-
【图像融合】基于RP、CVT、DTCWT、NSCT-SR+DWT-SR+拉普拉斯金字塔算法-SR等实现MRT图像融合附matlab源码
1 内容介绍
在图像融合文献中,多尺度变换(MST)和稀疏表示(SR)是最常用的两个
广泛使用的信号/图像表示理论。本文提出了一个通用的图像融合框架
通过结合 MST 和 SR 同时克服基于 MST 和 SR 的融合方法的固有缺陷。在我们的融合框架中,首先对每个预注册的源图像以获得它们的低通和高通系数。然后,合并低通带使用基于 SR 的融合方法,而高通带使用 coef- 的绝对值进行融合ficients 作为活动水平的测量。最后通过逆MST得到融合图像
关于合并系数。所提出的融合框架相对于单个 MST 或首先从理论的角度详细展示了基于 SR 的方法,然后通过实验通过多焦点、可见红外和医学图像融合验证。特别是六大流行的多尺度变换,包括拉普拉斯金字塔 (LP)、低通金字塔比 (RP)、离散小波变换(DWT)、双树复小波变换 (DTCWT)、曲波变换 (CVT) 和非下采样Contourlet 变换 (NSCT),测试了从 1 到 4 的不同分解级别在我们的实验中。通过对融合结果进行主观和客观的比较,我们给出了在所提出的框架下对每一类图像融合的最佳融合方法。效果还研究了滑动窗口的步长。此外,实验结果表明所提出的融合框架可以获得最先进的性能,特别是对于融合多模态图像。


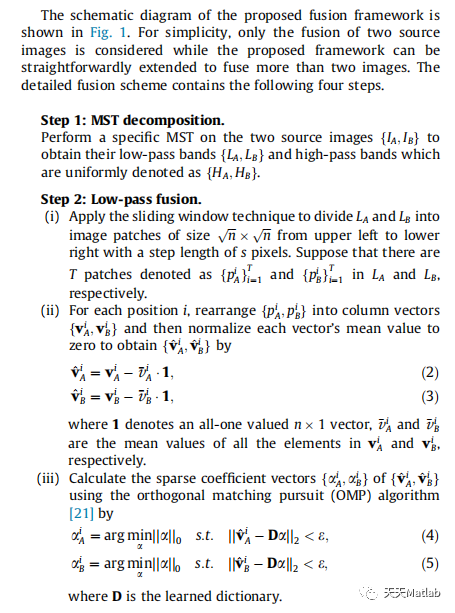

2 仿真代码
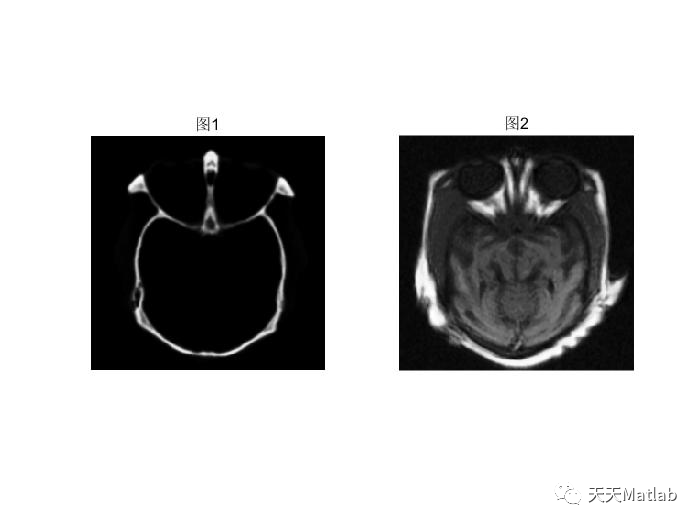
clear all;close all;clc;addpath(genpath('sparsefusion'));addpath(genpath('dtcwt_toolbox'));addpath(genpath('fdct_wrapping_matlab'));addpath(genpath('nsct_toolbox'));load('sparsefusion/Dictionary/D_100000_256_8.mat');[imagename1 imagepath1]=uigetfile('source_images\*.jpg;*.bmp;*.png;*.tif;*.tiff;*.pgm;*.gif','Please choose the first input image');image_input1=imread(strcat(imagepath1,imagename1));[imagename2 imagepath2]=uigetfile('source_images\*.jpg;*.bmp;*.png;*.tif;*.tiff;*.pgm;*.gif','Please choose the second input image');image_input2=imread(strcat(imagepath2,imagename2));figure;subplot(121);imshow(image_input1);title('图1');subplot(122);imshow(image_input2);title('图2')if size(image_input1)~=size(image_input2)error('two images are not the same size.');endimg1=double(image_input1);img2=double(image_input2);overlap = 6;epsilon=0.1;level=4;% To make a comparison, please use% LP-SR for medical image fusion,% DTCWT-SR for visible-infrared image fusion,% NSCT-SR for multi-focus image fusion.tic;if size(img1,3)==1 %for gray imagesimgf = lp_sr_fuse(img1,img2,level,3,3,D,overlap,epsilon); %LP-SRimgf1 = rp_sr_fuse(img1,img2,level,3,3,D,overlap,epsilon); %RP-SRimgf2 = dwt_sr_fuse(img1,img2,level,D,overlap,epsilon); %DWT-SRimgf3 = dtcwt_sr_fuse(img1,img2,level,D,overlap,epsilon); %DTCWT-SRimgf4 = curvelet_sr_fuse(img1,img2,level+1,D,overlap,epsilon); %CVT-SRimgf5 = nsct_sr_fuse(img1,img2,[2,3,3,4],D,overlap,epsilon); %NSCT-SRelse %for color imagesimgf=zeros(size(img1));imgf1=zeros(size(img1));imgf2=zeros(size(img1));imgf3=zeros(size(img1));imgf4=zeros(size(img1));imgf5=zeros(size(img1));for i=1:3imgf(:,:,i) = lp_sr_fuse(img1(:,:,i),img2(:,:,i),level,3,3,D,overlap,epsilon); %LP-SRimgf1(:,:,i) = rp_sr_fuse(img1(:,:,i),img2(:,:,i),level,3,3,D,overlap,epsilon); %RP-SRimgf2(:,:,i) = dwt_sr_fuse(img1(:,:,i),img2(:,:,i),level,D,overlap,epsilon); %DWT-SRimgf3(:,:,i) = dtcwt_sr_fuse(img1(:,:,i),img2(:,:,i),level,D,overlap,epsilon); %DTCWT-SRimgf4(:,:,i) = curvelet_sr_fuse(img1(:,:,i),img2(:,:,i),level+1,D,overlap,epsilon); %CVT-SRimgf5(:,:,i) = nsct_sr_fuse(img1(:,:,i),img2(:,:,i),[2,3,3,4],D,overlap,epsilon); %NSCT-SRendendtoc;figure;;subplot(231);imshow(uint8(imgf));title('LP-SR');subplot(232);imshow(uint8(imgf1));title('RP-SR')subplot(233);imshow(uint8(imgf2));title('DWT-SR')subplot(234);imshow(uint8(imgf3));title('DTCWT-SR')subplot(235);imshow(uint8(imgf4));title('CVT-SR')subplot(236);imshow(uint8(imgf5));title('NSCT-SR')imwrite(uint8(imgf),'Results/fused_mstsr.tif');3 运行结果

4 参考文献
[1] A. Goshtasby, S. Nikolov, Image fusion: advances in the state of the art, Inform.
Fusion 8 (2) (2007) 114–118.
[2] P. Burt, E. Adelson, The laplacian pyramid as a compact image code, IEEE Trans.
Commun. 31 (4) (1983) 532–540.
[3] A. Toet, Image fusion by a ratio of low pass pyramid, Pattern Recogn. Lett. 9 (4)
(1989) 245–253.
[4] V. Petrovic, C. Xydeas, Gradient-based multiresolution image fusion, IEEE
Trans. Image Process. 13 (2) (2004) 228–237.
[5] H. Li, B. Manjunath, S. Mitra, Multisensor image fusion using the wavelet
transform, Graph. Models Image Process. 57 (3) (1995) 235–245.
[6] M. Beaulieu, S. Foucher, L. Gagnon, Multi-spectral image resolution refifinement
using stationary wavelet transform, in: Proceedings of 3rd IEEE International
Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2003, pp. 4032–4034.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。
-
相关阅读:
pidof
通过mysql更改wordpress密码(md5类型)
5.k8s jenkins集成k8s一键发布案例
Mybatis-Plus之连表查询
车载音频系统外置功放+主机联调实验
Spring Boot FailureAnalyzer 应用场景
360关键词指数查询易语言代码
TypeScript(零) —— 简介、环境搭建、第一个实例
基于Java的新闻资讯平台系统设计与实现(源码+lw+部署文档+讲解等)
[附源码]计算机毕业设计springbootQ宝商城
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/matlab_dingdang/article/details/126079179
