-
Vue计算属性computed,全选反选案例
计算属性
一个变量的值,依赖另外一些数据计算而来的结果
注意:计算属性也是vue数据变量,所以不能和data里变量重名,用法和data相同的
语法:
computed:{ "计算属性名"(){ return 值 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
{{计算属性名}}- 1
简单的例子
<div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model.number="num1"> + <input type="text" v-model.number="num2"> = <input type="text" v-model.number="sum"> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
达到改变num1或num2的值,sum值会随着改变 的效果
new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ num1:0, num2:0, // sum:0 }, computed:{ sum(){ // 必须有return return的值就是计算属性的值 //console.log(1) return this.num1 + this.num2; } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
1:计算属性和data属性都是变量——不能重名
2:页面第一次加载,计算属性会执行——赋初始值
3:函数内的依赖的变量变化,会自动重新计算结果返回优势:
1.带缓存
2.计算属性对应的函数执行后,会把return值缓存起来
3.依赖的变量不变,多次调用都是从缓存取值
4.依赖的变量改变, 函数会"自动" 重新执行–并缓存新的值案例:
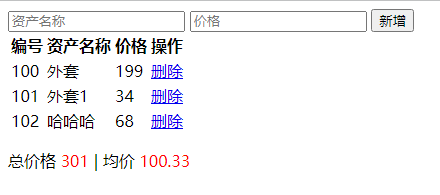
增加物品时,总价格和均价会随之改变:<div id="app"> <input type="text" @focus="flag = true" :class="{'bor':flag}" placeholder="资产名称" v-model="name"> <input type="text" placeholder="价格" v-model.number="price"> <button @click="add">新增button> <table> <tr> <th>编号th> <th>资产名称th> <th>价格th> <th>操作th> tr> <tbody v-if="arr.length>0"> <tr v-for="(item,i) in arr"> <td>{{item.id}}td> <td>{{item.name}}td> <td>{{item.price}}td> <td> <a href="#" @click.prevent="del(i)">删除a> td> tr> tbody> <tbody v-else> <tr> <td colspan="5">暂无数据td> tr> tbody> table> <p>总价格 <span class="red">{{allprice}}span> | 均价 <span class="red">{{avgprice}}span>p> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ flag:false, name:"",//资产名称 price:"", //价格 arr:[ { id:100, name:"外套", price:199, ischeck:false }, { id:101, name:"外套1", price:34, ischeck:false } ] }, computed:{ // 总价来源于所有数据计算而来的结果 allprice(){ //总价格 var sum = 0; this.arr.forEach(item=>{ sum += item.price }) return sum; }, avgprice(){ return (this.allprice/this.arr.length).toFixed(2) } }, methods:{ add(){ //新增 // 判断用户输入是否为空 if(this.name.length===0 || this.price.length===0){ alert("不能为空") return } // 创建一条要添加的数据 var obj = { id:this.arr[this.arr.length-1]?(this.arr[this.arr.length-1].id+1):100, name:this.name, price:this.price, time:new Date(), ischeck:false } // 添加到数组种 this.arr.push(obj) // 表单内容清空 this.name = "" this.price = "" }, del(i){ //删除 if(confirm("确定要删除吗?")){ this.arr.splice(i,1) } } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
完整写法
计算属性也是变量,如果想要直接赋值,需要使用完整写法
语法:
computed:{ "计算属性名":{ set(值){ }, get(){ return '值' } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
来自网友的总结:
1.计算属性有一个get和set平常我们只用他的get是-一个简写
2.get的意思是通过别的数据得到这个计算属性的值
3.set的意思是如果这个计算属性的值发生变化就会触发set方法参数(newValue就是sum改变后的值)
4.set什么时候会用到呢?计算属性用在表单元素中的时候会用到这个set链接
大概就是这样用:<div id="app"> 姓名:<input type="text" v-model="full"/> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{}, computed:{ full:{ // 给full赋值触发set方法 set(val){ console.log(val) }, // 使用full的值触发get方法 // return的值就是计算属性的值 get(){ console.log("get") return "hello" } } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
使用场景:全选反选
- 给每一条数据添加ischeck
- 点击全选,每一条数据的状态和全选的状态一致 (改变全选的状态 )–set方法
- 全选的状态依赖于每一条数据的状态,每一条数据都选中,全选就选中;只要有一条数据不选中,全选就不选中 (get方法)
案例:

<div id="app"> <table> <tr> <th> <input type="checkbox" v-model="allcheck"> 全选 th> <th>编号th> <th>名称th> <th>价格th> <th>操作th> tr> <tr v-for="(item,i) in arr"> <td> <input type="checkbox" v-model="item.ischeck"> td> <td>{{item.id}}td> <td>{{item.name}}td> <td>{{item.price}}td> <td><a href="#">删除a>td> tr> table> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ flag:false, name:"",//资产名称 price:"", //价格 arr:[ { id:100, name:"外套", price:199, ischeck:false }, { id:101, name:"裤子", price:34, ischeck:false }, { id:102, name:"鞋", price:50, ischeck:false } ] }, computed:{ allcheck:{ //全选 set(val){ // val是全选状态 (true/false) this.arr.forEach(item=>{ item.ischeck = val }) }, get(){ // 判断数组中的每一条数据是否全部选中,全选中 全选就选中 // 只要有一条数据不选中 全选就不选中 return this.arr.every(item=>{ return item.ischeck == true }) } } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
侦听器
-
相关阅读:
Lambda 表达式捕获列表
复习单片机:流水灯(内含2种方法(左移操作符法+crol法)+设计思路+原始代码)
【小月电子】FPGA开发板(XLOGIC_V1)系统学习教程-LESSON3
实用TCP协议(2):TCP 参数优化
JAVA-GUI工具的编写-----请求篇
OJ练习第173题——单词接龙 II
“蔚来杯“2022牛客暑期多校训练营1,签到题GADI
C++小练习:字符串分割的高性能实现
【Java】智慧医院绩效考核系统源码
Mybatis——使用步骤
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45025670/article/details/126268754
