-
Vue中的Pinia状态管理工具 | 一篇文章教会你全部使用细节
Pinia状态管理
Pinia和Vuex的对比
Pinia(发音为/piːnjʌ/,如英语中的“peenya”)是最接近piña(西班牙语中的菠萝)的词;
Pinia开始于大概2019年,最初是
作为一个实验为Vue重新设计状态管理,让它用起来适合组合式API(Composition API)。从那时到现在,最初的设计原则依然是相同的,并且目前同时兼容Vue2、Vue3,也并不要求你使用Composition API;
Pinia本质上依然是一个状态管理的库,用于
跨组件、页面进行状态共享(这点和Vuex、Redux一样);那么我们不是已经有Vuex了吗?为什么还要用Pinia呢?
Pinia 最初是为了探索 Vuex 的下一次迭代会是什么样子,结合了 Vuex 5 核心团队讨论中的许多想法;
最终,团队意识到Pinia已经实现了Vuex5中大部分内容,所以最终决定用Pinia来替代Vuex;
与 Vuex 相比,Pinia 提供了一个更简单的 API,具有更少的仪式,
提供了 Composition-API 风格的 API;最重要的是,在与 TypeScript 一起使用时具有可靠的类型推断支持;
和Vuex相比,Pinia有很多的优势:
优势一: mutations 不再存在:
- 他们经常被认为是非常冗长;
- 他们最初带来了 devtools 集成,但这不再是问题;
优势二: 更友好的TypeScript支持,Vuex之前对TS的支持很不友好;
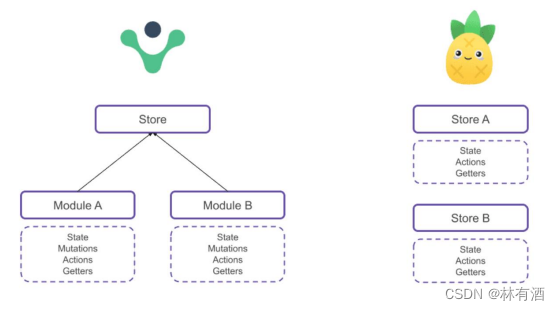
优势三: 不再有modules的嵌套结构:
- 你可以灵活使用每一个store,它们是通过扁平化的方式来相互使用的;
优势四: 也不再有命名空间的概念,不需要记住它们的复杂关系;
Pinia基本使用
🍤创建Pinia
使用Pinia之前,我们需要先对其进行安装:
yarn add pinianpm install pinia使用pinia我们需要在单独的js文件中创建一个pinia, 并且在main.js中将其注册, 如下:
这样我们项目中就已经存在pinia了
import { createPinia } from "pinia"; // 创建pinia const pinia = createPinia() // 导出pinia export default pinia- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
import { createApp } from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' // 导入pinia import pinia from './stores' const app = createApp(App) // 注册pinia app.use(pinia) app.mount('#app')- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
🍤创建Store
什么是Store?
一个 Store (如 Pinia)是一个实体,它会持有为绑定到你组件树的状态和业务逻辑,也就是保存了全局的状态;
它有点像始终存在,并且每个人都可以读取和写入的组件;
你可以在你的应用程序中定义
任意数量的Store来管理你的状态;Store有三个核心概念(接下来会一一讲到):
state、getters、actions;
等同于组件的data、computed、methods;
一旦 store 被实例化,你就
可以直接在 store 上访问 state、getters 和 actions 中定义的任何属性;定义一个Store:
Store 是使用 defineStore() 定义的, 我们一般都会在一个单独的js的文件创建store, 不同组件的数据, 我们会定义在不同的js文件中创建不同的store
由于pinia中可以定义多个store, 所以每一个store它都需要一个
唯一名称,作为第一个参数传递;// 定义关于counter的store import { defineStore } from "pinia" // 调用defineStore定义store, defineStore返回一个函数 const useCounter = defineStore("counter", { state: () => ({ counter: 101 }) }) // 将useCounter函数导出 export default useCounter- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
第一个参数 name,也称为 id,
是必要的,Pinia 使用它来将 store 连接到 devtools。defineStore()返回的函数统一使用
useXXX作为命名方案, 且XXX一般就使用传入的id,这是约定的规范;调用defineStore()返回的函数才会创建store
Store在它被使用之前是不会创建的,我们可以通过调用use函数来使用Store:
<template> <h2>{{ counterStore.counter }}h2> template> <script setup> // 导入我们自定义关于counter的store import useCounter from '../stores/counter'; // 调用函数才会创建store, 不调用不会创建 const counterStore = useCounter() script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
注意Store获取到后, 如果我们想要对其解构, 不能直接解构,直接解构的话会失去响应式:
为了从 Store 中提取属性同时保持其响应式我们有两种方式
-
方式一: 解构时包裹一层toRefs
-
方式二: pinia给我们提供了一个方法, 使用
storeToRefs()方法可以保持数据的响应式。
方式一
<script setup> import { toRefs } from 'vue'; import useCounter from '../stores/counter'; const counterStore = useCounter() // 包裹一层toRefs const { counter } = toRefs(counterStore) </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
方式二
<script setup> import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; import useCounter from '../stores/counter'; const counterStore = useCounter() // 包裹一层storeToRefs const { counter } = storeToRefs(counterStore) </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Pinia核心概念State
🍟state基本使用
state 是 store 的核心部分,因为store是用来帮助我们管理状态的。
在 Pinia 中,状态被定义为返回初始状态的函数;
前面我们创建了一个counter.js文件用于定义counter的store, 接下来我们创建一个urse.js文件, 定义一个用户信息的store来演示state
在pinia中state和vuex中一样, state是一个函数, 返回一个对象
import { defineStore } from "pinia" const useUser = defineStore("user", { // state定义状态 state: () => ({ name: "chenyq", age: 18, height: 1.88 }) }) export default useUser- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
将定义的Store展示到组件中
<template> <div class="home"> <h2>{{ name }}h2> <h2>{{ age }}h2> <h2>{{ height }}h2> div> template> <script setup> import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; // 导入我们自定义的store import useUser from "../stores/user" // 调用函数创建store const userStore = useUser() // 将store中的状态解构出来 const { name, age, height } = storeToRefs(userStore) script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
🍟state其他操作
读取和写入 state
默认情况下,您可以通过 store 实例访问状态来直接读取, 刚刚我们就是这样读取状态的
写入状态其实也同理, 通过store实例访问状态直接修改
<template> <div class="home"> <h2>{{ name }}h2> <h2>{{ age }}h2> <h2>{{ height }}h2> <button @click="changeInfo">修改信息button> div> template> <script setup> import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; import useUser from "../stores/user" const userStore = useUser() const { name, age, height } = storeToRefs(userStore) function changeInfo() { // 使用实例访问状态, 进行修改 userStore.name = "王老五" userStore.age = 20 userStore.height = 1.89 } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
重置 State
当我们对某些状态进行了修改之后, 我们可以通过调用 store 上的 $reset() 方法将状态
重置到其初始值;$reset()方法会将所有的状态重置到初始值
<template> <div class="home"> <h2>{{ name }}h2> <h2>{{ age }}h2> <h2>{{ height }}h2> <button @click="changeInfo">修改信息button> <button @click="resetInfo">重置信息button> div> template> <script setup> import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; import useUser from "../stores/user" const userStore = useUser() const { name, age, height } = storeToRefs(userStore) function changeInfo() { userStore.name = "王老五" userStore.age = 20 userStore.height = 1.89 } function resetInfo() { // 重置状态 userStore.$reset() } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
同时修改多个状态
可以调用 $patch 方法 , 它允许您使用部分“state”对象同时应用多个更改;
<template> <div class="home"> <h2>{{ name }}h2> <h2>{{ age }}h2> <h2>{{ height }}h2> <button @click="changeInfo">修改信息button> div> template> <script setup> import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'; import useUser from "../stores/user" const userStore = useUser() const { name, age, height } = storeToRefs(userStore) function changeInfo() { // $patch一次性修改多个状态 userStore.$patch({ name: "罗三炮", age: 50, height: 1.58 }) } script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
Pinia核心Getters
🍕getters基本使用
Getters相当于Store的计算属性:
它们可以用 defineStore() 中的 getters 属性定义;
getters中可以定义接受一个state作为参数的函数;
- 在defineStore中定义getters
import { defineStore } from "pinia" const useCounter = defineStore("counter", { state: () => ({ counter: 101 }), // 定义getters getters: { doubleCounter(state) { return state.counter * 2 } } }) export default useCounter- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 直接通过store对象就可以访问当前store的Getters
<template> <h2>{{ counterStore.doubleCounter }}h2> template> <script setup> import useCounter from "../stores/counter" const counterStore = useCounter() script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
🍕getters其他操作
Getters中访问自己的其他Getters
我们可以通过
this来访问到当前store实例的所有其他属性;this相当于是绑定的store实例
- 例如在getter中访问自己的doubleCounter
getters: { doubleCounter(state) { return state.counter * 2 }, doubleCounterAddOne() { return this.doubleCounter + 1 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Getters也可以返回一个函数,这样就可以接受参数:
const useCounter = defineStore("counter", { state: () => ({ counter: 101, friend: [ {id: 111, name: "chenyq"}, {id: 112, name: "王老五"}, {id: 113, name: "罗三炮"}, ] }), getters: { // getter可以返回一个函数 getfriendById() { return (id) => { return this.friend.find(item => item.id == id) } } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
<h2>{{ counterStore.getfriendById(111) }}h2> <h2>{{ counterStore.getfriendById(112) }}h2>- 1
- 2
当前Getters访问其他store中的state/getters
// 导入usrUser import useUser from "./user" const useCounter = defineStore("counter", { state: () => ({ counter: 101 }), getters: { showMessage(state) { // 拿到userStore对象, 获取userStore中的信息 const userStore = useUser() // 返回自己store的信息拼接上userStore中的信息 return `${state.counter}${userStore.name}` } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
<h2>{{ counterStore.showMessage }}h2>- 1
Pinia核心Actions
🥧Actions基本使用
Actions 相当于组件中的 methods。
可以使用 defineStore() 中的 actions 属性定义,并且它们非常适合定义业务逻辑;
和getters一样,在action中可以通过
this访问整个store实例的所有操作;const useCounter = defineStore("counter", { state: () => ({ counter: 101 }), actions: { increment() { this.counter++ } } })- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
<h2>{{ counterStore.counter }}</h2> <button @click="changeState">+1</button> <script setup> import useCounter from "../stores/counter" const counterStore = useCounter() function changeState() { // 通过store实例调用即可 counterStore.increment() } </script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
🥧Actions异步操作
Actions中是支持异步操作的,并且我们可以编写异步函数,在函数中使用await
例如在Actions发生网络请求
import { defineStore } from 'pinia' const useHome = defineStore("home", { state: () => ({ // 定义空数组用于接收网络请求数据 banners: [], recommends: [] }), actions: { // 支持异步操作 async fetchHomeMultidata() { // 发送网络请求获取数据 const res = await fetch("http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata") const data = await res.json() // 将获取的数据添加到state中 this.banners = data.data.banner.list this.recommends = data.data.recommend.list } } }) export default useHome- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
展示网络请求获取到homeStore中的数据
<template> <div class="about"> <ul v-for="item in homeStore.banners" :key="item.acm"> <li>{{ item.title }}li> ul> div> template> <script setup> import useHome from "../stores/home" const homeStore = useHome() // 告知发送网络请求 homeStore.fetchHomeMultidata() script>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
-
相关阅读:
MyBatisPlus(十七)通用枚举
移相全桥DCDC通过Simulink扫频得到其传递函数方法及(非m脚本)
【2023年11月第四版教材】第18章《项目绩效域》(合集篇)
ASP.NET Core的几种服务器类型[共6篇]
开环和闭环是什么意思?
使用IntelliJ Idea必备的插件!
RabbitMQ快速入门--simple简单模式
【LeetCode与《代码随想录》】数组篇:做题笔记与总结-JavaScript版
抽象类和接口
记一次由于google新版本限制升级导致的跨域问题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_71485750/article/details/125982691
