-
第二十三章 反射和注解
1. 反射
Java的反射机制是指在Java程序运行的过程中,对于任何一个类,都可以获得这个类的所有属性和方法,对于给定的一个对象, 都能够调用它的任意一个属性和方法,这种动态获取类的内容以及动态调用对象的方法称为反射机制。
反射机制允许在对类未知的情况下,获取类相关信息的方式变得更加多样灵活,调用类中相应方法,是Java增加其灵活性与动态性的一种机制。
2. 反射的常用类
2.1 Class类(类的类型对象)
Class 类的实例表示正在运行的Java程序中的类和接口;
Class 没有公共构造方法,Class对象是在加载类时由Java虚拟机以及通过调用类加载器中的defineClass方法自动构造的。
java代码在执行中有三个阶段:
①源代码(source)阶段;
②字节码(class)阶段,在源代码编译之后;
③运行阶段(runTime)阶段。
2.1.1 获取Class对象的三种方式
①Class.forName("全类名"):把字节码文件加载到内存
- System.out.println("=====通过反射器加载类获取类的类型=====");
- Class clz2 = Class.forName("com.wen.entity.Student");
②类名.class:通过类名的class属性获取
- System.out.println("=====通过类型属性获取类的类型=====");
- Class clz1 = Student.class;
③对象.getClass():通过对象的getClass()获取
- System.out.println("=====通过实例对象的getClass获取类的类型=====");
- Class clz3 = new Student().getClass();
- System.out.println(clz3);
拓展:双亲委派模型
①启动类加载器(Bootstrap ClassLoader),是属于虚拟机自身的一部分,用C++实现,主要负责加载
\lib 目录中或者被 -Xbootclasspath 指定的路径中的且文件名是被虚拟机识别的文件,它等于所有类加载器的父亲; ②扩展类加载器(Extension ClassLoader),是Java实现的,独立于虚拟机,主要负责加载
\lib\ex 目录中或者被 java.ext.dirs 系统变量所指定的路径的类库 ; ③应用程序类加载器(Application ClassLoader),Java实现的,独立于虚拟机,主要负责加载用户路径(classPath)上的类库,如果没有实现自定义的类加载器那么这个就是程序中默认的加载器。
原理: 当一个类加载器收到类加载任务时,会先交给自己的父加载器去完成,因此最终加载任务都会传递到最顶层的BootstrapClassLoader,只有当父类加载器无法完成加载任务时,才会尝试自己来加载。
具体:根据双亲委派模式,在加载类文件的时候,子类加载器首先将加载请求委托给它的父加载器,父加载器会检测自己是否已经加载过类,如果已经加载则加载过程结束,如果没有加载的话则请求继续向上传递直Bootstrap ClassLoader。请求向上委托过程中,如果始终没有检测到该类已经加载,则Bootstrap ClassLoader开始尝试从其对应路劲中加载该类文件,如果失败则由子类加载器继续尝试加载,直至发起加载请求的子加载器为止。
采用双亲委派模式可以保证类型加载的安全性,不管是哪个加载器加载这个类,最终都是委 托给顶层的BootstrapClassLoader来加载的,只有父类无法加载自己才尝试加载,这样就可以保证任何的类加载器最终得到的都是同样一个Object对象。
2.1.2 Class类的常用方法
getName():以String的形式返回此Class对象所表示的实体(类,接口,数组类,基本类型或者void)名称;- System.out.println("=====类名=====");
- Class clz = Class.forName("com.wen.entity.Student");
- System.out.println(clz.getName());
getSimpleName():返回源代码中给出的基础类的简称;System.out.println(clz.getSimpleName());newInstance():创建此Class对象所表示的类的一个新实例
与new()的区别:
弱类型,效率低,只能调用无参构造,返回的是Object类型
- System.out.println("=====创建新实例对象=====");
- Object o = clz.newInstance();
- System.out.println(o);
forName(String className):返回与带有给定字符串名的类或接口相关联的Class对象
getConstructors():返回一个包含某些Constructor对象的数组,是次Class对象所表示的类的所有公共构造方法
- System.out.println("======类中的构造器=======");
- Constructor[] constructors = clz.getConstructors();
- for (Constructor c: constructors) {
- System.out.println(c);
- }
getDeclaredField(String name) :返回一个Field对象,反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的所有成员字段
- System.out.println("====student中的name属性(字段)====");
- Field field = clz.getDeclaredField("name");
- System.out.println(field);
getDeclaredFields() :返回一个包含某些 Field 对象的数组,这些对象反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的所有可访问字段
- System.out.println("=====类的所有可访问字段======");
- Field[] declaredFields = clz.getDeclaredFields();
- for (Field f:declaredFields) {
- System.out.println(f);
- }
getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class... parameterTypes) : 返回一个 Method对象,它反映此 Class 对象所表示的类或接口的指定成员方法;有参要带参- System.out.println("===类中的eat方法===");
- Method eat = clz.getDeclaredMethod("eat", String.class);
- System.out.println(eat);
getDeclaredMethods() :返回一个包含某些 Method 对象的数组,这些对象反映此 Class对象表示的类或接口声明的所有方法,包含私有方法- System.out.println("=====类中的所有方法=====");
- Method[] declaredMethods = clz.getDeclaredMethods();
- for (Method m:declaredMethods) {
- System.out.println(m);
- }
- System.out.println("======类中的public方法=======");
- Method[] methods = clz.getMethods();
- for (Method m: methods) {
- System.out.println(m);
- }
2.2 Method类
Method提供关于类或接口上单独某个方法(以及如何访问该方法)的信息,所反映的方方法可能是类方法或实例方法(包括抽象方法)
getName() :以String形式返回此 Method 对象表示的方法名称;
getParameterTypes():按照声明顺序返回 Class 对象的数组,这些对象描述了此Method 对象所表示的方法的形参类型;getReturnType() :返回一个 Class 对象,该对象描述了此 Method 对象所表示的方法的正式返回类型;invoke(Object obj, Object... args):对带有指定参数的指定对象调用由此 Method 对象表示的基础方法。- Student student = new Student();
- Class aClass = Class.forName("com.wen.entity.Student");
- Method setName = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
- Class[] parameterTypes = setName.getParameterTypes();
- for (Class c:parameterTypes) {
- System.out.println(c);
- }
- System.out.println(setName.getName()+" "+setName.getReturnType());
- //调用方法
- setName.invoke(student,"张三");
- System.out.println(student);
2.3 Field类
Field提供有关类或接口的单个字段的信息,以及对它的动态访问权限。
get(Object obj) :返回指定对象上此 Field 表示的字段的值;set(Object obj, Object value) :将指定对象变量上此Field对象表示的字段设置为指定的新值;getName():返回此 Field 对象表示的字段的名称- Student student1 = new Student("张三","男",20);
- Field name = Student.class.getDeclaredField("name");
- System.out.println(name.getName());
- //设置可以访问私有字段
- name.setAccessible(true);
- System.out.println(name.get(student1));
- name.set(student1,"王五");
- System.out.println(name.get(student1));
3. 通过反射实现对象的创建

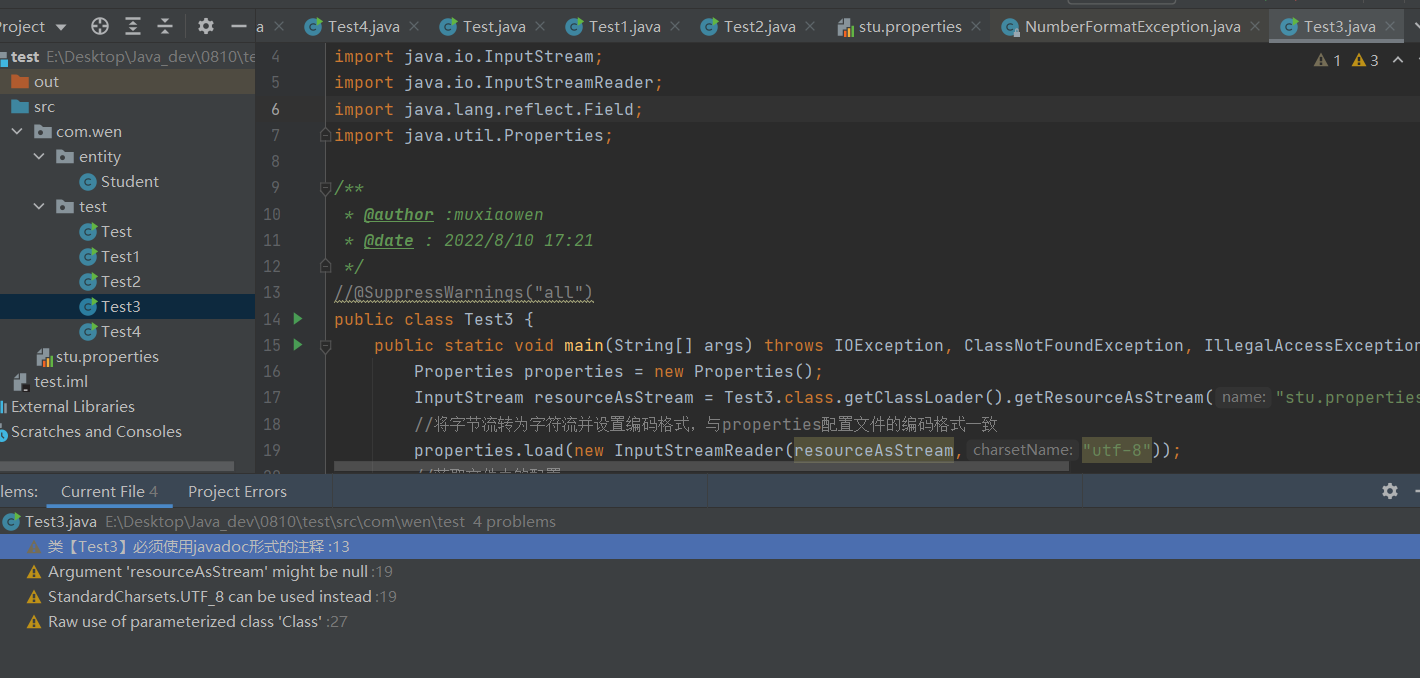
- public class Test3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
- Properties properties = new Properties();
- InputStream resourceAsStream = Test3.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("stu.properties");
- //将字节流转为字符流并设置编码格式,与properties配置文件的编码格式一致
- properties.load(new InputStreamReader(resourceAsStream,"utf-8"));
- //获取文件中的配置
- String cls = properties.getProperty("cls");
- String f1 = properties.getProperty("f1");
- String f2 = properties.getProperty("f2");
- String f3 = properties.getProperty("f3");
- //加载类
- Class c = Class.forName(cls);
- Object o = c.newInstance();
- //获取特定字段类型
- Field name = c.getDeclaredField("name");
- Field sex = c.getDeclaredField("sex");
- Field age = c.getDeclaredField("age");
- name.setAccessible(true);
- sex.setAccessible(true);
- age.setAccessible(true);
- //设置数据
- name.set(o,f1.split(":")[1]);
- sex.set(o,f2.split(":")[1]);
- age.set(o,Integer.valueOf(f3.split(":")[1]));
- System.out.println(o);
- }
- }
4. 注解
注解(Annotation),使用注释的方式加入一些程序信息;
java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口是所有的Annotation都必须实现的接。4.1 系统内建的三个注解
@Override:方法重写的注解
@Deprecated:不赞成使用的注解
@SuppressWarnings:压制安全警告的注解
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Student{" +
- "name='" + name + '\'' +
- ", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
- ", age=" + age +
- '}';
- }
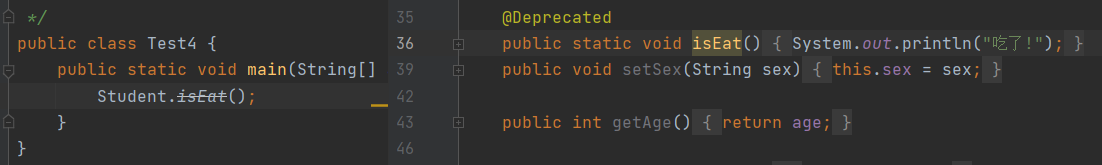
使用@SuppressWarnings之前:
使用之后:

@SuppressWarnings中的关键字 关键字 描述 deprecation 使用了不赞成使用的类或者方法时的警告 unchecked 执行了未检查的转换时的警告 fallthrough 当switch程序块直接通往下种情况而没有break时的警告 path 在类路径,源文件路径等中又不存在的路径时警告 serial 当在可序列化的类上缺少serialVersionUID时的警告 finally 在任何finally子句不能正常完成时的警告 all 关于以上所有情况的警告 4.2 系统元注解
用于标记注解的注解;通过元注解,可以标记我们自定义注解使用目标(类,属性,方法,构造,局部变量...),还可以标记注解的保留阶段(源代码,字节码,运行时)
元注解 说明 @Target 用于指定被修饰的Annotation可用于什么地方 @retention 表示需要在什么级别/阶段保存该注解信息 @Documented 将此注解包含在JavaDoc中 @Inherited 允许子类继承父类中的注解 4.2.1 @Target目标设定
可用的ElementType参数:
类型 说明 ANNOTATION_TYPE 指定该策略的Annotation只能修饰Annotation CONSTRUCTOR 只能修饰构造器 FIELD 只能修饰成员变量 LOCAL_VARIABLE 只能修饰局部变量 METHOD 只能修饰方法定义 PACKAGE 只能修饰包定义 PARAMETER 只能修饰参数 TYPE 可以修饰类,接口或枚举类型 
4.2.2 @Retention和RetentionPolicy
定义一个注解(Annottion)的保存范围:
三个范围:
source,class,runtime
4.3 自定义注解
语法:
public @interface 注解名{
数据类型 变量名();
}
数据类型:只能是8中基本类型,String,基本类型的数组,枚举
注解分类:
①标记注解:没有成员变量的注解类型,这种注解仅仅提供存在与否的标识信息,如:@Override;
②元数据注解:包含成员变量注解类型,这种注解可以接收更多的元数据;
- //自定义的注解
- public @interface MyAnnotation {
- int num() default 100;
- String value();
- String value1();
- String[] values() default {"a","b"};
- }

测试注解是否存在:
- public class Test5 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //判断目标类是否有对应的注解
- //要使得运行时对应注解依然有效,则需要在注解上设置元注解:@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- boolean b = Student.class.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class);
- System.out.println(b);
- }
- }
- @Target(TYPE)
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- public @interface MyAnnotation {
- int num() default 20;
- String value();
- String value1();
- String[] values() default {"a","b"};
- }
4.4 使用反射获取注解,设置对象值
- public class Test6 {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
- Class stuClass = Class.forName("com.wen.entity.Student");
- if(stuClass.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){
- MyAnnotation annotation = stuClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
- System.out.println(annotation.num());
- System.out.println(annotation.value());
- System.out.println(annotation.value1());
- Object o = stuClass.newInstance();
- Field name = stuClass.getDeclaredField("name");
- Field sex = stuClass.getDeclaredField("sex");
- Field age = stuClass.getDeclaredField("age");
- name.setAccessible(true);
- sex.setAccessible(true);
- age.setAccessible(true);
- name.set(o,annotation.value());
- sex.set(o,annotation.value1());
- age.set(o,annotation.num());
- String introduce = (String)stuClass.getDeclaredMethod("toString").invoke(o);
- System.out.println(introduce);
- }
- }
- }
-
相关阅读:
性能优化篇(二) 静态合批步骤与所有注意事项\游戏运行时使用代码启动静态合批
Java8方法引用和Lambda表达式实例源码+笔记分享
kubernetes 初始化
字符函数和字符串函数的使用及模拟实现(上)
Java毕业设计心得体会
力扣经典150题第四十题:同构字符串
【C语言】【结构体的位段】位段的内存分配及注意事项
vue 把echarts封装成一个方法 并且从后端读取数据 +转换数据格式 =动态echarts 联动echarts表
OA项目之待开会议&所有会议
【网络工程师笔记】——ACL
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_71674778/article/details/126267293
