-
linux-自定义进程通信方式
背景
我们知道linux的进程的间通信的组件有管道,消息队列,socket, 信号量,共享内存等
但是我们如果自己实现一套进程间通信的机制的话,要怎么做?了解android 开发的可能会知道,android里面有个binder机制,简单来说,就是一个进程往binder里面写数据,另一个进程从binder里面读出数据。
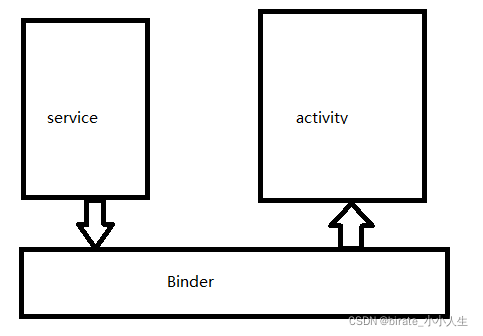
原理
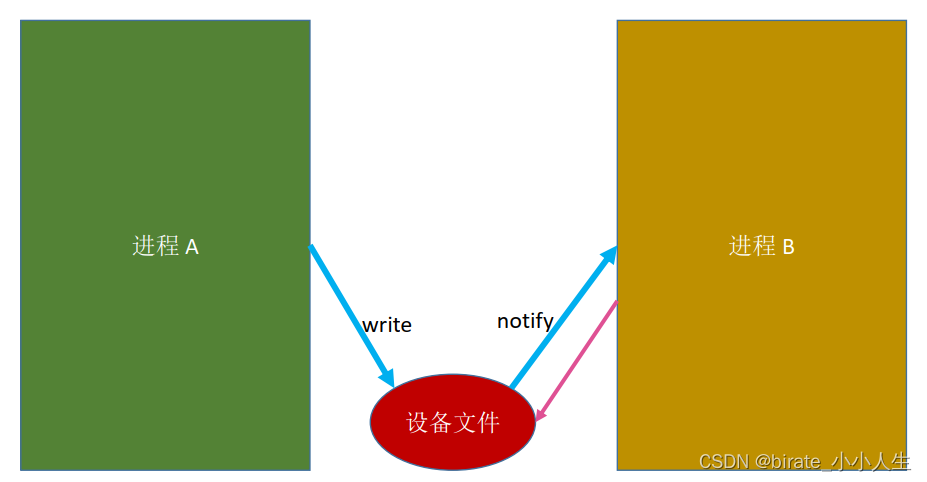
我们首先需要注册一个字符设备文件叫/dev/channel, 同时需要为这个设备编写驱动,此时某个进程A向设备文件写数据,同时如果该设备可读,我们就通知另一个进程B去读该进程。 我们怎么知道该设备是否可读可写呢?使用poll来管理,因为该设备驱动属于一个IO, 打开一个设备就有fd, 有了fd我们就可以使用poll来管理。
如:
发送方:

接收方:
代码:
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #ifndef CHANNEL_MAJOR
- #define CHANNEL_MAJOR 96
- #endif
- #ifndef CHANNEL_NR_DEVS
- #define CHANNEL_NR_DEVS 2
- #endif
- #ifndef CHANNEL_SIZE
- #define CHANNEL_SIZE 4096
- #endif
- #define ENABLE_POLL 1
- struct channel {
- char *data;
- unsigned long size;
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- wait_queue_head_t inq;
- #endif
- };
- static int channel_major = CHANNEL_MAJOR;
- module_param(channel_major, int, S_IRUGO);
- struct channel *channel_devp;
- struct cdev cdev;
- char have_data = 0;
- int channel_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
- struct channel *channel;
- int num = MINOR(inode->i_rdev); //设备读了多少次
- if (num >= CHANNEL_NR_DEVS)
- return -ENODEV;
- channel = &channel_devp[num];
- filp->private_data = channel;
- return 0;
- }
- int channel_release (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
- return 0;
- }
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- unsigned int channel_poll (struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *wait) {
- struct channel *channel = filp->private_data;
- unsigned int mask = 0;
- poll_wait(filp, &channel->inq, wait); // poll 阻塞
- if (have_data)
- mask |= (POLLIN | POLLRDNORM);
- return mask;
- }
- #endif
- int channel_mmap (struct file *filp, struct vm_area_struct *vma) {
- struct channel *channel = filp->private_data;
- vma->vm_flags |= VM_IO;
- vma->vm_flags |= (VM_DONTEXPAND | VM_DONTDUMP);
- if (remap_pfn_range(vma, vma->vm_start, virt_to_phys(channel->data) >> PAGE_SHIFT,
- vma->vm_end-vma->vm_start, vma->vm_page_prot)) {
- return -EAGAIN;
- }
- return 0;
- }
- ssize_t channel_read (struct file *filp, char __user * buffer, size_t size, loff_t *ppos) {
- unsigned long p = *ppos;
- unsigned int count = size;
- int ret = 0;
- struct channel *channel = filp->private_data; // 读私有空间
- if (p >= CHANNEL_SIZE) return 0;
- if (count > CHANNEL_SIZE- p)
- count = CHANNEL_SIZE- p;
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- while (!have_data) {
- if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) return -EAGAIN;
- wait_event_interruptible(channel->inq, have_data);
- }
- #endif
- if (copy_to_user(buffer, (void*)(channel->data + p), count)) { //拷贝到用户空间
- ret = -EFAULT;
- } else {
- ret = strlen(buffer);
- channel->size -= ret;
- printk(KERN_INFO "read %d byte(s) from %ld\n", ret, p);
- }
- have_data = 0;
- return ret;
- }
- ssize_t channel_write (struct file *filp , const char __user * buffer, size_t size, loff_t *ppos) {
- int ret = 0;
- unsigned long p = *ppos;
- unsigned int count = size;
- struct channel *channel = filp->private_data; // 写道文件的私有空间
- if (p >= CHANNEL_SIZE) return 0;
- if (count > CHANNEL_SIZE- p)
- count = CHANNEL_SIZE- p;
- if (copy_from_user(channel->data +p, buffer, count)) { // 从user -> kernel
- return -EFAULT;
- } else {
- *ppos += count;
- ret = count;
- channel->size += count;
- *(channel->data+p + count) = '\0';
- printk(KERN_INFO "written %d byte(s) from %ld\n", count, p);
- }
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- have_data = 1;
- wake_up(&channel->inq);
- #endif
- return ret;
- }
- loff_t channel_llseek (struct file *filp, loff_t offset, int whence) { //偏移
- loff_t newpos;
- switch (whence)
- {
- case 0:
- newpos = offset;
- break;
- case 1:
- newpos = filp->f_pos + offset;
- break;
- case 2:
- newpos = CHANNEL_SIZE - 1 + offset;
- break;
- default:
- return -EINVAL;
- }
- if (newpos < 0 || newpos > CHANNEL_SIZE) return -EINVAL;
- filp->f_pos = newpos;
- return newpos;
- }
- static const struct file_operations channel_fops =
- {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .llseek = channel_llseek,
- .read = channel_read,
- .write = channel_write,
- .open = channel_open,
- .release = channel_release,
- .poll = channel_poll,
- .mmap = channel_mmap,
- };
- static int channel_init(void) {
- int reslut;
- int i;
- dev_t devno = MKDEV(channel_major, 0); // 创建一个主设备号为96,次设备号为0的设备
- if (channel_major) {
- reslut = register_chrdev_region(devno, CHANNEL_NR_DEVS, "channel"); // 注册设备
- } else {
- reslut = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, CHANNEL_NR_DEVS, "channel");
- }
- if (reslut < 0) return reslut;
- cdev_init(&cdev, &channel_fops); //初始化字符设备
- cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
- cdev_add(&cdev, MKDEV(channel_major, 0), CHANNEL_NR_DEVS); //添加到字符设备中
- channel_devp = kmalloc(CHANNEL_NR_DEVS *sizeof(struct channel), GFP_KERNEL); //为 我们的buffer 分配一块空间
- if (!channel_devp) {
- reslut = -ENOMEM;
- goto fail_malloc;
- }
- memset(channel_devp, 0, sizeof(struct channel));
- for (i = 0; i < CHANNEL_NR_DEVS; i++) {
- channel_devp[i].size = CHANNEL_SIZE;
- channel_devp[i].data = kmalloc(CHANNEL_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
- memset(channel_devp[i].data, 0, CHANNEL_SIZE);
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- init_waitqueue_head(&(channel_devp[i].inq));
- #endif
- }
- printk(KERN_INFO "ntychannel_init");
- return 0;
- fail_malloc:
- unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);
- return reslut;
- }
- static void channel_exit(void) {
- printk(KERN_INFO "channel_exit");
- cdev_del(&cdev);
- int i = 0;
- for (i = 0; i < CHANNEL_NR_DEVS; i++) {
- kfree(channel_devp[i].data);
- }
- kfree(channel_devp);
- unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(channel_major, 0), 2);
- }
- MODULE_AUTHOR("birate");
- MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
- module_init(channel_init); // 设备初始化
- module_exit(channel_exit); //设备退出
编写Makefile文件:
- obj-m += channel.o
- KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
- all:
- make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
- clean:
- make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) clean
使用 make 命令。编译出我们需要的channel.ko文件。
使用 insmod channel.ko, 向kernel中插入 我们的module
使用mknod /dev/channel c 96 0, 创建一个/dev/channel 的字符设备,主设备号为96,次设备号为0;
测试程序:- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #include
- #define BUFFER_LENGTH 128
- int main () {
- int fd = open("/dev/channel", O_RDWR);
- if (fd < 0) {
- printf("open failed: errno : %s\n", strerror(errno));
- return -1;
- }
- char *buffer = (char *)malloc(BUFFER_LENGTH);
- memset(buffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
- char *start = mmap(NULL, BUFFER_LENGTH, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
- fd_set rds;
- FD_ZERO(&rds);
- FD_SET(fd, &rds);
- while(1) {
- int ret = select(fd+1, &rds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
- if (ret < 0) {
- printf("select error\n");
- exit(1);
- }
- if (FD_ISSET(fd, &rds)) {
- #if 0
- strcpy(buffer, start);
- printf("channel: %s\n", buffer);
- #else
- read(fd, buffer, BUFFER_LENGTH);
- printf("channel: %s\n", buffer);
- #endif
- }
- }
- munmap(start, BUFFER_LENGTH);
- free(buffer);
- close(fd);
- return 0;
- }
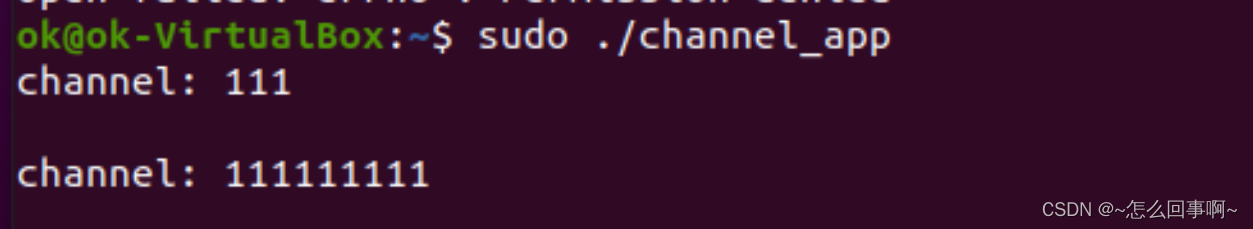
gcc -o channel_app channel_app.c , 编译出可执行文件,在一个进程中执行channel_app, 另一个进程使用echo " " > /dev/channel 去向设备文件中写就可以
系统调用 system_call
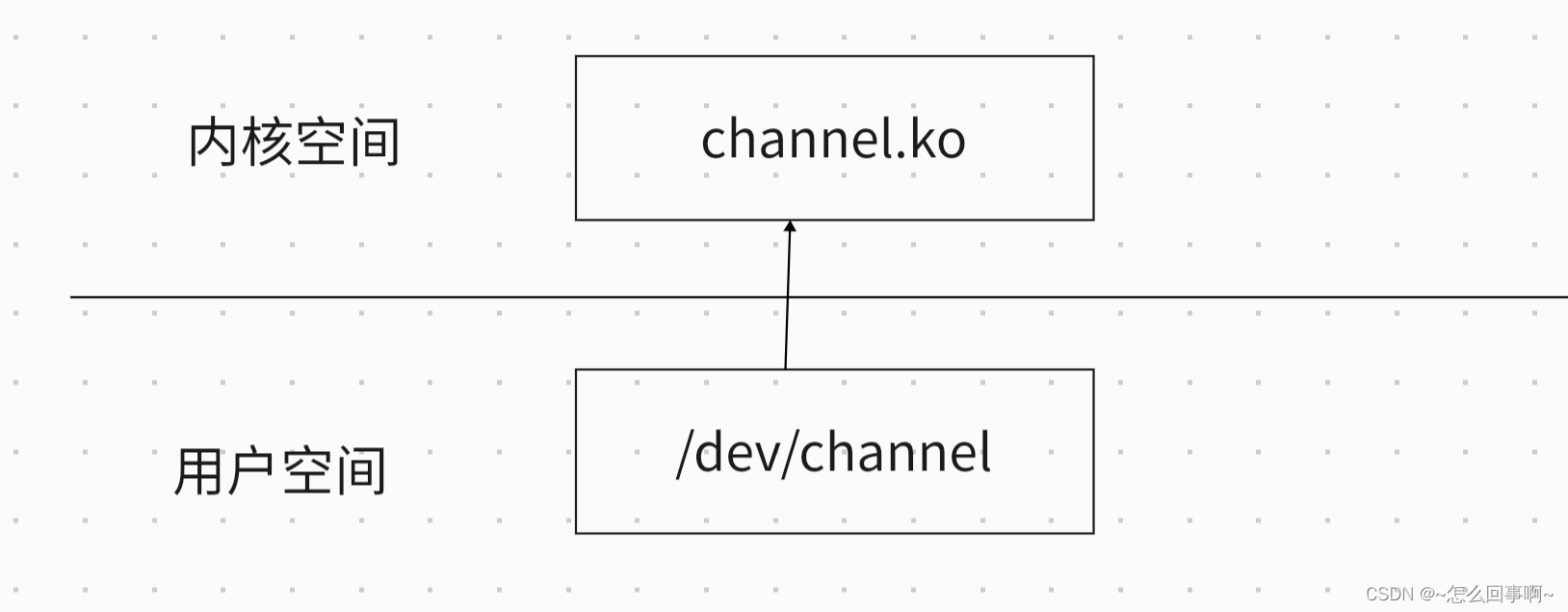
用户空间的 :
- static const struct file_operations channel_fops =
- {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .llseek = channel_llseek,
- .read = channel_read,
- .write = channel_write,
- .open = channel_open,
- .release = channel_release,
- .poll = channel_poll,
- .mmap = channel_mmap,
- };
read,write等等是如何调用到内核空间的呢?
Oldlinux.org -- Linux plinux - Early Linux Kernel Analysis and Comments
linux老版本下载:Index of /Linux.old/
代码以0.11版本为例
系统调用是一个软中断,中断号是0x80,它是上层应用程序与Linux系统内核进行交互通信的唯一接口。
如:tools\build.c
调用open :
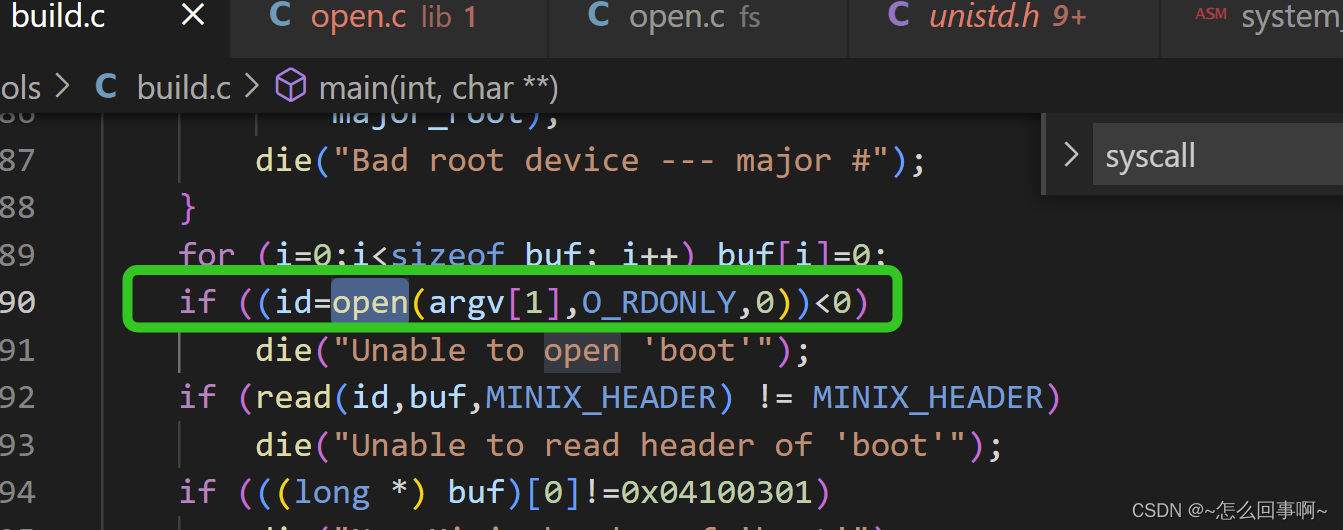
open的源码路径lib\open.c
- /*
- * linux/lib/open.c
- *
- * (C) 1991 Linus Torvalds
- */
- #define __LIBRARY__
- #include
- #include
- int open(const char * filename, int flag, ...)
- {
- register int res;
- va_list arg;
- va_start(arg,flag);
- __asm__("int $0x80"
- :"=a" (res)
- :"0" (__NR_open),"b" (filename),"c" (flag),
- "d" (va_arg(arg,int)));
- if (res>=0)
- return res;
- errno = -res;
- return -1;
- }
在汇编语言中调用0x80 ....进入系统调用
在include\unistd.h中定义了
- #define __NR_setup 0 /* used only by init, to get system going */
- #define __NR_exit 1
- #define __NR_fork 2
- #define __NR_read 3
- #define __NR_write 4
- #define __NR_open 5 // open是5
- ......
- _syscall0(type,name) 其中 0 表示参数个数,type 表示返回值name表示函数名称
- #define _syscall0(type,name) \
- type name(void) \
- { \
- long __res; \
- __asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
- : "=a" (__res) \
- : "0" (__NR_##name)); \
- if (__res >= 0) \
- return (type) __res; \
- errno = -__res; \
- return -1; \
- }
- #define _syscall1(type,name,atype,a) \
- type name(atype a) \
- { \
- long __res; \
- __asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
- : "=a" (__res) \
- : "0" (__NR_##name),"b" ((long)(a))); \
- if (__res >= 0) \
- return (type) __res; \
- errno = -__res; \
- return -1; \
- }
- #define _syscall2(type,name,atype,a,btype,b) \
- type name(atype a,btype b) \
- { \
- long __res; \
- __asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
- : "=a" (__res) \
- : "0" (__NR_##name),"b" ((long)(a)),"c" ((long)(b))); \
- if (__res >= 0) \
- return (type) __res; \
- errno = -__res; \
- return -1; \
- }
- #define _syscall3(type,name,atype,a,btype,b,ctype,c) \
- type name(atype a,btype b,ctype c) \
- { \
- long __res; \
- __asm__ volatile ("int $0x80" \
- : "=a" (__res) \
- : "0" (__NR_##name),"b" ((long)(a)),"c" ((long)(b)),"d" ((long)(c))); \
- if (__res>=0) \
- return (type) __res; \
- errno=-__res; \
- return -1; \
- }
kernel\system_call.s
- _system_call:
- cmpl $nr_system_calls-1,%eax
- ja bad_sys_call
- push %ds
- push %es
- push %fs
- pushl %edx
- pushl %ecx # push %ebx,%ecx,%edx as parameters
- pushl %ebx # to the system call
- movl $0x10,%edx # set up ds,es to kernel space
- mov %dx,%ds
- mov %dx,%es
- movl $0x17,%edx # fs points to local data space
- mov %dx,%fs
- call _sys_call_table(,%eax,4)
- pushl %eax
- movl _current,%eax
- cmpl $0,state(%eax) # state
- jne reschedule
- cmpl $0,counter(%eax) # counter
- je reschedule
调用了系统调用表 call _sys_call_table(,%eax,4),%eax表示下标
include\linux\sys.h
- fn_ptr sys_call_table[] = { sys_setup, sys_exit, sys_fork, sys_read,
- sys_write, sys_open, sys_close, sys_waitpid, sys_creat, sys_link,
- sys_unlink, sys_execve, sys_chdir, sys_time, sys_mknod, sys_chmod,
- sys_chown, sys_break, sys_stat, sys_lseek, sys_getpid, sys_mount,
- sys_umount, sys_setuid, sys_getuid, sys_stime, sys_ptrace, sys_alarm,
- sys_fstat, sys_pause, sys_utime, sys_stty, sys_gtty, sys_access,
- sys_nice, sys_ftime, sys_sync, sys_kill, sys_rename, sys_mkdir,
- sys_rmdir, sys_dup, sys_pipe, sys_times, sys_prof, sys_brk, sys_setgid,
- sys_getgid, sys_signal, sys_geteuid, sys_getegid, sys_acct, sys_phys,
- sys_lock, sys_ioctl, sys_fcntl, sys_mpx, sys_setpgid, sys_ulimit,
- sys_uname, sys_umask, sys_chroot, sys_ustat, sys_dup2, sys_getppid,
- sys_getpgrp, sys_setsid, sys_sigaction, sys_sgetmask, sys_ssetmask,
- sys_setreuid,sys_setregid };
可以看出系统调用表示一个函数数组,在include\unistd.h 定义了#define __NR_open 5,这里对应函数数组的下标5 :sys_open,调用内核函数:
fs\open.c
- int sys_open(const char * filename,int flag,int mode)
- {
- struct m_inode * inode;
- struct file * f;
- int i,fd;
- mode &= 0777 & ~current->umask;
- for(fd=0 ; fdif (!current->filp[fd])break;if (fd>=NR_OPEN)return -EINVAL;current->close_on_exec &= ~(1<f=0+file_table;for (i=0 ; iif (!f->f_count) break;if (i>=NR_FILE)return -EINVAL;(current->filp[fd]=f)->f_count++;if ((i=open_namei(filename,flag,mode,&inode))<0) {current->filp[fd]=NULL;f->f_count=0;return i;}/* ttys are somewhat special (ttyxx major==4, tty major==5) */if (S_ISCHR(inode->i_mode))if (MAJOR(inode->i_zone[0])==4) {if (current->leader && current->tty<0) {current->tty = MINOR(inode->i_zone[0]);tty_table[current->tty].pgrp = current->pgrp;}} else if (MAJOR(inode->i_zone[0])==5)if (current->tty<0) {iput(inode);current->filp[fd]=NULL;f->f_count=0;return -EPERM;}/* Likewise with block-devices: check for floppy_change */if (S_ISBLK(inode->i_mode))check_disk_change(inode->i_zone[0]);f->f_mode = inode->i_mode;f->f_flags = flag;f->f_count = 1;f->f_inode = inode;f->f_pos = 0;return (fd);}
那么 :
- static const struct file_operations channel_fops =
- {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .llseek = channel_llseek,
- .read = channel_read,
- .write = channel_write,
- .open = channel_open,
- .release = channel_release,
- .poll = channel_poll,
- .mmap = channel_mmap,
- };
int channel_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
inode:文件具体数据 file:路径属性
是通过系统调用的
int sys_open(const char * filename,int flag,int mode) 完成的
主次设备号
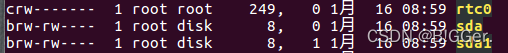
/dev目录下执行ls -l
设备文件项的最后修改日期前的用逗号分割的两个数,对设备文件来说就是相应的主设备号和次设备号。
第一个字符c表示字符设备,b表示块设备
主设备号标识设备对应的驱动程序,次设备号由内核使用,用于正确确定设备文件所指的设备。依赖于驱动程序的编写方式,我们可以通过次设备号获得一个指向内核设备的直接指针,也可将次设备号当作设备本地数组的索引
在代码中:
- static int channel_init(void) {
- int reslut;
- int i;
- dev_t devno = MKDEV(channel_major, 0); // 创建一个主设备号为96,次设备号为0的设备
- if (channel_major) {
- reslut = register_chrdev_region(devno, CHANNEL_NR_DEVS, "channel"); // 注册设备
- } else {
- reslut = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, CHANNEL_NR_DEVS, "channel");
- }
- if (reslut < 0) return reslut;
- cdev_init(&cdev, &channel_fops); //初始化字符设备
- cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
- cdev_add(&cdev, MKDEV(channel_major, 0), CHANNEL_NR_DEVS); //添加到字符设备中
- channel_devp = kmalloc(CHANNEL_NR_DEVS *sizeof(struct channel), GFP_KERNEL); //为 我们的buffer 分配一块空间
- if (!channel_devp) {
- reslut = -ENOMEM;
- goto fail_malloc;
- }
- memset(channel_devp, 0, sizeof(struct channel));
- for (i = 0; i < CHANNEL_NR_DEVS; i++) {
- channel_devp[i].size = CHANNEL_SIZE;
- channel_devp[i].data = kmalloc(CHANNEL_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
- memset(channel_devp[i].data, 0, CHANNEL_SIZE);
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- init_waitqueue_head(&(channel_devp[i].inq));
- #endif
- }
- printk(KERN_INFO "ntychannel_init");
- return 0;
- fail_malloc:
- unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);
- return reslut;
- }
在调用过:
- sudo insmod channel.ko
- sudo mknod /dev/channel c 96 0
- cd /dev
- ls -l | grep channel

可以看到注册的设备
sudo insmod channel.ko 实质是执行channel_init 函数
1 向内核申请注册一个设备:主次设备号 register_chrdev_region
2 初始化一个字符设备 cdev_init
3 加入到内核 cdev_add
4 初始化private_date
open
将file 和private_date关联起来
- int channel_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) {
- struct channel *channel;
- int num = MINOR(inode->i_rdev); //设备读了多少次
- if (num >= CHANNEL_NR_DEVS)
- return -ENODEV;
- channel = &channel_devp[num];
- filp->private_data = channel;
- return 0;
- }
rmmod与模块退出
- static void channel_exit(void) {
- printk(KERN_INFO "channel_exit");
- cdev_del(&cdev);
- int i = 0;
- for (i = 0; i < CHANNEL_NR_DEVS; i++) {
- kfree(channel_devp[i].data);
- }
- kfree(channel_devp);
- unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(channel_major, 0), 2);
- }
write
通过:
root@ok-VirtualBox:/home/ok/channel# echo "111111111" > /dev/channel查看日志:dmesg
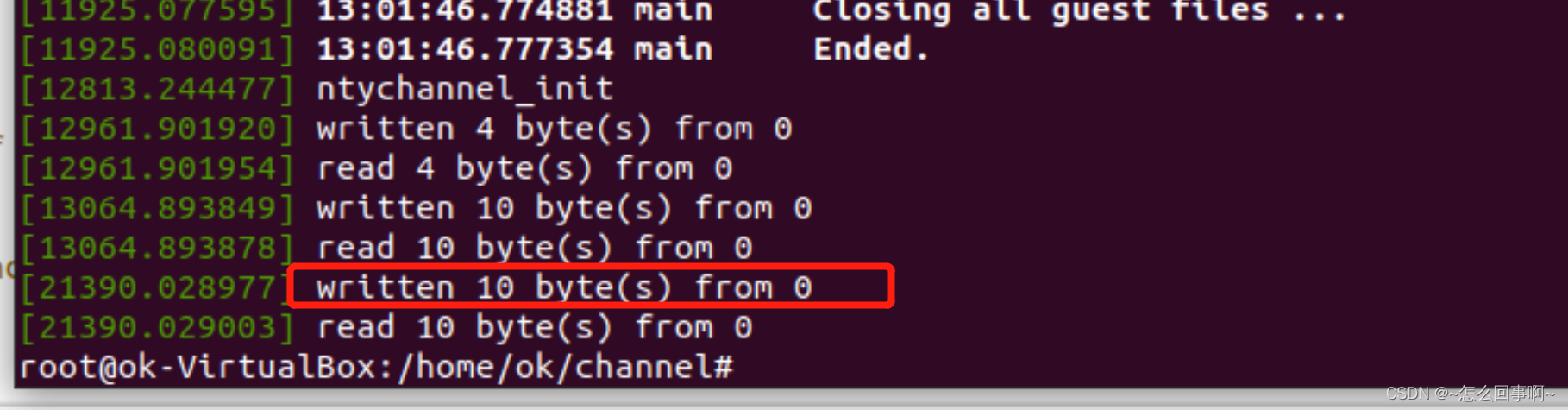
可以看到写入数据的日志
从用户空间的buffer ->copy to -> channel.date
- //filp 文件属性
- //buffer 用户写入数据buffer 如:123\0
- //size 数据大小
- //ppos 偏移量
- ssize_t channel_write (struct file *filp , const char __user * buffer, size_t size, loff_t *ppos) {
- int ret = 0;
- unsigned long p = *ppos;
- unsigned int count = size;
- struct channel *channel = filp->private_data; // 写到文件的私有空间
- if (p >= CHANNEL_SIZE) return 0;
- //判断容量是否可以放下所有Buffer数据,防止数组越界
- if (count > CHANNEL_SIZE- p)
- count = CHANNEL_SIZE- p;
- //从用户空间的数据 copy to 内核空间, 返回0表示成功 ,执行else
- if (copy_from_user(channel->data +p, buffer, count)) { // 从user -> kernel
- return -EFAULT;
- } else {
- //修改相关标志位
- *ppos += count;
- ret = count;
- channel->size += count;
- *(channel->data+p + count) = '\0';
- printk(KERN_INFO "written %d byte(s) from %ld\n", count, p);
- }
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- have_data = 1;
- wake_up(&channel->inq);
- #endif
- return ret;
- }
1 检查参数
2 拷贝数据
3 上下文参数调整
read
- ssize_t channel_read (struct file *filp, char __user * buffer, size_t size, loff_t *ppos) {
- unsigned long p = *ppos;
- unsigned int count = size;
- int ret = 0;
- struct channel *channel = filp->private_data; // 读私有空间
- if (p >= CHANNEL_SIZE) return 0;
- if (count > CHANNEL_SIZE- p)
- count = CHANNEL_SIZE- p;
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- while (!have_data) {
- if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) return -EAGAIN;
- wait_event_interruptible(channel->inq, have_data);
- }
- #endif
- if (copy_to_user(buffer, (void*)(channel->data + p), count)) { //拷贝到用户空间
- ret = -EFAULT;
- } else {
- ret = strlen(buffer);
- channel->size -= ret;
- printk(KERN_INFO "read %d byte(s) from %ld\n", ret, p);
- }
- have_data = 0;
- return ret;
- }
poll
在应用层使用select 时,内核层会调用poll
- #if ENABLE_POLL
- unsigned int channel_poll (struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *wait) {
- struct channel *channel = filp->private_data;
- unsigned int mask = 0;
- poll_wait(filp, &channel->inq, wait); // poll 阻塞
- if (have_data)
- mask |= (POLLIN | POLLRDNORM);
- return mask;
- }
- #endif
- 相关阅读:
【Python3】【力扣题】338. 比特位计数
飞天使-学以致用-devops知识点4-SpringBoot项目CICD实现(实验失败,了解大概流程)
Hadoop-15-Hive 元数据管理与存储 Metadata 内嵌模式 本地模式 远程模式 集群规划配置 启动服务 3节点云服务器实测
第六章 Scala if..else与循环
search——id映射
Javascript笔记
L1-018 大笨钟
windows nodejs 15.0.0下载安装
sql调优之:字符集不一致导致的索引失效案例
Mendix与Java组件的完美结合实践
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/LIJIWEI0611/article/details/126110890


