-
[持续更新中...] Vue核心
1. Vue核心(一)
1.1 模板语法
-
插值语法
功能:用于解析标签体的内容
写法:{{xxx}}, xxx是
js表达式,且可以直接读取到data中的所有属性 -
指令语法:
功能:用于解析标签,(包括标签属性,标签体内容,绑定事件…)
形式都是
v-???
v-band
<a v-bind:href="url">baidua>- 1
v-band相当于把后面引号内的属性当作js表达式,可以简写为:1.2 数据绑定
Vue中有2中数据绑定的方式:
- 单向绑定
v-bind: 数据只能从data流向页面 - 双向绑定
v-model: 数据不仅能从data流向页面,还可以从页面流向data- 双向绑定一般都应用在表单类元素上
v-model:value可以简写为v-model
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>初识Vuetitle> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <div> 单向数据绑定:<input type="text" :value="data1"> div> <div> 双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model:value="data1"> div> div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.config.productionTip = false // 阻止 vue 启动时生成生产提示 const x = new Vue({ el: '#root', // el 用于指定当前 Vue 实例为哪个容器服务,值通常为css选择器字符串 data: { // data中用于存储数据,数据供el所指定的容器去使用,值我们暂定先写成一个对象 data1: '中国', } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
v-model只能用在表单,输入类元素中简写
<div> 单向数据绑定:<input type="text" :value="data1"> div> <div> 双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model="data1"> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.3 el 与 data 两种写法
el
Vue.config.productionTip = false // 阻止 vue 启动时生成生产提示 const x = new Vue({ // el: '#root', // 方式一 data: { // data中用于存储数据,数据供el所指定的容器去使用,值我们暂定先写成一个对象 data1: '中国', } }) setTimeout(() => { x.$mount('#root') // 方式二 }, 1000);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
data
对象式
data:{ data1:'xxxx' }- 1
- 2
- 3
函数式
data:function(){ return{ data1:'xfdsaf' } } data(){ return{ data1:'fdsfa' } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
一个重要原则:
由
Vue管理的函数,一定不要写箭头函数,一旦写了箭头函数,this就不再是Vue的实例了1.4 MVVM模型
- M:模型:data中的数据
- V:视图:模板代码
- VM:视图模型:Vue实例
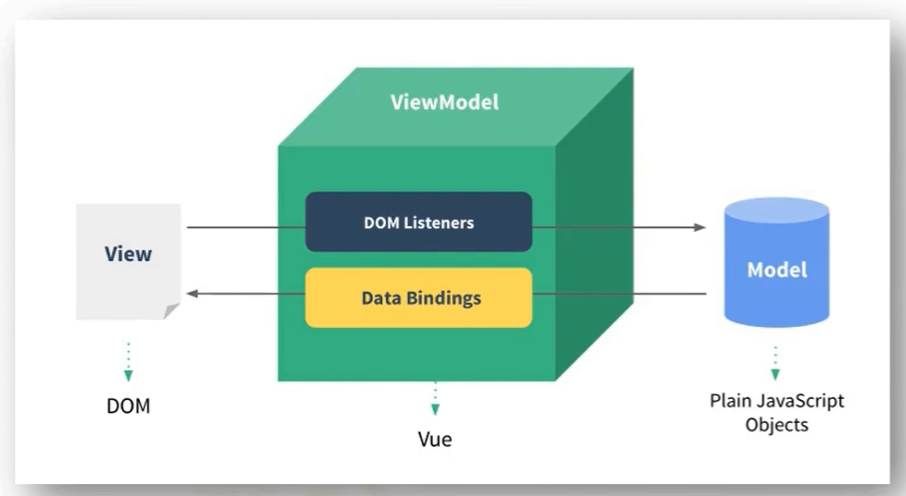
观察发现:
data中所有属性,最后都出现在vm上vm上所有的属性及 Vue原型上所有属性,在 Vue 模板中都可以直接使用
1.5 数据代理
Object.defineProperty
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>初识Vuetitle> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> let number = 18 let person = { name:'wy', sex:'male' } Object.defineProperty(person, 'age',{ // value:13, enumerable:true, // 控制属性是否可以枚举,默认值为false // writable:true, // 控制属性是否可以被修改,默认值为false // configurable:true, // 控制属性是否可以被删除,默认值为false // 当 age 属性被读取时,get函数会被调用,且返回值是 age get(){ return number }, // 当 age 属性被修改时,set函数会被调用,且会收到修改的值 set(value){ number = value; } }) console.log(person); console.log(Object.keys(person)); script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
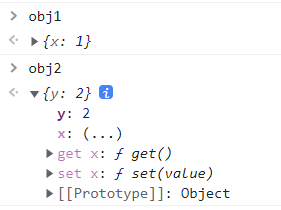
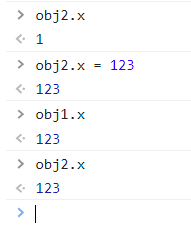
深入理解
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Vue核心title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <script type="text/javascript"> let obj1 = {x:1} let obj2 = {y:2} Object.defineProperty(obj2, 'x',{ get(){ return obj1.x }, set(value){ obj1.x = value; } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
控制台验证
Vue中的数据代理
-
通过
vm对象来代理data对象中属性的操作 (读/写) -
更加方便地操作
data中的数据 -
基本原理
通过
Object.defineProperty()把data对象中所有属性添加到vm上。为每一个添加到vm上的属性,都指定一个getter/setter,在getter/setter内部去操作data中对应的属性
1.6 事件处理
事件基本使用
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Vue核心title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>{{name}}h1> <button v-on:click="showInfo1">点我提示信息1button> <button @click="showInfo2(666, $event)">点我提示信息2button> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ name:'hh', }, methods:{ showInfo1(event){ console.log(event.target.innerText); }, showInfo2(number, event){ console.log(number); console.log(event); } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 使用
v-on:xxx或@xxx绑定事件, xxx为事件名 - 事件的回调需要配置在
methods对象中,最终会在vm上 methods中配置的函数,都是被Vue所管理的函数,this的指向是vm或组件实例对象@click="demo"和@click="demo($event)"效果一致,但后者可以传递参数- 绑定事件时,
xxx可以写一些简单的语句,不过最好在methods中写函数封装。
事件修饰符
-
prevent: 阻止默认事件(常用)DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>事件修饰符/title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>{{name}}h1> <a href="https://www.baidu.com" @click="showInfo">点击a> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ name:'hh', }, methods:{ showInfo(event){ alert('你好') }, } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
可以发现,
a标签的默认行为不会被执行 -
stop: 阻止事件冒泡(常用)<script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ name:'hh', }, methods:{ showInfo(t){ console.log(t); }, } }) script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
未添加阻止冒泡时
<div id="root"> <h1>{{name}}h1> <div @click="showInfo(1)"> <button @click="showInfo(2)">点击button> div> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
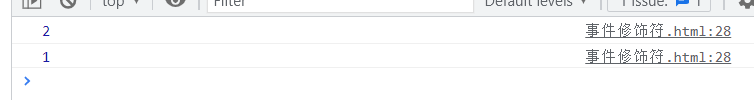
阻止冒泡后
<div id="root"> <h1>{{name}}h1> <div @click="showInfo(1)"> <button @click.stop="showInfo(2)">点击button> div> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

-
once: 事件只触发一次(常用)<div id="root"> <h1>{{name}}h1> <div> <button @click.once="showInfo(2)">点击button> div> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
多次点击后,只会执行一次
showInfo(2) -
capture: 使用事件的捕获模式 -
self: 只有event.target是当前操作的元素时才触发事件 -
passive:事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕
键盘事件
Vue常用按键别名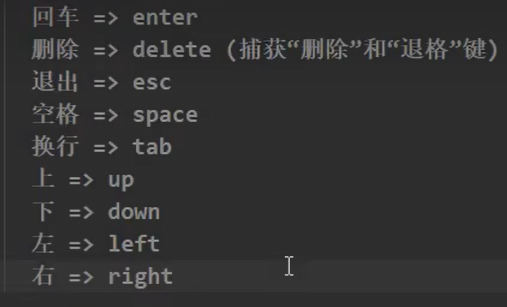
触发条件:
keydown和keyupDOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>键盘事件title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <input type="text" @keydown.tab="showInfo"> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ name:'hh', }, methods:{ showInfo(e){ console.log(e.target.value); }, } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
补充
组合按键:
修饰符组合:
<div id="root"> <h1>{{name}}h1> <div @click="showInfo(1)"> <a href="https://baidu.com" @click.stop.prevent="showInfo(2)">点击button> div> div>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
不会跳转
1.7 计算属性
基本使用
- 定义:要用的属性不存在,要通过已有属性计算得来
- 原理:底层借助了
Object.defineproperty方法提供的getter和setter get函数什么时候执行?- 初次读取时会执行一次
- 当计算属性所依赖的数据发生改变时会被调用
- 优势:与
methods实现对比,内部有缓存机制(可复用),效率更高,调试方便 - 备注:
- 计算属性最终会出现在
vm上,直接读取使用即可 - 如果计算属性被修改,那必须写
set函数去响应修改,且set中要引起计算时依赖的属性的数据发生改变
- 计算属性最终会出现在
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>计算属性title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br/> <input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br/> <div> <h3>{{fullName}}h3> div> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ firstName:'张', lastName:'三', }, computed:{ fullName:{ get(){ console.log('调用get函数') return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName }, set(value){ console.log('调用set函数') const arr = value.split('-') this.firstName = arr[0] this.lastName = arr[1] } } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
修改姓
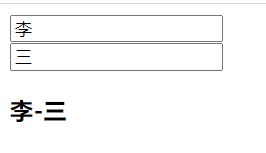
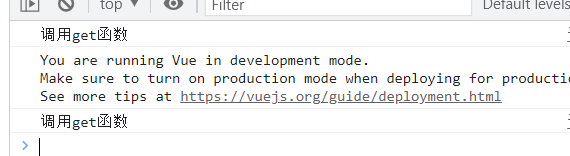
修改计算属性


简写
计算属性只考虑读取,不考虑修改时,才可以进行简写
computed:{ fullName(){ console.log('调用get函数') return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.8 监视属性
- 当被监视的属性变化时,回调函数自动调用,进行相关操作
- 监视的属性必须存在,才能进行监视
- 监视的两种写法:
new Vue时传入watch配置- 通过
vm.$watch监视
基本使用
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>监视属性title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <div> <h2>今天天气很{{info}}h2> <button @click="change">点击切换天气button> div> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ ishot:true, }, methods: { change(){ this.ishot = !this.ishot } }, computed:{ info(){ return this.ishot ? '炎热' : '凉爽' } }, // 第一种写法 watch:{ ishot:{ immediate:true, // 初始化时会被调用一次 handler(newValue, oldValue){ // 当 ishot 被修改时会被调用 console.log('ishot被修改', newValue, oldValue); } } } }) // 第二种写法 vm.$watch('ishot', { immediate:true, handler(newValue, oldValue){ console.log('ishot被修改', newValue, oldValue); } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
深度监视
Vue中的watch默认不监测对象内部值的改变(一层)- 配置
deep:true可以监测对象内部值改变(多层)
备注:
Vue自身可以监测到对象内部值的改变,但Vue提供的watch默认不可以- 使用
watch时根据数据的具体结构,决定是否采用深度监视
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>监视属性title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <div> <h2 @click="number.a++">{{number.a}}h2> <h2 @click="number.b++">{{number.b}}h2> div> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ number:{ a:1, b:1 } }, watch:{ // 多级结构时写字符串形式 'number.a':{ handler(){ console.log('a变化'); } } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
此时点击
a会输出 a变化watch:{ number:{ deep:true, // 深度监视配置deep属性 handler(){ console.log('number变化'); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
简写
当
wathch配置项只有handler时可以简写vm.$watch('ishot',function(newValue, oldValue){ console.log('ishot被修改', newValue, oldValue) })- 1
- 2
- 3
watch:{ ishot(newValue, oldValue){ console.log('ishot被修改', newValue, oldValue); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Watch vs Computed
二者区别:
- computed 能完成的功能,watch 都能完成
- watch 能完成的功能,computed 不一定能完成,例如:watch 可以进行异步操作
两个重要的小原则:
- 被
Vue管理的函数,最好写成普通函数,这样this的指向才是vm或组件实例对象 - 所有不被
Vue管理的函数(定时器的回调函数、ajax的回调函数、promise的回调函数等),最好写成箭头函数,这样this的指向才是vm或 组件实例对象
1.9 绑定class和style
class
基本写法
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>绑定样式title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <style> .happy{ background-color: red; } .sad{ background-color: blue; } .normal{ background-color: wheat; } .basic{ height: 100px; width: 200px; border: solid red 1px; } style> head> <body> <div id="root"> <div class="basic" :class="css" @click="change">div> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ css:'normal' }, methods: { change(){ styles = ['normal', 'sad', 'happy'] this.css = styles[Math.floor(Math.random()*3)] } }, }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
以上示例可以通过点击实现样式随机切换
和绑定属性值类似
:class="xxx"xxx可填变量,数组或对象数组:
<body> <div id="root"> <div class="basic" :class="arr">div> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ css:'normal', arr:['normal', 'sad', 'happy'], }, methods: { }, }) script> body>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
对象:
<body> <div id="root"> <div class="basic" :class="cssObj">div> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ cssObj:{ 'normal':true, // 使用 normal样式 'sad':false, 'happy':false, } }, }) script> body>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
style
原始写法
<div class="basic" style="font-size: 50px;">你好div>- 1
绑定后
<div class="basic" :style="{fontSize: size + 'px'}">你好div>- 1
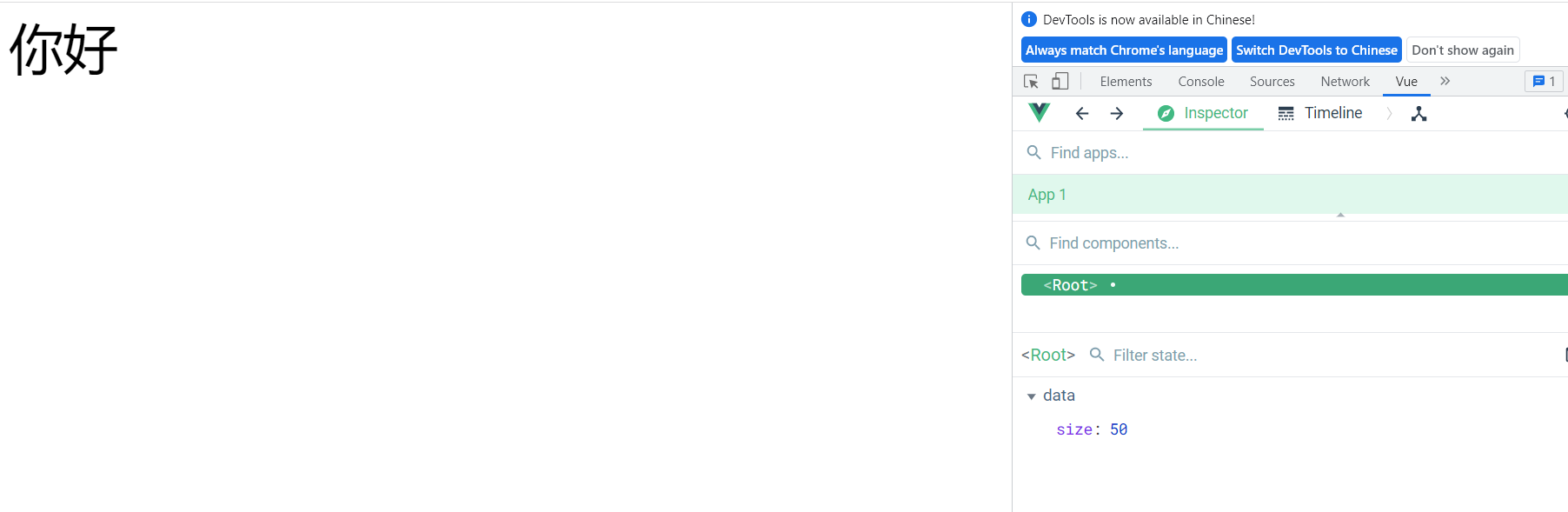

对象写法
data:{ styleObj:{ fontSize: '60px', color: 'green', backgroundColor: 'yellow' } },- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
前面的 key 不能乱写,一个单词正常写,两个单词用
-连接的需要将第二个单词首字母大写,然后去掉-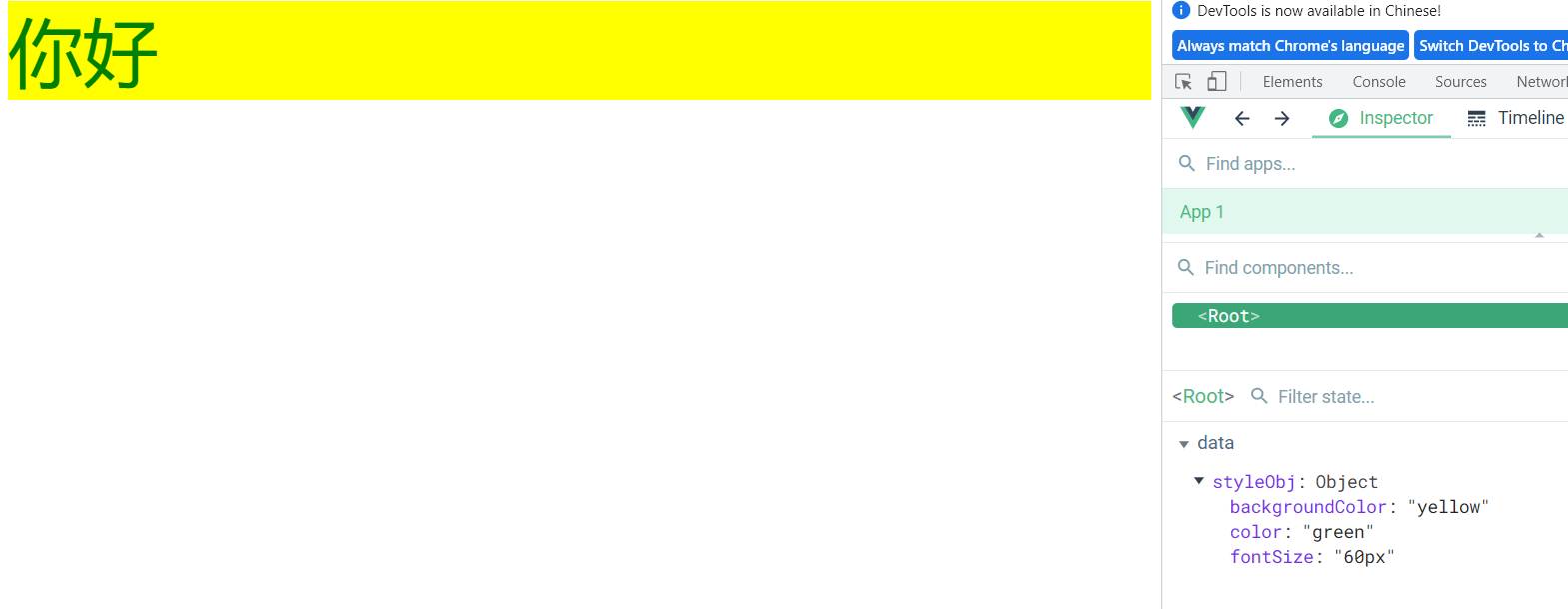
style中也可以写 数组,但不常用
1.10 条件渲染
v-if- 写法:
v-if="表达式"v-else-if="表达式"v-else="表达式"
- 适用于:切换频率较低的场景
- 特点:不展示的
DOM元素直接被移除 - 注意:
v-if可以和v-else-if、v-else一起使用,但要求结构不能被打断
- 写法:
v-show- 写法:
v-show="表达式" - 适用于:切换频率较高的场景
- 特点:不展示的
DOM元素未被移出,仅仅是使用样式隐藏掉
- 写法:
- 备注:使用
v-if时,元素可能无法获取到,而使用v-show时一定可以获取到
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>条件渲染title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1 v-show="0">你好h1> <h1 v-if="1 === 3">helloh1> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ }, }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
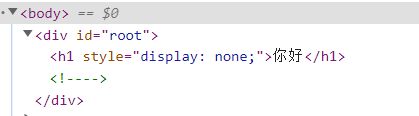
1.11 列表渲染
v-for指令- 用于展示列表数据
- 语法:
v-for="(item, index) in xxx" :key="yyy" - 可遍历:数组、对象、字符串(使用较少)、指定次数(使用较少)
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>列表渲染title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <ul> <li v-for="(val, k) in persons" :key="k"> {{val.name}}--{{val.age}} li> ul> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ persons:[ {'name':'wy', 'age':20}, {'name':'wm', 'age':16}, {'name':'xx', 'age':10}, ] } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
Key作用

列表过滤
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>列表过滤title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <input type="text" v-model="keyword"> <ul> <li v-for="(val, k) in persons_fill" :key="k"> {{val.name}}--{{val.age}} li> ul> div> <script type="text/javascript"> // const vm = new Vue({ // el:'#root', // data:{ // keyword:'', // persons:[ // {'name':'wyy', 'age':20}, // {'name':'wmx', 'age':16}, // {'name':'xxw', 'age':10}, // {'name':'adsf', 'age':20}, // {'name':'vcx', 'age':16}, // {'name':'xwe', 'age':10}, // {'name':'wyy', 'age':20}, // {'name':'wmx', 'age':16}, // {'name':'xxw', 'age':10}, // {'name':'adsf', 'age':20}, // {'name':'vcx', 'age':16}, // {'name':'xwe', 'age':10}, // ], // persons_fill:[ // ] // }, // watch:{ // keyword:{ // immediate:true, // handler(val){ // this.persons_fill = this.persons.filter((p)=>{ // return p.name.indexOf(val) !== -1 // }) // } // } // } // }) const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ keyword:'', persons:[ {'name':'wyy', 'age':20}, {'name':'wmx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xxw', 'age':10}, {'name':'adsf', 'age':20}, {'name':'vcx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xwe', 'age':10}, {'name':'wyy', 'age':20}, {'name':'wmx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xxw', 'age':10}, {'name':'adsf', 'age':20}, {'name':'vcx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xwe', 'age':10}, ], }, computed:{ persons_fill(){ return this.persons.filter((p)=>{ return p.name.indexOf(this.keyword) !== -1 }) } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
测试结果:
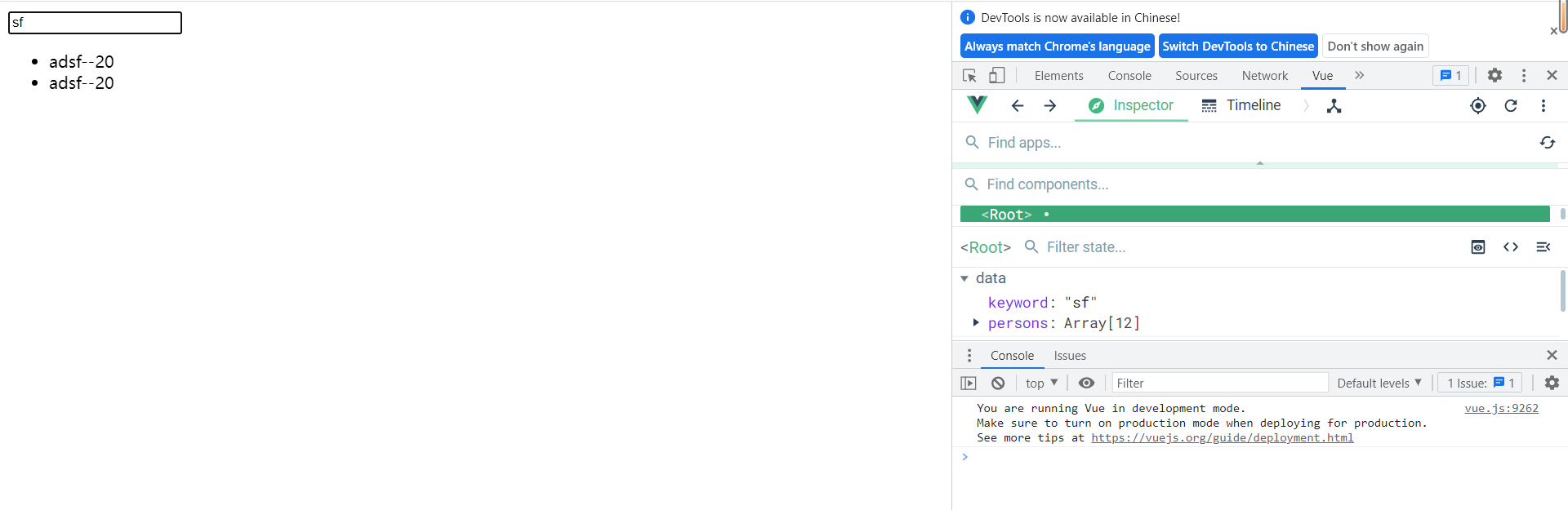
列表排序
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>列表排序title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>人员列表h1> <input type="text" v-model="keyword"> <button @click="sortType = 1">升序button> <button @click="sortType = 2">降序button> <button @click="sortType = 0">原序button> <ul> <li v-for="(val, k) in persons_fill" :key="k"> {{val.name}}--{{val.age}} li> ul> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ keyword:'', sortType:0, persons:[ {'name':'wyy', 'age':20}, {'name':'wmx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xxw', 'age':10}, {'name':'adsf', 'age':20}, {'name':'vcx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xwe', 'age':10}, {'name':'wyy', 'age':20}, {'name':'wmx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xxw', 'age':10}, {'name':'adsf', 'age':20}, {'name':'vcx', 'age':16}, {'name':'xwe', 'age':10}, ], }, computed:{ persons_fill(){ const a = this.persons.filter((p)=>{ return p.name.indexOf(this.keyword) !== -1 }) if (this.sortType) { a.sort((a, b)=>{ return this.sortType === 1 ? a.age - b.age : b.age - a.age; }) } return a; } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
测试结果:
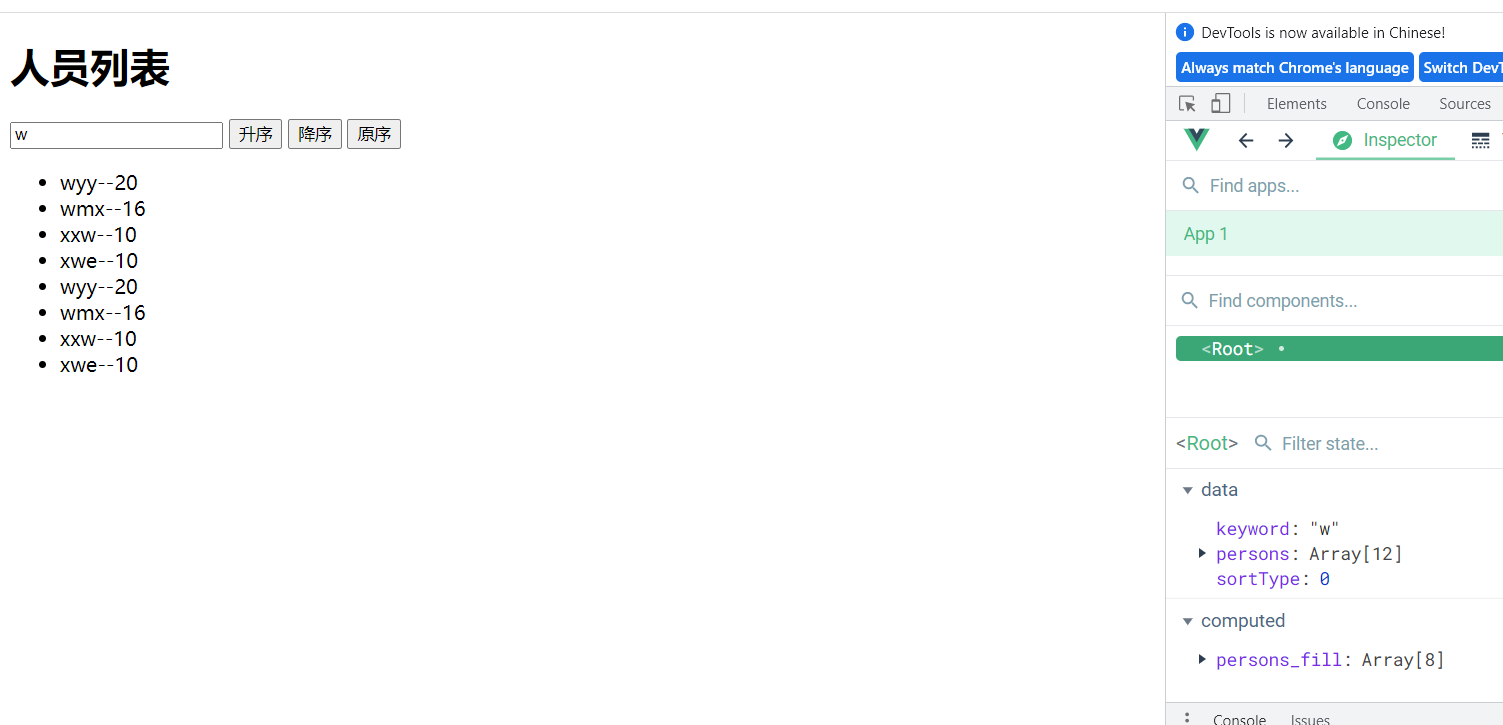
升序和降序


模拟Vue进行数据监测(对象)
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>模拟数据监测title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> div> <script type="text/javascript"> let data = { name:'wy', age:23, } // 创建一个监视的实例对象,用于监视data中属性的变化 const obs = new Observer(data) let vm = {} vm._data = data = obs function Observer(obj) { const keys = Object.keys(obj) // 汇总对象中所有属性形成一个数组 keys.forEach((k)=>{ Object.defineProperty(this, k, { get(){ return obj[k] }, set(val){ obj[k] = val } }) }) } script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
测试结果
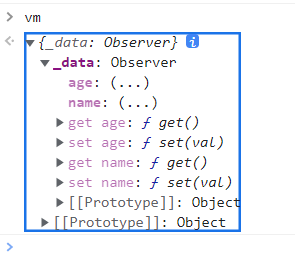
Vue.set使用
向
Vue中添加属性注意:
tartget不能为vm本身或者vm._dataDOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Vue.set使用title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>name: {{name}}h1> <h1>age: {{age}}h1> <h2>schoolh2> <h3>name: {{school.name}}h3> <h3 v-if="school.loc">loc: {{school.loc}}h3> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ name:'wy', age:18, school:{ name:'zzu', } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
方式一:
Vue.set(vm.school, 'loc', 'zz')- 1
方式二:
vm.$set(vm.school, 'loc', 'zz')- 1
执行结果:

Vue监测数组

DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>模拟数据监测数组title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>爱好h1> <ul> <li v-for="(val, k) in hobby" :key="k"> {{val}} li> ul> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ hobby:['听音乐', '打游戏', '唱歌', '跑步'] } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
数组中的元素没有
getter和setter方法
直接使用数组下标对其修改在页面上不会体现效果
vm._data.hobby[0] = '睡觉'- 1
Vue将被侦听的数组的变更方法进行了包裹,所以它们也将会触发视图更新。这些被包裹过的方法包括:-
push() -
pop() -
shift() -
unshift() -
splice()vm.hobby.splice(0, 1, '吃饭')- 1
-
sort() -
reverse()
1.12 收集表单数据
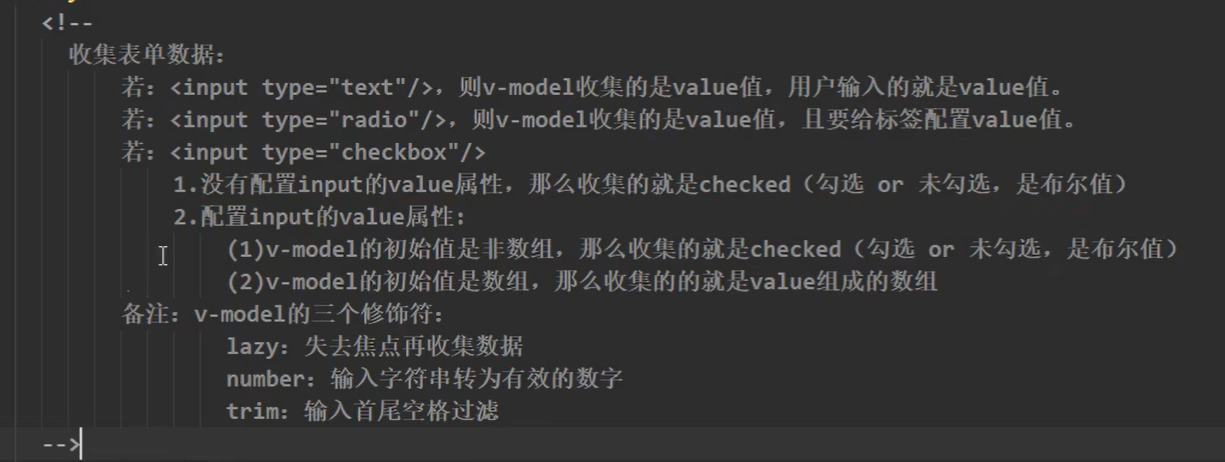
实例
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>收集表单数据title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root" @submit.prevent="submit"> <form> <div> 账户: <input type="text" v-model.trim="userinfo.username"> div> <div> 密码: <input type="password" v-model="userinfo.password"> div> <div> 性别: 男<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userinfo.sex" value="male">女<input type="radio" name="sex" v-model="userinfo.sex" value="female"> div> <div> 年龄: <input type="number" v-model.number="userinfo.age"> div> <div> 爱好: <input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.hobby" value="eat">吃饭 <input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.hobby" value="sleep">睡觉 <input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.hobby" value="drink">喝酒 <input type="checkbox" v-model="userinfo.hobby" value="gameing">打游戏 div> <div> 其他: <textarea name="" id="" cols="30" rows="10" v-model.lazy="userinfo.other">textarea> div> <button>提交button> form> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ userinfo:{ username:'', password:'', sex:'', age:'', hobby:[], other:'', } }, methods: { submit(){ console.log(JSON.stringify(this.userinfo)); } }, }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
1.13 过滤器
**定义:**对要显示的数据进行特定格式化后再显示(适用于一些简单逻辑的处理)
语法:
- 注册过滤器:
Vue.filter(name, callback) 或 new Vue{filters:{}} - 使用过滤器:
{{ xxx | 过滤器名 }} 或 v-bind:属性 = "xxx | 过滤器名"
备注:
- 过滤器也可以接收额外参数、多个过滤器也可以串联
- 并没有改变原本的数据,是产生新的对应数据
实例:
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>过滤器title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.4/dayjs.min.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>显示当前日期和时间h1> <h2>{{ time | getTime }}h2> <h1>显示时间h1> <h2>{{ time | getTime('HH:mm:ss') }}h2> <h1>属性绑定h1> <h2 :x="time | getTime">你好h2> <h1>截取前4位h1> <h2>{{ time | getTime | slice(0, 4) }}h2> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ time:1659925371764 }, methods:{ }, filters:{ getTime(value, str='YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss'){ return dayjs(value).format(str) }, slice(str, st=0, ed=0) { return str.slice(st, ed) } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
全局注册
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>过滤器title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.4/dayjs.min.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>显示当前日期和时间h1> <h2>{{ time | getTime | slice(0, 4) }}h2> <h1>显示时间h1> <h2>{{ time | getTime('HH:mm:ss') }}h2> <h1>属性绑定h1> <h2 :x="time | getTime">你好h2> <h1>截取前4位h1> <h2>{{ time | getTime | slice(0, 4) }}h2> div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.filter('getTime', function(value, str='YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss'){ return dayjs(value).format(str) }) Vue.filter('slice', function(str, st=0, ed=0){ return str.slice(st, ed) }) const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ time:1659925371764 }, methods:{ }, }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
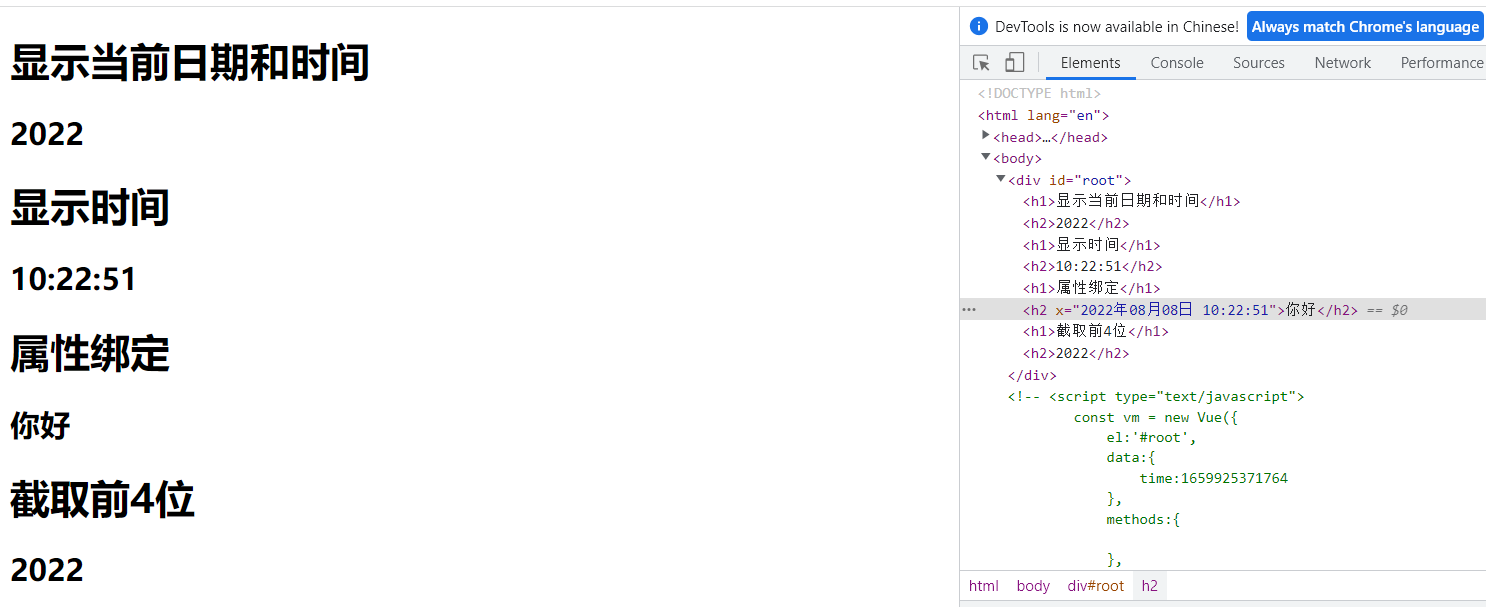
1.14 内置指令
v-text
- 作用:向其所在节点中渲染文本内容
- 与插值语法的区别:
v-text会替换掉节点的内容,{{xx}}不会
v-html
- 作用:向指定节点中渲染包含html结构的内容
- 与插值语法的区别:
v-html会替换掉节点中所有内容,{{xxx}}不会v-html可以识别为html结构
- 严重注意:
v-html有安全性问题- 在网站上动态渲染任意 html 是非常危险的,容易导致 XSS 攻击
- 一定在可信的内容上使用
v-html,永远不要用在用户提交的内容上
v-cloak
- 本质是一个特殊的属性,Vue实例创建完毕并接管容器后,会删掉
v-cloak属性 - 使用 css 配合
v-cloak可以解决网速慢时页面展示出{{xxx}}的问题
实例
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>v-cloaktitle> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.4/dayjs.min.js">script> <style> [v-cloak]{ display: none; } style> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1 v-cloak>{{name}}h1> div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.filter('getTime', function(value, str='YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss'){ return dayjs(value).format(str) }) Vue.filter('slice', function(str, st=0, ed=0){ return str.slice(st, ed) }) const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ name:'张三' } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
v-once
v-once所在节点在初次动态渲染后,就视为静态内容了- 以后数据的改变不会引起
v-once所在结构的更新,可以用于优化性能
v-pre
- 跳过其所在节点的编译过程
- 可利用它跳过节点:没有使用指令语法、没有使用插值语法的节点,加快编译
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>v-cloaktitle> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.4/dayjs.min.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1 v-pre @click="name += '1'">{{name}}h1> div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.filter('getTime', function(value, str='YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss'){ return dayjs(value).format(str) }) Vue.filter('slice', function(str, st=0, ed=0){ return str.slice(st, ed) }) const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ name:'张三' } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
1.15 自定义指令
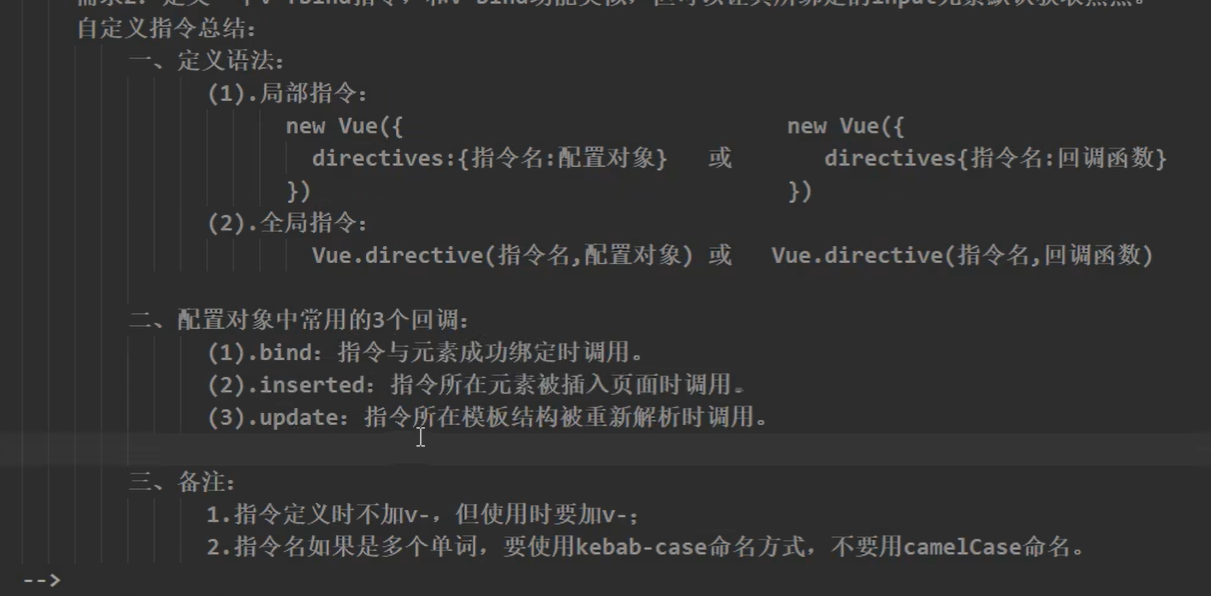
注意自定义命令中的
this是 WindowsDOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>自定义指令title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.4/dayjs.min.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1>{{n}}h1> <button @click="n++">点击button> <input type="nubmer" v-fbind="n"> div> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.filter('getTime', function(value, str='YYYY年MM月DD日 HH:mm:ss'){ return dayjs(value).format(str) }) Vue.filter('slice', function(str, st=0, ed=0){ return str.slice(st, ed) }) const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ n:1, }, directives:{ // fbind(element, binding){ // console.log(element, binding); // element.value = binding.value; // element.focus() // 在第一次绑定时,还没有将所在元素插入页面中,因此不会生效 // } fbind:{ bind(elem, binding){ console.log('bind'); elem.value = binding.value }, inserted(elem, binding){ console.log('inserted'); elem.focus() }, update(elem, binding){ console.log('update'); elem.value = binding.value } } } }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
1.16 生命周期
- 又名:生命周期回调函数、生命周期函数,生命周期钩子
- 是什么:Vue 在关键时期帮我们调用的一些特殊函数
- 生命周期函数的名字不可更改,但函数的具体内容是程序员根据需求编写的
- 生命周期函数中的
this指向的是 vm 或组件实例对象
生命周期 DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>生命周期title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.4/dayjs.min.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1 :style="{opacity}">Hello, World!h1> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ opacity:1 }, mounted() { setInterval(()=>{ this.opacity -= 0.01 if (this.opacity <= 0) this.opacity = 1 }, 16) }, }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
常用的生命周期钩子:
- mounted: 发送 ajax请求、启动定时器、绑定自定义事件、订阅消息等【初始化操作】
- beforeDestroy: 清除定时器、解绑自定义事件取消订阅消息等【收尾工作】
关于销毁 Vue 实例
- 销毁后借助 Vue 开发工具看不到任何信息
- 销毁后自定义事件会失败,但原生DOM事件依然有效
- 一般不会在 beforedestroy操作数据,因为即便操作数据,也不会触发更新流程了
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>生命周期title> <script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js">script> <script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/dayjs/1.11.4/dayjs.min.js">script> head> <body> <div id="root"> <h1 :style="{opacity}">Hello, World!h1> <button @click="hack">点击销毁vm实例button> div> <script type="text/javascript"> const vm = new Vue({ el:'#root', data:{ opacity:1 }, methods: { hack(){ this.$destroy() } }, beforeCreate() { console.log('beforeCreate'); }, created() { console.log('created'); }, beforeMount() { console.log('beforeMount'); }, mounted() { console.log('mounted'); setInterval(()=>{ this.opacity -= 0.01 if (this.opacity <= 0) this.opacity = 1 }, 16) }, beforeUpdate() { console.log('beforeUpdate') }, updated() { console.log('updated'); }, beforeDestroy() { console.log('beforeDestroy'); }, destroyed() { console.log('destroyed'); }, }) script> body> html>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
参考资料
尚硅谷Vue2.0+Vue3.0全套教程丨vuejs从入门到精通
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Zy4y1K7SH?p=15&share_source=copy_web&vd_source=d3c9ceb0642f45fbe95f795c0d074040Vue 官方文档
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/
Vue api 文档
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/
-
-
相关阅读:
工作流---流程变量
丁鹿学堂:typescript轻松入门
迁移Linux服务器用户数据(将一个服务器的Linux用户数据迁移到另一个Linux服务器用户的流程)
tls版本过低如何升级成1.2
算法— — 归并排序的应用
Dive into TensorFlow - 解析 TF 核心抽象 op 算子
Docker | 容器数据卷详解
Kibana8.4在Linux系统上的安装(ELK安装part3)
图像噪声--添加噪声
Flink 内存模型
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Joker15517/article/details/126156037
