-
中望龙腾后端开发工程师23届7-28笔试记录
选择多选题
- java类相关知识
- static块
- 抽象类和接口
- 面向对象特点
- 多线程ThreadLocal
- JVM常量池
- IP字段计算
唉,这些东西,背了又忘,忘了又背,背了还忘
编程题
编程题1

题解
- 直接遍历获取主对角线和副对角线元素的和
- 然后如果矩阵为奇数方阵,需要减去重复的元素
public class Solution { /** * 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可 * * * @param mat int整型二维数组 * @return int整型 */ public int diagonalSum (int[][] mat) { // write code here int res = 0; int n = mat.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { res += mat[i][i] + mat[n-1-i][i]; } if (n % 2 != 0) res -= mat[n/2][n/2]; return res; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20

编程题2

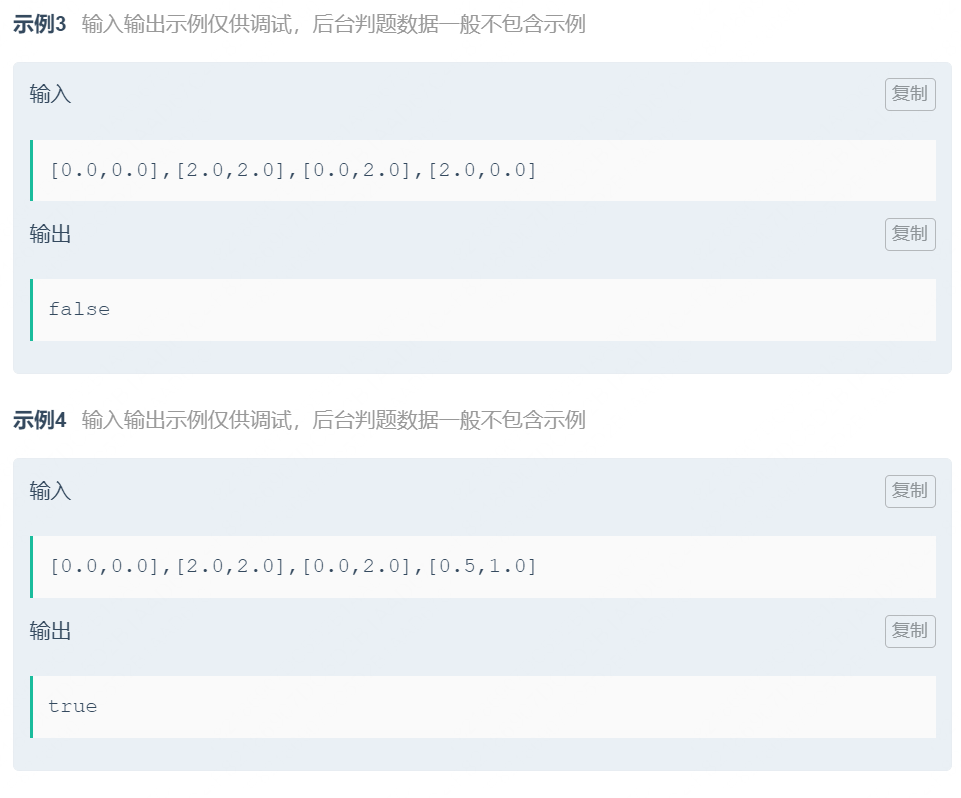
题解
这道题其实还挺常见的,特别是在游戏相关的岗位面试,结果我这菜鸡还是第一次遇到,直接蒙了…
现在下来想的话,有以下几种方法判断点是否在三角形内部:
- 三角形内角和为360度,也就是点和三角形任意两边组成一个角,这三个角的和为360度,但是浮点数计算存在无法,无法严格等于360度,该方法舍弃
- 三角形面积和,同样也是上一种方法,三角形内的点和三个顶点分别做直线,连接划分三个三角形,这三个三角形的面积和同原三角形面积相等,同样也存在浮点数计算误差的问题
- 第三种方法就是叉乘法,这一种方法比较适用,不会因为浮点数计算误差出现结果混淆的情况
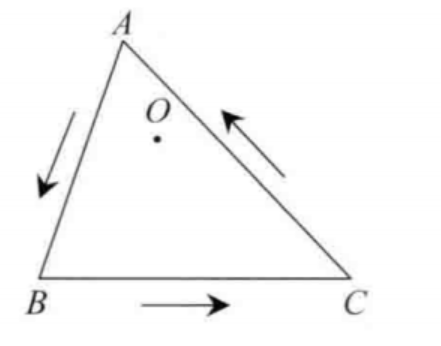
如上图所示,三角形的各个边的向量方向是逆时针方向,计算边和三角形内点o的叉乘,例如
C O → × C A → \overrightarrow{CO} \times \overrightarrow{CA} CO×CA
如果点在三角形内部,按照叉乘的计算方式,上式的结果为正数,这就是叉乘判断的原理但是在题目中,可能存在给的三角形顶点的顺序不是逆时针的顺序,所以需要进行判断
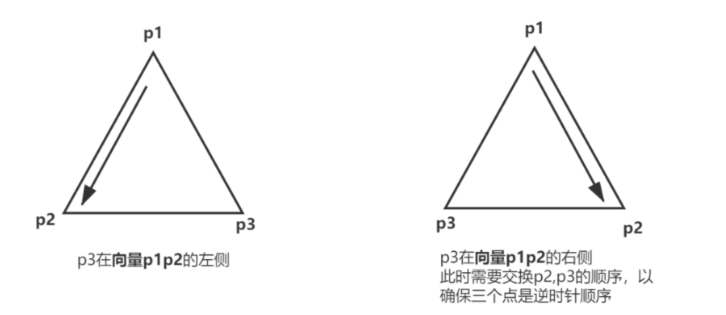
同样的也是判断叉乘公式
p 1 p 2 → × p 1 p 3 → \overrightarrow{p_1 p_2} \times \overrightarrow{p_1 p_3} p1p2×p1p3
如果为正数,则说明为逆时针方向,否则,调换 p 2 , p 3 p2, p3 p2,p3 的顺序double product(double p1,double p2,double p3) { //首先根据坐标计算p1p2和p1p3的向量,然后再计算叉乘 return (p2[0]-p1[0])*(p3[1]-p1[0]) - (p2[1]-p1[1])*(p3[0]-p1[0]); } bool isInTriangle(double p1,double p2, double p3, double o) { //保证p1,p2,p3是逆时针顺序 if(product(p1, p2, p3)<0) return isInTriangle(p1,p3,p2,o); if(product(p1, p2, o)>0 && product(p2, p3, o)>0 && product(p3, p1, o)>0) return true; return false; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
编程题3
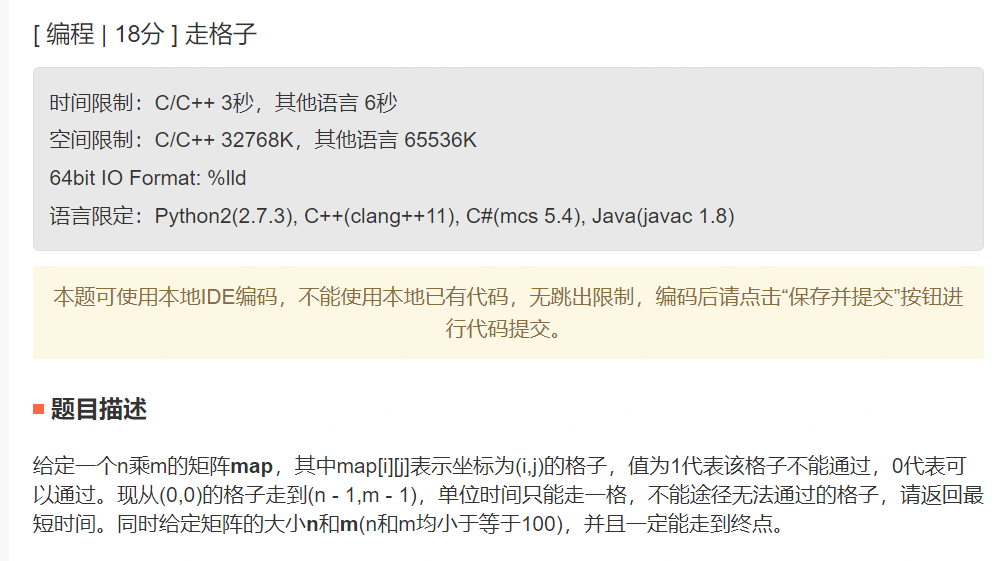
题解
这道题和 1091.二进制矩阵中的最短路径 不能说不像,只能说是一摸一样,唉,做了的题没做出来,太菜了
class Solution { public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) { int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{-1, -1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, 1}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 0}, {1, 1}}; int n = grid.length, m = grid[0].length; // 起点或终点不连通,直接返回-1 if (grid[0][0] == 1 || grid[n-1][m-1] == 1) return -1; boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m]; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>(); int[] start = new int[]{0, 0, 1}; queue.add(start); while(!queue.isEmpty()) { int[] temp = queue.poll(); for (int[] dir : dirs) { int x = temp[0] + dir[0]; int y = temp[1] + dir[1]; int weight = temp[2]; if (temp[0] == n-1 && temp[1] == m-1) return weight; if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >=0 && y < m && grid[x][y] == 0 && !visited[x][y]) { queue.add(new int[]{x, y, temp[2] + 1}); visited[x][y] = true; } } } return -1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
-
相关阅读:
web安全-原发抗抵赖
CVPR2022 | 弱监督多标签分类中的损失问题
TS的类型规则 类型排名
2021蓝桥杯真题 小蓝卡片 数学+二分查找+前缀和优化
shiro的实现认证
Mysql中自增主键是如何工作的
算法12.从暴力递归到动态规划5
Python可以处理Excel文件
【C++·峰顶计划】缺省参数操作与函数重载细则
【设计模式-2】策略模式 - 避免冗余的if-else判断
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36178962/article/details/126034966
