-
Java基础-IO流(字节流)
上一篇文章Java基础-File
1、IO的概述




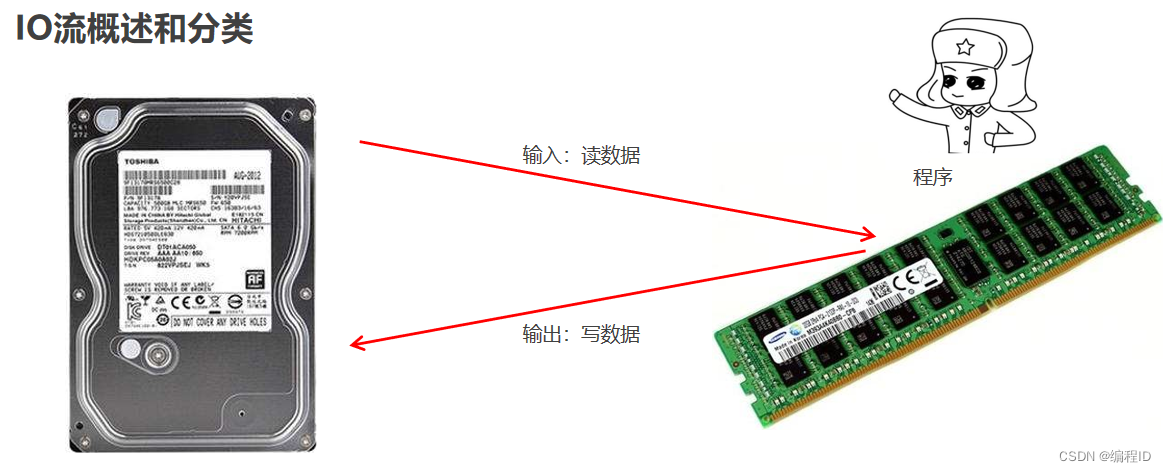
2、IO的分类
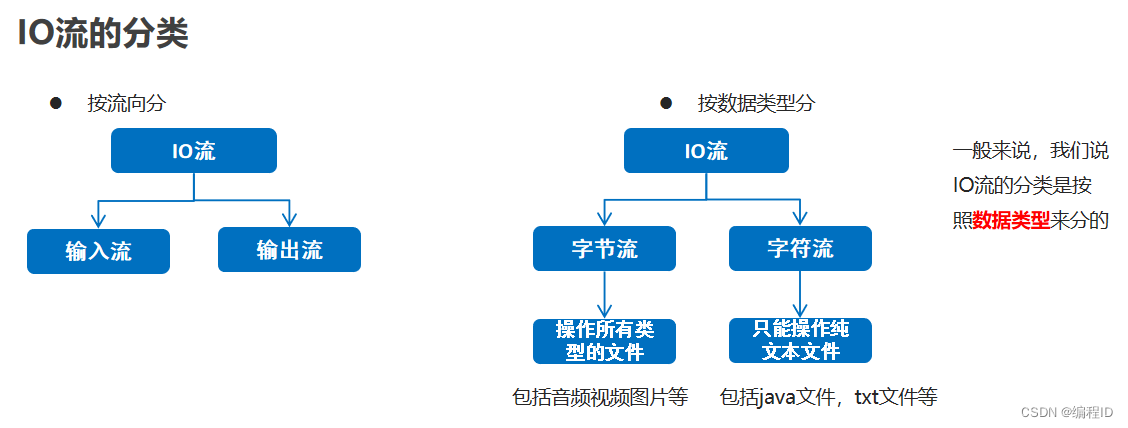
3、字节输出流

public class OutputDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建字节输出流的对象 --- 告诉虚拟机我要往哪个文件中写数据了 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\a.txt"); //FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\a.txt")); //2,写数据 fos.write(97); //3,释放资源 fos.close();//每次使用完流必须要释放资源。 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13

4、字节流注意事项

5、字节流一次写多个数据
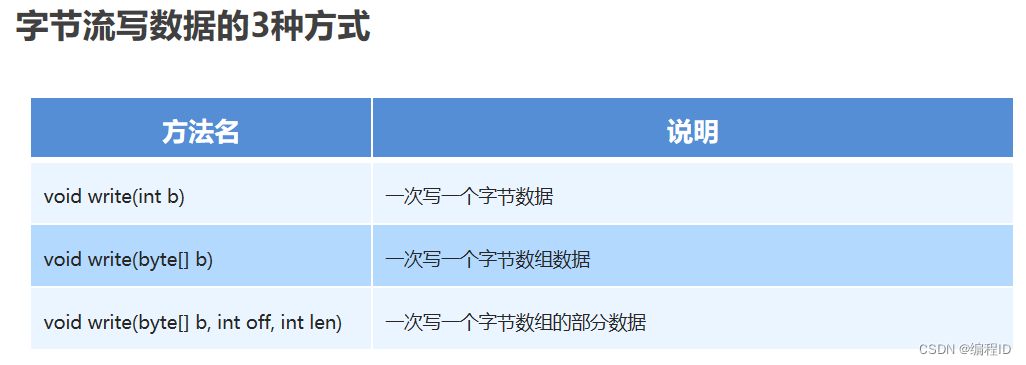
第2、3种就是一次写多个数据public class OutputDemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("bytestream\\a.txt"); //一次写一个数组;作者:编程ID /*byte [] bys = {97,98,99}; fos.write(bys);*/ byte [] bys = {97,98,99,100,101,102,103}; fos.write(bys,1,2);//从bys数组第一个索引开始写两个 fos.close();//每次使用完流必须要释放资源。 } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
6、字节流-两个问题

public class OutputDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //第二个参数就是续写开关,如果没有传递,默认就是false, //表示不打开续写功能,那么创建对象的这行代码会清空文件. //如果第二个参数为true,表示打开续写功能 //那么创建对象的这行代码不会清空文件. FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:KuGou\\a.txt",true); fos.write(97); //能加一个换行 fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); fos.write(98); //能加一个换行 fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); fos.write(99); //能加一个换行 fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); fos.write(100); //能加一个换行 fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); fos.write(101); //能加一个换行 fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); fos.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28

7、字节流-trycatch捕获异常
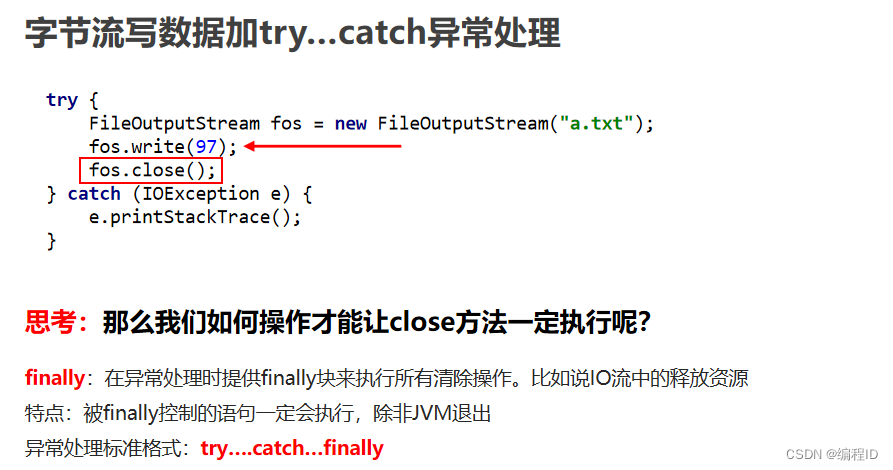

public class OutputDemo6 { public static void main(String[] args) { FileOutputStream fos = null; try { //System.out.println(2/0); fos = new FileOutputStream("C:KuGou\\a.txt"); fos.write(97); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //finally语句里面的代码,一定会被执行. if(fos != null){ try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
8、字节流小结

9、字节流输入流

public class OutputDemo7 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //如果文件存在,那么就不会报错. //如果文件不存在,那么就直接报错. FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:KuGou\\a.txt"); int read = fis.read(); //一次读取一个字节,返回值就是本次读到的那个字节数据. //也就是字符在码表中对应的那个数字. //如果我们想要看到的是字符数据,那么一定要强转成char System.out.println((char)read); //释放资源 fis.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
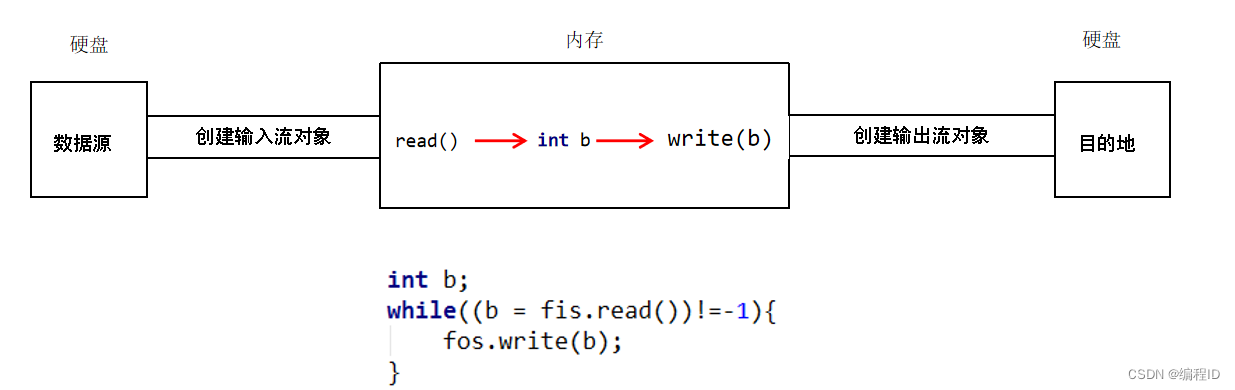
10、字节流读多个字节
public class OutputDemo8 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\KuGou\\a.txt"); //1,文件中多个字节我怎么办? /*while(true){ int i1 = fis.read(); System.out.println(i1); }*/ int b; while ((b = fis.read())!=-1){ System.out.println((char) b); } fis.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
11、文件复制


public class OutputDemo9 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //创建了字节输入流,准备读数据. FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\KUGou\\a.avi"); //创建了字节输出流,准备写数据. FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\a.avi"); int b; while((b = fis.read())!=-1){ fos.write(b); } fis.close(); fos.close(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
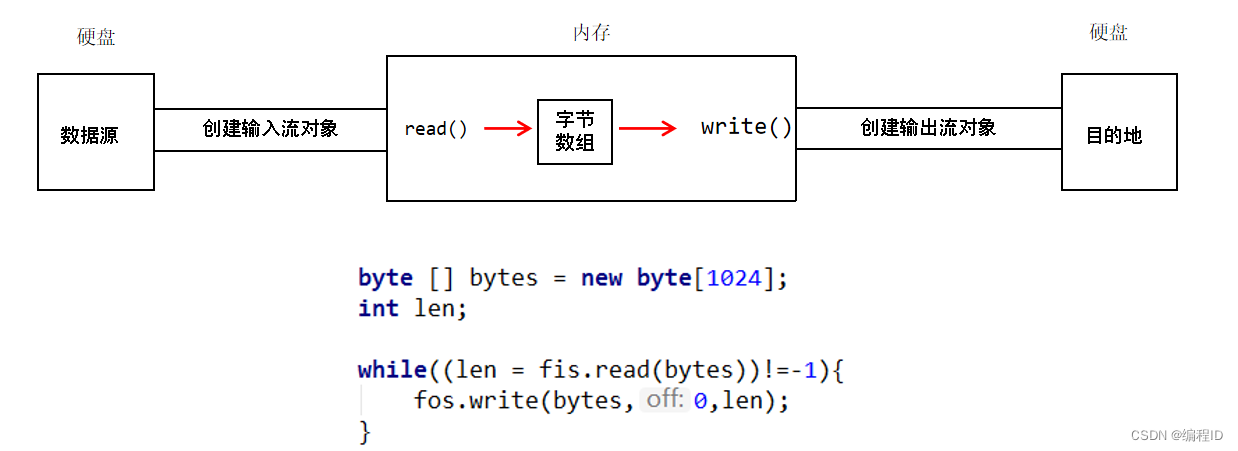
12、字节流定义小数组拷贝



public class OutputDemo10 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\itheima\\a.avi"); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("bytestream\\a.avi"); byte [] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len; //本次读到的有效字节个数 -- 这次读了几个字节. while((len = fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ fos.write(bytes,0,len); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
13、字节流小数组拷贝原理
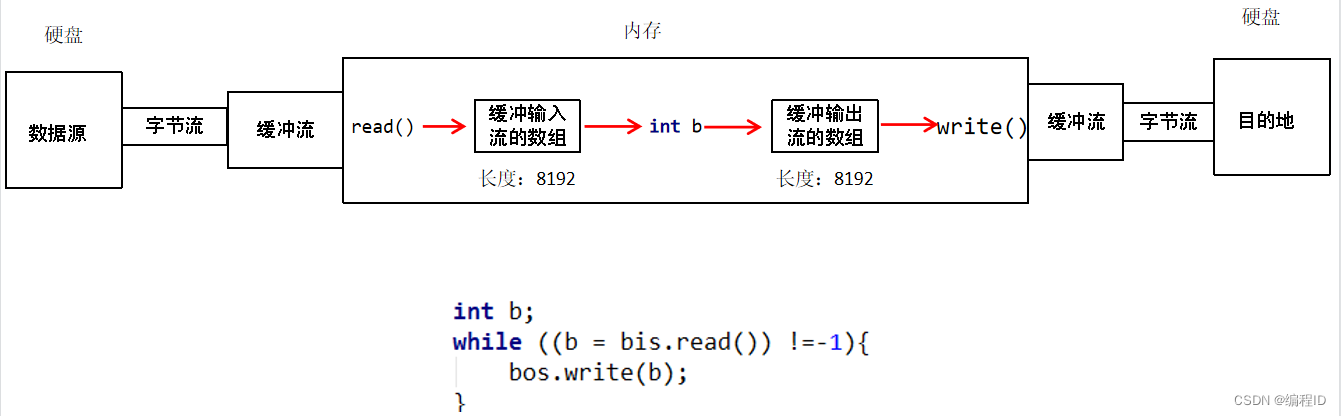
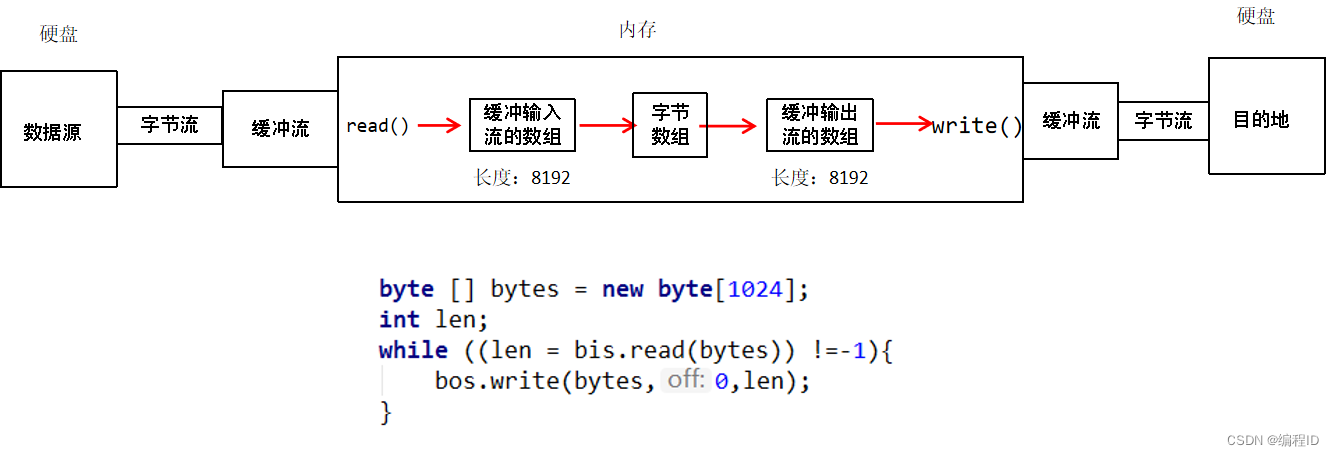

-
相关阅读:
ubuntu 显卡驱动、Cuda、Cudnn、Pytorch安装教程
数据结构(线性表-队列)
机器学习中 TP FP TN FN的概念
学习Java8 Stream流,让我们更加便捷的操纵集合
SOLIDWORKS 2024 Electrical全新升级
自动控制原理4.2---根轨迹绘制的基本法则
处理机调度算法
Enzo丨Enzo 抗原回收试剂,pH 6方案
JUC并发编程学习(五)集合类不安全
V-Value in fiber(光纤中的V值)
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43474701/article/details/126024176
