-
链表---OJ题
练习题1
移除链表元素
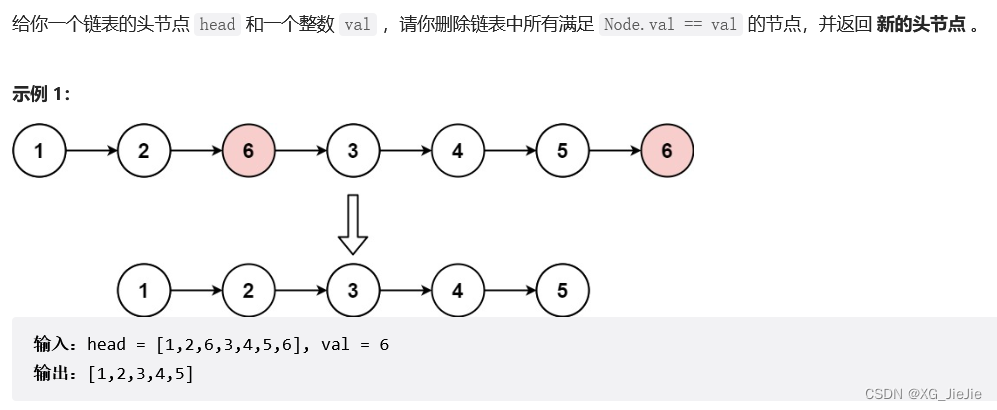

解决方案:
1.创建一个新的头节点,不相等尾插即可。
2.使用cur和prev遍历数组,遇到相等的删除即可。//定义一个新链表 不是val尾插 struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* tail = guard; while(cur) { if(cur->val != val) { tail->next = cur; tail = tail->next; cur = cur->next; } else { struct ListNode* del = cur; cur = cur->next; free(del); } } if(tail != NULL) { tail->next = NULL; } head = guard->next; free(guard); return head; } //遍历删除 struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){ struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* prev = head; while(cur) { if(cur->val == val) { //1、头删 if(cur == head) { head = head->next; free(cur); cur = head; } //2、非头删 else { prev->next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = prev->next; } } else { prev = cur; cur = cur->next; } } return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
练习题2
反转链表
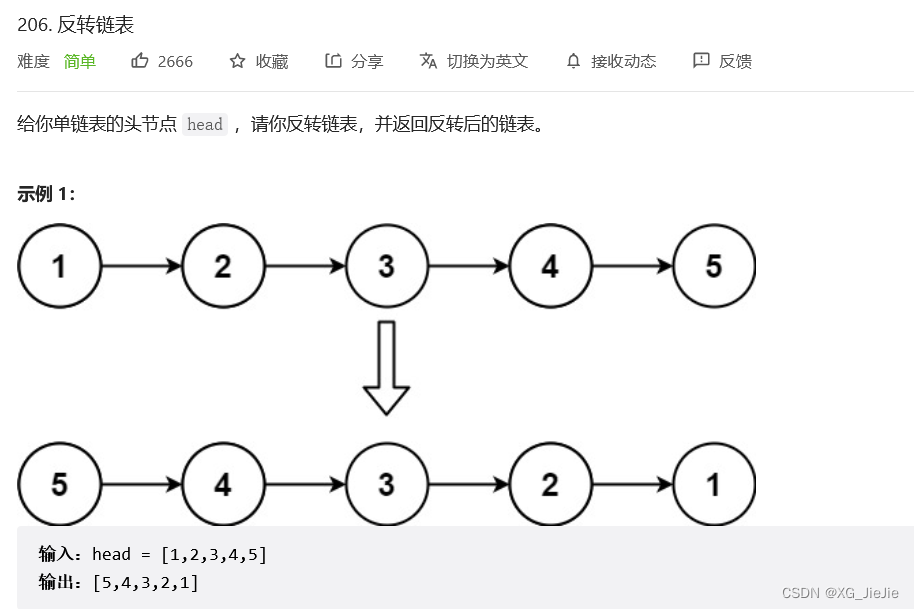
解决方案:
1.尾插变头插。
2.改变指针的指向。//1.尾插变头插 struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* newhead = NULL; while(cur) { struct ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = newhead; newhead = cur; cur = next; } return newhead; } //2.改变指针的指向 struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* cur = head; //struct ListNode* next = NULL; struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); guard->next = NULL; while(cur) { struct ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = guard->next; guard->next = cur; cur = next; } head = guard->next; free(guard); return head; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
练习题3
链表的中间节点


解决方案:
使用快慢指针,快指针每次+2,慢指针每次+1。结束条件为fast且fast->next不为空,如果没有fast->next这个条件,会出现问题,因为一次需要+2。画图说明原因:
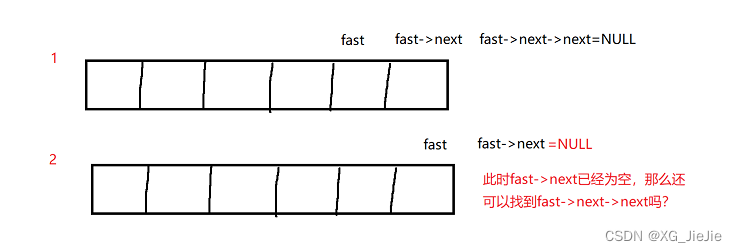
//只能遍历一遍 快慢指针 快+2 慢+1 struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* slow = head; struct ListNode* fast = head; while(fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } return slow; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
练习题4
链表中倒数第k个节点
解决方案:
使用快慢指针解决问题,首先让快指针向后移动k步,此时fast和slow相差k步(这个过程要注意边界问题),然后让fast继续向后直到为空为止,每一次slow++,那么就找到了倒数第K个节点的位置,就是slow。struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) { // write code here if(pListHead == NULL) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* fast = pListHead; struct ListNode* slow = pListHead; while(k--) { fast = fast->next; if(fast == NULL) break; } if(k < 1) { while(fast) { fast=fast->next; slow=slow->next; } } else { slow = NULL; } return slow; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
练习题5
合并两个有序链表

解决方案:
新建一个有哨兵位的头节点,然后通过三个指针做这个题,两个指针用来遍历给定的两个升序链表,另一个用来做新开辟的节点的指针,每次插入+1。struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){ struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); struct ListNode* cur1 = list1; struct ListNode* cur2 = list2; struct ListNode* cur = guard; cur->next = NULL; while(cur1 && cur2) { if(cur1->val <= cur2->val) { cur->next = cur1; cur = cur->next; cur1 = cur1->next; } else { cur->next = cur2; cur = cur->next; cur2 = cur2->next; } } if(cur1) { cur->next = cur1; } if(cur2) { cur->next = cur2; } struct ListNode* newhead = guard->next; free(guard); return newhead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
练习题6
链表分割
解决方案:
新开辟两个带哨兵位的头节点,第一个存储大于等于x的节点,第二个存储小于x节点。将小于x的最后一个节点的next指向第一个哨兵位的next地方,最后一定要将大于等于x的最后一个节点的next置空,否则会造成回环。class Partition { public: ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) { struct ListNode* lessGuard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); struct ListNode* greaterGuard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); lessGuard->next = NULL; greaterGuard->next =NULL; struct ListNode* lesstail = lessGuard; struct ListNode* greatertail = greaterGuard; struct ListNode* cur = pHead; while(cur) { if(cur->val < x) { lesstail->next = cur; lesstail = lesstail->next; } else { greatertail->next = cur; greatertail = greatertail->next; } cur = cur->next; } lesstail->next = greaterGuard->next; //尾节点的数据置NULL 否则会形成回环 greatertail->next = NULL; struct ListNode* head = lessGuard->next; free(lessGuard); free(greaterGuard); return head; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
练习题7
链表的回文结构
 解决方案:
解决方案:
1.找到中间的节点
2.从中间的节点开始向后开始逆置 3.从head和rmid开始遍历至NULL结束,若一直相等,那么证明是回文结构。class PalindromeList { public: struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* slow = head; struct ListNode* fast = head; while(fast && fast->next) { fast = fast->next->next; slow=slow->next; } return slow; } struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){ struct ListNode* prev = NULL; struct ListNode* cur = head; while(cur) { struct ListNode* next = cur->next; cur->next = prev; prev = cur; cur = next; } return prev; } bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head) { // write code here struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(head); struct ListNode* rmid = reverseList(mid); while(head && rmid) { if(head->val != rmid->val) { return false; } head = head->next; rmid = rmid->next; } return true; } };- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
练习题8
相交链表
 解决方案:
解决方案:
1.判断两个链表的尾节点是否相同,如果相同证明是相交的,否则不是相交的。
2.计算两个链表的长度
3.让长链表遍历abs(lenB - lenA)
4.长短链表分别开始遍历,遍历至相同的时候,说明招到了相交的节点。//尾节点的地址是否相同 struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) { struct ListNode* curA = headA, *curB = headB; //判断是否为空链表 if(curA == NULL || curB == NULL) { return NULL; } //判断长度 int lenA = 1; while(curA->next) { curA = curA->next; ++lenA; } int lenB = 1; while(curB->next) { curB = curB->next; ++lenB; } if(curB != curA) { return NULL; } struct ListNode* longList = headA, *shortList = headB; if(lenA < lenB) { longList = headB; shortList = headA; } int gap = abs(lenB - lenA); while(gap--) { longList = longList->next; } while(longList != shortList) { longList = longList->next; shortList = shortList->next; } return shortList; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
练习题9
判断是否有回环
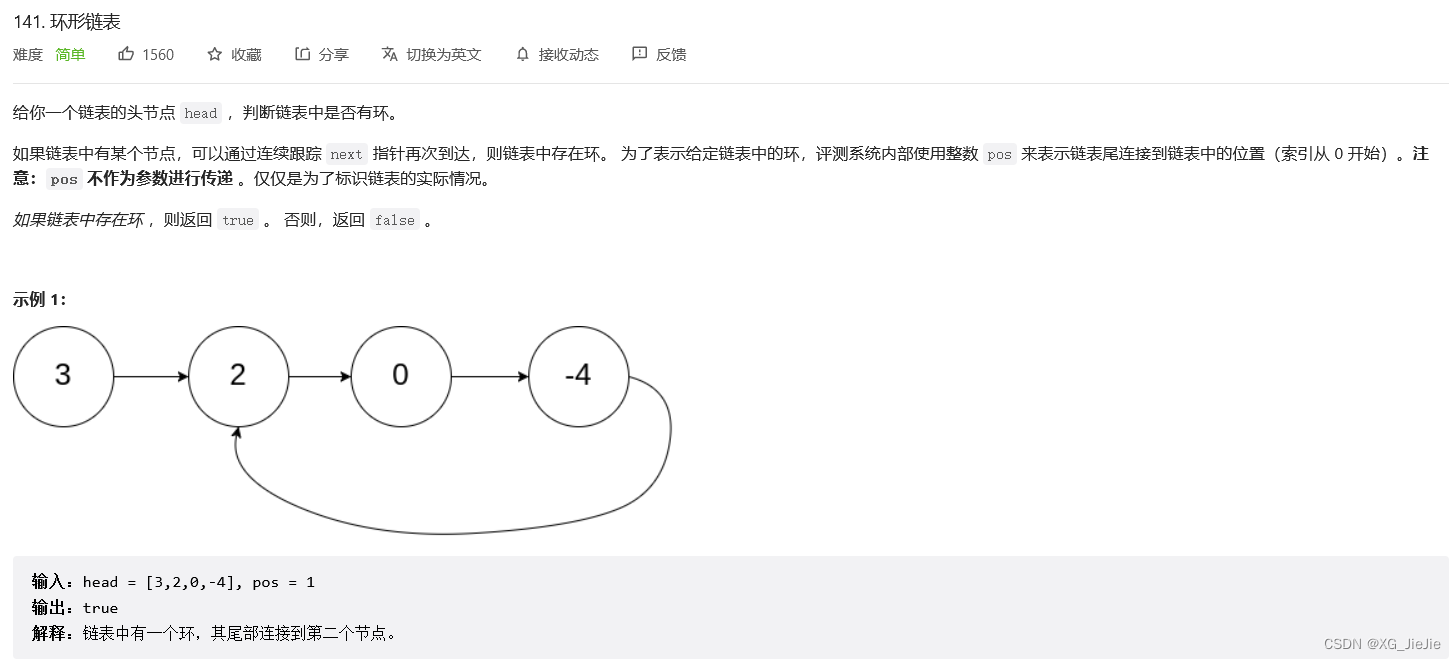
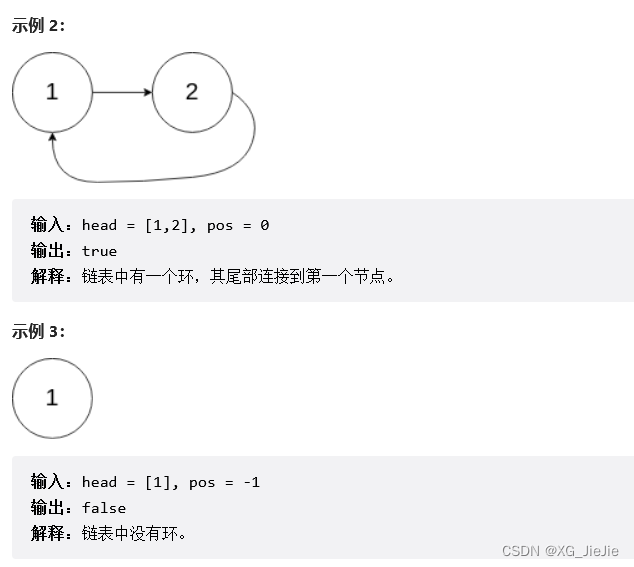
解决方案:
1.定义两个指针,快慢指针解决这个问题。
2.快指针每次+2,慢指针每次+1。
3.直到快指针 = 满指针 证明有回环。为什么快指针+2 慢指针+1就一定可以找到呢?
因为每次相差1,当慢指针进入回环的时候,假设和快指针相差N,那么每走一步,距离都会缩小1,N N-1 N-2 ------ 1 ------0 , 因此这个方向是可以使用的。如果快指针一次+3 慢指针+1可以找到吗?
因为每次相差2,当慢指针进入回环的时候,假设和快指针相差N,那么每走一步,距离都会缩小2,如果N为偶数,那么可以找到。如果为奇数,会出现1 -----> - 1的情况,当距离为-1时,代表着慢指针会超过快指针,若圆环内的元素为C ,则新的距离差为C-1,C-1为偶数则有机会相等,C-1为奇数的话一定相等。//快慢指针解决问题 bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode* fast, *slow; fast = slow =head; while(fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) return true; } return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
练习题10
找到环行链表的入口
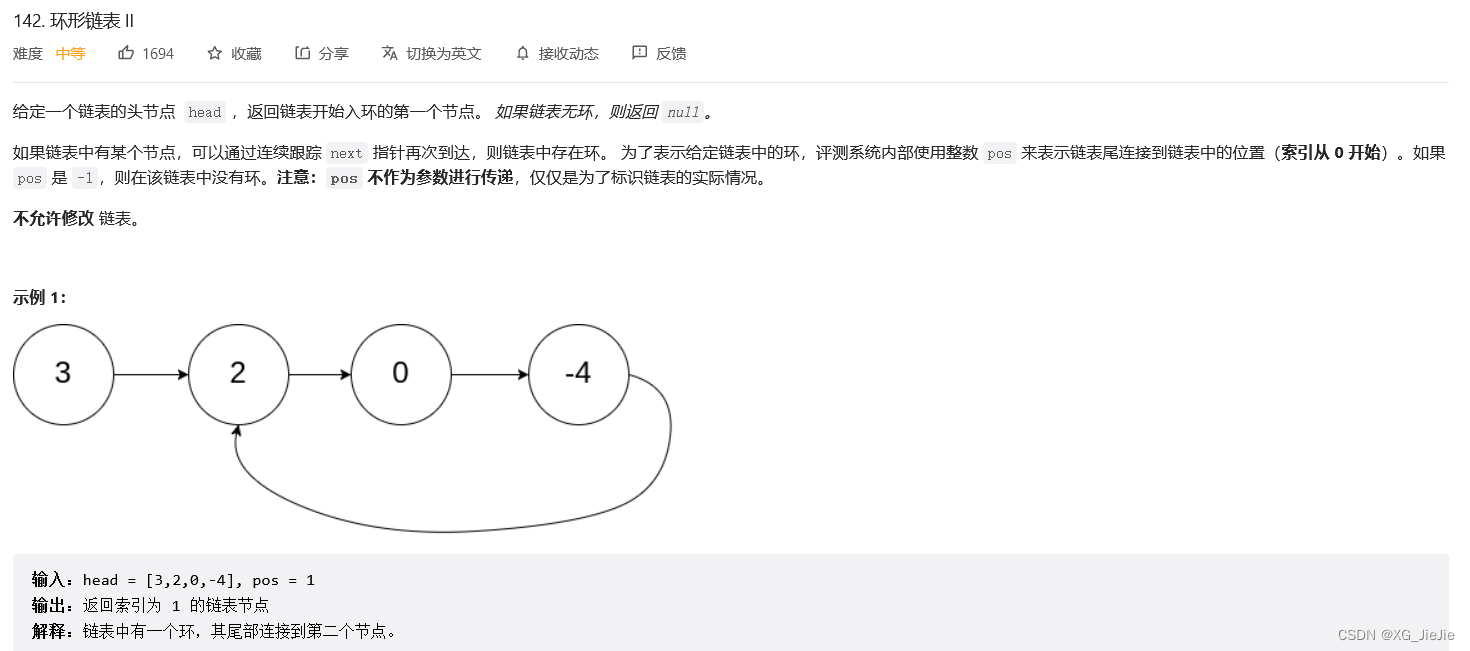
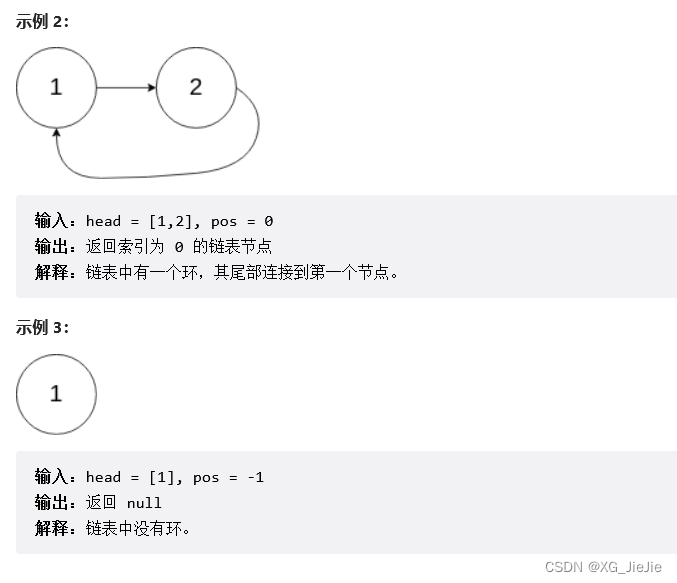
解决方案1:
这个问题类似与找两个链表的相交节点
1.判断是否有回环
2.将相遇的前一个节点的next置NULL
3.一个指针从head开始,另一个从相遇点开始
4.分别计算lenA , lenB 长链表先遍历abs(lenB-lenA)
5.长短链表依次向后遍历,相等即是交点,即环形链表的入口解决方案2:

Solution1 struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) { int is_circle = 0;//有无环的标志 struct ListNode* fast, *slow, *prev_fast; fast = slow = head; prev_fast = NULL; if(fast == NULL) { return NULL; } while(fast && fast->next) { prev_fast = fast->next; fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow -> next; if(slow == fast) { is_circle = 1;//有环 prev_fast->next = NULL;//交点的前一个next置NULL break; } } if(is_circle == 0) { return NULL; } else { struct ListNode* curA = head; struct ListNode* curB = slow; if(head==NULL || slow==NULL) { return NULL; } int lenA = 1; while(curA->next) { curA = curA->next; lenA += 1; } int lenB = 1; while(curB->next) { curB = curB->next; lenB += 1; } struct ListNode* LongList = head; struct ListNode* ShortList = slow; if(lenA < lenB) { LongList = slow; ShortList = head; } int gap = abs(lenB - lenA); while(gap--) { LongList = LongList->next; } while(LongList != ShortList) { LongList = LongList->next; ShortList = ShortList->next; } return LongList; } } Solution2 struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head; while(fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) { struct ListNode* meet = slow; while(meet != head) { meet = meet->next; head = head->next; } return meet; } } return NULL; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
练习题11
复制带随机指针的链表
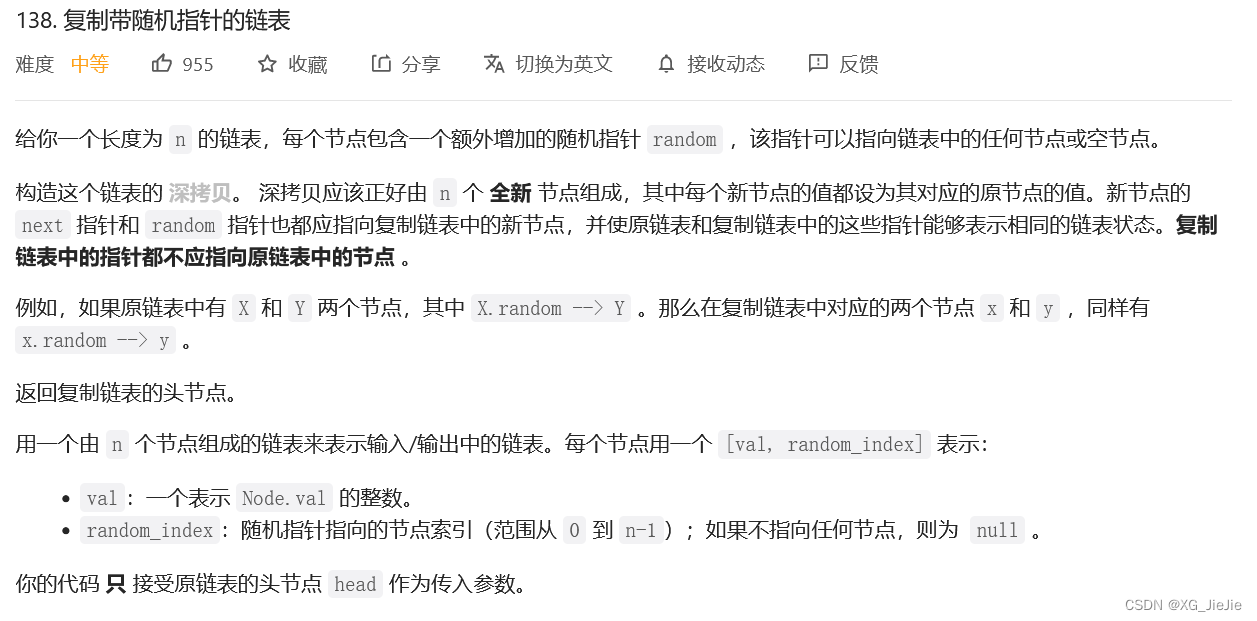
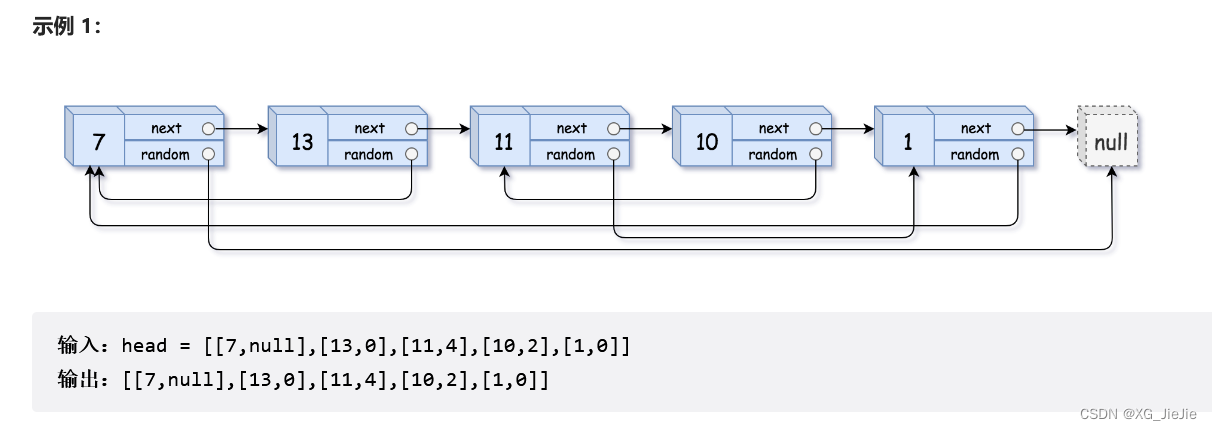
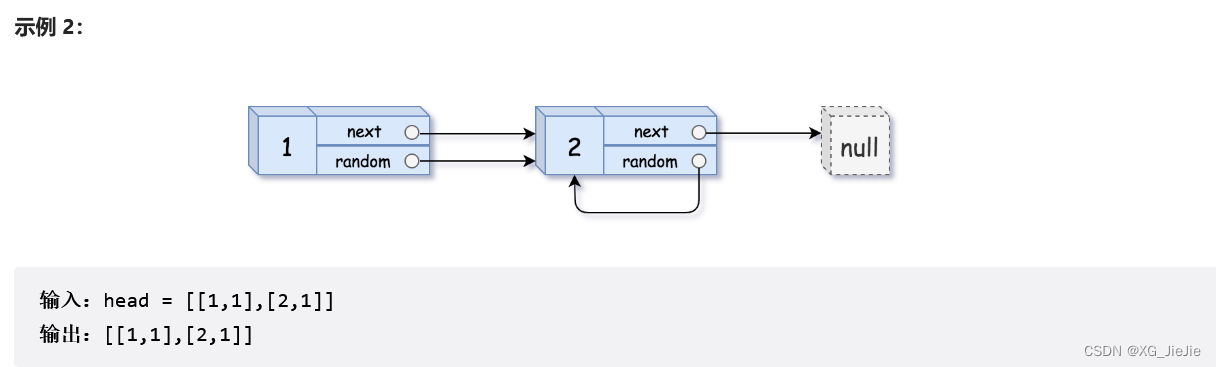
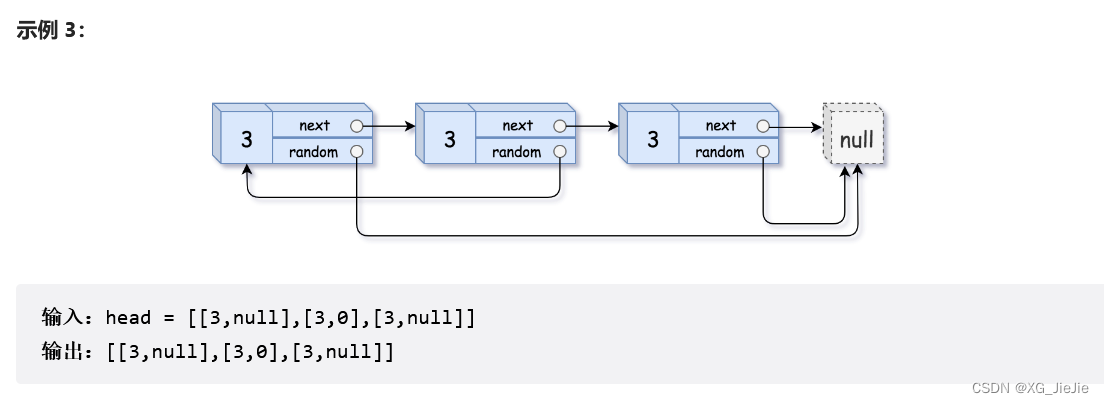

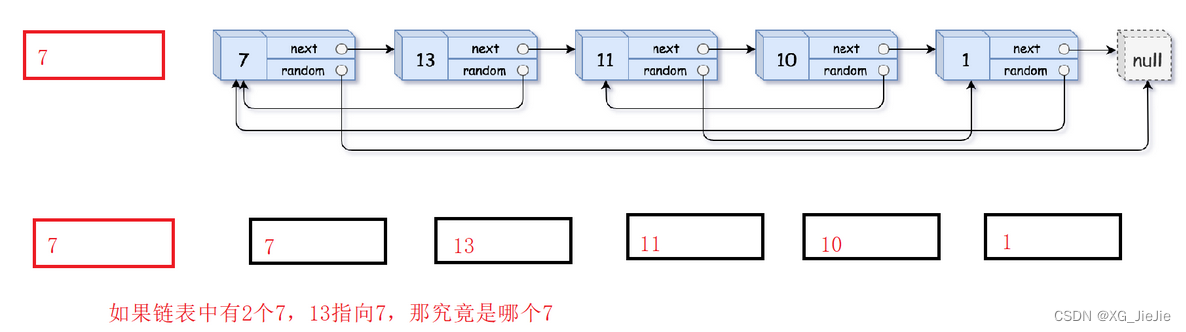
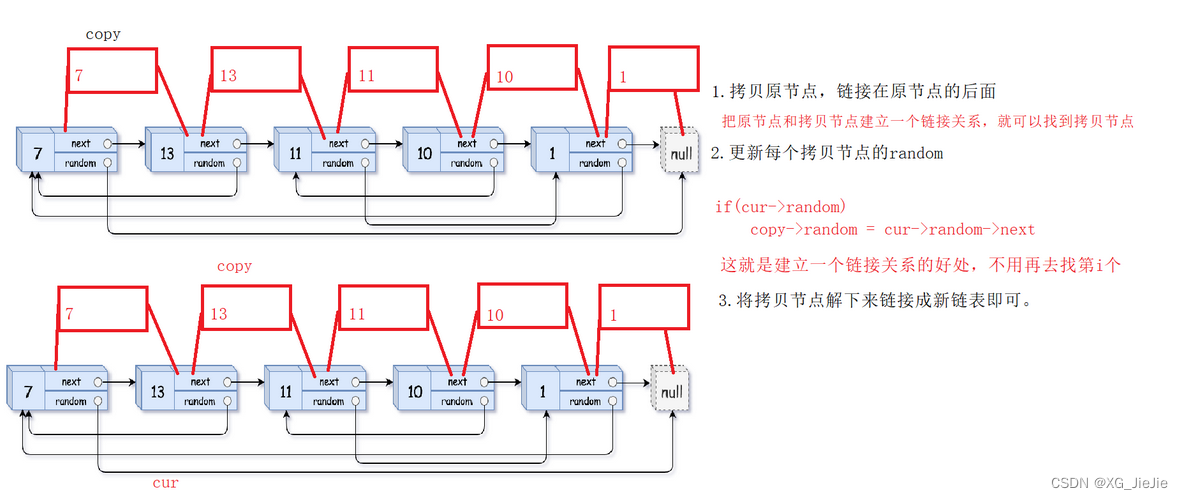
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) { //1.插入copy节点 struct Node* cur = head; struct Node* copy = NULL; struct Node* next = NULL; while(cur) { //赋值链接 next = cur->next; copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); copy->val = cur->val; cur->next = copy; copy->next = next; //迭代向后走 cur = next; } //2.更新copy的random cur = head; while(cur && cur->next) { copy = cur->next; if(cur->random == NULL) { copy->random = NULL; } else { copy->random = cur->random->next; } //迭代 cur = copy->next; } //3.copy节点剪下来链接到一起,恢复原链表 cur = head; struct Node* compHead = NULL, *copyTail = NULL; while(cur && cur->next) { copy = cur->next; next = copy->next; //取节点尾插 if(copyTail == NULL) { compHead = copyTail = copy; } else { copyTail->next = copy; copyTail = copyTail->next; } //恢复原链表链接 cur->next = next; //迭代 cur = copy->next; } //尾节点的next置NULL if(cur) cur->next = NULL; return compHead; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
-
相关阅读:
【webrtc】VCMSessionInfo 合并一个可解码的帧
Jenkins Manage and Assign Roles角色权限控制
c++网络编程
JavaScript --04. 流程控制语句介绍
Kasisto AI:金融对话人工智能
LeetCode每日一题——672. 灯泡开关 Ⅱ
C语言代码质量与架构调整(三)
基于51单片机音乐盒LCD1602显示( proteus仿真+程序+原理图+设计报告+讲解视频)
壳聚糖-聚乙二醇-炔基|炔基-PEG-壳聚糖|Chitosan-PEG-Alkyne
低成本、高效率!华为云桌面助力企业数字化转型
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jiejiezuishuai/article/details/126132606
