-
基于Keras搭建LSTM网络实现文本情感分类
基于Keras搭建LSTM网络实现文本情感分类
版本在jupyter notbook中执行
import keras as ks import tensorflow as tf print(ks.__version__) print(tf.__version__)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
2.3.1
2.0.0一、语料概况
本次项目主要以电商网站下的用户评论数据作为实验数据集,数据集已经做好了标注。其中该数据集一共有4310条评论数据,文本的情感分为两类:“正面”和“反面”
其中evaluation为评论内容,label为情感倾向。
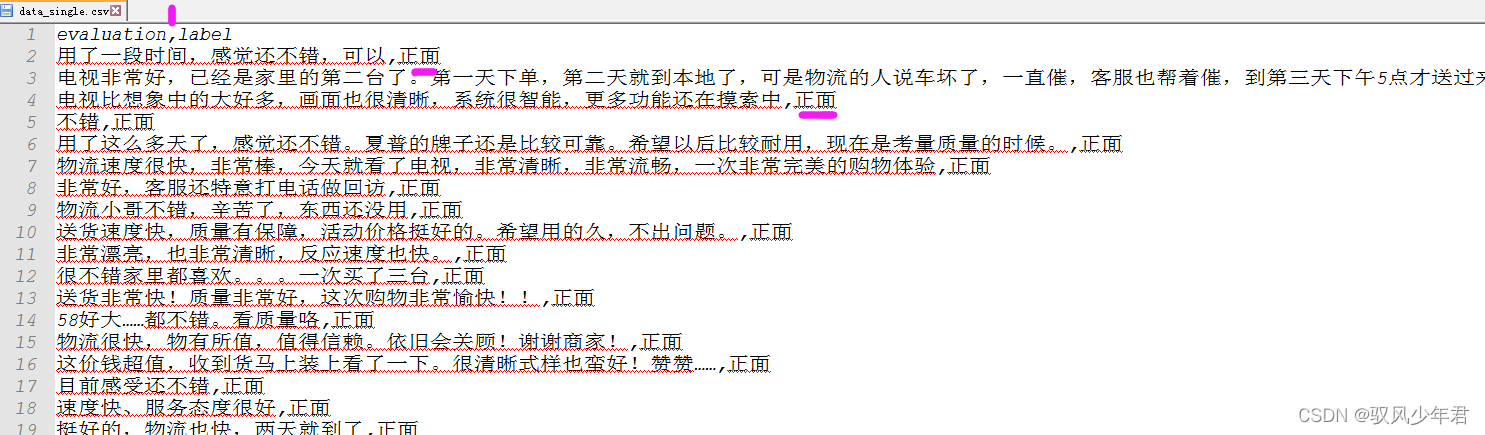
1.1 数据统计
先整体查看不同类别下的样本均衡情况,样本的不均衡会影响模型的分类效果
导入相应的库
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import font_manager from itertools import accumulate plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] #图中文字体设置为黑体- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
1.1.1 查看样本均衡情况,对label进行统计
df = pd.read_csv('./data_single.csv') print(df.groupby('label')['label'].count())- 1
- 2
label 正面 1908 负面 2375 Name: label, dtype: int64- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
整体来看样本还算均衡,正面1908条,负面2375条。可以达到需求了
深度学习中需要定义文本的最长长度,大于该长度就需要将文本切割,不够就填充0处理,所以还是需要整体统计出样本大致的文本长度分布。、
1.1.2 计句子长度及长度出现的频数
先计算句子的长度,在对句子的长度进行分组统计分析,看下不同长度下一共有几个样本
df[:30] df[:30].groupby('length').count()- 1
- 2
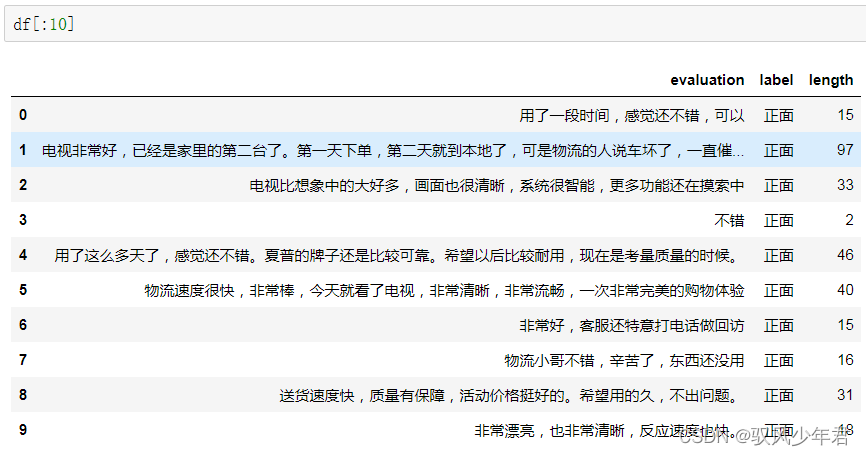
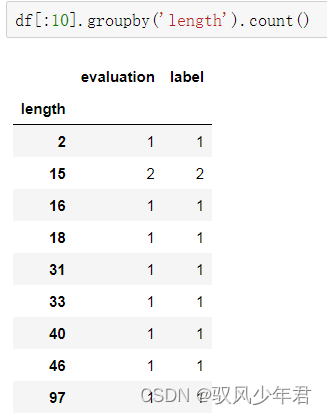
可以看出长度15的有两个,length是句子长度,evaluation代表该长度下有几个样本,根据这两个值就可以画图了
df['length'] = df['evaluation'].apply(lambda x: len(x)) len_df = df.groupby('length').count() sent_length = len_df.index.tolist() sent_freq = len_df['evaluation'].tolist()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
获取数据中样本的所有长度sent_length,和该长度下sent_freq的样本数量绘图
# 绘制句子长度及出现频数统计图 plt.figure(figsize=(10,12)) plt.bar(sent_length, sent_freq,2) plt.title("句子长度及出现频数统计图", ) plt.xlabel("句子长度") plt.ylabel("句子长度出现的频数") plt.savefig("./句子长度及出现频数统计图.png") plt.show- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
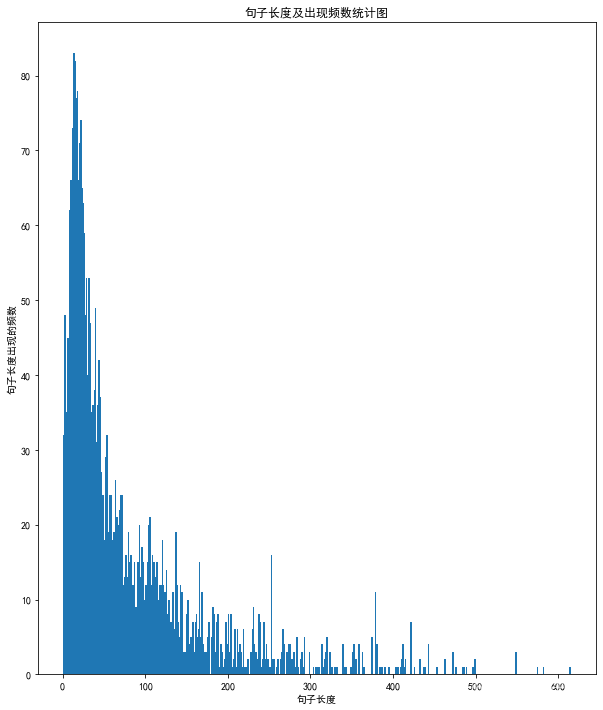
大部分长度在20左右。
1.1.3 绘制句子长度累积分布函数(CDF)
到句子累加到90%的时候,返回其对应长度值
### 绘制句子长度累积分布函数(CDF) sent_pentage_list = [(count/sum(sent_freq)) for count in accumulate(sent_freq)] plt.figure(figsize=(10,12)) # 绘制CDF plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list) # 寻找分位点为quantile的句子长度 quantile = 0.90 for length, per in zip(sent_length, sent_pentage_list): if round(per, 2) == quantile: index = length break print("\n分位点为%s的句子长度:%d." % (quantile, index)) # 绘制句子长度累积分布函数图 plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list,linewidth=4) plt.hlines(quantile, 0, index, colors="c", linestyles="dashed",linewidth=4) plt.vlines(index, 0, quantile, colors="c", linestyles="dashed",linewidth=4) plt.text(0, quantile, str(quantile),fontsize=10) plt.text(index, 0, str(index)) plt.title("句子长度累积分布函数图",fontsize=20) plt.xlabel("句子长度",fontsize=15) plt.ylabel("句子长度累积频率",fontsize=15) plt.savefig("./句子长度累积分布函数图.png") plt.show- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
分位点为0.9的句子长度:172.
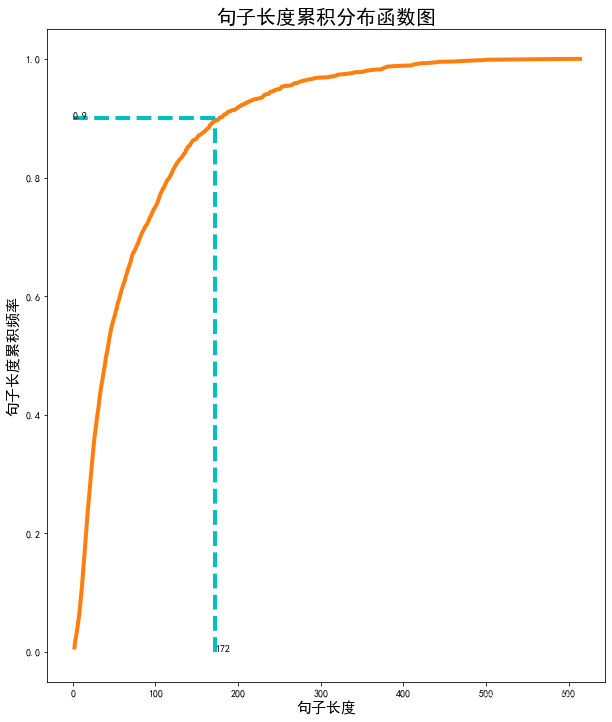
大多数样本的句子长度集中在1-200之间,句子长度累计频率取0.90分位点,则长度为172左右。
二、LSTM模型构建与评估
LSTM模型架构

导库import pickle import numpy as np import pandas as pd from keras.utils import np_utils, plot_model from keras.models import Sequential from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Embedding, Dropout from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
2.1 数据导入预处理
filepath = 'data_single.csv' #数据 input_shape = 180 #设置长度 model_save_path = 'corpus_model.h5' #模型保存位置 df = pd.read_csv(filepath) df.head()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
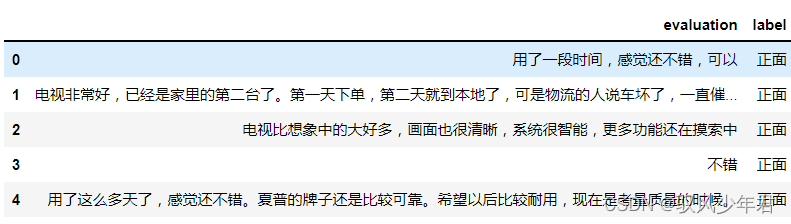
2.1.1 获取标签和字符字典列表
取出标签,和数据;再去重。
# 标签及词汇表 labels, vocabulary = list(df['label'].unique()), list(df['evaluation'].unique()) labels- 1
- 2
- 3
[‘正面’, ‘负面’]
vocabulary- 1
[‘用了一段时间,感觉还不错,可以’,
‘电视非常好,已经是家里的第二台了。第一天下单,第二天就到本地了,可是物流的人说车坏了,一直催,客服也帮着催,到第三天下午5点才送过来。父母年纪大了,买个大电视画面清晰,趁着耳朵还好使,享受几年。’,
‘电视比想象中的大好多,画面也很清晰,系统很智能,更多功能还在摸索中’,
‘不错’,
‘用了这么多天了,感觉还不错。夏普的牌子还是比较可靠。希望以后比较耐用,现在是考量质量的时候。’,
‘物流速度很快,非常棒,今天就看了电视,非常清晰,非常流畅,一次非常完美的购物体验’,
‘非常好,客服还特意打电话做回访’,
‘物流小哥不错,辛苦了,东西还没用’,
‘送货速度快,质量有保障,活动价格挺好的。希望用的久,不出问题。’,
‘非常漂亮,也非常清晰,反应速度也快。’,
‘很不错家里都喜欢。。。一次买了三台’,
‘送货非常快!质量非常好,这次购物非常愉快!!’,
‘58好大……都不错。看质量咯’,
‘物流很快,物有所值,值得信赖。依旧会关顾!谢谢商家!’,
‘这价钱超值,收到货马上装上看了一下。很清晰式样也蛮好!赞赞……’,构建每个字符,去重后的集合。
# 构造字符级别的特征 string = '' for word in vocabulary: # print(word) string += word vocabulary = set(string) print(vocabulary) print(len(vocabulary))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

2154一共有2154个词,2个类别
对每个字符都进行编码
word_dictionary = {word: i+1 for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)} word_dictionary- 1
- 2

获取反转的字符编码inverse_word_dictionary = {i+1: word for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)} inverse_word_dictionary- 1
- 2

设置词汇表大小,标签类别数量
vocab_size = len(word_dictionary.keys()) # 词汇表大小 label_size = len(label_dictionary.keys()) # 标签类别数量- 1
- 2
2.1.2 将文本和类别编码
将文本按照字典进行编码
x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent] for sent in df['evaluation']] x- 1
- 2

编码后,还需要切割填充,网络对于每一个样本数据的特征长度要求都是一致的
x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0) x- 1
- 2
array([[1460, 325, 641, …, 0, 0, 0],
[1902, 2024, 905, …, 0, 0, 0],
[1902, 2024, 2023, …, 0, 0, 0],
…,
[ 641, 703, 868, …, 0, 0, 0],
[ 633, 1902, 2024, …, 0, 0, 0],
[ 641, 1233, 1233, …, 0, 0, 0]])类别需要编码成0,1的one_hot编码
y = [[label_dictionary[sent]] for sent in df['label']] y- 1
- 2
[[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],
[0],转为one_hot编码
y = [np_utils.to_categorical(label, num_classes=label_size) for label in y] y- 1
- 2
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),
array([[1., 0.]], dtype=float32),转为标准化的输入
y = np.array([list(_[0]) for _ in y]) y- 1
- 2
array([[1., 0.],
[1., 0.],
[1., 0.],
…,
[0., 1.],
[0., 1.],
[0., 1.]], dtype=float32)封装成函数,将字典保存下来
设置默认shape为20
# 导入数据 # 文件的数据中,特征为evaluation, 类别为label. def load_data(filepath, input_shape=20): df = pd.read_csv(filepath) # 标签及词汇表 labels, vocabulary = list(df['label'].unique()), list(df['evaluation'].unique()) # 构造字符级别的特征 string = '' for word in vocabulary: string += word vocabulary = set(string) # 字典列表 word_dictionary = {word: i+1 for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)} with open('word_dict.pk', 'wb') as f: pickle.dump(word_dictionary, f) inverse_word_dictionary = {i+1: word for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)} label_dictionary = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(labels)} with open('label_dict.pk', 'wb') as f: pickle.dump(label_dictionary, f) output_dictionary = {i: labels for i, labels in enumerate(labels)} vocab_size = len(word_dictionary.keys()) # 词汇表大小 label_size = len(label_dictionary.keys()) # 标签类别数量 # 序列填充,按input_shape填充,长度不足的按0补充 x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent] for sent in df['evaluation']] x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0) y = [[label_dictionary[sent]] for sent in df['label']] y = [np_utils.to_categorical(label, num_classes=label_size) for label in y] y = np.array([list(_[0]) for _ in y]) return x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
2.2 构建LSTM模型
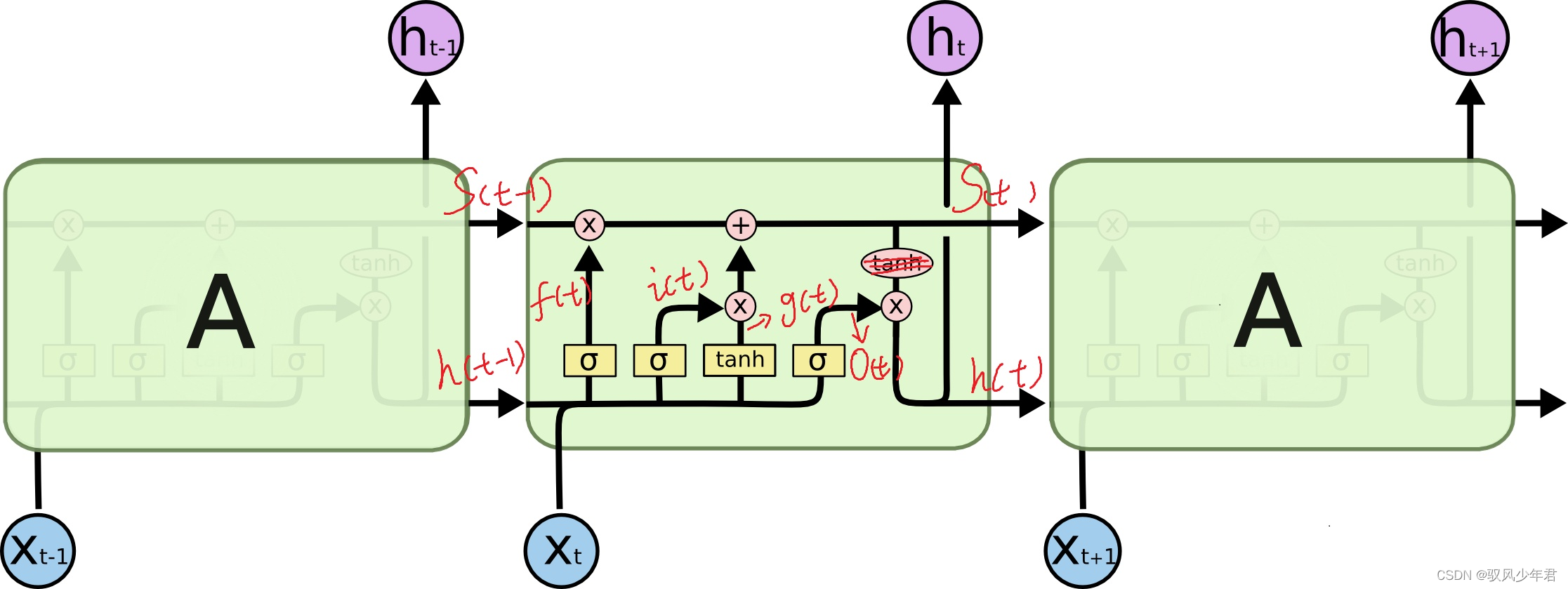
可以看到中间的cell里面有四个黄色小框,你如果理解了那个代表的含义一切就明白了,每一个小黄框代表一个前馈网络层,对,就是经典的神经网络的结构,num_units就是这个层的隐藏神经元个数,就这么简单。其中1,2,4的激活函数是sigmoid,第三个的激活函数是tanh。

假设units = 64
根据上图,我们可以计算,假设a向量是128维向量,x向量是28维向量,那么二者concat以后就是156维向量,为了能相乘,那么Wf就应该是(64,156),同理其余三个框,也应该是同样的shape。于是,在第一层就有参数64x156x4 + 64x4个。若是把cell外面的参数也算进去,那么假设有10个类,那么对于最终的shape为(64,1)的输出at,还要有一个shape为(10,64)的W跟一个shape为(10,1)的b。
# 模型输入参数,需要自己根据需要调整 n_units = 100 #LSTM神经元数量 batch_size = 32 #每次迭代数据量,一般为2的次方 epochs = 5 #训练批次 output_dim = 20 #输出维度 model = Sequential() model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size + 1, output_dim=output_dim, input_length=input_shape, mask_zero=True)) model.add(LSTM(n_units, input_shape=(x.shape[0], x.shape[1]))) model.add(Dropout(0.2)) model.add(Dense(label_size, activation='softmax')) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) # plot_model(model, to_file='./model_lstm.png', show_shapes=True) model.summary()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
模型架构:
Model: "sequential_8" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_7 (Embedding) (None, 180, 20) 43100 _________________________________________________________________ lstm_7 (LSTM) (None, 100) 48400 _________________________________________________________________ dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 100) 0 _________________________________________________________________ dense_7 (Dense) (None, 2) 202 ================================================================= Total params: 91,702 Trainable params: 91,702 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
函数封装
# 创建深度学习模型, Embedding + LSTM + Softmax. def create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath): x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath) model = Sequential() model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size + 1, output_dim=output_dim, input_length=input_shape, mask_zero=True)) model.add(LSTM(n_units, input_shape=(x.shape[0], x.shape[1]))) # model.add(Dropout(0.2)) model.add(Dense(label_size, activation='softmax')) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) # plot_model(model, to_file='./model_lstm.png', show_shapes=True) model.summary() return model- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
2.3 划分数据集-LSTM模型训练-验证
用sk-learn划分数据集,9:1的比例
x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath, input_shape) train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.1, random_state = 42) # 模型输入参数,需要自己根据需要调整 n_units = 100 batch_size = 32 epochs = 5 output_dim = 20 # 模型训练 lstm_model = create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath) lstm_model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=1) # 模型保存 lstm_model.save(model_save_path)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
Model: "sequential_9" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= embedding_8 (Embedding) (None, 180, 20) 43100 _________________________________________________________________ lstm_8 (LSTM) (None, 100) 48400 _________________________________________________________________ dense_8 (Dense) (None, 2) 202 ================================================================= Total params: 91,702 Trainable params: 91,702 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ D:\Anaconda3\envs\tf3\lib\site-packages\tensorflow_core\python\framework\indexed_slices.py:424: UserWarning: Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. This may consume a large amount of memory. "Converting sparse IndexedSlices to a dense Tensor of unknown shape. " Epoch 1/5 3854/3854 [==============================] - 15s 4ms/step - loss: 0.4679 - accuracy: 0.7706 Epoch 2/5 3854/3854 [==============================] - 14s 4ms/step - loss: 0.2244 - accuracy: 0.9266 Epoch 3/5 3854/3854 [==============================] - 14s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1719 - accuracy: 0.9463 Epoch 4/5 3854/3854 [==============================] - 14s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1406 - accuracy: 0.9595 Epoch 5/5 3854/3854 [==============================] - 15s 4ms/step - loss: 0.1274 - accuracy: 0.9606- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
测试数据
N = test_x.shape[0] # 测试的条数 predict = [] label = [] for start, end in zip(range(0, N, 1), range(1, N+1, 1)): sentence = [inverse_word_dictionary[i] for i in test_x[start] if i != 0] y_predict = lstm_model.predict(test_x[start:end]) label_predict = output_dictionary[np.argmax(y_predict[0])] label_true = output_dictionary[np.argmax(test_y[start:end])] print(''.join(sentence), label_true, label_predict) # 输出预测结果 predict.append(label_predict) label.append(label_true) acc = accuracy_score(predict, label) # 预测准确率 print('模型在测试集上的准确率为: %s.' % acc)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
给家里老人买的,很不错哦,价格实惠 正面 正面
给父母买的,特意用了一段时间再来评价,电视非常好,没有坏点和损坏,界面也很简洁,便于操作,稍微不足就是开机会比普通电视慢一些,这应该是智能电视的通病吧,如果可以希望微鲸大大可以更新系统优化下开机时间~电视真的很棒,性价比爆棚,值得大家考虑购买。 客服很细心,快递小哥很耐心的等我通电验货,态度非常好。 负面 正面
长须鲸和海狮回答都很及时,虽然物流不够快但是服务不错电视不错,对比了乐视小米和微鲸论性价比还是微鲸好点 负面 负面
所以看不到4k效果,但是应该可以。 自带音响,中规中矩吧,好像没有别人说的好。而且,到现在没连接上我的漫步者,这个非常不满意,因为看到网上说好像普通3.5mm的连不上或者连上了声音小。希望厂家接下来开发的电视有改进。不知道我要不要换个音响。其他的用用再说。 放在地上的是跟我混了两年的tcl,天气受潮,修了一次,下岗了。 最后,我也觉得底座不算太稳,凑合着用。 负面 负面
电视机一般,低端机不要求那么高咯。 负面 负面
很好,两点下单上午就到了,服务很好。 正面 正面
帮朋友买的,好好好好好好好好 正面 正面
模型在测试集上的准确率为: 0.9254079254079254.函数封装
# 模型训练 def model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path): # 将数据集分为训练集和测试集,占比为9:1 # input_shape = 100 x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath, input_shape) train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.1, random_state = 42) # 模型输入参数,需要自己根据需要调整 n_units = 100 batch_size = 32 epochs = 5 output_dim = 20 # 模型训练 lstm_model = create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath) lstm_model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=1) # 模型保存 lstm_model.save(model_save_path) N = test_x.shape[0] # 测试的条数 predict = [] label = [] for start, end in zip(range(0, N, 1), range(1, N+1, 1)): sentence = [inverse_word_dictionary[i] for i in test_x[start] if i != 0] y_predict = lstm_model.predict(test_x[start:end]) label_predict = output_dictionary[np.argmax(y_predict[0])] label_true = output_dictionary[np.argmax(test_y[start:end])] print(''.join(sentence), label_true, label_predict) # 输出预测结果 predict.append(label_predict) label.append(label_true) acc = accuracy_score(predict, label) # 预测准确率 print('模型在测试集上的准确率为: %s.' % acc)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
2.4 模型实际应用
在模型实际应用的时候,需要导入对应的字符和标签字典,转为相应的编码。
# Import the necessary modules import pickle import numpy as np from keras.models import load_model from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences # 导入字典 with open('word_dict.pk', 'rb') as f: word_dictionary = pickle.load(f) with open('label_dict.pk', 'rb') as f: output_dictionary = pickle.load(f) try: # 数据预处理 input_shape = 180 sent = "很满意,电视非常好。护眼模式,很好,也很清晰。" x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent]] print('--------x转为编码--------') x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0) print('--------x填充完成--------') # 载入模型 model_save_path = './corpus_model.h5' lstm_model = load_model(model_save_path) # 模型预测 y_predict = lstm_model.predict(x) label_dict = {v: k for k, v in output_dictionary.items()} print('输入语句: %s' % sent) print('情感预测结果: %s' % label_dict[np.argmax(y_predict)]) except KeyError as err: print("您输入的句子有汉字不在词汇表中,请重新输入!") print("不在词汇表中的单词为:%s." % err)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
--------x转为编码--------
--------x填充完成--------
输入语句: 很满意,电视非常好。护眼模式,很好,也很清晰。
情感预测结果: 正面2.5 完整代码
统计出数据集中的情感分布以及评论句子长度分布
data_print.py
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib import font_manager from itertools import accumulate # 设置matplotlib绘图时的字体 my_font = font_manager.FontProperties(fname='C:\Windows\Fonts\simfang.ttf') # 统计句子长度及出现次数的频数 df = pd.read_csv('./data_single.csv') print(df.groupby('label')['label'].count()) df['length'] = df['evaluation'].apply(lambda x: len(x)) # print(df) len_df = df.groupby('length').count() sent_length = len_df.index.tolist() sent_freq = len_df['evaluation'].tolist() # 绘制句子长度及出现频数统计图 plt.bar(sent_length, sent_freq) plt.title("句子长度及出现频数统计图", fontproperties=my_font) plt.xlabel("句子长度", fontproperties=my_font) plt.ylabel("句子长度出现的频数", fontproperties=my_font) plt.savefig("./句子长度及出现频数统计图.png") plt.close() # 绘制句子长度累计分布函数(CDF) sent_pentage_list = [(count / sum(sent_freq)) for count in accumulate(sent_freq)] # 绘制CDF plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list) # 寻找分位点为quantile的句子长度 quantile = 0.91 # print(list(sent_pentage_list)) for length, per in zip(sent_length, sent_pentage_list): if round(per, 2) == quantile: index = length break print('\n分位点为%s的句子长度:%d' % (quantile, index)) # 绘制句子长度累积分布函数图 plt.plot(sent_length, sent_pentage_list) plt.hlines(quantile, 0, index, colors="c", linestyles="dashed") plt.vlines(index, 0, quantile, colors="c", linestyles="dashed") plt.text(0, quantile, str(quantile)) plt.text(index, 0, str(index)) plt.title("句子长度累积分布函数图", fontproperties=my_font) plt.xlabel("句子长度", fontproperties=my_font) plt.ylabel("句子长度累积频率", fontproperties=my_font) plt.savefig("./句子长度累积分布函数图.png") plt.close()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
import pickle import numpy as np import pandas as pd from keras.utils import np_utils, plot_model from keras.models import Sequential from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Embedding, Dropout from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score # 导入数据 # 文件的数据中,特征为evaluation, 类别为label. def load_data(filepath, input_shape=20): df = pd.read_csv(filepath) # 标签及词汇表 labels, vocabulary = list(df['label'].unique()), list(df['evaluation'].unique()) # print(len(labels)) # print(len(vocabulary)) # 构造字符级别的特征 string = '' for word in vocabulary: string += word # print(string) vocabulary = set(string) # print(vocabulary) # 字典列表 word_dictionary = {word: i + 1 for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)} with open('word_dict.pk', 'wb') as f: pickle.dump(word_dictionary, f) inverse_word_dictionary = {i + 1: word for i, word in enumerate(vocabulary)} label_dictionary = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(labels)} with open('label_dict.pk', 'wb') as f: pickle.dump(label_dictionary, f) output_dictionary = {i: labels for i, labels in enumerate(labels)} vocab_size = len(word_dictionary.keys()) # 词汇表大小 label_size = len(label_dictionary.keys()) # 标签类别数量 # print(vocab_size, labels) # 序列填充,按input_shape填充,长度不足的按0补充 x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent] for sent in df['evaluation']] x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0) y = [[label_dictionary[sent]] for sent in df['label']] y = [np_utils.to_categorical(label, num_classes=label_size) for label in y] y = np.array([list(_[0]) for _ in y]) return x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary # 创建深度学习模型, Embedding + LSTM + Softmax. def create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath): x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath) model = Sequential() model.add(Embedding(input_dim=vocab_size + 1, output_dim=output_dim, input_length=input_shape, mask_zero=True)) model.add(LSTM(n_units, input_shape=(x.shape[0], x.shape[1]))) model.add(Dropout(0.2)) model.add(Dense(label_size, activation='softmax')) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) plot_model(model, to_file='./model_lstm.png', show_shapes=True) model.summary() return model # 模型训练 def model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path): # 将数据集分为训练集和测试集,占比为9:1 # input_shape = 100 x, y, output_dictionary, vocab_size, label_size, inverse_word_dictionary = load_data(filepath, input_shape) train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.1, random_state=42) # 模型输入参数,需要自己根据需要调整 n_units = 100 batch_size = 32 epochs = 5 output_dim = 20 # 模型训练 lstm_model = create_LSTM(n_units, input_shape, output_dim, filepath) lstm_model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=epochs, batch_size=batch_size, verbose=1) # 模型保存 lstm_model.save(model_save_path) N = test_x.shape[0] # 测试的条数 predict = [] label = [] for start, end in zip(range(0, N, 1), range(1, N + 1, 1)): sentence = [inverse_word_dictionary[i] for i in test_x[start] if i != 0] y_predict = lstm_model.predict(test_x[start:end]) label_predict = output_dictionary[np.argmax(y_predict[0])] label_true = output_dictionary[np.argmax(test_y[start:end])] print(''.join(sentence), label_true, label_predict) # 输出预测结果 predict.append(label_predict) label.append(label_true) acc = accuracy_score(predict, label) # 预测准确率 print('模型在测试集上的准确率为: %s.' % acc) if __name__ == '__main__': filepath = './data_single.csv' input_shape = 180 # load_data(filepath, input_shape) model_save_path = './corpus_model.h5' model_train(input_shape, filepath, model_save_path)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
模型预测代码
# Import the necessary modules import pickle import numpy as np from keras.models import load_model from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences # 导入字典 with open('word_dict.pk', 'rb') as f: word_dictionary = pickle.load(f) with open('label_dict.pk', 'rb') as f: output_dictionary = pickle.load(f) try: # 数据预处理 input_shape = 180 sent = "很满意,电视非常好。护眼模式,很好,也很清晰。" x = [[word_dictionary[word] for word in sent]] x = pad_sequences(maxlen=input_shape, sequences=x, padding='post', value=0) # 载入模型 model_save_path = './corpus_model.h5' lstm_model = load_model(model_save_path) # 模型预测 y_predict = lstm_model.predict(x) label_dict = {v: k for k, v in output_dictionary.items()} print('输入语句: %s' % sent) print('情感预测结果: %s' % label_dict[np.argmax(y_predict)]) except KeyError as err: print("您输入的句子有汉字不在词汇表中,请重新输入!") print("不在词汇表中的单词为:%s." % err)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
-
相关阅读:
nifi从入门到实战(保姆级教程)——flow
Redis Key-Value数据库 【高级】
正则匹配删除指令
手机备忘录可以设置密码吗 能锁屏加密的备忘录
学成在线-网站搭建
笔试强训day28(猴子分桃,反转部分单向列表)
Transformer解码层用mask解释
VoLTE基础自学系列 | 什么是VoLTE中的Silent Redial?它和CSFB什么关系?
Mysql 通过binlog伪装master恢复数据库
面试__编程
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44951759/article/details/126103940