-
【第3天】SQL快速入门-高级查询(SQL 小虚竹)
回城传送–》《32天SQL筑基》
零、前言
今天是学习 SQL 打卡的第 3 天,每天我会提供一篇文章供群成员阅读( 不需要订阅付钱 )。
希望大家先自己思考,如果实在没有想法,再看下面的解题思路,自己再实现一遍。在小虚竹JAVA社区 中对应的 【打卡贴】打卡,今天的任务就算完成了,养成每天学习打卡的好习惯。
虚竹哥会组织大家一起学习同一篇文章,所以有什么问题都可以在群里问,群里的小伙伴可以迅速地帮到你,一个人可以走得很快,一群人可以走得很远,有一起学习交流的战友,是多么幸运的事情。
我的学习策略很简单,题海策略+ 费曼学习法。如果能把这些题都认认真真自己实现一遍,那意味着 SQL 已经筑基成功了。后面的进阶学习,可以继续跟着我,一起走向架构师之路。
今天的学习内容是:高级查询
一、练习题目
题目链接 难度 计算函数:SQL16 查找GPA最高值 ★★☆☆☆ 计算函数:SQL17 计算男生人数以及平均GPA ★★☆☆☆ 分组查询:SQL18 分组计算练习题 ★★★☆☆ 分组查询:SQL19 分组过滤练习题 ★★☆☆☆ 分组查询:SQL20 分组排序练习题 ★★☆☆☆ 二、SQL思路
计算函数:SQL16 查找GPA最高值

初始化数据
drop table if exists user_profile; CREATE TABLE `user_profile` ( `id` int NOT NULL, `device_id` int NOT NULL, `gender` varchar(14) NOT NULL, `age` int , `university` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `gpa` float); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2234,'male',21,'北京大学',3.2); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,2235,'male',null,'复旦大学',3.8); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,2236,'female',20,'复旦大学',3.5); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2237,'female',23,'浙江大学',3.3); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,2238,'male',25,'复旦大学',3.1); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(6,2239,'male',25,'北京大学',3.6); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(7,2240,'male',null,'清华大学',3.3); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(8,2241,'female',null,'北京大学',3.7);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
解法
第一种解法:
使用最大值函数:max补充:最小值函数:min
select max(gpa) from user_profile where university='复旦大学';- 1
- 2
- 3
第二种解法:
对gpa字段进行倒序排列,然后取第一个值select gpa from user_profile where university='复旦大学' order by gpa DESC LIMIT 0,1;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
第三种解法:
使用mysql 的all 函数,all关键字必须与一个比较操作符一起使用。any关键词可以理解为“对于子查询返回的列中的任一数值,如果比较结果为true,则返回true”
select gpa from user_profile where university = '复旦大学' and gpa >= all (select gpa from user_profile where university = '复旦大学')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
注:这个用法其实用在这题不合适,效率差,只为了演示all 函数的用法
计算函数:SQL17 计算男生人数以及平均GPA
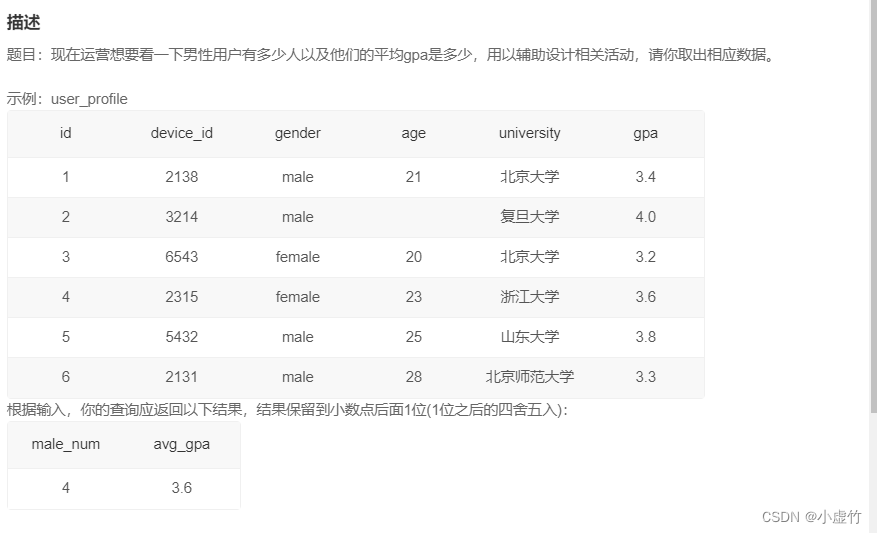
初始化数据
drop table if exists user_profile; CREATE TABLE `user_profile` ( `id` int NOT NULL, `device_id` int NOT NULL, `gender` varchar(14) NOT NULL, `age` int , `university` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `gpa` float); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,'male',21,'北京大学',3.4); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,'male',null,'复旦大学',4.0); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,'female',20,'北京大学',3.2); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,'female',23,'浙江大学',3.6); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,'male',25,'山东大学',3.8); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(6,2131,'male',28,'北京师范大学',3.3);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
解法
要求统计:
- 男性用户有多少人
- 他们的平均gpa是多少
- 平均gpa结果保留到小数点后面1位(1位之后的四舍五入)
分析: - 所以条件是男性
- 多少人要用计数,所以用count函数
- 计算平均gpa,要用avg函数
- 平均值可能小数点位数很多,按照示例保存一位小数,用round函数
- 对查询的结果列要进行重命名,才符合题目要求
SELECT count(gender) as male_num ,round(avg(gpa),1) as avg_gpa from user_profile where gender='male'- 1
- 2
- 3
分组查询:SQL18 分组计算练习题


初始化数据
drop table if exists user_profile; CREATE TABLE `user_profile` ( `id` int NOT NULL, `device_id` int NOT NULL, `gender` varchar(14) NOT NULL, `age` int , `university` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `gpa` float, `active_days_within_30` float, `question_cnt` float, `answer_cnt` float ); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,'male',21,'北京大学',3.4,7,2,12); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,'male',null,'复旦大学',4.0,15,5,25); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,'female',20,'北京大学',3.2,12,3,30); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,'female',23,'浙江大学',3.6,5,1,2); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,'male',25,'山东大学',3.8,20,15,70); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(6,2131,'male',28,'山东大学',3.3,15,7,13); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(7,4321,'male',28,'复旦大学',3.6,9,6,52);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
解法
要求统计:
- 每个学校每种性别的用户数
- 30天内平均活跃天数
- 平均发帖数量
分析:
- 每个学校的每种性别,这里就是要学校和性别进行分组,使用关键词:group by
- 每个学校每种性别的用户数,就是要对设备ID进行计数,在分组的基础上进行计数,使用关键字:count
- 30天内平均活跃天数,是对字段active_days_within_30进行求平均,使用关键词:avg ,而且结果保留1位小数,1位小数之后的四舍五入,这里要用上:round函数
- 平均发帖数量,是对字段question_cnt进行求平均,使用关键词:avg ,而且结果保留1位小数,1位小数之后的四舍五入,这里要用上:round函数
- 按题目要求进行对查询列的重命名。
SELECT gender, university, count(device_id) as user_num, round(avg(active_days_within_30),1) as avg_active_day, round(avg(question_cnt),1) as avg_question_cnt FROM user_profile group by university, gender- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
分组查询:SQL19 分组过滤练习题


初始化数据
drop table if exists user_profile; CREATE TABLE `user_profile` ( `id` int NOT NULL, `device_id` int NOT NULL, `gender` varchar(14) NOT NULL, `age` int , `university` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `gpa` float, `active_days_within_30` int , `question_cnt` float, `answer_cnt` float ); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,'male',21,'北京大学',3.4,7,2,12); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,'male',null,'复旦大学',4.0,15,5,25); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,'female',20,'北京大学',3.2,12,3,30); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,'female',23,'浙江大学',3.6,5,1,2); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,'male',25,'山东大学',3.8,20,15,70); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(6,2131,'male',28,'山东大学',3.3,15,7,13); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(7,4321,'male',28,'复旦大学',3.6,9,6,52);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
解法
要求统计:
- 每个学校用户的平均发贴数
- 每个学校用户的平均回帖数
- 条件是平均发贴数低于5的学校或平均回帖数小于20的学校。
分析:
- 这里是要学校进行分组,使用关键词:group by
- 平均发贴,是对字段question_cnt进行求平均,使用关键词:avg ,而且结果保留3位小数,3位小数之后的四舍五入,这里要用上:round函数
- 回帖情况,是对字段answer_cnt进行求平均,使用关键词:avg ,而且结果保留3位小数,3位小数之后的四舍五入,这里要用上:round函数
- 条件是平均发贴数低于5的学校或平均回帖数小于20的学校,聚合函数结果作为筛选条件时,不能用where,而是用:having语法
- 按题目要求进行对查询列的重命名。
-- 查询1 SELECT university, round(AVG(question_cnt),3) as avg_question_cnt, round(AVG(answer_cnt),3) as avg_answer_cnt FROM user_profile GROUP BY university HAVING avg_question_cnt < 5 OR avg_answer_cnt < 20;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
分组查询:SQL20 分组排序练习题


初始化数据
drop table if exists user_profile; CREATE TABLE `user_profile` ( `id` int NOT NULL, `device_id` int NOT NULL, `gender` varchar(14) NOT NULL, `age` int , `university` varchar(32) NOT NULL, `gpa` float, `active_days_within_30` int , `question_cnt` int , `answer_cnt` int ); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(1,2138,'male',21,'北京大学',3.4,7,2,12); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(2,3214,'male',null,'复旦大学',4.0,15,5,25); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(3,6543,'female',20,'北京大学',3.2,12,3,30); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(4,2315,'female',23,'浙江大学',3.6,5,1,2); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(5,5432,'male',25,'山东大学',3.8,20,15,70); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(6,2131,'male',28,'山东大学',3.3,15,7,13); INSERT INTO user_profile VALUES(7,4321,'male',28,'复旦大学',3.6,9,6,52);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
解法
要求统计:
- 查看不同大学的用户平均发帖情况
- 按照平均发帖情况进行升序排列
- 隐藏需求:平均发帖情况,结果保留4位小数。
分析:
- 这里是要学校进行分组,使用关键词:group by
- 平均发贴,是对字段question_cnt进行求平均,使用关键词:avg ,而且结果保留4位小数,4位小数之后的四舍五入,这里要用上:round函数
- 按题目要求进行对查询列的重命名。
- 按照平均发帖情况进行升序排列,使用关键词:order by
select university, round(avg(question_cnt),4) as avg_question_cnt from user_profile group by university order by avg_question_cnt asc- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
-
相关阅读:
性能测试 —— 吞吐量和并发量的关系? 有什么区别?
2024深圳杯数学建模竞赛A题(东三省数学建模竞赛A题):建立火箭残骸音爆多源定位模型
领悟《信号与系统》之 非周期信号的傅里叶变换及性质
React 中的延迟加载Lazy loading
使用vue-cli创建Vue工程化项目及单文件组件的创建和调用
【C++笔试强训】第五天
这几个与windows10有关的操作,可以帮助你更好地使用电脑
深入理解机器学习——类别不平衡学习(Imbalanced Learning):样本采样技术-[基础知识]
软件设计模式(五):代理模式
Linux操作系统第一讲
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/shi_hong_fei_hei/article/details/125954351
