-
C语言:堆
1. 堆
1. 建堆:
堆的内核是数组(如下结构体代码),一般堆建好后,已经是小顶堆或大顶堆,以下全部以下顶堆为例。
结构体代码typedef struct Head { HPDataType* a; int size; int capacity; }HP;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
建堆过程:通过push()建堆
建堆过程是依次拿数组中的元素做push,每push一个,做一次向上调整
1.1Push()过程:
- 给数组最后一个位置放值
- 做向上调整,当前位置设为child,依次与 parent = (child - 1 / 2)位置做比较。若小(当前按小顶堆处理),则交换位置。令child = parent,然后parent继续往上游,也就是更小的下标走。
- 要注意的是循环条件是 :while(child>0),因为每做一次,孩子位置向上走,变为父亲即:局部的堆根节点,最终当child比较过父亲为0时,该停止,所以child>0时,终有父亲为0,后,child拿到0的值,此时该停止。但是如果while为:parent>=0后,如果最后一次parent==0,孩子为1时,比完后,先是child = 0(把parent给它),下次parent = (0-1) /2 = 0,C语言中-1除以2还是0,所以下次while中还会再次去比较parent为0和child为0,所以这里一定注意拿child>0来做判断,当child等于0时,说明parent已经经过0了,意思是0位置已经比较过了,所以停止即可。
void Swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b) { HPDataType t = *a; *a = *b; *b = t; } // **注意这里参数是*a,改变数组即可 分析其中用父亲判断可能存在的坑 // 向上调整:拿当前和父亲比较,大或小则交换 这里是小根堆 void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child) { // 这里的par都是逻辑上的,我们利用堆调整的过程是为了让连续地址的数组中存储的数字符合堆特征。 int parent = (child - 1) / 2; // 父亲等于0也要比 因向上调要连根也查 //while (parent>=0) // 最好用孩子来做:孩子>0就继续 等于0就停 意思是 父亲p=0也比过了 而用par>=0 会报错,多比一次,因为par = 0-1/2还是0 while(child>0) { if (a[child]<a[parent]) { // 这里换两个位置的值 Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); child = parent; // 父等于孩-1除以2 parent = (child - 1)/2; } // 如果插入值 小于了某个爹,停就行 else { break; } } } ////// 插入步骤: /// 1。查否需要扩容 /// 2。插入val 并size++ /// 3。向上调整,因为插入在尾部,且可能影响父,但堆从不考虑兄弟 /// void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x) { assert(php); printf("在做push\n"); // 为什么先看看要不要扩容 if (php->size == php->capacity) { int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0?4:php->capacity*2; HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, newcapacity*sizeof(HPDataType)); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("push :realloc fail\n"); exit(-1); } php->a = tmp; php->capacity = newcapacity; } php->a[php->size] = x; // 插完了,然后向上调整 AdjustUp(php->a, php->size-1); php->size++; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
1.2Pop出堆首:
pop时得到堆首元素,是最小元素(以小根堆为例),然后我们的堆需要调整顺序,从堆尾(数组最后)拿值交换到堆首,然后size–,再不断从底部向上调整,保证最小(小根堆)的在上面。
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent) { // 这是左孩子 int minchild = parent * 2+1; // 小于才对,等于都错了,因为下标从0开始。 while (minchild < n) { // 找两个孩子中更小的,做比较,一开始parent处是一个稍微小的数 if (minchild + 1 < n && a[minchild + 1] < a[minchild]) { minchild++; } // 现在minchild一定在最小位置:如果孩子小于父亲 if (a[minchild] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[minchild], &a[parent]); parent = minchild; minchild = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } } } // 删除堆顶:删顶,补最小,后调整 // O(logN) : 1000个数10次,100W20次,1e个30次,logn非常牛 ////// 做法: /// 1. 交换首尾,size--,因在做pop /// 2. /// void HeapPop(HP* php) { assert(php); assert(!HeapEmpty(php)); Swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]); php->size--; AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0); } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
3. 完整代码
头文件
#pragma once #include#include #include #include #include typedef int HPDataType; // 堆的内核是数组:也只是特殊在逻辑结构,成员变量并不特别 typedef struct Head { HPDataType* a; int size; int capacity; }HP; void HeapInit(HP* php); void HeapDestroy(HP* php); // 堆顶 插入x void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x); // 删除堆顶 void HeapPop(HP* php); // 返回堆顶的元素 HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php); bool HeapEmpty(HP* php); // 大小 int HeapSize(HP* php); // 打印 void HeapPrint(HP* php); - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
实现文件
#include"ds_5_heap.h" void HeapInit(HP* php) { assert(php); php->a = NULL; php->capacity = php->size = 0; } void HeapDestroy(HP* php) { ; } void Swap(HPDataType* a, HPDataType* b) { HPDataType t = *a; *a = *b; *b = t; } // **注意这里参数是*a,改变数组即可 分析其中用父亲判断可能存在的坑 // 向上调整:拿当前和父亲比较,大或小则交换 这里是小根堆 void AdjustUp(HPDataType* a, int child) { // 这里的par都是逻辑上的,我们利用堆调整的过程是为了让连续地址的数组中存储的数字符合堆特征。 int parent = (child - 1) / 2; // 父亲等于0也要比 因向上调要连根也查 //while (parent>=0) // 最好用孩子来做:孩子>0就继续 等于0就停 意思是 父亲p=0也比过了 而用par>=0 会报错,多比一次,因为par = 0-1/2还是0 while(child>0) { if (a[child]<a[parent]) { // 这里换两个位置的值 Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); child = parent; // 父等于孩-1除以2 parent = (child - 1)/2; } // 如果插入值 小于了某个爹,停就行 else { break; } } } ////// 插入步骤: /// 1。查否需要扩容 /// 2。插入val 并size++ /// 3。向上调整,因为插入在尾部,且可能影响父,但堆从不考虑兄弟 /// void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x) { assert(php); printf("在做push\n"); // 为什么先看看要不要扩容 if (php->size == php->capacity) { int newcapacity = php->capacity == 0?4:php->capacity*2; HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, newcapacity*sizeof(HPDataType)); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("push :realloc fail\n"); exit(-1); } php->a = tmp; php->capacity = newcapacity; } php->a[php->size] = x; // 插完了,然后向上调整 AdjustUp(php->a, php->size-1); php->size++; } // 需要数组、最后一个节点位置、孩子位置 // 它从最高的起点:0位置到最下一层 // l1:minchild可能越界,因为可能左右孩子不存在:如果小于n就存在 // 我现在对n不太了解怎么给的,怎么知道是多少 // l3:可能右孩子更小,但是需要判断右孩子是否存在 void AdjustDown(HPDataType* a, int n, int parent) { // 这是左孩子 int minchild = parent * 2+1; // 小于才对,等于都错了,因为下标从0开始。 while (minchild < n) { // 找两个孩子中更小的,做比较,一开始parent处是一个稍微小的数 if (minchild + 1 < n && a[minchild + 1] < a[minchild]) { minchild++; } // 现在minchild一定在最小位置:如果孩子小于父亲 if (a[minchild] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[minchild], &a[parent]); parent = minchild; minchild = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } } } // 删除堆顶:删顶,补最小,后调整 // O(logN) : 1000个数10次,100W20次,1e个30次,logn非常牛 /// /// 做法: /// 1. 交换首尾,size--,因在做pop /// 2. /// void HeapPop(HP* php) { assert(php); assert(!HeapEmpty(php)); Swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]); php->size--; AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0); } // 返回堆顶的元素 HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php) { assert(php); assert(!HeapEmpty(php)); // 最大或最小一定在a[0]处 return php->a[0]; } // 打印堆 void HeapPrint(HP* php) { for (int i = 0; i < php->size; i++) { printf("%d ", php->a[i]); } printf("\n"); } bool HeapEmpty(HP* php) { return php->size == 0; } // 大小 int HeapSize(HP* php) { retunr php->size; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
main()测试
int main() { // 查前两天 如何输入多行数组,在百度题上。 // 初始化数组,直接用[]即可 int a[] = { 15, 18, 19, 25, 34, 65, 49, 2, 37, 1 }; HP* hp; hp = (HP*)malloc(sizeof(HP)); // 初始化一般是为结构体:用指针也行,但是应该要另外申请空间 用结构体也行。。 // 用指针需要申请空间 HeapInit(hp); for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]); i++) { printf("现在的i:%d\n", i); HeapPush(hp, a[i]); } // 走完是小堆,1在第一位 HeapPush(hp, 10); HeapPrint(hp); HeapPop(hp); HeapPrint(hp); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
运行效果

4. 复杂度分析:
1.建堆
建堆有两种做法:一种是本文提到的边插变调(不论向上还是向下调,都是O(NlogN)),另外一种在下一篇博客中会详细介绍,那就是先插完,再让从最后一个父至根节点每个节点向下调整。时间复杂度是O(N)。
我们知道堆排序是不断建堆过程还能保证有序的,每次插入,都涉及调整,一次插入是LogN复杂度,那么N个节点的插入就是:O(NlogN)2. 向上向下调整
因为每次向上向下调整,最多经过的是树高次,树高也就是树深度:LogN。O(logN)非常了不起,1W次只需要10次,而100W只需要20次,1e只要30次。
5. 玩代码过程中遇到的realloc问题:
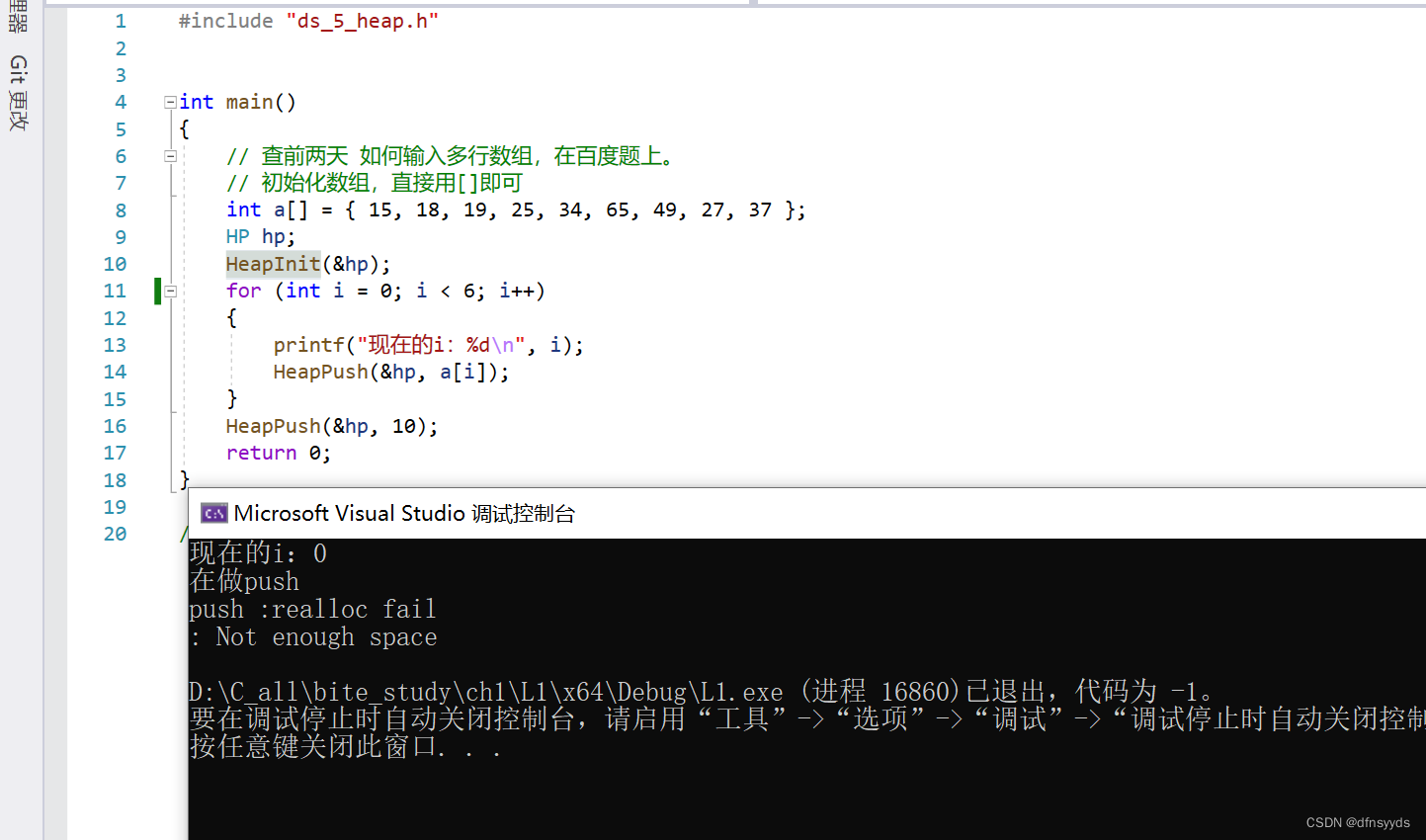
realloc失败,后来我发现,原来是我的init中没有初始化capacity,即因为capacity没有值,所以程序出现了读错数据,数据过大,导致realloc申请空间太大必然失败。 -
相关阅读:
Linux上安装虚拟conda环境和神经网络学习框架pytorch
BLE抓包调试信息分析
【C++】动态内存管理 ③ ( C++ 对象的动态创建和释放 | new 运算符 为类对象 分配内存 | delete 运算符 释放对象内存 )
JUC编程
Swin Transformer算法解读
-tf.reduce_sum(one_hot_labels * log_probs, axis=-1)是什么损失函数?
react实现一个搜索部门(input + tree)
AVProVideo☀️十、来给视频设置封面
C++-openssl-aes-cbc-pkcs5
『忘了再学』Shell基础 — 16、位置参数变量
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/myscratch/article/details/126429842
