背景:介绍两种python用于语句优化的用法
一、推导式
1.推导式简介:
Python 推导式是一种独特的数据处理方式,可以从一个数据序列构建另一个新的数据序列的结构体。
支持:列表(list)、元组(tuple)、集合(set)、 字典(dict)
如原有的修改列表(list)内元素(数字)+1需要使用的循环语句:
#原有的修改列表(list)内元素(数字)+1
l1 = [1,3,5,7,9] for i in range(len(l1)): l1[i]+=1 print(l1)
查看运行结果:

如使用推导式,语句将更加简介
2.列表推导式:
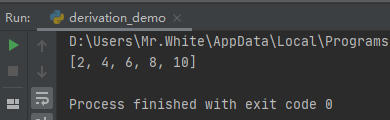
#2.列表推导式: list_before = [1,3,5,7,9] list_after = [i+1 for i in list_before] print(list_after)
查看运行结果:
3.元组推导式
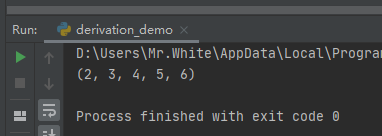
#3.元组推导式: tuple_before = (1,2,3,4,5) tuple_after =tuple(i+1 for i in tuple_before) print(tuple_after)
查看运行结果:
4.集合推导式:
#4.集合推导式: set_before = {0,1,2,3,4} set_after = {i+1 for i in set_before} print(set_after)
查看运行结果:

5.字典推导式(修改字典的key与value):
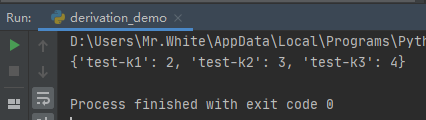
#5.字典推导式 dict_befory = {"k1":1,"k2":2,"k3":3} dict_after = {"test-"+x:dict_befory[x]+1 for x in dict_befory} print(dict_after)
查看运行结果:
二、海象运算符(python3.8+)
1.概念:
海象运算符:=作为一项新奇的python语法,在最新发布的python3.8中被首次提出来。
海象运算符即一个变量名后跟一个表达式或者一个值,这个和赋值运算符 = 类似,可以看作是一种新的赋值运算符。
在合适的场景中使用海象运算符可以降低程序复杂性,简化代码
2.使用场景:
(1)用于 if-else 条件表达式
(1.1)原有写法:
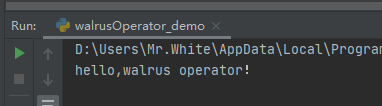
a = 0 if a < 15: print("hello,walrus operator!")
查看运行结果:
(1.2)海象运算符:
if a := 15 > 10: print("hello,walrus operator!")
查看运行结果:

(2) 用于 while 循环
(2.1)原有写法:
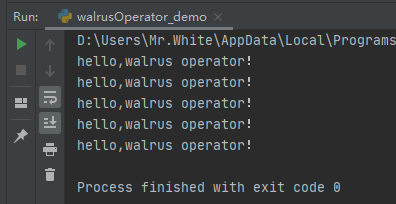
count = 5 while count: print("hello,walrus operator!") count -= 1
查看运行结果:
(2.2)海象运算符:
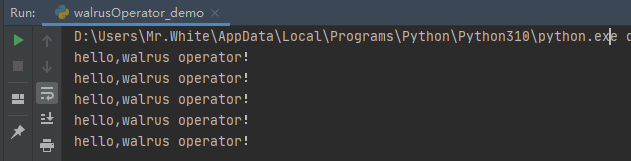
count = 5 while (count := count - 1)+1: # 需要加1是因为执行输出前count就减1了 print("hello,walrus operator!")
查看运行结果:
(3)用于列表推导式
(3.1)原有写法:
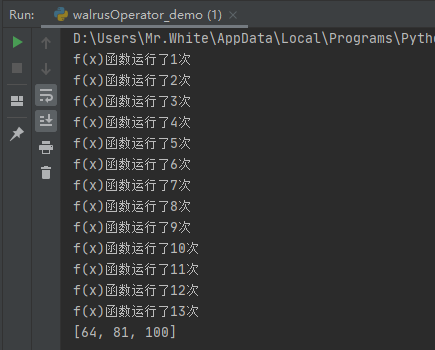
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | nums1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]count = 1def f(x):global countprint(f"f(x)函数运行了{count}次")count += 1return x ** 2nums2 = [f(i) for i in nums1 if f(i) > 50]print(nums2) |
查看运行结果:
(3.2)海象运算符:
nums1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] count = 1 def f(x): global count print(f"f(x)函数运行了{count}次") count += 1 return x ** 2 nums2 = [j for i in nums1 if (j := f(i)) > 50] print(nums2)
查看运行结果:
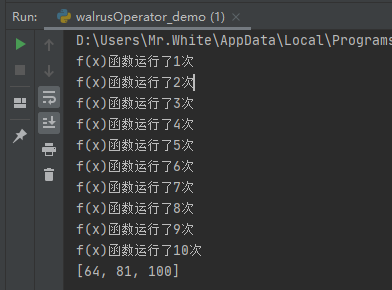
可以看出:
使用海象运算符时:三个数字满足列表推导式的条件,节省 3次的函数调用。当程序数据巨大的时候,这将起到提升性能的作用。
