-
共享模型之无锁 - 08
CAS (compareAndSet 或者 compareAndSwap) 比较并且设置
private AtomicInteger account = new AtomicInteger(30); private void cas (int amount){ while (true) { int prev = account.get(); int next = prev - amount; if(account.compareAndSet(prev,next)){ break; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
CAS原理图
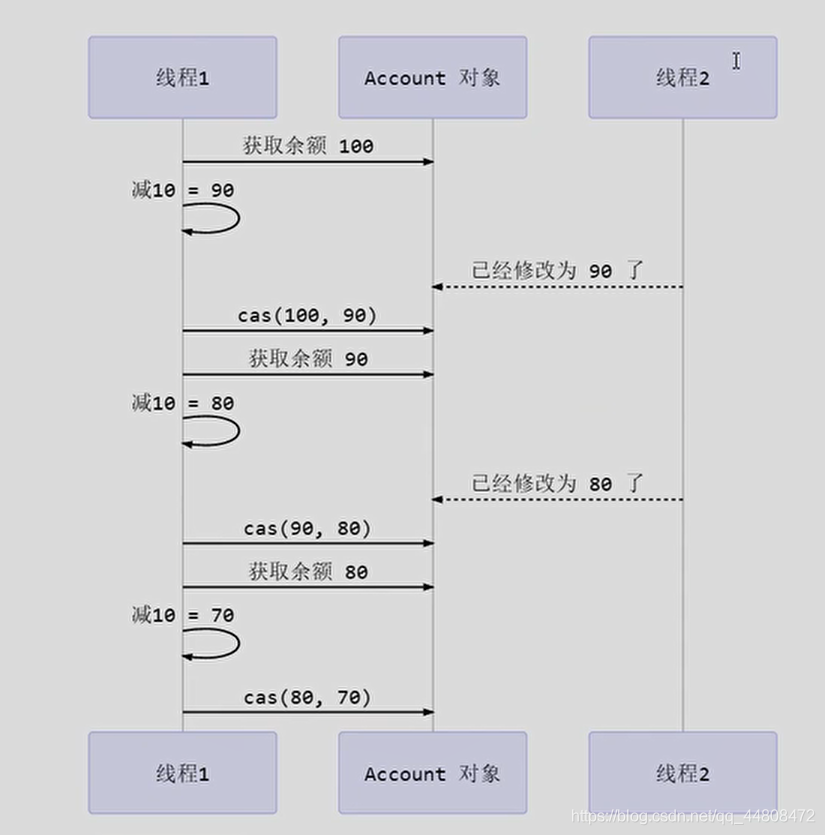
其实CAS底层是 lock cmpxchg 指令 (X86架构),在单核CPU和多核CPU下都能保证【比较-交换】的原子性。public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update); }- 1
- 2
- 3
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object o, long offset, int expected, int x);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
CAS 与 volatile
获取共享变量时,为了保证该变量的可见性,需要是要 volatile 修饰。
volatile 可以用来修饰成员变量,静态变量,它可以避免线程从自己的工作缓存中查找变量的值,必须要到主存中获取他的值,线程操作volatile 变量都是直接操作主存,即一个线程对vlolatile变量的修改,对两一个线程可见。
- vlolatle 仅仅保证了共享变量的可见性,让其他线程能够看到子u心智,但不能解决原型性问题
CAS必须接注 volatile 才能读取到共享内存的最新值来实现【比较并交换】的效果。
为什么无锁的效果高
- 无锁的情况下,及时重试失败,线程始终在运行,没有停下,而 sychronized 会让线程在没有获取锁的时候,发生上下文切换,净土阻塞发生上下文切换,需要重新唤醒,代价比较大
- 无锁情况下,线程保存运行,需要额外CPU的支持 ,虽然不会进入阻塞,但是由于没有分到时间片,仍然会进图可运行状态,还是会导致上下文切换。线程数少于 CPU 核心数建议使用 CAS
CAS 特点
适合线程数较少,多核CPU的场景下
- CAS时基于乐观锁的思想: 乐观的估计不怕线程修改共享变量
- sychronized 时基于悲观锁的思想 : 最悲观的估计,时刻都认为会修改共享变量
- CAS体现的时无锁并发,无阻塞并发
- 因为没有使用synchronized ,所以线程不会会陷入阻塞
- 如果竞争激烈,重试可能频繁发生,反而效率会受影响
CAS 原理实现的工具类
J.U.C - java.util.concurrent
原子整数
- AtomicBoolean
- AtomicInteger
- AtomicLong
AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); // 获取并自增 count = 0 返回 0 结果 1 类似与 i++ System.out.println(count.getAndIncrement()); // 自增并获取 count = 1 返回 2 结果 2 类似与 ++i System.out.println(count.incrementAndGet()); //获取并自减 count = 2 返回 2 结果 1 类似于 i-- System.out.println(count.getAndDecrement()); //自减并获取 count = 1 返回 0 结果 0 类似于 i-- System.out.println(count.decrementAndGet()); //获取并加值 count = 0 返回 0 结果 5 System.out.println(count.getAndAdd(5)); //加值并获取 count = 5 返回 10 结果 10 System.out.println(count.addAndGet(5)); // 更新并获取 count = 10 返回50 结果 50 System.out.println(count.updateAndGet(value -> {return value * 5;})); // 获取并更新 count = 50 返回50 结果 10 System.out.println(count.getAndUpdate(value -> {return value / 5;}));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
原子引用
- AtomicReference 不关心是否修改引用的对象
- AtomicMarkableReference 关心是否修改过引用的对象
- AtomicStampedReference 关心修改过几次引用的对象
class DecimalAccountSafeCas implements DecimalAccount { AtomicReference<BigDecimal> ref; public DecimalAccountSafeCas(BigDecimal balance) { ref = new AtomicReference<>(balance); } public BigDecimal getBalance() { return ref.get(); } @Override public void withdraw(BigDecimal amount) { while (true) { //自旋 BigDecimal prev = ref.get(); BigDecimal next = prev.subtract(amount); if (ref.compareAndSet(prev, next)) { // 使用 CAS 比较并替换 break; } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
ABA问题
ABA 也就是说 线程感知不到其他线程对变量的修改。
// 主线程仅能判断出共享变量的值与最初值 A 是否相同,不能感知到这种从 A 改为 B 又 改回 A 的情况 static AtomicReference<String> ref = new AtomicReference<>("A"); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { log.debug("main start..."); // 获取值 A // 这个共享变量被它线程修改过? String prev = ref.get(); other(); Thread.sleep(2); // 尝试改为 C log.debug("change A->C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C")); } private static void other() throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change A->B {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "B")); }, "t1").start(); Thread.sleep(1); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change B->A {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.get(), "A")); }, "t2").start(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
20:08:13 [main] c.test - main start... 20:08:13 [t1] c.test - change A->B true 20:08:13 [t2] c.test - change B->A true 20:08:13 [main] c.test - change A->C true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
解决方案
CAS 不仅比较值,而且还比较版本号 AtomicStampedReference 增加了版本号的属性来记录引用被更改的版本,以至于知道引用是否被更改过,解决aba的问题static AtomicStampedReference<String> ref = new AtomicStampedReference<>("A", 0); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { log.debug("main start..."); String prev = ref.getReference(); //获取值 int stamp = ref.getStamp(); // 获取版本号 log.debug("版本 {}", stamp); // 如果中间有其它线程干扰,发生了 ABA 现象 other(); Thread.sleep(2); // 尝试改为 C log.debug("change A->C {}", ref.compareAndSet(prev, "C", stamp, stamp + 1)); } private static void other() throws InterruptedException { new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change A->B {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "B", ref.getStamp(), ref.getStamp() + 1)); log.debug("更新版本为 {}", ref.getStamp()); }, "t1").start(); Thread.sleep(1); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("change B->A {}", ref.compareAndSet(ref.getReference(), "A", ref.getStamp(), ref.getStamp() + 1)); log.debug("更新版本为 {}", ref.getStamp()); }, "t2").start(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
AtomicMarkableReference 维护了一个 mark 标记 用于判断引用的状态
public class TestABAAtomicMarkableReference { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { GarbageBag bag = new GarbageBag("装满了垃圾"); // 参数2 mark 可以看作一个标记,表示垃圾袋满了 AtomicMarkableReference<GarbageBag> ref = new AtomicMarkableReference<>(bag, true); log.debug("主线程 start..."); GarbageBag prev = ref.getReference(); log.debug(prev.toString()); new Thread(() -> { log.debug("打扫卫生的线程 start..."); bag.setDesc("空垃圾袋"); while (!ref.compareAndSet(bag, bag, true, false)) {} log.debug(bag.toString()); }).start(); Thread.sleep(1000); log.debug("主线程想换一只新垃圾袋?"); boolean success = ref.compareAndSet(prev, new GarbageBag("空垃圾袋"), true, false); log.debug("换了么?" + success); log.debug(ref.getReference().toString()); } } class GarbageBag { String desc; public GarbageBag(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } @Override public String toString() { return super.toString() + " " + desc; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
原子数组
- AtomicIntegerArray
- AtomicLongArray
- AtomicReferenceArray
/** 参数1,提供数组、可以是线程不安全数组或线程安全数组 参数2,获取数组长度的方法 参数3,自增方法,回传 array, index 参数4,打印数组的方法 */ // supplier 提供者 无中生有 ()->结果 // function 函数 一个参数一个结果 (参数)->结果 , BiFunction (参数1,参数2)->结果 // consumer 消费者 一个参数没结果 (参数)->void, BiConsumer (参数1,参数2)-> private static <T> void demo( Supplier<T> arraySupplier, Function<T, Integer> lengthFun, BiConsumer<T, Integer> putConsumer, Consumer<T> printConsumer ) { List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>(); T array = arraySupplier.get(); int length = lengthFun.apply(array); for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { // 每个线程对数组作 10000 次操作 ts.add(new Thread(() -> { for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) { putConsumer.accept(array, j%length); } })); } ts.forEach(t -> t.start()); // 启动所有线程 ts.forEach(t -> { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); // 等所有线程结束 printConsumer.accept(array); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 线程不安全数组
demo( ()->new int[10], (array)->array.length, (array, index) -> array[index]++, array-> System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)) ); [9870, 9862, 9774, 9697, 9683, 9678, 9679, 9668, 9680, 9698]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 安全的数组
demo( ()-> new AtomicIntegerArray(10), (array) -> array.length(), (array, index) -> array.getAndIncrement(index), array -> System.out.println(array) ); [10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000, 10000]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
字段更新器
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater // 域 字段
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater
利用字段更新器,可以针对对象的某个域(Field)进行原子操作,只能配合 volatile 修饰的字段使用,否则会出现异常
private volatile int field; public static void main(String[] args) { AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater fieldUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Test5.class, "field"); // 初始化字段更新器 Test5 test5 = new Test5(); fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(test5, 0, 10); // 比较并替换 field 的值 // 修改成功 field = 10 System.out.println(test5.field); // 修改成功 field = 20 fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(test5, 10, 20); System.out.println(test5.field); // 修改失败 field = 20 fieldUpdater.compareAndSet(test5, 10, 30); System.out.println(test5.field); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
字段累加器
字段累加器比其他原子类操作性能要高
- LongAdder()
- DoubleAdder
性能提升的原因很简单,就是在有竞争时,设置多个累加单元,Therad-0 累加 Cell[0],而 Thread-1 累加Cell[1]… 最后将结果汇总。这样它们在累加时操作的不同的 Cell 变量,因此减少了 CAS 重试失败,从而提高性能。
LongAdder 类有几个关键域
// 累加单元数组, 懒惰初始化 transient volatile Cell[] cells; // 基础值, 如果没有竞争, 则用 cas 累加这个域 transient volatile long base; // 在 cells 创建或扩容时, 置为 1, 表示加锁 transient volatile int cellsBusy;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
伪共享
@sun.misc.Contended // 竞争注解 防止缓存行伪共享 static final class Cell { volatile long value; Cell(long x) { value = x; } final boolean cas(long cmp, long val) { // cmp 旧值 val 新值 return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapLong(this, valueOffset, cmp, val); // 用cas的方式进行累加 } // Unsafe mechanics private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; private static final long valueOffset; static { try { UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class<?> ak = Cell.class; valueOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (ak.getDeclaredField("value")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
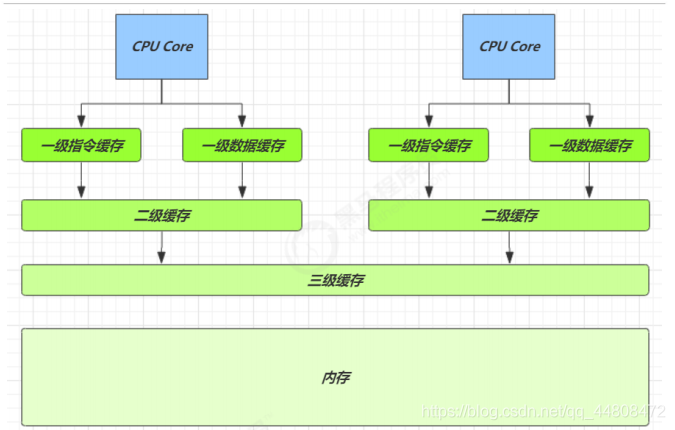
cpu内存结构
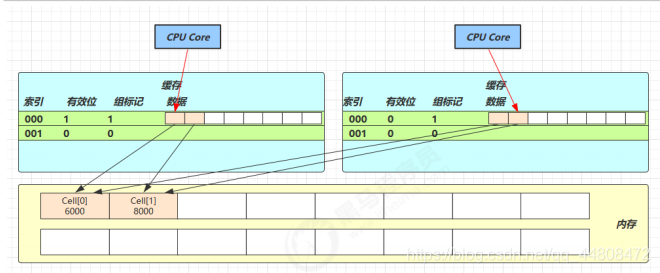
因为 Cell 是数组形式,在内存中是连续存储的,一个 Cell 为 24 字节(16 字节的对象头和 8 字节的 value),因此缓存行可以存下 2 个的 Cell 对象。这样问题来了:
Core-0 要修改 Cell[0]
Core-1 要修改 Cell[1]
无论谁修改成功,都会导致对方 Core 的缓存行失效,比如 Core-0 中 Cell[0]=6000, Cell[1]=8000 要累加Cell[0]=6001, Cell[1]=8000 ,这时会让 Core-1 的缓存行失效@sun.misc.Contended 用来解决这个问题,它的原理是在使用此注解的对象或字段的前后各增加 128 字节大小的
padding,从而让 CPU 将对象预读至缓存时占用不同的缓存行,这样,不会造成对方缓存行的失效
在这里插入图片描述这里做个标记以后再深入
Unsafe
Unsafe 对象提供了非常底层的,操作内存、线程的方法,Unsafe 是单例 对象不能直接调用,只能通过反射获得
Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe"); theUnsafe.setAccessible(true); Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe)theUnsafe.get(null);- 1
- 2
- 3
这里做个标记以后再深入
不可变类
日期转换问题
// SimpleDateFormat 是可变类 有线程安全问题 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(() -> { try { log.debug("{}", sdf.parse("1951-04-21")); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("{}", e); } }).start(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
解决方案 - 同步锁
// 具有性能问题 SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { new Thread(() -> { synchronized (sdf) { try { log.debug("{}", sdf.parse("1951-04-21")); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("{}", e); } } }).start(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
解决方案 - 不可变类
DateTimeFormatter 是不可变类
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd"); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(() -> { LocalDate date = dtf.parse("2018-10-01", LocalDate::from); log.debug("{}", date); }).start(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
不可变设计
final 的使用
- 属性用 final 修饰保证了该属性是只读的, 不能修改
- 类用 final 修饰保证了该类中的方法不能被覆盖,防止子类无意间破坏不可变性
保护性拷贝
不在原有对象上操作永远返回新对象且对象不可见
-
相关阅读:
力扣(83.643)补8.29
Linux学习笔记(7)
MongoDB(三)之SpringBoot整合
对小程序开发,掌握GUI编程和数据库开发
线程练习题
Golang — template
Rust借用几种变化情况分析
羽夏逆向指引——注入
QT性能分析调优
Python 使用类的属性和方法
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44808472/article/details/119057496
