-
【PyTorchVideo教程01】快速实现视频动作识别
1 PyTorchVideo介绍
PyTorchVideo是Facebook2021年4月份发布,主要针对视频深度学习应用。
b站:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1QT411j7M31.1 参考资料:
pytorchvideo官网:https://pytorchvideo.org/
pytorchvideo Github:https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorchvideo
Tutorials:https://pytorchvideo.org/docs/tutorial_torchhub_inference
深入浅出PyTorch:8.3 PyTorchVideo简介
PyTorchVideo: 针对视频深度学习,你想要的它都有:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/390909705
PyTorchVideo: A Deep Learning Library for Video Understanding:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2111.09887.pdf1.2 介绍
近几年来,随着传播媒介和视频平台的发展,视频正在取代图片成为下一代的主流媒体,这也使得有关视频的深度学习模型正在获得越来越多的关注。
然而,有关视频的深度学习模型仍然有着许多缺点:- 计算资源耗费更多,并且没有高质量的 model zoo,不能像图片一样进行迁移学习和论文复现。
- 数据集处理较麻烦,但没有一个很好的视频处理工具。
- 随着多模态越来越流行,亟需一个工具来处理其他模态。
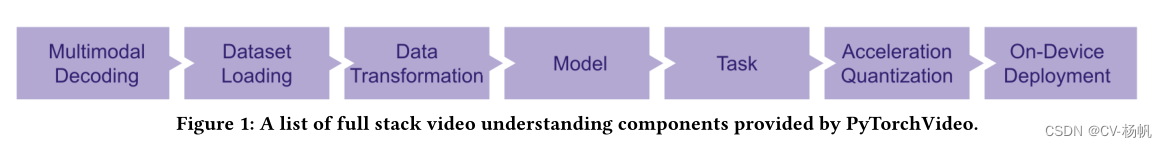
除此之外,还有部署优化等问题,为了解决这些问题,Meta推出了PyTorchVideo深度学习库(包含组件如Figure 1所示)。PyTorchVideo 是一个专注于视频理解工作的深度学习库。PytorchVideo 提供了加速视频理解研究所需的可重用、模块化和高效的组件。PyTorchVideo 是使用PyTorch开发的,支持不同的深度学习视频组件,如视频模型、视频数据集和视频特定转换。
正文开始之前先放一个demo,PyTorchVideo通过模型部署优化模组(accelerator)率先实现了移动端的实时视频动作识别(基于X3D模型),未来视频模型跑在移动端不再是梦想。
PyTorchVideo 移动端的实时视频动作识别
PyTorchVideo A deep learning library for video understanding
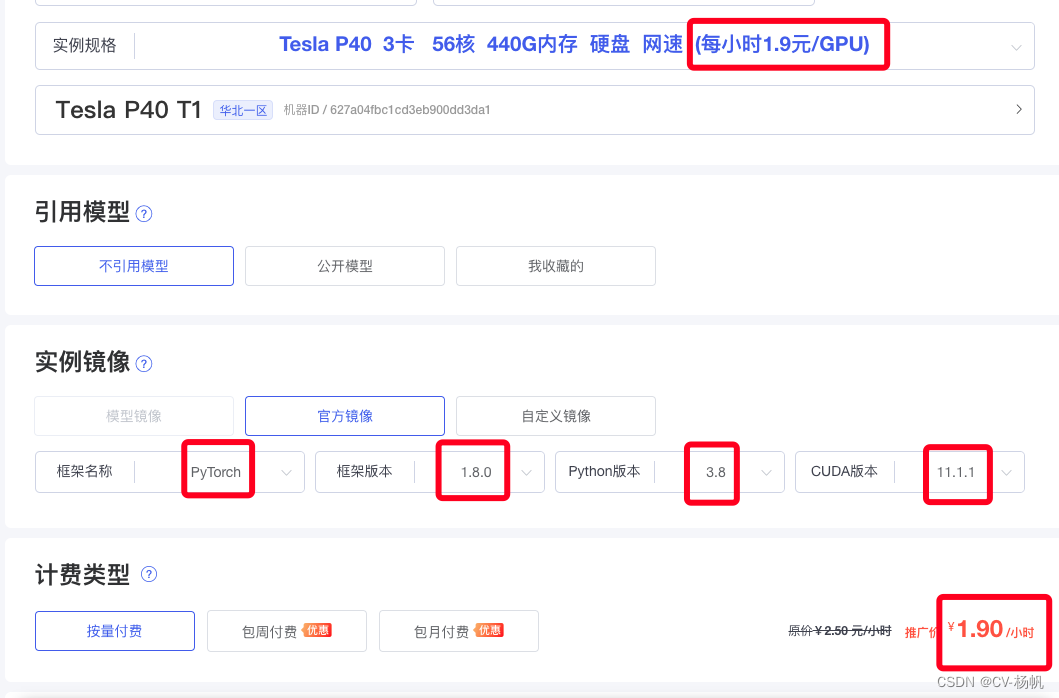
3 GPU平台
极链AI:https://cloud.videojj.com/auth/register?inviter=18452&activityChannel=student_invite
镜像快速搭建
4 安装pytorchvideo
cd /home pip install pytorchvideo wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/pyslowfast/dataset/class_names/kinetics_classnames.json wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/pytorchvideo/projects/archery.mp4- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
如果archery.mp4无法下载,可以先下载好,然后上传,视频资源我已经上传到了阿里云盘:
https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/xjzfmH3uoFB我在csdn上也上传了视频资源:archery.mp4 行为识别 pytorchvideo demo演示视频(行为识别)
5 demo演示
需要提前准备好一个视频
开始搭建(使用Notebook,主要是查看中间的步骤)
import torch import json from torchvision.transforms import Compose, Lambda from torchvision.transforms._transforms_video import ( CenterCropVideo, NormalizeVideo, ) from pytorchvideo.data.encoded_video import EncodedVideo from pytorchvideo.transforms import ( ApplyTransformToKey, ShortSideScale, UniformTemporalSubsample, UniformCropVideo ) from typing import Dict- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
# Device on which to run the model # Set to cuda to load on GPU device = "cpu" # Pick a pretrained model and load the pretrained weights model_name = "slowfast_r50" model = torch.hub.load("facebookresearch/pytorchvideo", model=model_name, pretrained=True) # Set to eval mode and move to desired device model = model.to(device) model = model.eval()- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
with open("kinetics_classnames.json", "r") as f: kinetics_classnames = json.load(f) # Create an id to label name mapping kinetics_id_to_classname = {} for k, v in kinetics_classnames.items(): kinetics_id_to_classname[v] = str(k).replace('"', "")- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
#################### # SlowFast transform #################### side_size = 256 mean = [0.45, 0.45, 0.45] std = [0.225, 0.225, 0.225] crop_size = 256 num_frames = 32 sampling_rate = 2 frames_per_second = 30 alpha = 4 class PackPathway(torch.nn.Module): """ Transform for converting video frames as a list of tensors. """ def __init__(self): super().__init__() def forward(self, frames: torch.Tensor): fast_pathway = frames # Perform temporal sampling from the fast pathway. slow_pathway = torch.index_select( frames, 1, torch.linspace( 0, frames.shape[1] - 1, frames.shape[1] // alpha ).long(), ) frame_list = [slow_pathway, fast_pathway] return frame_list transform = ApplyTransformToKey( key="video", transform=Compose( [ UniformTemporalSubsample(num_frames), Lambda(lambda x: x/255.0), NormalizeVideo(mean, std), ShortSideScale( size=side_size ), CenterCropVideo(crop_size), PackPathway() ] ), ) # The duration of the input clip is also specific to the model. clip_duration = (num_frames * sampling_rate)/frames_per_second- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
# Load the example video video_path = "archery.mp4" # Select the duration of the clip to load by specifying the start and end duration # The start_sec should correspond to where the action occurs in the video start_sec = 0 end_sec = start_sec + clip_duration # Initialize an EncodedVideo helper class video = EncodedVideo.from_path(video_path) # Load the desired clip video_data = video.get_clip(start_sec=start_sec, end_sec=end_sec) # Apply a transform to normalize the video input video_data = transform(video_data) # Move the inputs to the desired device inputs = video_data["video"] inputs = [i.to(device)[None, ...] for i in inputs]- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
# Pass the input clip through the model preds = model(inputs)- 1
- 2
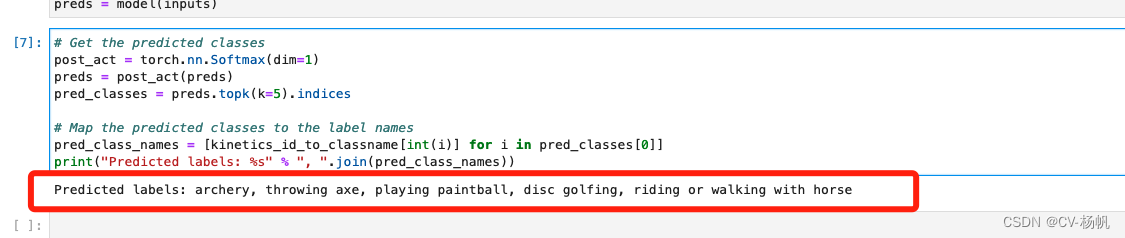
# Get the predicted classes post_act = torch.nn.Softmax(dim=1) preds = post_act(preds) pred_classes = preds.topk(k=5).indices # Map the predicted classes to the label names pred_class_names = [kinetics_id_to_classname[int(i)] for i in pred_classes[0]] print("Predicted labels: %s" % ", ".join(pred_class_names))- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
处理结果:
Predicted labels: archery, throwing axe, playing paintball, disc golfing, riding or walking with horse- 1
-
相关阅读:
vite +vue3-ts架构,我要打包的时候打包成压缩包zip文件
学神经网络需要什么基础,神经网络快速入门
笔训day1
零售数据分析师熬夜整理:人、货、场、供、财这样做
Docker安装canal、mysql进行简单测试与实现redis和mysql缓存一致性
基于PHP实现微信客服欢迎语发送
如何通俗地解释云计算、私有云、公有云、混合云、专有云、分布式云?
国开大学教育学形考任务
一年后斩获腾讯T5,这份呕心之作Java学习笔记有多厉害
前端面试题目(二十四)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/WhiffeYF/article/details/126067008
