-
分布式session ——Spring Session原理、实战解决 子域之间的 session 共享问题、不同服务器 session 共享解决方案
一、分布式 session 的问题
解决方法直接看
实战:四- session 是将用户信息按键值对的方式存储到服务器中
- 在微服务情景下,不能跨不同域名共享
- 不同服务之间是不能共享 session 的
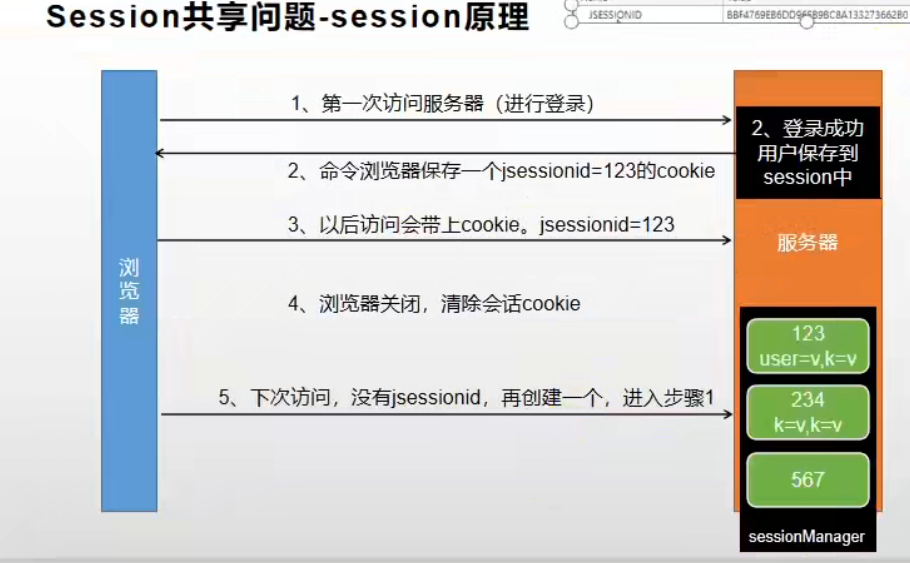
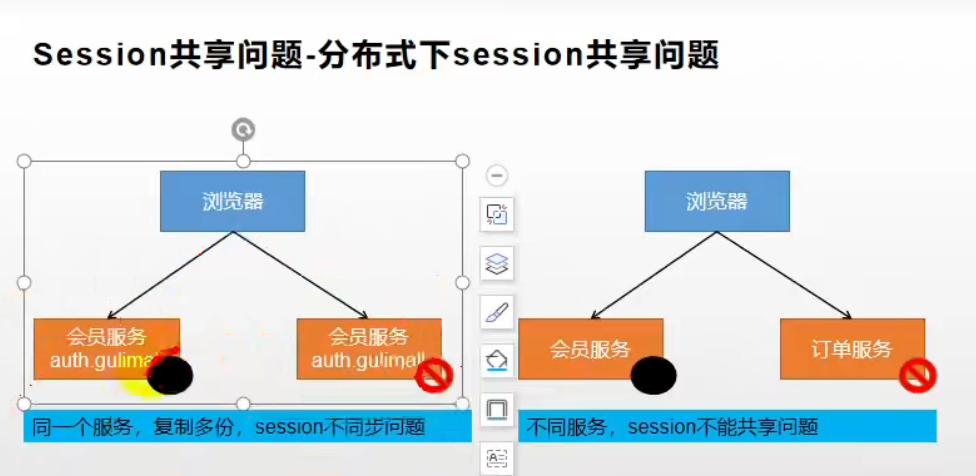
二、不同服务器 session 共享解决方案
1.session 复制
在大型项目中,一个 Tomcat 需要保存其他所有 Tomcat 的 session 数据,之间的来回复制占用资源,同时保存数据占用内存
适用场景:
- 小型项目,几个 Tomcat 服务器

2.客户端存储 session
不安全
使用场景:
- 无

3.hash一致性
根据用户访问的 ip 地址固定用户访问的服务器
适用场景:
- 基本适用各种需求
- 虽然横向扩展(增加服务器需要重新解决 ip 分配问题)会丢失数据,但是不是很影响,可以使用

4.统一存储(真正的解决方法)
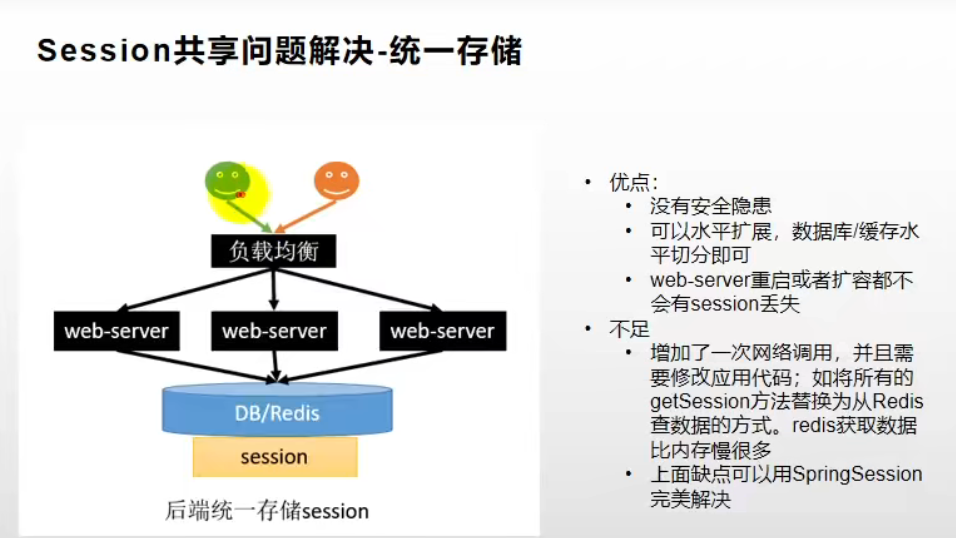
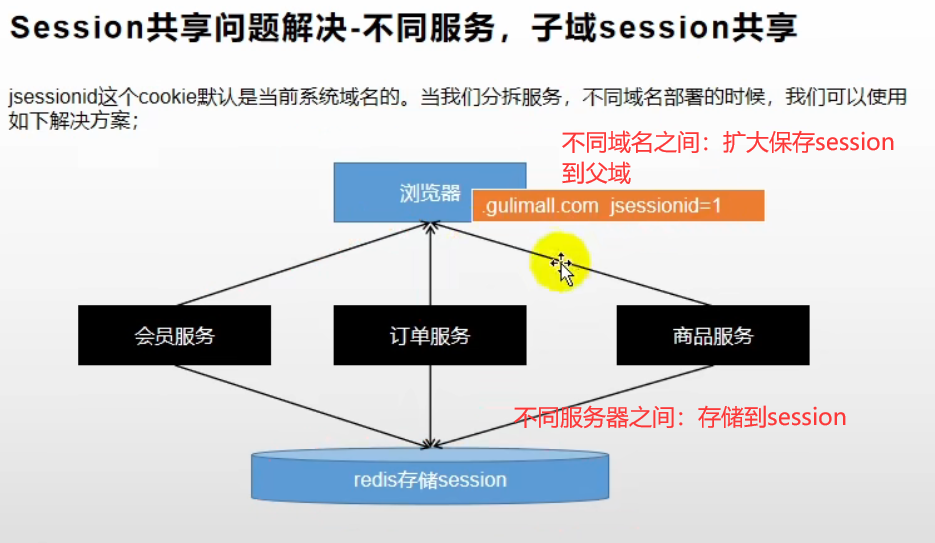
三、子域之间的 session 共享解决方案
- 第一次使用session的时候,浏览器会保存 JSESSIONID 这个 cookie
- 以后浏览器访问哪个子域就会带上这个网站的 cookie
解决方法:
- 在保存 session 的时候,即使在子域操作的,也保存在父域
使用SpringSession 解决以下两个问题
四、Spring Session 实战解决
Spring Session官网:Spring Session
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.sessiongroupId> <artifactId>spring-session-data-redisartifactId> dependency>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
配置:
spring.redis.host=192.168.137.128 spring.redis.port=6379 # session 存储方式 spring.session.store-type=redis # session 过期时间 server.servlet.session.timeout=30m # Spring Session 的刷新模式, # spring.session.redis.flush-mode=on_save # 命名空间 (默认 ‘spring:session ’) # spring.session.redis.namespace=spring:session- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
主类加上
@EnableRedisHttpSession注意:如果是以实体类的形式向 redis 存储 session,相关的实体类要实现序列化
implements Serializableredis 中 保存的 session
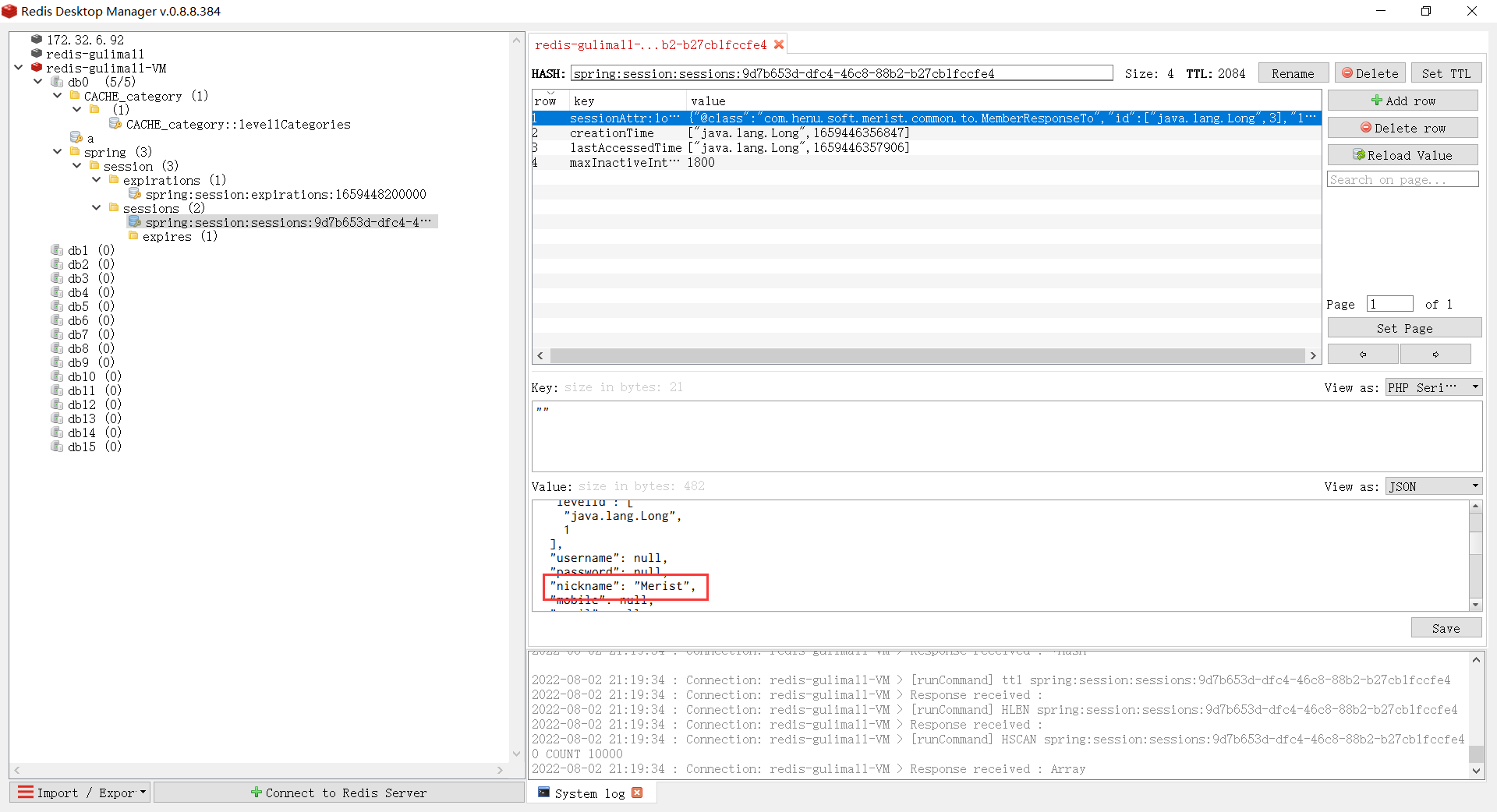
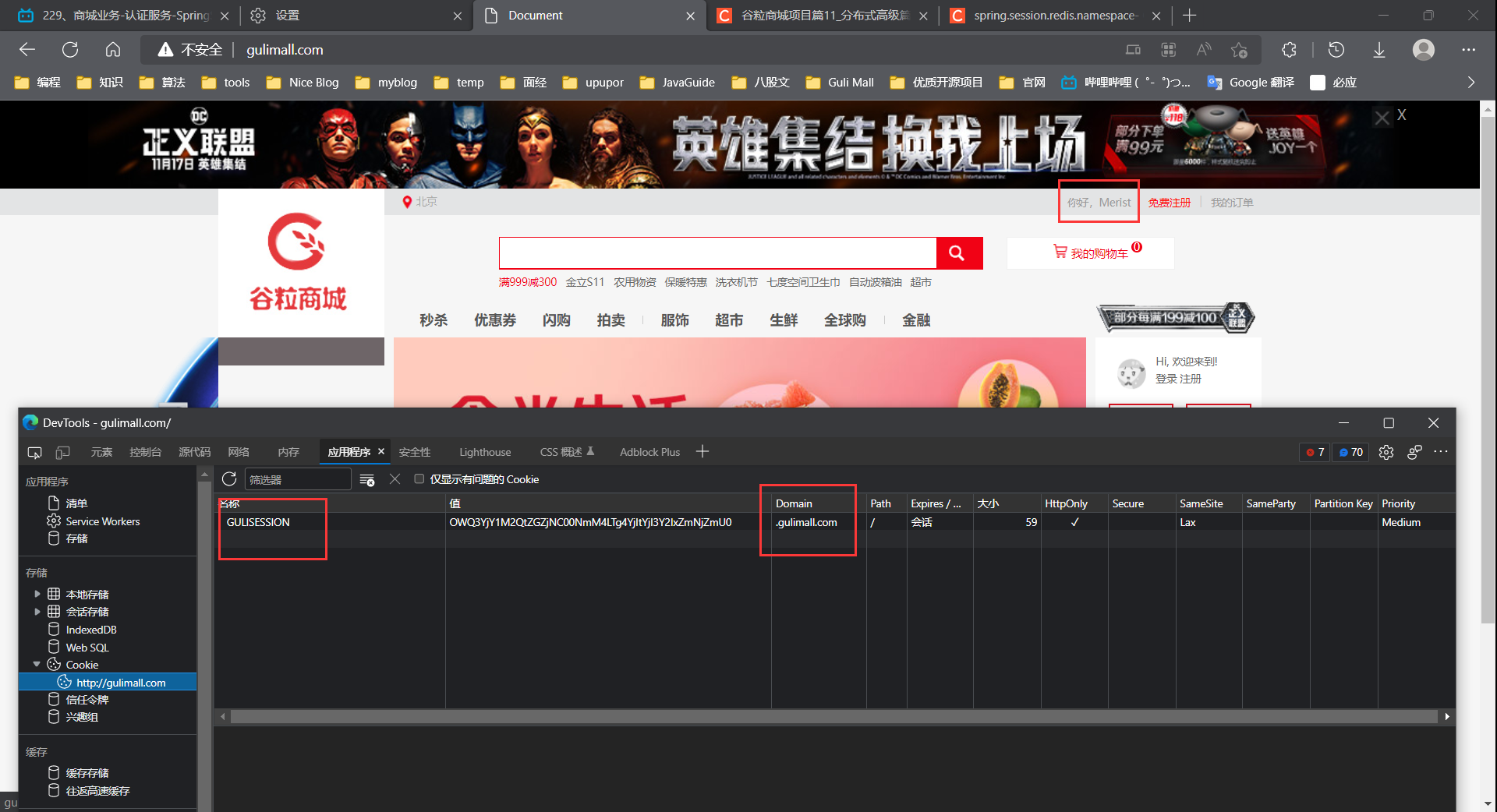
解决 session 共享域问题:
根据官方文档新建一个配置类来设置存储的 CookieName 以及 设置保存到父域
@Configuration public class MySessionConfig { @Bean public CookieSerializer cookieSerializer(){ DefaultCookieSerializer cookieSerializer = new DefaultCookieSerializer(); cookieSerializer.setDomainName("gulimall.com");//父域 cookieSerializer.setCookieName("GULISESSION");//cookie name return cookieSerializer; } @Bean public RedisSerializer<Object> springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer(){ return new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
五、Spring Session 原理
通过实战发现,Spring Session的实现非常简单,主要通过一个注解、一个配置类就可以解决分布式 session 的问题,接下来通过源码探究 Spring Session 的原理
1.注解
@EnableRedisHttpSession注解
@EnableRedisHttpSession默认了:-
在 redis 中的命名空间(spring:session)
-
默认的刷新模式为 ON_SAVE:
-
Spring Session 有两种刷新模式:
-
ON_SAVE:只有当 SessionRepository.save(Session)方法被调用时,才会将session中的数据同步到redis中。在web 应用中,当请求完成响应后,才开始同步。也就是说在执行response 之前session数据都是缓存在本地的.
-
IMMEDIATE:实时同步session 数据到redis。当执行 SessionRepository.createSession()时, 会将session数据同步到redis中;当对 session的attribute进行set/remove 等操作时,也会同步session中的数据到redis中
-
@Deprecated public enum RedisFlushMode { ON_SAVE(FlushMode.ON_SAVE), IMMEDIATE(FlushMode.IMMEDIATE); private final FlushMode flushMode; private RedisFlushMode(FlushMode flushMode) { this.flushMode = flushMode; } public FlushMode getFlushMode() { return this.flushMode; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
-
-
-
默认的保存模式为 ON_SET_ATTRIBUTE:
-
public enum SaveMode { ON_SET_ATTRIBUTE, ON_GET_ATTRIBUTE, ALWAYS; private SaveMode() { } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
-
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by FernFlower decompiler) // package org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import; import org.springframework.session.FlushMode; import org.springframework.session.SaveMode; import org.springframework.session.data.redis.RedisFlushMode; @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Documented @Import({RedisHttpSessionConfiguration.class}) @Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) public @interface EnableRedisHttpSession { int maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds() default 1800; String redisNamespace() default "spring:session"; /** @deprecated */ @Deprecated RedisFlushMode redisFlushMode() default RedisFlushMode.ON_SAVE; FlushMode flushMode() default FlushMode.ON_SAVE; String cleanupCron() default "0 * * * * *"; SaveMode saveMode() default SaveMode.ON_SET_ATTRIBUTE; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
2.
RedisHttpSessionConfiguration配置类在注解
@EnableRedisHttpSession中导入了RedisHttpSessionConfiguration配置类其中又注册了一个
RedisIndexedSessionRepository组件,这个组件主要包括 在 redis 中对 session CRUD的封装类,以及一些默认的配置,如序列化配置、刷新模式等,等会我们可以自定义覆盖配置[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mCvlvbdn-1659493462963)(C:\Users\10418\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220803093946245.png)]
RedisIndexedSessionRepository相当于redis 中 session 的仓库,包含了一系列CRUD的操作。(后面还有仓库的过滤器)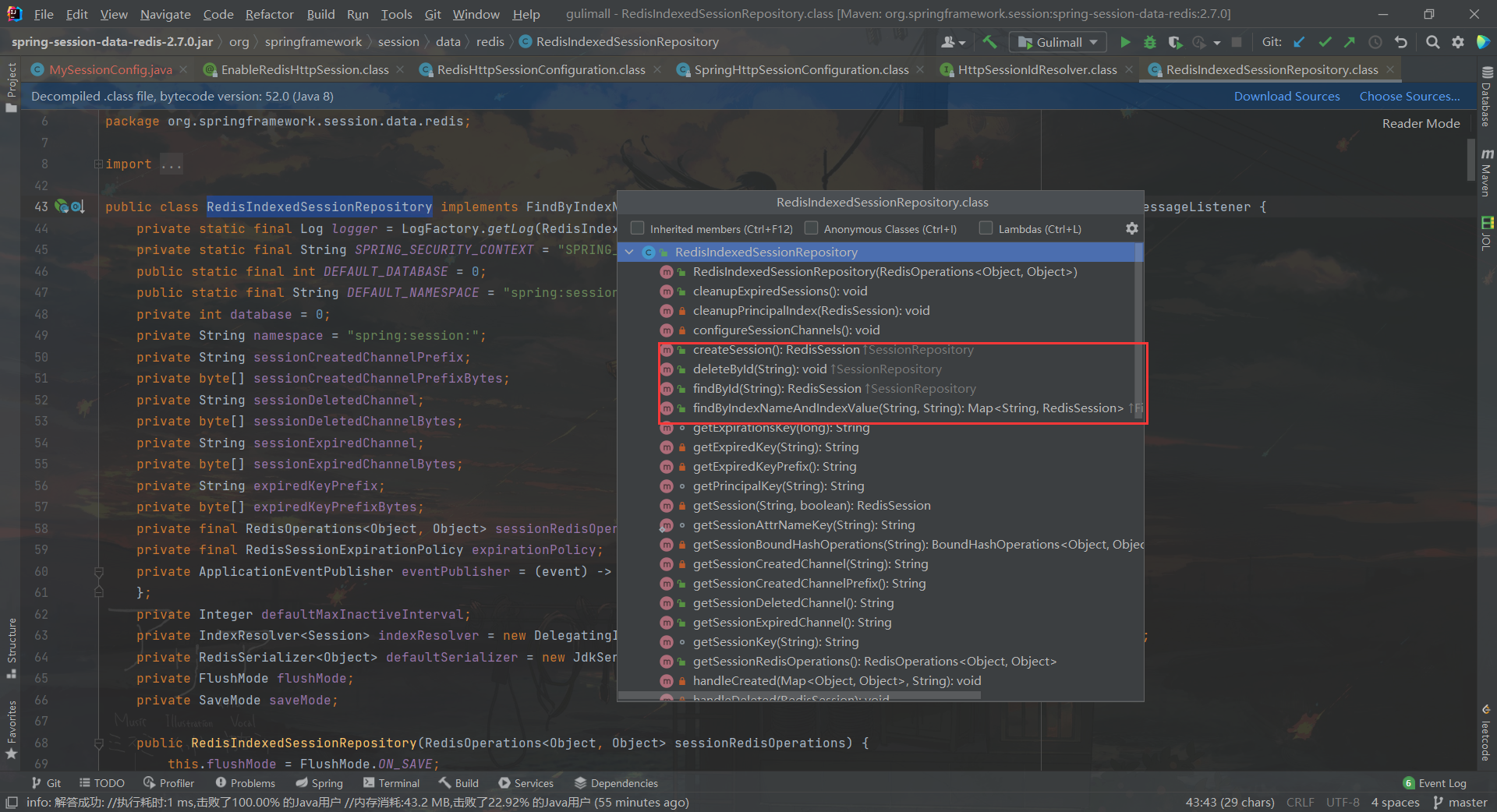
同时
RedisHttpSessionConfiguration又继承了SpringHttpSessionConfiguration配置类3.
SpringHttpSessionConfiguration配置类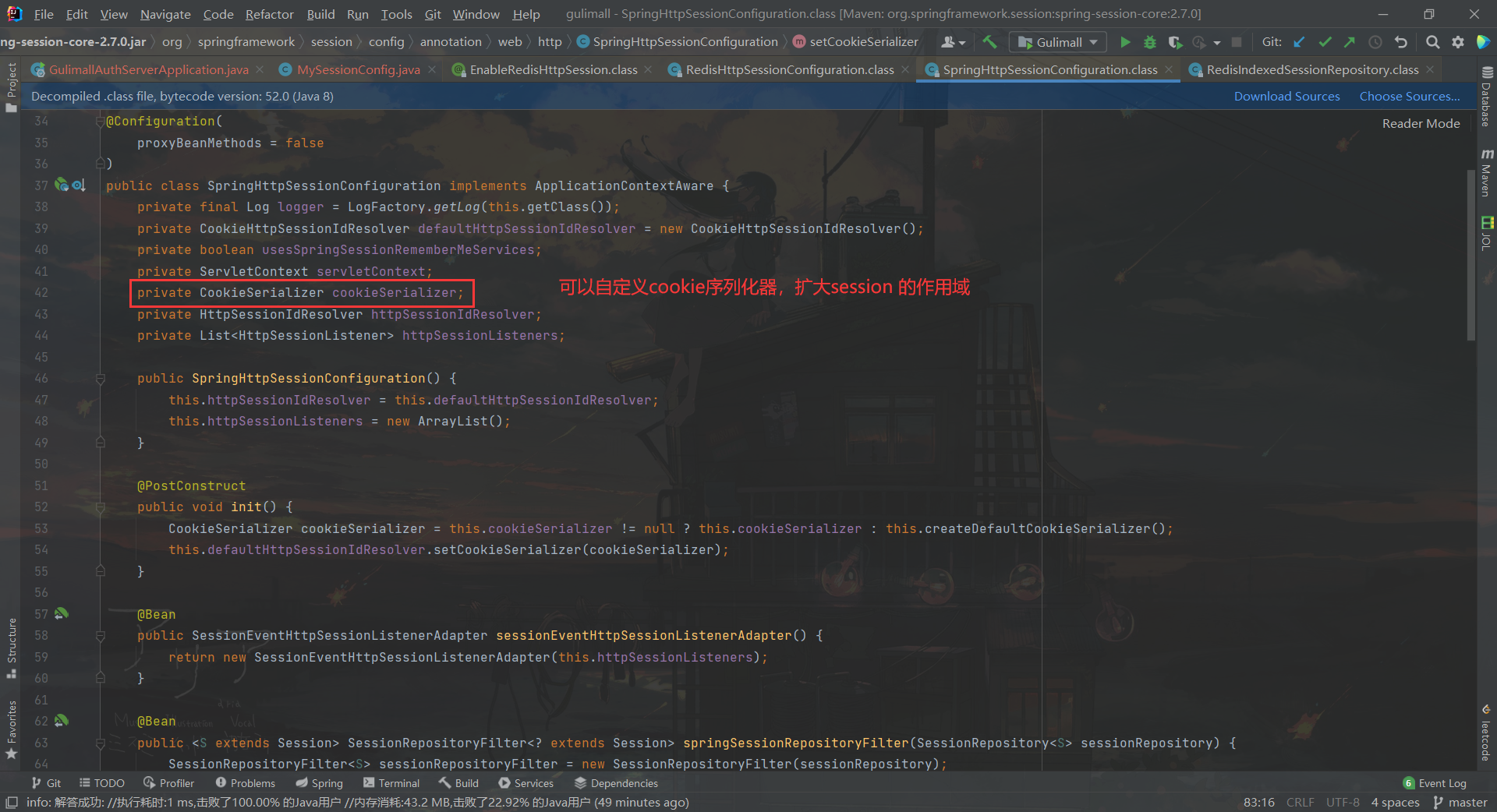
自定义序列化器,扩大 session 作用域,解决子域session 不共享问题:
@Configuration public class MySessionConfig { /** * 配置session 的一些信息 * @return */ @Bean public CookieSerializer cookieSerializer(){ DefaultCookieSerializer cookieSerializer = new DefaultCookieSerializer(); cookieSerializer.setDomainName("gulimall.com");//父域 cookieSerializer.setCookieName("GULISESSION");//cookie name return cookieSerializer; } /** * 序列化方式 * @return */ @Bean public RedisSerializer<Object> springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer(){ return new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
SessionRepositoryFilter过滤器,前面提到的仓库的过滤器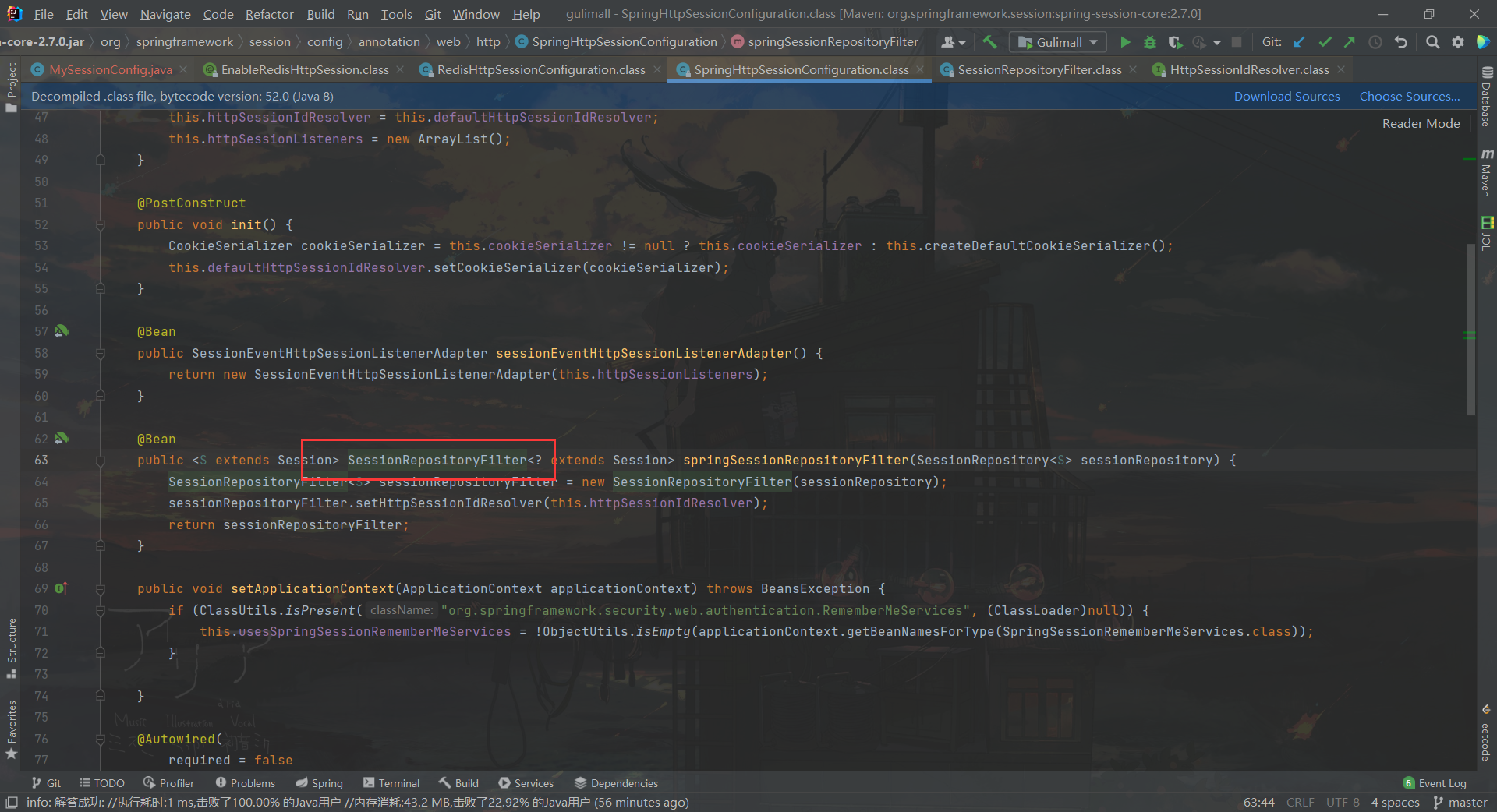
3.
SessionRepositoryFilter仓库过滤器
核心:
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException { //一次请求中的所有 session 的CRUD操作,都是在这一个 sessionRepository request.setAttribute(SESSION_REPOSITORY_ATTR, this.sessionRepository); //对原生的 HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse 进行包装=》SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper、SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper SessionRepositoryFilter<S>.SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper wrappedRequest = new SessionRepositoryFilter.SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper(request, response); SessionRepositoryFilter.SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper wrappedResponse = new SessionRepositoryFilter.SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper(wrappedRequest, response); try { //将包装后的wrappedRequest、wrappedResponse 执行过滤链 filterChain.doFilter(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse); } finally { wrappedRequest.commitSession(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
包装成
SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper、SessionRepositoryResponseWrapper的目的是为了将整个操作包括 获取session(getSession())的的操作都在RedisIndexedSessionRepository中执行原生的 session 获取方法:
HttpServletRequest request = new HttpServletRequest(); HttpSession session1 = request.getSession()- 1
- 2
从
RedisIndexedSessionRepository中获取session,也就是存到redis中的session
public SessionRepositoryFilter<S>.SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.HttpSessionWrapper getSession(boolean create) { SessionRepositoryFilter<S>.SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.HttpSessionWrapper currentSession = this.getCurrentSession(); if (currentSession != null) { return currentSession; } else { S requestedSession = this.getRequestedSession(); if (requestedSession != null) { if (this.getAttribute(SessionRepositoryFilter.INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR) == null) { requestedSession.setLastAccessedTime(Instant.now()); this.requestedSessionIdValid = true; currentSession = new SessionRepositoryFilter.SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.HttpSessionWrapper(requestedSession, this.getServletContext()); currentSession.markNotNew(); this.setCurrentSession(currentSession); return currentSession; } } else { if (SessionRepositoryFilter.SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { SessionRepositoryFilter.SESSION_LOGGER.debug("No session found by id: Caching result for getSession(false) for this HttpServletRequest."); } this.setAttribute(SessionRepositoryFilter.INVALID_SESSION_ID_ATTR, "true"); } if (!create) { return null; } else if (SessionRepositoryFilter.this.httpSessionIdResolver instanceof CookieHttpSessionIdResolver && this.response.isCommitted()) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot create a session after the response has been committed"); } else { if (SessionRepositoryFilter.SESSION_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { SessionRepositoryFilter.SESSION_LOGGER.debug("A new session was created. To help you troubleshoot where the session was created we provided a StackTrace (this is not an error). You can prevent this from appearing by disabling DEBUG logging for " + SessionRepositoryFilter.SESSION_LOGGER_NAME, new RuntimeException("For debugging purposes only (not an error)")); } S session = SessionRepositoryFilter.this.sessionRepository.createSession(); session.setLastAccessedTime(Instant.now()); currentSession = new SessionRepositoryFilter.SessionRepositoryRequestWrapper.HttpSessionWrapper(session, this.getServletContext()); this.setCurrentSession(currentSession); return currentSession; } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
-
相关阅读:
un7.27:redis数据库常用命令。
如何保障需求质量(下):你应该做到的
RL 基础 | Policy Gradient 的推导
[Mybatis-Plus笔记] MybatisPlus-03-QueryWrapper条件构造器
特征交叉系列:FM和深度神经网络的结合,DeepFM原理简述和实践
MathType需要安装一个较新版本的MT Extra(TrueType)字体解决办法
OV5640的参数与配置方法
视频监控/视频汇聚/安防视频监控平台EasyCVR配置集群后有一台显示离线是什么原因?
生产环境java程序存活监测脚本
React源码分析2-深入理解fiber
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52476654/article/details/126130668
