-
SpringBoot配置文件
目录
1.配置文件作用
整个项目中所有重要的数据都是在配置文件中配置的,比如:
- 数据库的连接信息;
- 项目的启动端口;
- 第三方系统的调用秘钥等信息;
- 用于发现和定位问题的普通日志和异常日志等。
2.配置文件的格式
Spring Boot 配置文件主要分为以下两种格式:
.properties.yml
如下图所示:
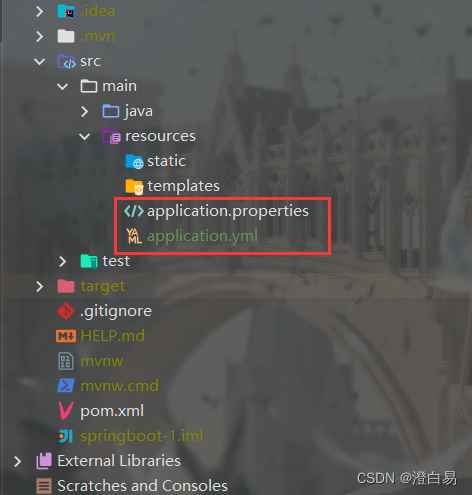
properties 类型的配置文件就属于旧版配置类型,也是创建 Spring Boot 项目时默认的文件格式,而 yml 属于新版配置类型。特殊说明
理论上讲 properties 可以和 yml 起存在于个项目当中,当 properties 和 yml 起存在个项目中时,如果配置文件中出现了同样的配置,那么这个时候会以 properties 中的配置为主,也就是
.properties配置文件的优先级最高,但加载完.properties文件之后,也会加载.yml文件的配置信息。例如,properties 和 yml 中都配置了“server.port”
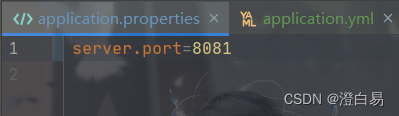
.properties将port配置为8081:
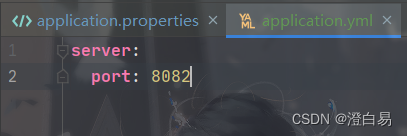
.yml将port配置为8082:
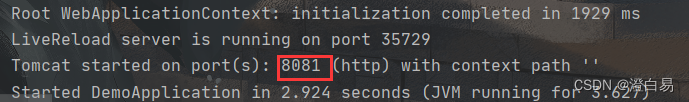
启动项目后可以看到端口为8081
3.properties 配置文件
properties配置文件是最早期的配置文件格式,也是创建 Spring Boot 项目默认的配置文件。3.1 properties 基本语法
properties是以键值的形式配置的,key 和 value 之间是以“=”连接的,如:# 配置项?端?号 server.port=8084 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/testdb? characterEncoding=utf8 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
3.2 读取配置文件
如果在项目中,想要主动的读取配置文件中的内容,可以使用
@Value注解来实现,@Value注解使用“${}”的格式读取,如下代码所示:@Component public class ReadController { @Value("${server.port}") private String port; @PostConstruct public void postConstruct() { System.out.println("read port:" + port); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
执行结果:
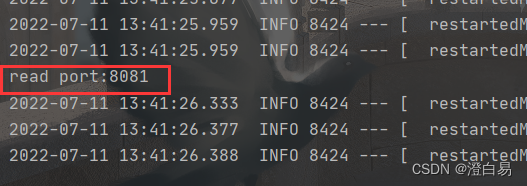
@Component 在 Spring Boot 启动时候会注入到框架中,注入到框架中时会执行 @PostConstruct 初始化方法,这个时候就能读取到配置信息了。
3.3 properties 缺点
properties配置是以key-value的形式配置的,properties 配置文件中会有很多的冗余的信息,比如这些:

想要解决这个问题,就可以使用 yml 配置文件的格式化了。4.yml 配置文件
yml是YMAL是缩写,它的全称 Yet Another Markup Language, 翻译成中就是“另种标记语言”。yml是一个可读性高,易于理解,用来表达数据序列化的格式。它的语法和其他高级语言类似,并且可以简单表达清单(数组)、散列表,标量等数据形态。它使用空白符号缩进和大量依赖外观的特色,特别适合用来表达或编辑数据结构、各种配置文件等。
yml最大的优势是可以跨语言,不止是 Java 中可以使用, golang、python 都可以使用yml作为配置文件。4.1 yml 基本语法
yml是树形结构的配置文件,它的基础语法是“key: value”,注意key和value之间使用英文冒号加空格的方式组成的,这里的空格是不能省略的。# 配置端口 server: port: 8082 # 配置数据库 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/database?charsetEncoding=utf8 username: root password: 12345678- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4.2 yml 配置读取
yml 读取配置的方式和 properties 相同,使用
@Value注解即可,实现代码如下:@Component public class ReadController { @Value("${spring.datasource.username}") private String username; @PostConstruct public void postConstruct() { System.out.println("read username:" + username); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
执行结果:
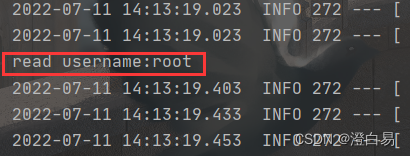
4.3 yml 使用进阶
4.3.1 配置不同数据类型及 null
# 字符串 string.value: yml # 布尔值,true或false boolean.value: true boolean.value1: false # 整数 int.value: 666 int.value1: 0b1010_0111_0100_1010_1110 # ?进制 # 浮点数 float.value: 3.14159 float.value1: 314159e-5 # 科学计数法 # Null,~代表null null.value: ~- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
注意:value 值加单双引号
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号,如果加英文的单双引号可以表示特殊的含义。
例如:string: str1: Hello Spring Boot. str2: 'Hello Spring Boot.' str3: "Hello Spring Boot."- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
读取代码如下:
@Component public class ReadController { @Value("${string.str1}") private String str1; @Value("${string.str2}") private String str2; @Value("${string.str3}") private String str3; @PostConstruct public void postConstruct() { System.out.println("string.str1:" + str1); System.out.println("string.str2:" + str2); System.out.println("string.str3:" + str3); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
执行结果:
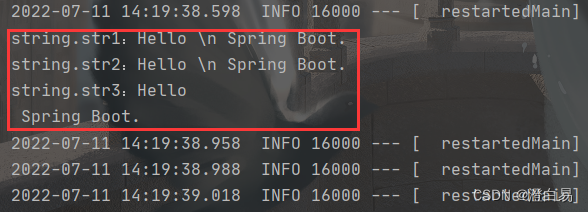
从上述结果可以看出:
- 字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号。
- 单引号会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据。
- 双引号不会转义字符串里的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思。
4.3.2 配置对象
也可以在 yml 中配置对象,如下配置:
student: id: 1 name: Java age: 20- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
或者是使用行内写法(与上面的写法作用致):
student: {id: 1,name: Java,age: 18}- 1
这个时候就不能用
@Value来读取配置中的对象了,此时要使用另个注解@ConfigurationProperties来读取,具体实现如下:
Student类:@Component @Data @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") public class Student { private int id; private String name; private int age; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
调用类:
@Component public class ReadController { @Autowired private Student student; @PostConstruct public void postConstruct() { System.out.println(student); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
执行结果:
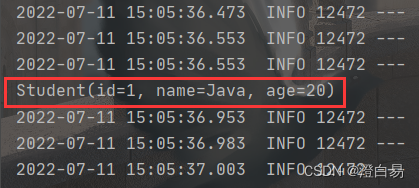
4.3.3 配置集合
配置文件也可以配置 list 集合,如下所示:
dbtypes: name: - Java - C++ - Python- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
或者是使用行内写法(与上面的写法作用致):
dbtypes: {name: [Java,C++,Python]}- 1
集合的读取和对象样,也是使用 @ConfigurationProperties 来读取的,具体实现如下:
@Component @Data @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dbtypes") public class DBTypes { private Listname; } - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
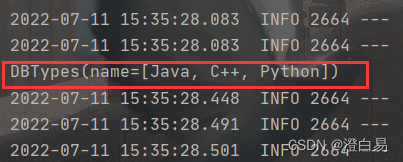
打印类:
@Component public class ReadController { @Autowired private DBTypes dbTypes; @PostConstruct public void postConstruct() { System.out.println(dbTypes); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
执行结果:
5.properties VS yml
properties是以key=value的形式配置的键值类型的配置件,而yml使用的是类似json 格式的树形配置方式进行配置的,yml 层级之间使用换行缩进的方式配置,key 和 value 之间使用“:”英文冒号加空格的方式设置,并且空格不可省略。properties为早期并且默认的配置文件格式,但其配置存在定的冗余数据,使用 yml 可以很好的解决数据冗余的问题。yml通用性更好,持更多语言,如 Java、Go、Python 等,如果是云服务器开发,可以使用份配置文件作为 Java 和 Go 的共同配置文件。yml虽然可以和properties共存,但个项目中建议使用统的配置类型文件。
-
相关阅读:
Leetcode 151. Reverse Words in a String (Python)
vue 自定义指令改data中数据
Linux---小练习
Django自动生成docs接口文档
基于当量因子法、InVEST、SolVES模型等多技术融合在生态系统服务功能社会价值评估中的应用及论文写作、拓展分析
Keras实战(一)
产业互联网周报:滴滴被处以80亿元巨额罚款;消息称中国正启动欧洲企业到中国上市计划;字节跳动确认自研专用芯片...
驱动开发day2
深入理解Java消息中间件-RabbitMQ
系列五、怎么查看默认的垃圾收集器是哪个?
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/emgexgb_sef/article/details/126041509
