-
MySQl数据库————DQL数据查询语言
系列文章目录

前言
前面我们学习了DDL和DML,学会了如何定义数据表,以及如何去根据需求来实现属性的约束,现在我们将学习如何利用DQL语言查询数据表中的类容,前半部分我们将讲解基本类容,后面会引进刷题网站中的题目进行讲解。
一.DQL
一.DQL数据查询语言
– 用于查询数据库中的数据表数据.
1.SQL查询语句
查询关键字:select查询语句的基本结构:
select <属性名> from [数据库名].表名<查询条件>;
2.查询所有字段
基本格式:
select * from <表名>; -- "*"表示所有字段;3.查询指定字段
基本格式:select <属性名> from <表名>;
eg:select s_id,s_name from student;二.DQL单表查询
1.基本条件查询
基本格式:
select <属性名> from <表名> where 【条件】;
条件运算符:<,>,<=,>=,=,!=(<>),(不存在==);
例如:select s_id from student where s_id>32.多条件查询
基本格式:
select <属性名> from [数据库名].表名 where [约束条件1,约束条件2·····];
逻辑运算符:AND/and(&&),OR/or(||)
例如:select s_id from student where s_id>3 and s_id<5;3.范围查找
范围查找关键字:
between ·······and·······;
例如:select s_id from student where s_id between 5 and 8; -- 在5到8的范围类查找;
select s_id from student where s_id not between 5 and 8 ;-- 在5到8 的范围之外查找4.集合范围类查找
集合范围类查找的关键字:
in
①.在集合范围类查找:
select s_name from student where s_id in(1,2,3,4,5,6); -- 查找学号在1,2,3,4,5,6这些条件下的s_name;
②.在集合之外查找
select s_name from student where s_id not in (1,2,3,4,5,6);
这里的语法和python中的语法相似,如果会python的可以i联想记忆;5.字符串模糊匹配
模糊匹配 :
like(用于字符串模糊匹配)
①.通配符:%:匹配0个,1个或者多个字符;
select s_id from student where s_name like "%小%";
匹配属性s_name中含有小字的记录,前后任意个字符,例如“王二小”,“李小华”;
②.通配符:_:匹配一个字符
select s_name from student where s_name like "小_";
匹配属性s_name中以小开头,且后面只有一个字符的元组,例如:"小华"6.空值查询
①.查询空值
select s_name from student where s_name is null;
查询属性s_name中取值为空的记录;
②.查询非空值 is not null
select s_name from student where s_name is not null;
查询属性s_name不为空的记录;7.分页查询
分页:
limit[偏移量n,记录条数m],是指查询从第n+1开始记录后面m+1的数据,偏移量n默认为0;和python中的索引相似;
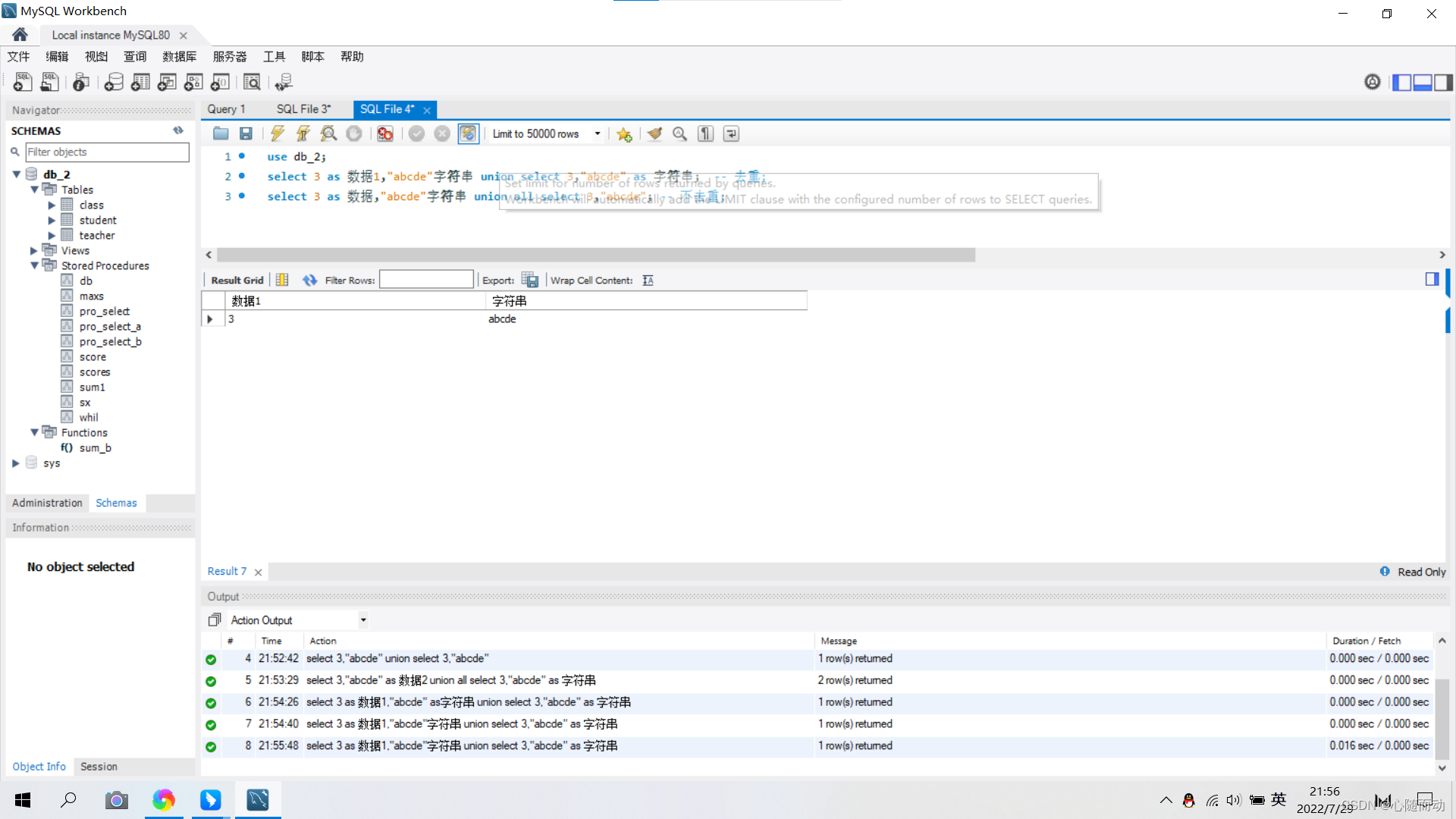
select s_id from student limit 3,6;8.合并查询
合并:union(合并)(union all(合并所有))
临时结果集:select语句查询的结果是一个虚拟表(临时表)。
— union 合并:去重
select 3,"abcde" union select 4,"achde";
注意:合并的多个查询结果必须列的数量相同;
— union all(合并):不去重,合并所有;
select 3,"abcde" union all select 3,"abcde";
9.排序查询
排序查询关键字:order by
对查询结果的排序默认是按照升序的,如果要使用降序,则后面加desc;
例如:默认升序排序:select * from student order by s_id;
降序排序:select * from student order by s_id desc;10.分组排序
分组:group by;

分组统计:
select count(s_id) as 男学生人数 from db_2.student group by s_sex having s_sex="男";

注意:分组查询中使用条件约束的时候用的是having关键字,不是where关键字;三.DQL多表查询
我们在查询表格的过程中,往往需要将 多个表组合使用,并且要实现多个表之间的数据查询,例如:查询学生成绩,需要将学生表和成绩表连接起来,查询满足的条件的数据,这个时候就需要用到多表查询;
1.测试数据表的创建
创建学生,班级,教师的关系表:
use db_2; -- 教师表; create table teacher( t_id int primary key auto_increment, t_name varchar(20) not null, t_sex varchar(4), t_age int ); -- 班级表; create table class( c_id int primary key auto_increment, c_name varchar(20) not null, c_tid int, c_stunum int default 0, constraint for_CT foreign key(c_tid) references teacher (t_id) ); -- 学生表 create table student( s_id int primary key auto_increment, s_name varchar(20) not null, s_cid int, s_sex varchar(4), s_age int, constraint for_SC foreign key (s_cid) references class(c_id) ); 后面进行数据的插入,读者根据自己的想法进行数据插入;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
2.交叉连接
交叉连接是基本的多表连接查询。
不带where条件子句的交叉连接,将会产生连接表的笛卡尔积,返回结果集的行数等于参与连接的表的行数的积。
带where的条件子句的交叉连接,往往会产生两个或者多个表行数乘积的笛卡尔级数据表,然后才根据where后的条件约束挑选相匹配的数据。
交叉连接的基本格式:select <表名1.属性名1>,<表名1.属性名2>·······from <表名2.属性名1>,<表名2.属性名2>- 1
交叉连接会产生笛卡尔积,再进行条件筛选,效率比较慢,将连接表格的所有元组都互相匹配一次,产生一个包含所有情况的大表
;3.内连接
交叉连接产生的笛卡尔积会进行额外的判断和比较,如果要查询较多的数据,交叉连接查询的效率相当低下,所以有了一个高效率的查询;
内连接的图示:
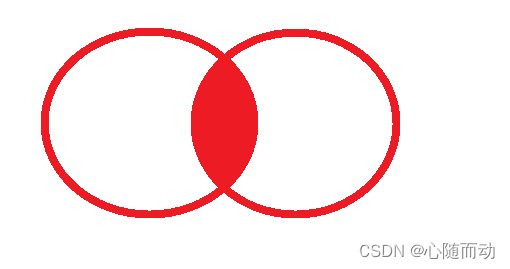
内连接的关键字:inner join
基本格式:
select [表名1.属性名1,表名2.属性名2,表名n.属性名n······] from [数据库名.表名1]inner join [数据库名.表名2] on 连接条件
例如:
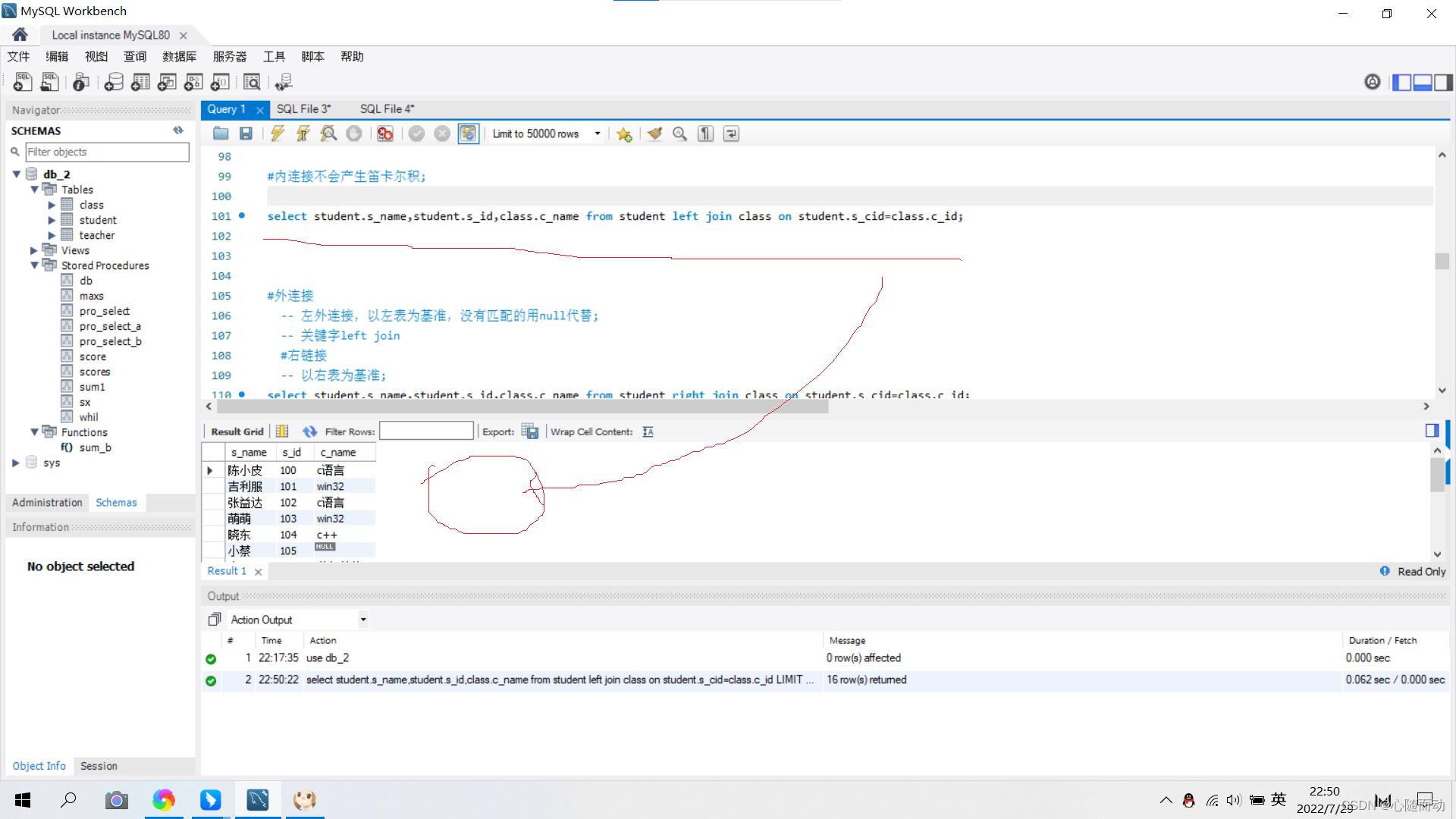
内连接时先筛选满足条件的数据,然后再进行连接,避免了很多不必要的冲突,极大的增加了效率。4.外连接
①.左外连接
左连接是以左表为基准,显示左表查询字段的所有记录,没有匹配的用null代替。
关键字:left join
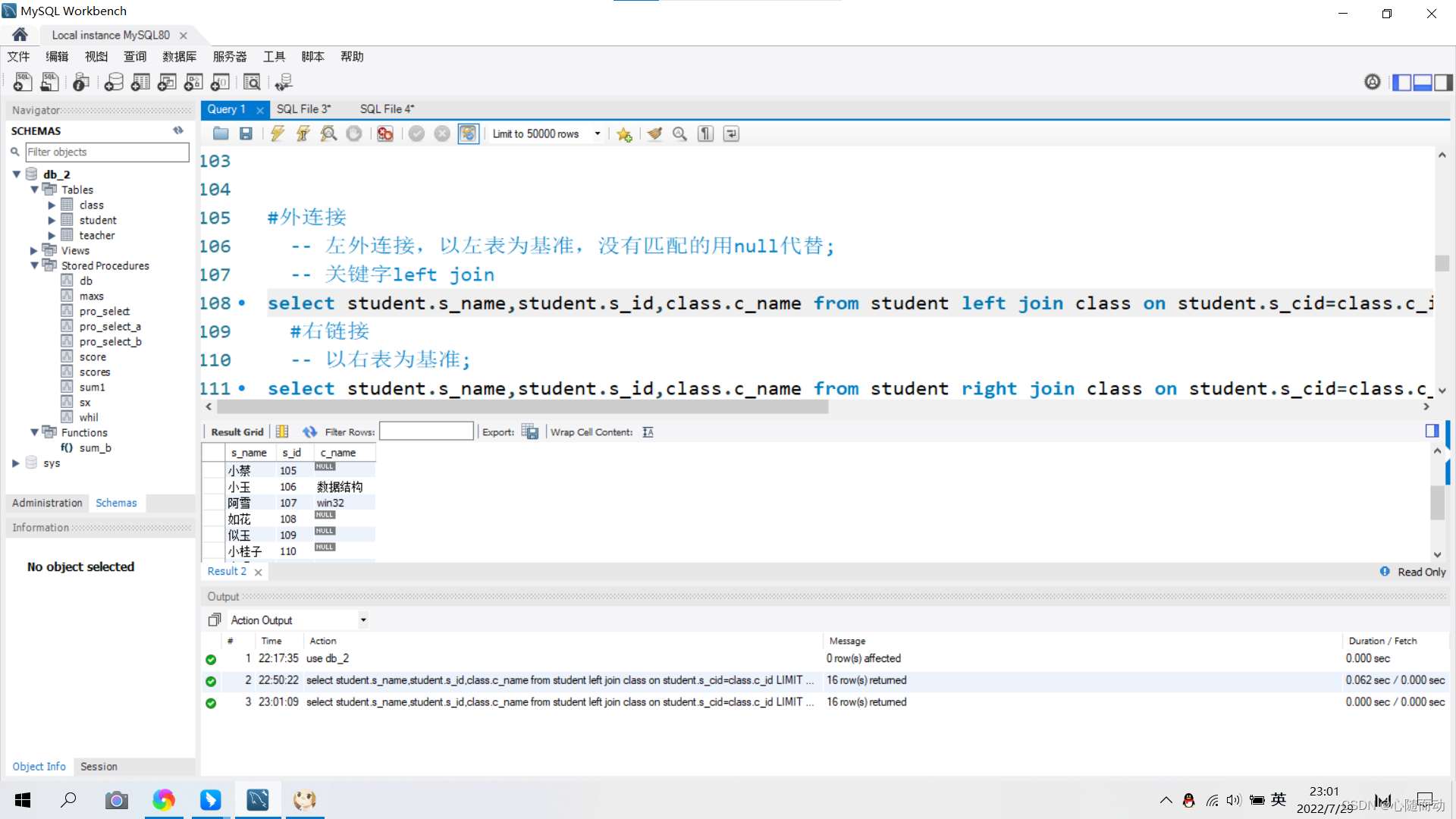
②.右外连接
右连接是以右表为基准,左表只是记录,没有匹配的用null代替。
关键字:right join

左右连接的表是可以互换的,也就是可以相互的替换。③.全外连接
全外连接左右表不被限制,显示全部数据,没有匹配的数据用null代替;
关键字:full join
select student.s_name,student.s_id,class.c_name from student full join class where student.s_cid=class.c_id;5.多表连接查询
一般来说,我们在使用多表查询的时候,最好不要超过4个,如果超过4个,很有可能是数据表的设置有问题。
二.力扣题目讲解
1.基础查询
①.查询所有列
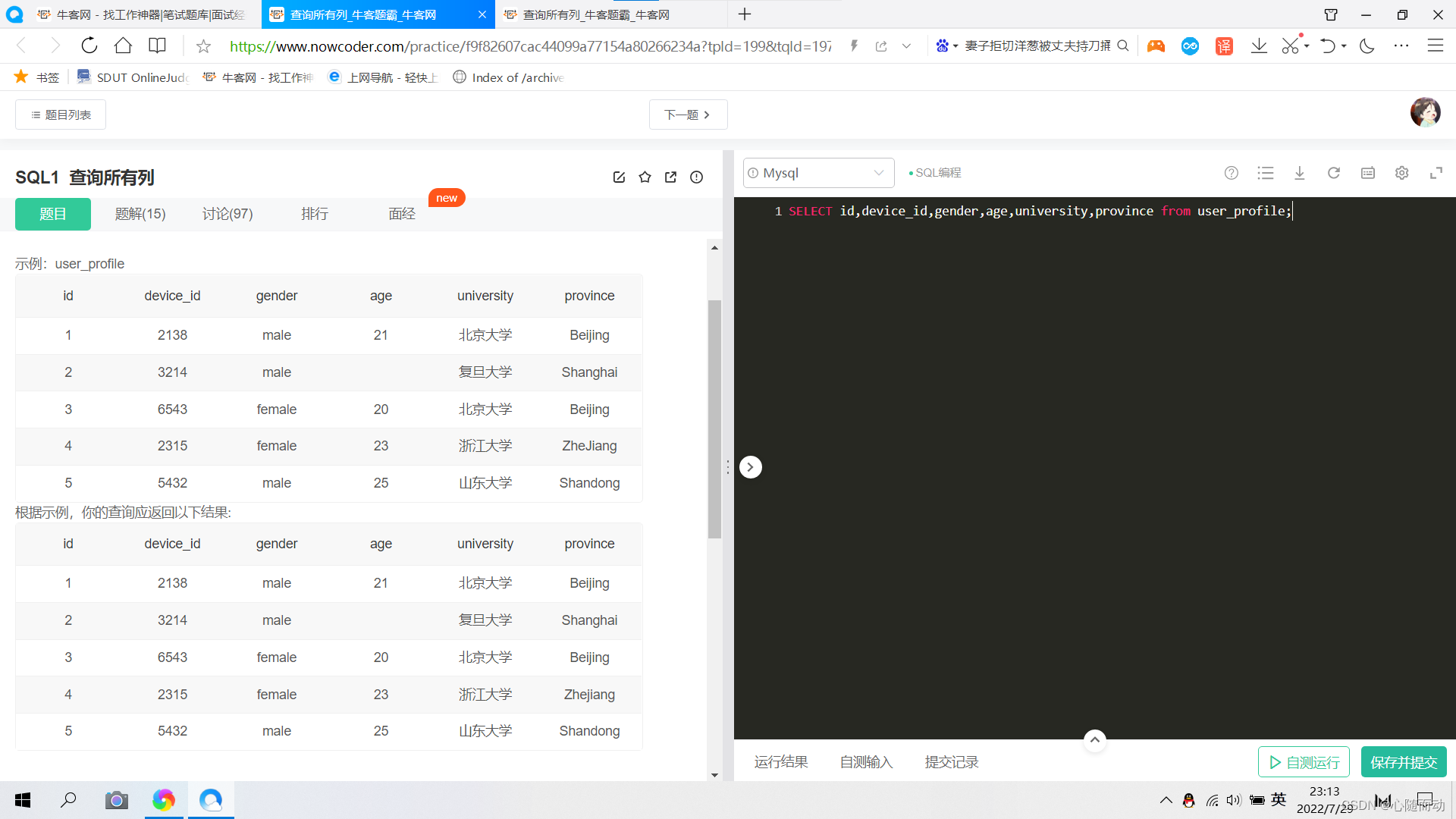
题目解答答案:SELECT id,device_id,gender,age,university,province from user_profile;②.查询多列
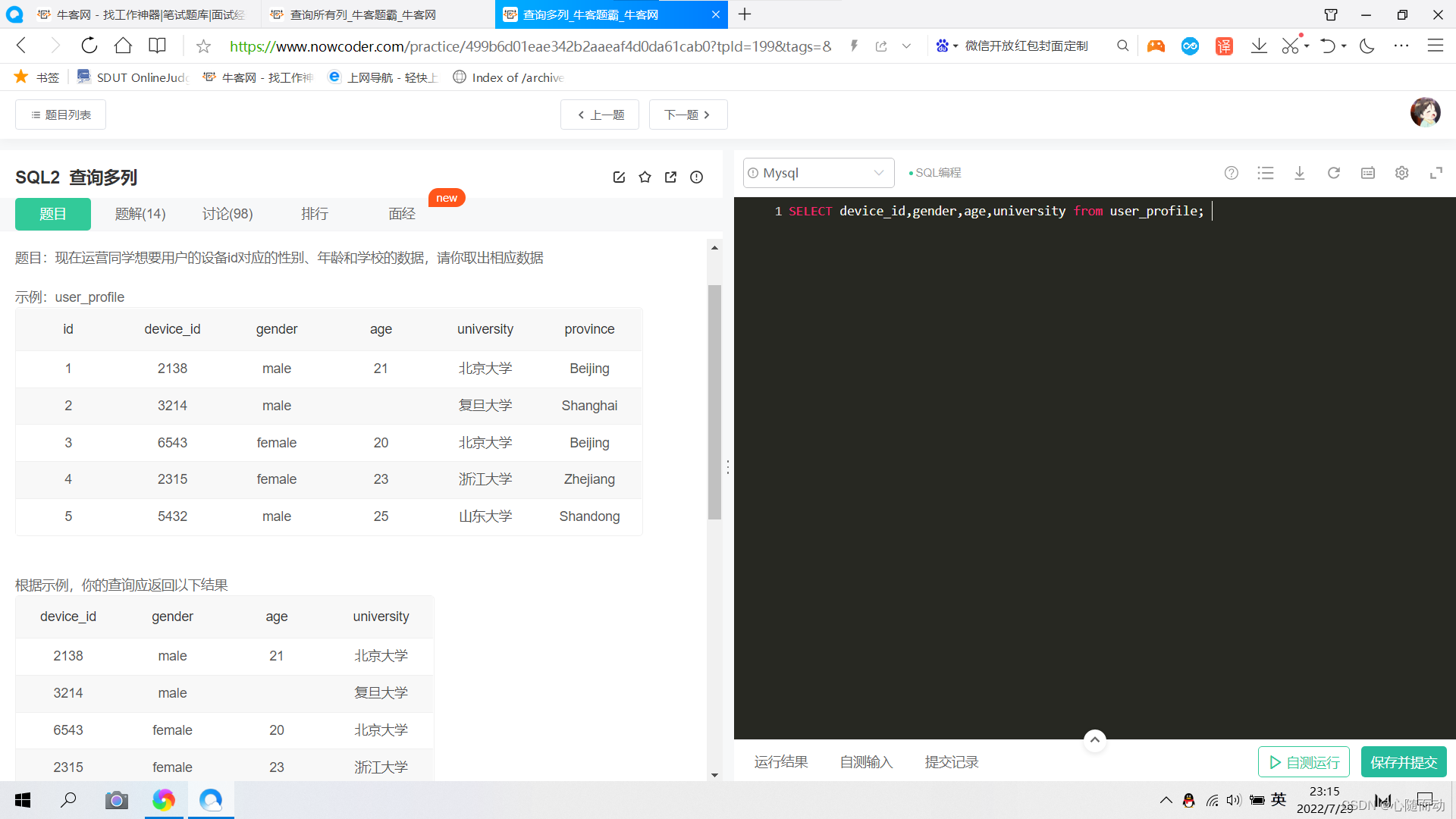
题目解答答案:SELECT device_id,gender,age,university from user_profile;简单处理查询结果
①.查询结果去重

我们在去重的时候可以用关键字distinct,使用该关键字就可以去重,如图中的第一句。
当然也可以使用分组查询来进行去重。第二句就是使用分组查询进行的去重,两句答案都可以通过。②.查询结果限制返回查询结果
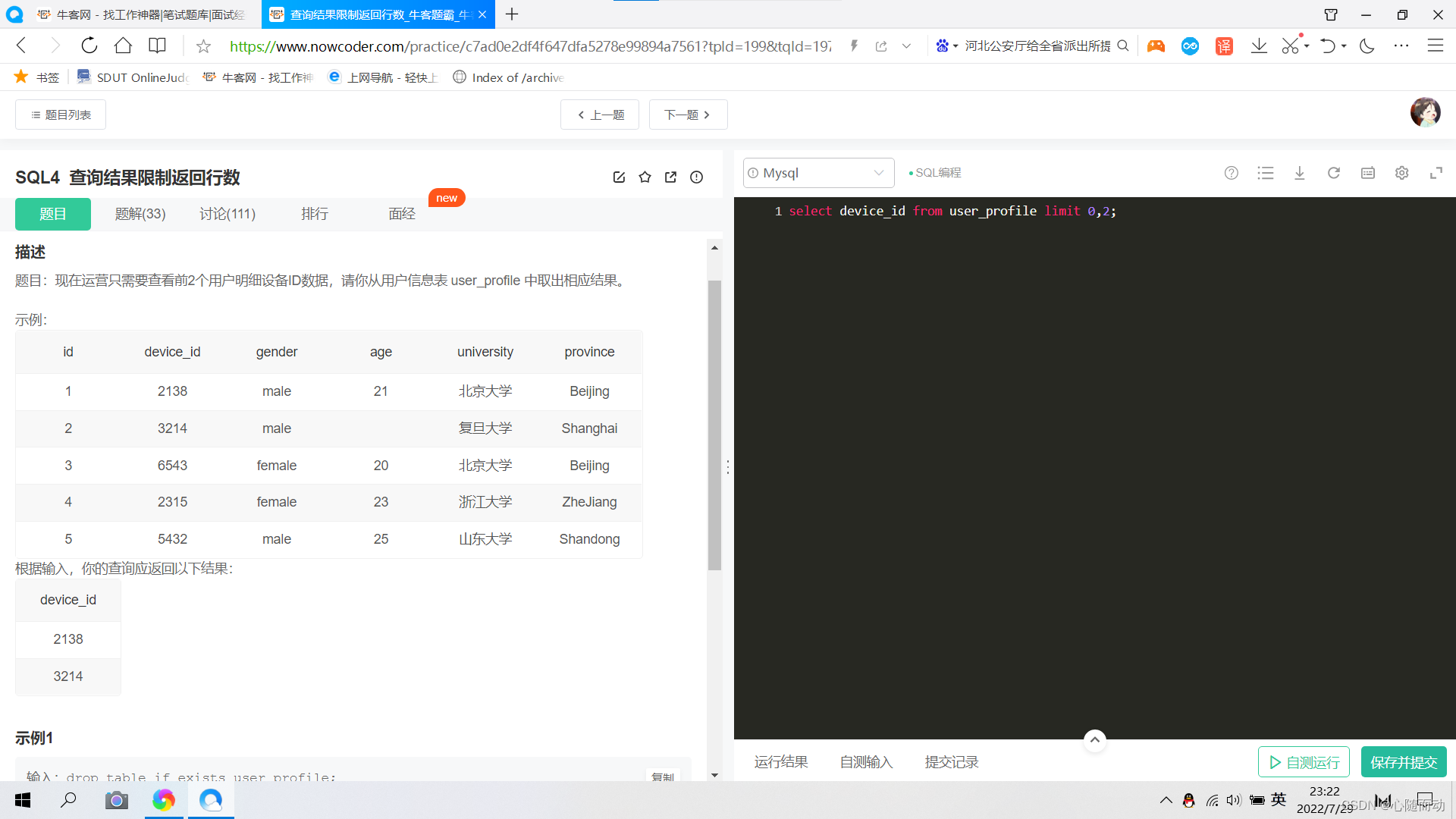
使用分页查询可以获得不同范围类的数据;
答案再现:select device_id from user_profile limit 0,2;③.将查询后的结果重新命名
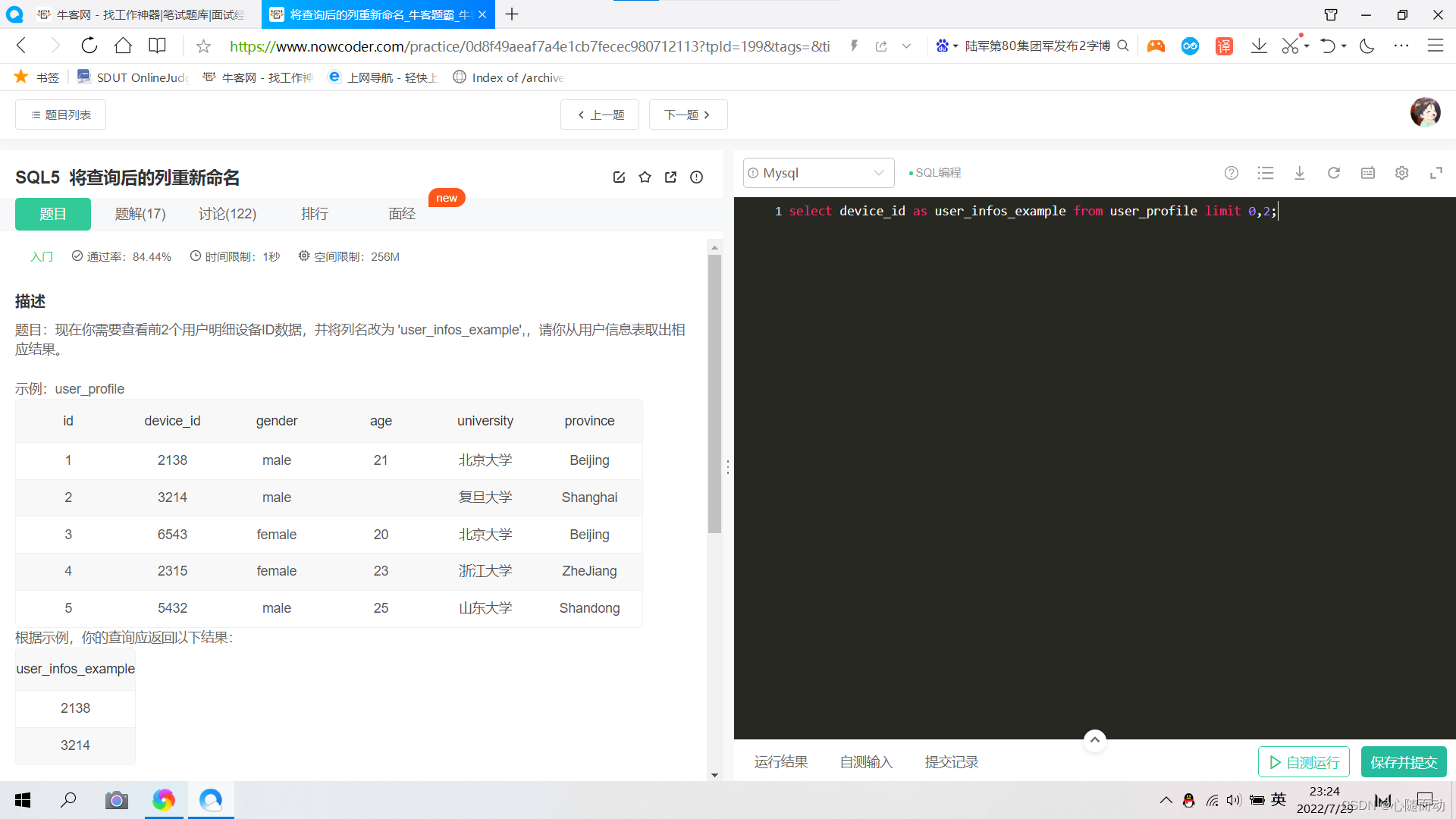
利用关键字as给查询的结果起一个别名;
答案再现:select device_id as user_infos_example from user_profile limit 0,2;三.条件查询
①.查找学校是北大的学生信息
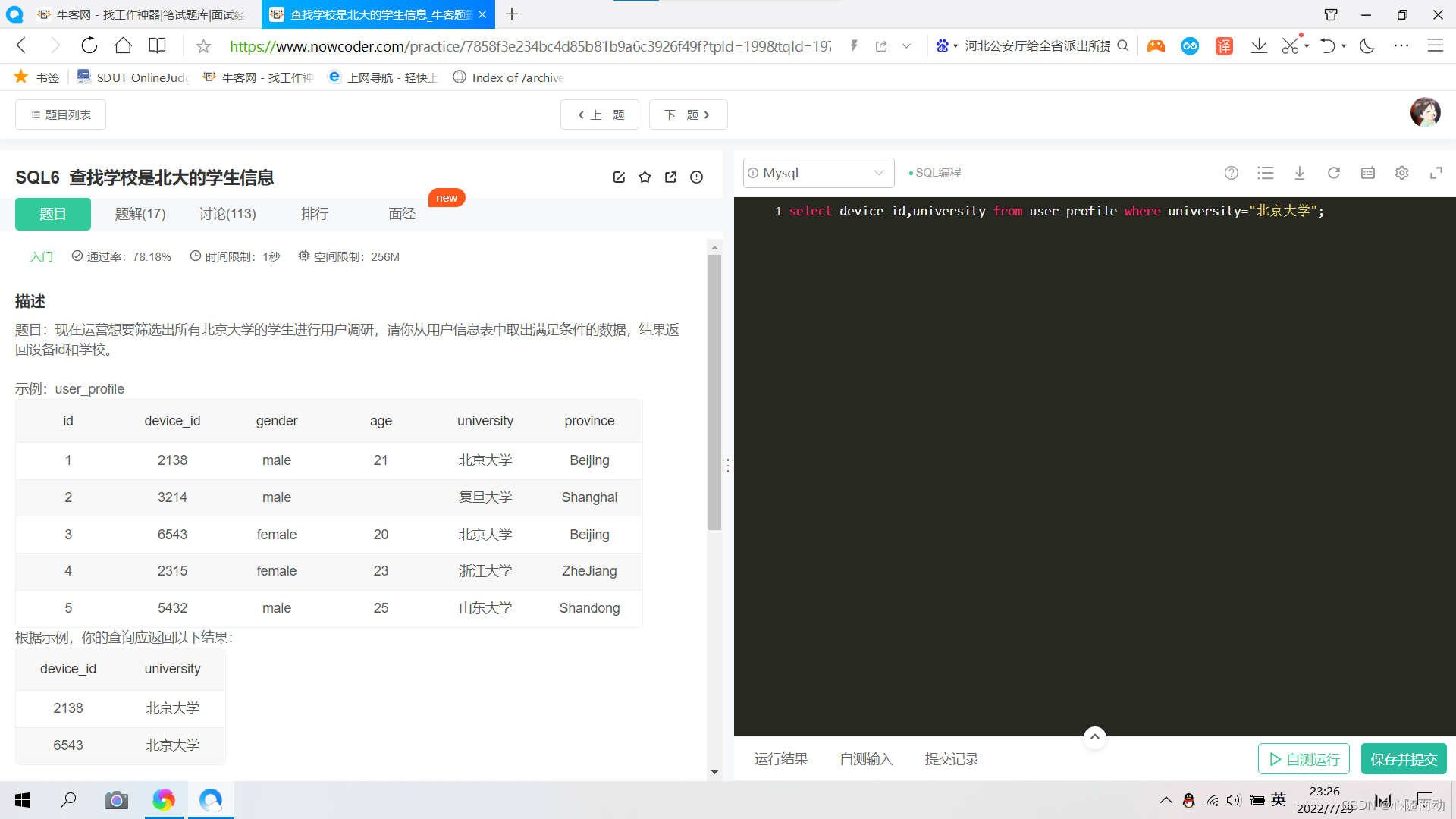
使用关键字where就可以进行条件查询;
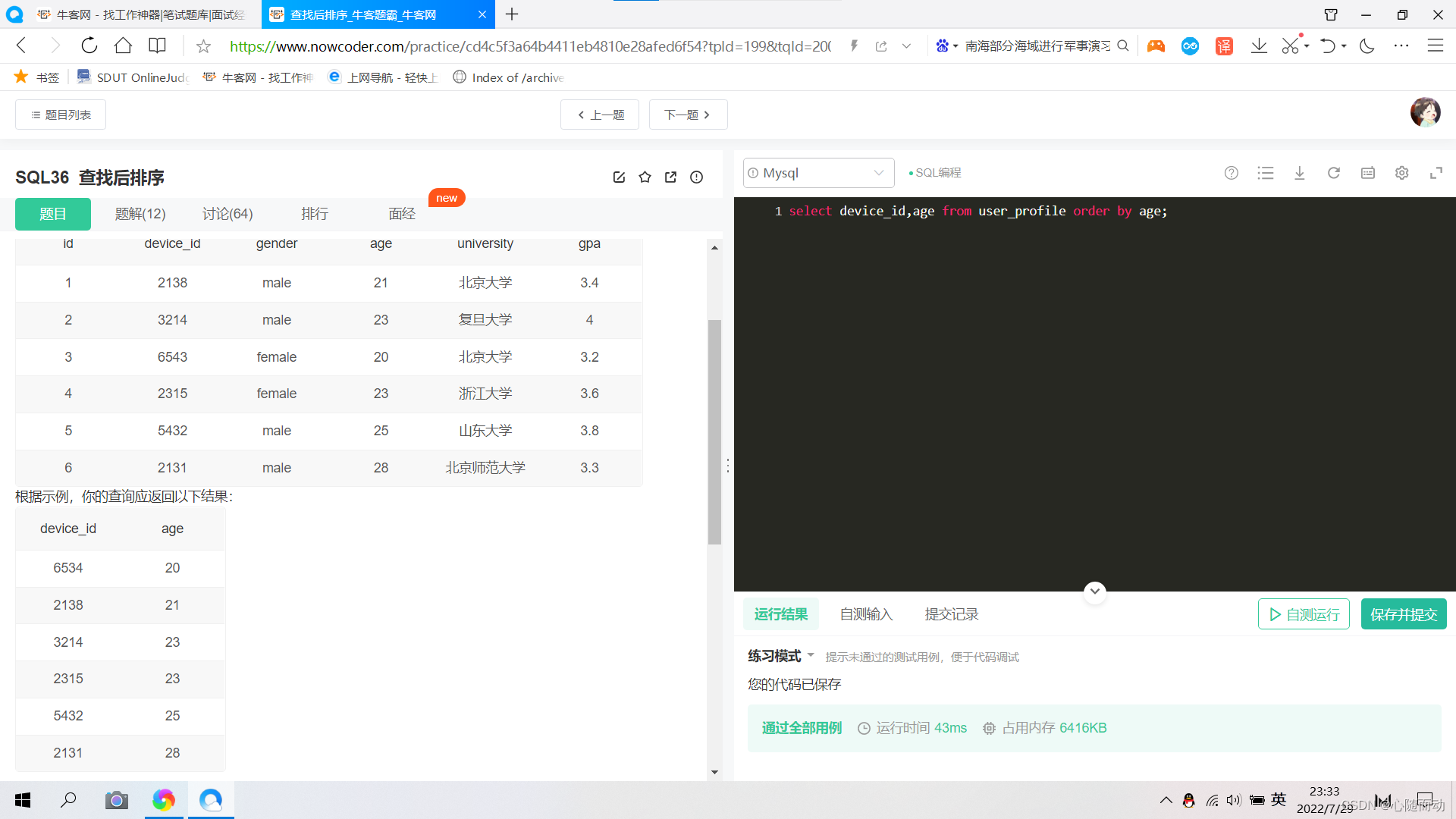
答案:select device_id,university from user_profile where university="北京大学";②.查找后排序
使用关键字order by进行排序,如果是降序,就在后面加一个desc;③.操作符的混合使用

答案:select device_id,gender,age,university,gpa from user_profile where (gpa>3.5 and university="山东大学") or (gpa>3.8 and university="复旦大学");
这里的题目我选择了一部分讲解,其余的后面学到了会继续讲解,如果有不会的,可以私聊博主,我会尽快为你解答的。总结
本节我们学习了DQL数据查询语言,无论是单表查询,还是多表查询,都是非常重要的知识,后面也讲解了部分力扣网站上的题目,只是选择几个比较有价值的讲解了的,如果想要彻底掌握,还是要多刷题,以及多想。不要怕不会做,如有不会可以私聊博主,博主会尽快为你解答。祝各位小伙伴学有所成。
-
相关阅读:
Kubernetes 深入理解kubernetes(一)
Ansible安装管理和模块的使用
使用第三方账号认证(一):钉钉扫码登录
H5画布绘制渐变
MySQL专有的SQL语句
前端自动化测试 —— Jest 测试框架应用
H3C无线控制器双链路备份配置
Virtio-PMD的路径选择与用法
大数据学习(2)Hadoop-分布式资源计算hive(1)
Tomcat部署及优化
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_59931372/article/details/126053520
