通吃所有设备。
-
相关阅读:
Aspose.Email 22.7 for Java Crack
瑞吉外卖项目实战Day02
【MySql】8- 实践篇(六)
第四章 继承
计网第六章(应用层)(三)(文件传输协议FTP)
低代码如何构建支持OAuth2.0的后端Web API
Solr plugin热部署原理
PatchCore原理与代码解读
git Husky
Redis基本全局命令(含key过期策略)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_23327993/article/details/126450175