-
darknet c++源码阅读笔记-01-activation_kernels.cu
目录
1. lhtan_activate_kernel
lhtan是light tanh,近似tanh激活函数。
- //! __device__ 函数限定符,指定函数在设备端执行。
- __device__ float lhtan_activate_kernel(float x)
- {
- if(x < 0) return .001*x;
- if(x > 1) return .001*(x-1) + 1;
- return x;
- }
红色的是tanh函数,绿色的是lhtan函数,值的范围是(负无穷小,正无穷大),梯度很小,看不出来是无穷大。

2. lhtan_gradient_kernel
是lhtan_activate_kernel函数的梯度,x<0时,-0.001*x的梯度是0.001,0<=x<=1时,梯度是1.
- //! lhtan_activate_kernel的梯度值
- __device__ float lhtan_gradient_kernel(float x)
- {
- if(x > 0 && x < 1) return 1;
- return .001;
- }

3. hardtan_activate_kernel
hard tanh激活函数。
- //! hard tanh激活函数
- __device__ float hardtan_activate_kernel(float x)
- {
- if (x < -1) return -1;
- if (x > 1) return 1;
- return x;
- }
红色是tanh正切函数,黑色是hard tanh函数,绿色是hard tanh的梯度函数。


4. linear_activate_kernel
线性激活函数.
__device__ float linear_activate_kernel(float x){return x;}5. logistic_activate_kernel
逻辑回归的激活函数,也称sigmoid激活函数,特点是将y值归一化到(0,1)之间。画图工具。
__device__ float logistic_activate_kernel(float x){return 1.f/(1.f + expf(-x));}红色的是sigmoid函数,绿色是其倒数f(x) * (1-f(x)),可以看到x=0时,梯度值最大。
求梯度代码:
__device__ float logistic_gradient_kernel(float x){return (1-x)*x;} // 这里的x应该是sigmoid的y值
6. loggy_activate_kernel
与上面的sigmoid函数形态类似,不同的是归一化后y范围是(-1,1).
y = 2 / ( 1 + exp(-x) ) - 1.
参考sigmoid函数求导方法,求导y’ = 2*sigmoid(x)(1-sigmoid(x))
紫色是loggy激活函数,红色是其倒数。
__device__ float loggy_activate_kernel(float x){return 2.f/(1.f + expf(-x)) - 1;} // 范围(-1,1)- __device__ float loggy_gradient_kernel(float x) // x = 2 / (1+exp(-a)) - 1
- {
- float y = (x+1.F)/2.F; // y = (2 / (1+exp(-a)) - 1 + 1) / 2 = 1 / (1+exp(-a)) = y,即sigmoid函数。
- return 2*(1-y)*y; //
- }

7.relu_activate_kernel
常用的relu激活函数。ReLU = max(0, x),小于0的梯度为0.
推荐一个好用的画图工具。
__device__ float relu_activate_kernel(float x){return x*(x>0);}__device__ float relu_gradient_kernel(float x){return (x>0);}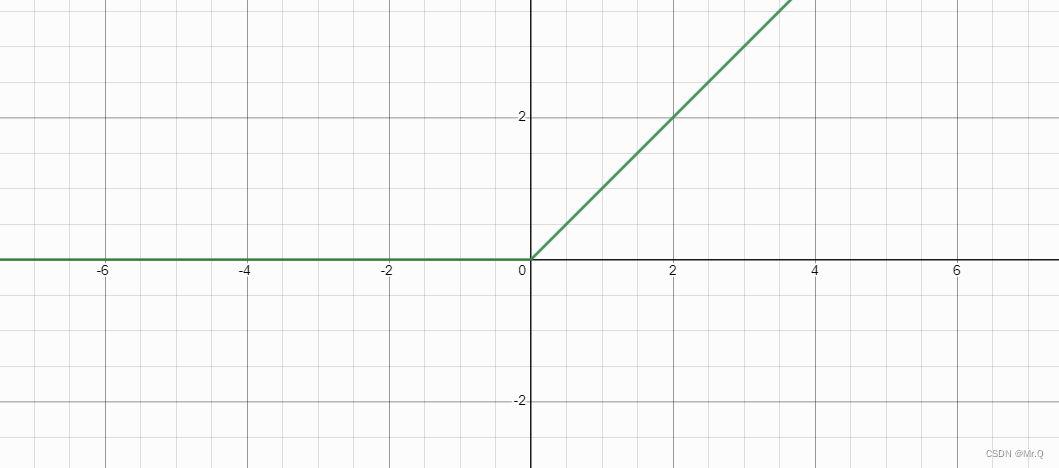
8. relu6_activate_kernel
相对于relu,不止抑制了小于0的值,也抑制了较大的值(大于6的值)。ReLU6=min(6, max(0,x))
__device__ float relu6_activate_kernel(float x) { return min_val_cmp(max_val_cmp(x, 0), 6); }__device__ float relu6_gradient_kernel(float x) { return (x > 0 && x < 6); }
9. elu_activate_kernel
ELU相对于ReLU的特点是多了个"e",即没有直接丢弃左边小于0的部分,而是用e^x激活。
(1)大于0的部分:(x >= 0)*x,和ReLU一样,不变;
(2)小于0的部分:(x < 0)*(expf(x)-1),即e^x-1;
__device__ float elu_activate_kernel(float x){return (x >= 0)*x + (x < 0)*(expf(x)-1);}- //! x = e^a-1, x'=-e^a = 1+x
- __device__ float elu_gradient_kernel(float x){return (x >= 0) + (x < 0)*(x + 1);} // 大于0时,梯度为1,小于0时,梯度为x+1
10. selu_activate_kernel
SELU(the scaled exponential linear units)相对于ELU多了个S,即前面加了大于1的系数。
大于0的部分系数是1.0507;小于0的部分系数是1.0507*1.6732;
__device__ float selu_activate_kernel(float x) { return (x >= 0)*1.0507f*x + (x < 0)*1.0507f*1.6732f*(expf(x) - 1); }- //! x = 1.0507*1.6732*(e^a-1), x' = x(1+b/x)=x+b
- __device__ float selu_gradient_kernel(float x) { return (x >= 0)*1.0507f + (x < 0)*(x + 1.0507f*1.6732f); }
蓝色的是ELU, 绿色的是SELU。

11. relie_activate_kernel
也就是leaky ReLU,相对于ReLU,保留了小于0时的梯度。
__device__ float relie_activate_kernel(float x){return (x>0) ? x : .01f*x;} // leaky ReLU__device__ float relie_gradient_kernel(float x){return (x>0) ? 1 : .01f;}
12. ramp_activate_kernel
ramp就是在ReLU+0.1*x
__device__ float ramp_activate_kernel(float x){return x*(x>0)+.1f*x;} // ReLU + 0.1*x__device__ float ramp_gradient_kernel(float x){return (x>0)+.1f;}
13. leaky_activate_kernel
相对于ReLU,保留了小于0时的梯度。
__device__ float leaky_activate_kernel(float x){return (x>0) ? x : .1f*x;} // 和relie_activate_kernel一样。__device__ float leaky_gradient_kernel(float x){return (x>0) ? 1 : .1f;}
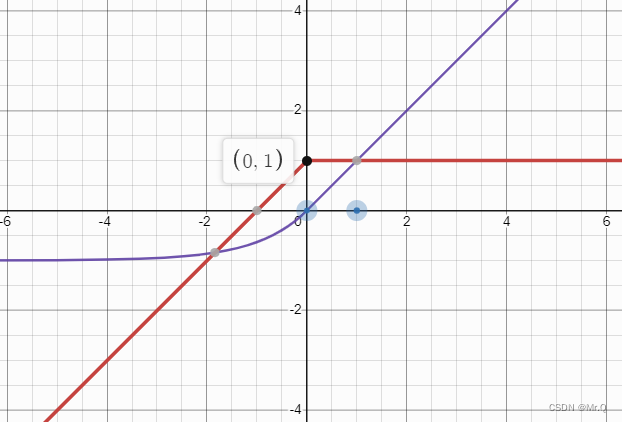
14. tanh_activate_kernel
tanh激活函数。范围 (-1, 1),相对于前面的loggy_activate_kernel:2.f/(1.f + expf(-x)) - 1,x系数变成了-2,梯度更大。
__device__ float tanh_activate_kernel(float x){return (2/(1 + expf(-2*x)) - 1);}- //! x = 2/(1+exp(-2a)) - 1, x'= (x+1)*2*(1-(x+1)/2) = (x+1)(1-x) = (1-x^2)
- __device__ float tanh_gradient_kernel(float x){return 1-x*x;}
红色的是tanh激活函数,绿色的是loggy_activate_kernel,紫色是tanh函数的梯度函数。

15. gelu_activate_kernel
GELU相对于ReLU,越大梯度值越接近1,越小越接近0,没有直接置为0. 范围是(0,无穷大],
__device__ float gelu_activate_kernel(float x){return (0.5*x*(1 + tanhf(0.797885*x + 0.035677*powf(x, 3))));}- __device__ float gelu_gradient_kernel(float x) {
- const float x3 = powf(x, 3);
- return 0.5*tanhf(0.0356774*x3 + 0.797885*x) + (0.0535161*x3 + 0.398942*x) * powf(sech_gpu(0.0356774*x3 + 0.797885*x), 2) + 0.5;
- }

16. softplus_kernel
softplus(x) = ln(1+exp(x)),范围(0,无穷大)具体实现如下。
(1)太大的,直接返回;
(2)太小的,返回e^x;
(3)中间的,返回ln(1+exp(x)).
- __device__ float softplus_kernel(float x, float threshold = 20) {
- if (x > threshold) return x; // too large
- else if (x < -threshold) return expf(x); // too small
- return log1pf(expf(x)); // log1pf(val)返回ln(val+1)
- //return logf(expf(x) + 1);
- }

17. plse_activate_kernel
分段线性激活。
- __device__ float plse_activate_kernel(float x)
- {
- if(x < -4) return .01f * (x + 4);
- if(x > 4) return .01f * (x - 4) + 1;
- return .125f*x + .5f;
- }

18. sech_gpu
__device__ float sech_gpu(float x) { return 2 / (expf(x) + expf(-x)); }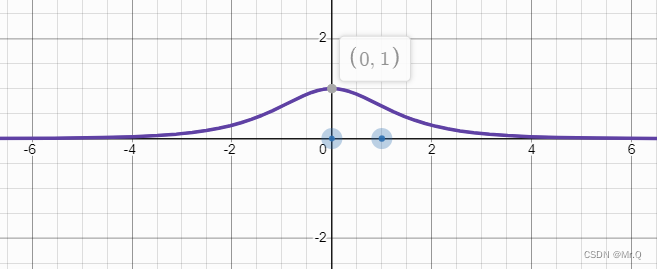
19. activate_kernel
使用上面定义的激活函数。
- /***
- * 根据传入的枚举类型,返回的激活值
- typedef enum {
- LOGISTIC, RELU, RELU6, RELIE, LINEAR, RAMP, TANH, PLSE, REVLEAKY, LEAKY, ELU, LOGGY, STAIR, HARDTAN, LHTAN, SELU, GELU, SWISH, MISH, HARD_MISH, NORM_CHAN, NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX, NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX_MAXVAL
- }ACTIVATION;
- ***/
- __device__ float activate_kernel(float x, ACTIVATION a)
- {
- switch(a){
- case LINEAR:
- return linear_activate_kernel(x);
- case LOGISTIC:
- return logistic_activate_kernel(x);
- case LOGGY:
- return loggy_activate_kernel(x);
- case RELU:
- return relu_activate_kernel(x);
- case RELU6:
- return relu6_activate_kernel(x);
- case ELU:
- return elu_activate_kernel(x);
- case SELU:
- return selu_activate_kernel(x);
- case GELU:
- return gelu_activate_kernel(x);
- case RELIE:
- return relie_activate_kernel(x);
- case RAMP:
- return ramp_activate_kernel(x);
- case LEAKY:
- return leaky_activate_kernel(x);
- case TANH:
- return tanh_activate_kernel(x);
- case PLSE:
- return plse_activate_kernel(x);
- case STAIR:
- return stair_activate_kernel(x);
- case HARDTAN:
- return hardtan_activate_kernel(x);
- case LHTAN:
- return lhtan_activate_kernel(x);
- }
- return 0;
- }
20. gradient_kernel
- /***
- 根据不同的激活函数,调用对应的梯度函数
- ***/
- __device__ float gradient_kernel(float x, ACTIVATION a)
- {
- switch (a) {
- case LINEAR:
- return linear_gradient_kernel(x);
- case LOGISTIC:
- return logistic_gradient_kernel(x);
- case LOGGY:
- return loggy_gradient_kernel(x);
- case RELU:
- return relu_gradient_kernel(x);
- case RELU6:
- return relu6_gradient_kernel(x);
- case NORM_CHAN:
- return relu_gradient_kernel(x);
- case ELU:
- return elu_gradient_kernel(x);
- case SELU:
- return selu_gradient_kernel(x);
- case GELU:
- return gelu_gradient_kernel(x);
- case RELIE:
- return relie_gradient_kernel(x);
- case RAMP:
- return ramp_gradient_kernel(x);
- case LEAKY:
- return leaky_gradient_kernel(x);
- case TANH:
- return tanh_gradient_kernel(x);
- case PLSE:
- return plse_gradient_kernel(x);
- case STAIR:
- return stair_gradient_kernel(x);
- case HARDTAN:
- return hardtan_gradient_kernel(x);
- case LHTAN:
- return lhtan_gradient_kernel(x);
- }
- return 0;
- }
-
相关阅读:
[pytorch]设备选择以及卷积神经网络的应用
matlab学习笔记
手机开机入网流程 && KPI接通率和掉线率
工业交换机选购标准,你知道多少?
Recurrent vs. Recursive Neural Networks | 递归神经网络和循环神经网络的RNN之争
零样本学习&Domain-aware Visual Bias Eliminating for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning
算法课作业2 OJ for Divide and Conquer
时间序列数据机器学习(ICML 2022)
kubernetespod控制器详解2与service详解1
深入探索Spring AI:源码分析流式回答
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/jizhidexiaoming/article/details/125997437