-
【算法】动态规划
1.传递信息(lcp-07-java)
小朋友 A 在和 ta 的小伙伴们玩传信息游戏,游戏规则如下:
有 n 名玩家,所有玩家编号分别为 0 ~ n-1,其中小朋友 A 的编号为 0
每个玩家都有固定的若干个可传信息的其他玩家(也可能没有)。传信息的关系是单向的(比如 A 可以向 B 传信息,但 B 不能向 A 传信息)。
每轮信息必须需要传递给另一个人,且信息可重复经过同一个人
给定总玩家数 n,以及按 [玩家编号,对应可传递玩家编号] 关系组成的二维数组 relation。返回信息从小 A (编号 0 ) 经过 k 轮传递到编号为 n-1 的小伙伴处的方案数;若不能到达,返回 0。示例 1:
输入:n = 5, relation = [[0,2],[2,1],[3,4],[2,3],[1,4],[2,0],[0,4]], k = 3
输出:3
解释:信息从小 A 编号 0 处开始,经 3 轮传递,到达编号 4。共有 3 种方案,分别是 0->2->0->4, 0->2->1->4, 0->2->3->4。
public class LC270_lcp_07_numWays { public static int numWays(int n, int[][] relation, int k) { //已经走了i步 位置j处的方案数量 int[][] ans = new int[k + 1][n]; ans[0][0] = 1; for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) { for (int[] ints : relation) { int a = ints[0], b = ints[1]; ans[i][b] += ans[i - 1][a]; } } return ans[k][n - 1]; } public static void main(String[] args) { int i = numWays(5, new int[][]{{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {3, 4}, {2, 3}, {1, 4}, {2, 0}, {0, 4}}, 3); System.out.println(i); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
2.杨辉三角(118-java)
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成「杨辉三角」的前 numRows 行。
在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
示例 1:
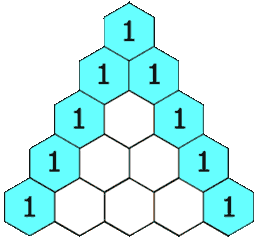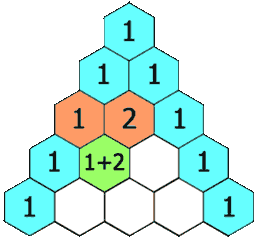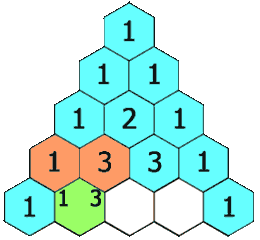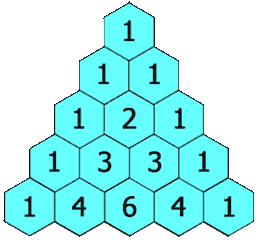
输入: numRows = 5
输出: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]]public class LC82_118_generate { //递归 public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (numRows == 0) { return res; } if (numRows == 1) { res.add(new ArrayList<>()); res.get(0).add(1); return res; } res = generate(numRows - 1); List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<>(); row.add(1); for (int i = 1; i < numRows - 1; i++) { row.add(res.get(numRows - 2).get(i - 1) + res.get(numRows - 2).get(i)); } row.add(1); res.add(row); return res; } //迭代 public static List<List<Integer>> generate111(int numRows) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (numRows == 0) { return res; } res.add(new ArrayList<>()); res.get(0).add(1); for (int i = 2; i <= numRows; i++) { List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> pre = res.get(i - 2); row.add(1); for (int j = 1; j < i - 1; j++) { row.add(pre.get(j - 1) + pre.get(j)); } row.add(1); res.add(row); } return res; } //动态规划 public static List<List<Integer>> generate1112(int numRows) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (numRows == 0) { return res; } int[][] dp = new int[numRows + 1][numRows + 1]; dp[0][0] = 1; res.add(Arrays.asList(1)); for (int i = 1; i < numRows; i++) { dp[i][0] = dp[i][i] = 1; List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<>(); row.add(1); for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - 1]; row.add(dp[i][j]); } row.add(1); res.add(row); } return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { int numRows = 5; List<List<Integer>> generate = generate1112(numRows); for (List<Integer> integers : generate) { for (Integer integer : integers) { System.out.print(integer + " "); } System.out.println(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
3.除数博弈(1025-java)
爱丽丝和鲍勃一起玩游戏,他们轮流行动。爱丽丝先手开局。
最初,黑板上有一个数字 N 。在每个玩家的回合,玩家需要执行以下操作:
选出任一 x,满足 0 < x < N 且 N % x == 0 。
用 N - x 替换黑板上的数字 N 。
如果玩家无法执行这些操作,就会输掉游戏。只有在爱丽丝在游戏中取得胜利时才返回 True,否则返回 False。假设两个玩家都以最佳状态参与游戏。
示例 1:
输入:2
输出:true
解释:爱丽丝选择 1,鲍勃无法进行操作。public class LC271_1025_divisorGame { public static boolean divisorGame(int n) { if (n == 1) { return false; } //桌面是i时候 做选择的是否能赢 boolean[] ans = new boolean[n + 1]; ans[1] = false; ans[2] = true; for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j < n / 2; j++) { if (i % j == 0 && !ans[i - j]) { ans[i] = true; break; } } } return ans[n]; } public static void main(String[] args) { boolean b = divisorGame(8); System.out.println(b); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
//数学逻辑 public static boolean divisorGame222(int n) { return (n & 1) == 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
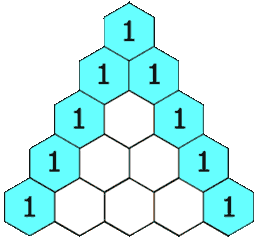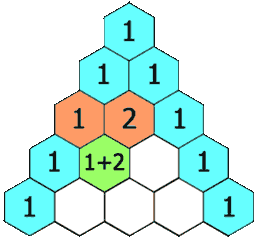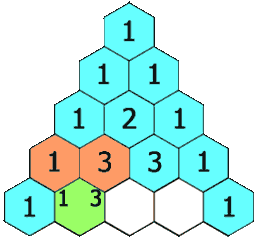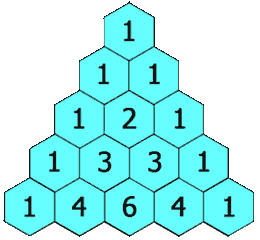
4.杨辉三角 II(119-go)
给定一个非负索引
rowIndex,返回「杨辉三角」的第rowIndex行。在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
//119. 杨辉三角 II func getRow(rowIndex int) []int { res := make([][]int, rowIndex+1) for i := 0; i <= rowIndex; i++ { res[i] = make([]int, i+1) res[i][0] = 1 res[i][i] = 1 } for i := 1; i <= rowIndex; i++ { for j := i; j < i; j++ { res[i][j] = res[i-1][j] + res[i-1][j-1] } } return res[rowIndex] } //空间复杂度优化 func getRow11(rowIndex int) []int { // 第rowIndex行的数组长度为rowIndex+1 res := make([]int, rowIndex+1) // 每一行的第一项都确定是1 res[0] = 1 // 从第二行开始遍历 for i := 1; i < rowIndex+1; i++ { // 第i行的首尾项确定是1 res[0] = 1 res[i] = 1 // 从第i行的倒数第二个开始遍历到第二个 for j := i - 1; j >= 1; j-- { // 用上一行的值求出当前res[j] res[j] = res[j] + res[j-1] } } // 返回出第rowIndex行的数组 return res }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
5.斐波那契数(509-java)
斐波那契数,通常用 F(n) 表示,形成的序列称为 斐波那契数列 。该数列由 0 和 1 开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:
F(0) = 0,F(1) = 1
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2),其中 n > 1
给你 n ,请计算 F(n) 。示例 1:
输入:2
输出:1
解释:F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1public class LC115_509_fib { //递归 public static int fib(int n) { if (n == 1 || n == 2) { return 1; } return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2); } //通讯录--自顶而下 public static int fib1111(int n) { if (n < 1) { return 0; } int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; return help(dp, n); } private static int help(int[] dp, int n) { if (n == 1 || n == 2) { return 1; } if (dp[n] != 0) { return dp[n]; } return help(dp, n - 1) + help(dp, n - 2); } //动态规划 public static int fib222(int n) { int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; //dp[0]默认为0 dp[1] = dp[2] = 1; for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]; } return dp[n]; } //动态规划剪枝 public static int fib2223333(int n) { if (n < 1) { return 0; } if (n == 1 || n == 2) { return 1; } int pre = 1;//前一项总和 int curr = 1;//当前总和 for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) { int sum = pre + curr; pre = curr; curr = sum; } return curr; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(fib2223333(5)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
6.第 N 个泰波那契数(1137-java)
泰波那契序列 Tn 定义如下:
T0 = 0, T1 = 1, T2 = 1, 且在 n >= 0 的条件下 Tn+3 = Tn + Tn+1 + Tn+2
给你整数 n,请返回第 n 个泰波那契数 Tn 的值。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4
输出:4
解释:
T_3 = 0 + 1 + 1 = 2
T_4 = 1 + 1 + 2 = 4public class LC190_1137_tribonacci { //递归--超时 public static int tribonacci(int n) { if (n == 0) { return 0; } if (n == 1) { return 1; } if (n == 2) { return 1; } return tribonacci(n - 1) + tribonacci(n - 2) + tribonacci(n - 3); } //动态规划 public static int tribonacci111(int n) { if (n == 0) { return 0; } if (n == 1) { return 1; } if (n == 2) { return 1; } int[] dp = new int[n + 1]; dp[0] = 0; dp[1] = 1; dp[2] = 1; for (int i = 3; i < n + 1; i++) { dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2] + dp[i - 3]; } return dp[n]; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(tribonacci(4)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
7.使用最小花费爬楼梯(746-java)
给你一个整数数组 cost ,其中 cost[i] 是从楼梯第 i 个台阶向上爬需要支付的费用。一旦你支付此费用,即可选择向上爬一个或者两个台阶。
你可以选择从下标为 0 或下标为 1 的台阶开始爬楼梯。
请你计算并返回达到楼梯顶部的最低花费。
示例 1:
输入:cost = [10,15,20]
输出:15
解释:你将从下标为 1 的台阶开始。- 支付 15 ,向上爬两个台阶,到达楼梯顶部。
总花费为 15 。
public class LC143_746_minCostClimbingStairs { //动态规划 public static int minCostClimbingStairs(int[] cost) { int[] dp = new int[cost.length]; dp[0] = cost[0]; dp[1] = cost[1]; for (int i = 2; i < dp.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1], dp[i - 2]) + cost[i]; } return Math.min(dp[cost.length - 1], dp[cost.length - 2]); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(minCostClimbingStairs(new int[]{1, 100, 1, 1, 1, 100, 1, 1, 100, 1})); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
8.最大子序和(53-java)
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
子数组 是数组中的一个连续部分。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
输出:6
解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。public class LC17_53_maxSubArray { /** * 注意判断的是sum ans 2个变量 * * @param nums * @return */ public static int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { int ans = nums[0]; int sum = 0; for (int num : nums) { if (sum >= 0) {//很关键 sum += num; } else { sum = num; } ans = Math.max(ans, sum); } return ans; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9}; System.out.println(maxSubArray(nums)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
9.买卖股票的最佳时机(121-java)
考察:动态规划
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出:5
解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。public class LC016_121_maxProfit { //暴力解法 超时 public static int maxProfit(int[] prices) { int ans = 0; if (prices == null || prices.length < 2) { return ans; } //遍历买入点 for (int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++) { //遍历卖出点 for (int j = i + 1; j < prices.length; j++) { ans = Math.max(ans, prices[j] - prices[i]); } } return ans; } //动态规划 public static int maxProfitDP(int[] prices) { int len = prices.length; // 特殊判断 if (len < 2) { return 0; } int[][] dp = new int[len][2]; // 初始化:不持股显然为 0,持股就需要减去第 1 天(下标为 0)的股价 dp[0][0] = 0; dp[0][1] = -prices[0]; // 从第 2 天开始遍历 for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { // dp[i][0] 下标为 i 这天结束的时候,不持股,手上拥有的现金数 //1.什么都不做,继续不持股;2.昨天持股,今天不持股 dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]); // dp[i][1] 下标为 i 这天结束的时候,持股,手上拥有的现金数 //1.今天什么都不做,继续持股;2.昨天之前不持股,今天持股 dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], -prices[i]); } return dp[len - 1][0]; } //空间复杂度为O(1)的解法 public static int maxProfitDPO(int[] prices) { if (prices == null || prices.length < 2) { return 0; } int length = prices.length; int[] dp = new int[2]; //第1天下标为0的时候可能持有 可能不持有 dp[0] = 0;//不持有 dp[1] = -prices[0];//持有 //第二天开始遍历 for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) { //分析每一天是否持有 //dp[0] 昨天不持股,今天也不持股; dp[1] + prices[i] 昨天持股,今天不持股 dp[0] = Math.max(dp[0], dp[1] + prices[i]); //dp[1] 昨天持股,今天也持股; -prices[i] 昨天不持股,今天持股 dp[1] = Math.max(dp[1], -prices[i]); } return dp[0];//最后一天不持股 } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = new int[]{1, 3, 5, 6}; System.out.println(maxProfitDP(nums)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
-
相关阅读:
Vert.x 源码解析(4.x)——Local EvnentBus入门使用和源码解析
LeetCode416:分割等和子集
Redis笔记进阶篇:万字长文-整理Redis,各种知识点,建议收藏
【数据结构】栈和队列
TS 类型体操还能这么玩,太秀了
进制转换(二进制、八进制、十进制、十六进制)
动态内存管理
QT开发之串口通信(四)
【图画】【终身学习】
快手发布Q2及半年度财报,哪些内容值得关注
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qyj19920704/article/details/126056404
