-
【Netty 的设计与应用】
一、粘包与半包
代码
server
public class StudyServer { static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyServer.class); void start() { NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class); // 调整channel的容量 serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10); serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker); serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // 连接建立时会执行该方法 log.debug("connected {}", ctx.channel()); super.channelActive(ctx); } @Override public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // 连接断开时会执行该方法 log.debug("disconnect {}", ctx.channel()); super.channelInactive(ctx); } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080); log.debug("{} binding...", channelFuture.channel()); channelFuture.sync(); log.debug("{} bound...", channelFuture.channel()); // 关闭channel channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("server error", e); } finally { boss.shutdownGracefully(); worker.shutdownGracefully(); log.debug("stopped"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { new StudyServer().start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
client
public class StudyClient { static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyClient.class); public static void main(String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class); bootstrap.group(worker); bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { log.debug("connected..."); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("sending..."); // 每次发送16个字节的数据,共发送10次 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(); buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } } }); } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { log.error("client error", e); } finally { worker.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
粘包: 多个包合并在一起了.
半包: 接受到的数据,是断断续续的字节,因为缓冲区有限制
注意:serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 10) 影响的底层接受缓冲区(即滑动窗口)的大小,仅决定了netty读取的最小单位**,netty 实际每次读取的一般是它的整数倍**
分析
粘包
- 现象: 发送abc def , 接受abcdef
- 原因
- 应用层: 接收方ByteBuf 设置太大 (Netty 默认 1024)
- tcp 滑动窗口: 假设发送方256bytes标识一个 完整报文,但由于接收方处理不及时且窗口很大时,这个报文就会缓冲在接收方的滑动窗口内,当滑动窗口中缓冲了多个报文就会形成粘包
- Nagle算法: 默认开启 造成粘包
半包
- 现象:发送abcdef , 接受 abc def
- 原因:
- 应用层: 接收方 ByteBuf 小于实际发送数量
- 滑动窗口: 假设接收方的窗口只剩下128 bytes, 发送方的报文大小是 256bytes, 这个时候放不下,只能先发送前128bytes,等到ack之后再发送剩余部分,造成半包.
- MSS 限制: 当发送的数据超过MSS 限制后,会将数据切分发送,就会造成半包.
本质
其实本质上就是因为 TCP是流式协议,消息无边界. (边界指的是在报文投的 消息大小).
解决方案
短连接
客户端每次向服务器发送数据以后,就与服务器断开连接,此时的消息边界为连接建立到连接断开。这时便无需使用滑动窗口等技术来缓冲数据,则不会发生粘包现象。但如果一次性数据发送过多,接收方无法一次性容纳所有数据,还是会发生半包现象,所以短链接无法解决半包现象
客户端修改
@Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { log.debug("sending..."); ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(16); buffer.writeBytes(new byte[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); // 使用短链接,每次发送完毕后就断开连接 ctx.channel().close(); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
然后调用10次send(), 模拟10次发送,其实就是10次短连接,但是无法解决半包,以为很有可能一次发送量超过接收方的窗口大小.
第一个option 是一个全局的
第二个是针对每个channel的.
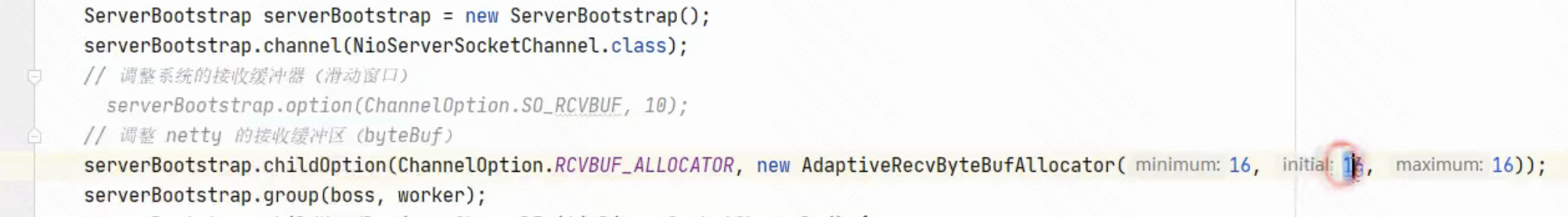
现象: **
客户端先于服务器建立连接,此时控制台打印ACTIVE,之后客户端向服务器发送了16B的数据,发送后断开连接,此时控制台打印INACTIVE,可见未出现粘包现象**定长解码器
客户端与服务器约定一个最大长度,保证客户端每次发送的数据长度都不会大于该长度。若发送数据长度不足则需要补齐至该长度。
服务器接收数据时,将接收到的数据按照约定的最大长度进行拆分,即使发送过程中产生了粘包,也可以通过定长解码器将数据正确地进行拆分。服务端需要用到FixedLengthFrameDecoder对数据进行定长解码,具体使用方法如下ch.pipline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(16));- 1
客户端改造
// 约定最大长度为16 final int maxLength = 16; // 被发送的数据 char c = 'a'; // 向服务器发送10个报文 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(maxLength); // 定长byte数组,未使用部分会以0进行填充 byte[] bytes = new byte[maxLength]; // 生成长度为0~15的数据 for (int j = 0; j < (int)(Math.random()*(maxLength-1)); j++) { bytes[j] = (byte) c; } buffer.writeBytes(bytes); c++; // 将数据发送给服务器 ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
服务器改造
使用FixedLengthFrameDecoder对粘包数据进行拆分,该handler需要添加在LoggingHandler之前,保证数据被打印时已被拆分.// 通过定长解码器对粘包数据进行拆分 ch.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(16)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));- 1
- 2
- 3
行解码器
行解码器的是通过分隔符对数据进行拆分来解决粘包半包问题的
可以通过LineBasedFrameDecoder(int maxLength)来拆分以换行符(\n)为分隔符的数据,也可以通过DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(int maxFrameLength, ByteBuf… delimiters)来指定通过什么分隔符来拆分数据(可以传入多个分隔符)
两种解码器都需要传入数据的最大长度,若超出最大长度,会抛出TooLongFrameException异常
以换行符 \n 为分隔符
客户端代码// 约定最大长度为 64 final int maxLength = 64; // 被发送的数据 char c = 'a'; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(maxLength); // 生成长度为0~62的数据 Random random = new Random(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int j = 0; j < (int)(random.nextInt(maxLength-2)); j++) { sb.append(c); } // 数据以 \n 结尾 sb.append("\n"); buffer.writeBytes(sb.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); c++; // 将数据发送给服务器 ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
服务器代码
// 通过行解码器对粘包数据进行拆分,以 \n 为分隔符 // 需要指定最大长度 ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(64)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
以自定义分隔符 \c 为分隔符
客户端代码... // 数据以 \c 结尾 sb.append("\\c"); buffer.writeBytes(sb.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); ...- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
服务器代码
// 将分隔符放入ByteBuf中 ByteBuf bufSet = ch.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("\\c".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); // 通过行解码器对粘包数据进行拆分,以 \c 为分隔符 ch.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(64, ch.alloc().buffer().writeBytes(bufSet))); ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
长度字段解码器
在传送数据时可以在数据中添加一个用于表示有用数据长度的字段,在解码时读取出这个用于表明长度的字段,同时读取其他相关参数,即可知道最终需要的数据是什么样子的
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder解码器可以提供更为丰富的拆分方法,其构造方法有五个参数public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder( int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
参数解析
- maxFrameLength** 数据最大长度**
- 表示数据的最大长度 (包括附加信息、长度标识等内容)
- lengthFieldOffset** 数据长度标识的起始偏移量**
- 起始就是标明数据长度区块的开始地址
- lengthFieldLength** 数据长度标识所占字节数**
- lengthAgjustment** 长度表示与有用数据的偏移量**
- 用于指明数据长度标识和有用数据之间的距离,因为两者之间还可能有附加信息
- initialBytesToStrip 数据读取起点
- 读取起点,不读取 0 ~ initialBytesToStrip 之间的数据
参数图解
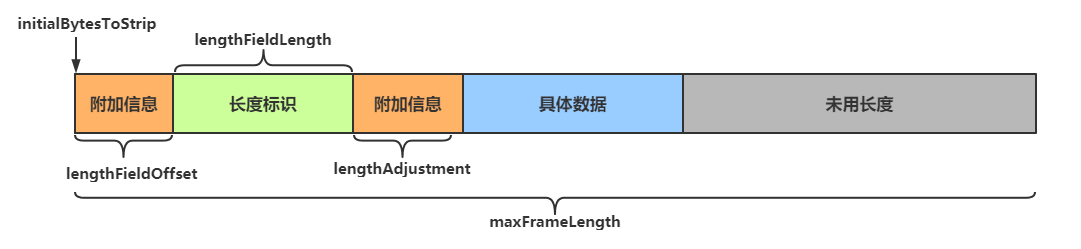
lengthFieldOffset = 1 (= the length of HDR1) lengthFieldLength = 2 lengthAdjustment = 1 (= the length of HDR2) initialBytesToStrip = 3 (= the length of HDR1 + LEN) BEFORE DECODE (16 bytes) AFTER DECODE (13 bytes) +------+--------+------+----------------+ +------+----------------+ | HDR1 | Length | HDR2 | Actual Content |----->| HDR2 | Actual Content | | 0xCA | 0x000C | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | | 0xFE | "HELLO, WORLD" | +------+--------+------+----------------+ +------+----------------+- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
长度标识前面有1个字节的其他内容,后面也有1个字节的其他内容,读取时从长度标识之后3个字节处开始读取,即读取 0xFE HELLO, WORLD
使用
通过 EmbeddedChannel 对 handler 进行测试public class EncoderStudy { public static void main(String[] args) { // 模拟服务器 // 使用EmbeddedChannel测试handler EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel( // 数据最大长度为1KB,长度标识前后各有1个字节的附加信息,长度标识长度为4个字节(int) new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 1, 4, 1, 0), new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG) ); // 模拟客户端,写入数据 ByteBuf buffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(); send(buffer, "Hello"); channel.writeInbound(buffer); send(buffer, "World"); channel.writeInbound(buffer); } private static void send(ByteBuf buf, String msg) { // 得到数据的长度 int length = msg.length(); byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // 将数据信息写入buf // 写入长度标识前的其他信息 buf.writeByte(0xCA); // 写入数据长度标识 buf.writeInt(length); // 写入长度标识后的其他信息 buf.writeByte(0xFE); // 写入具体的数据 buf.writeBytes(bytes); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
运行结果:
146 [main] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xembedded, L:embedded - R:embedded] READ: 11B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| ca 00 00 00 05 fe 48 65 6c 6c 6f |......Hello | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ 146 [main] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0xembedded, L:embedded - R:embedded] READ: 11B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| ca 00 00 00 05 fe 57 6f 72 6c 64 |......World | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
二、协议设计与解析
协议的作用
TCP/IP 中消息传输基于流的方式,没有边界
协议的目的就是划定消息的边界,制定通信双方要共同遵守的通信规则Redis 协议
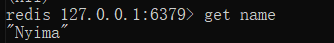
如果我们要向Redis服务器发送一条set name Nyima的指令,需要遵守如下协议
// 该指令一共有3部分,每条指令之后都要添加回车与换行符 *3\r\n // 第一个指令的长度是3 $3\r\n // 第一个指令是set指令 set\r\n // 下面的指令以此类推 $4\r\n name\r\n $5\r\n Nyima\r\n- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
客户端代码如下
public class RedisClient { static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyServer.class); public static void main(String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ChannelFuture channelFuture = new Bootstrap() .group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) { // 打印日志 ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)); ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // 回车与换行符 final byte[] LINE = {'\r','\n'}; // 获得ByteBuf ByteBuf buffer = ctx.alloc().buffer(); // 连接建立后,向Redis中发送一条指令,注意添加回车与换行 // set name Nyima buffer.writeBytes("*3".getBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(LINE); buffer.writeBytes("$3".getBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(LINE); buffer.writeBytes("set".getBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(LINE); buffer.writeBytes("$4".getBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(LINE); buffer.writeBytes("name".getBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(LINE); buffer.writeBytes("$5".getBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(LINE); buffer.writeBytes("Nyima".getBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(LINE); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } }); } }) .connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 6379)); channelFuture.sync(); // 关闭channel channelFuture.channel().close().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭group group.shutdownGracefully(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
控制台打印结果
1600 [nioEventLoopGroup-2-1] DEBUG io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler - [id: 0x28c994f1, L:/127.0.0.1:60792 - R:localhost/127.0.0.1:6379] WRITE: 34B +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+ |00000000| 2a 33 0d 0a 24 33 0d 0a 73 65 74 0d 0a 24 34 0d |*3..$3..set..$4.| |00000010| 0a 6e 61 6d 65 0d 0a 24 35 0d 0a 4e 79 69 6d 61 |.name..$5..Nyima| |00000020| 0d 0a |.. | +--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Redis中查询执行结果
HTTP协议
Http 协议在请求行请求头中国都有很多的内容,自己实现比较困难,可以使用HttpServerCodec为服务器端的解码器与编码器,来处理HTTP请求
// HttpServerCodec 中既有请求的解码器 HttpRequestDecoder 又有响应的编码器 HttpResponseEncoder // Codec(CodeCombine) 一般代表该类既作为 编码器 又作为 解码器 public final class HttpServerCodec extends CombinedChannelDuplexHandler<HttpRequestDecoder, HttpResponseEncoder> implements HttpServerUpgradeHandler.SourceCodec- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
服务器代码
public class HttpServer { static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StudyServer.class); public static void main(String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); new ServerBootstrap() .group(group) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)); // 作为服务器,使用 HttpServerCodec 作为编码器与解码器 ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec()); // 服务器只处理HTTPRequest ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpRequest msg) { // 获得请求uri log.debug(msg.uri()); // 获得完整响应,设置版本号与状态码 DefaultFullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK); // 设置响应内容 byte[] bytes = "<h1>Hello, World!</h1>".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); // 设置响应体长度,避免浏览器一直接收响应内容 response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length); // 设置响应体 response.content().writeBytes(bytes); // 写回响应 ctx.writeAndFlush(response); } }); } }) .bind(8080); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
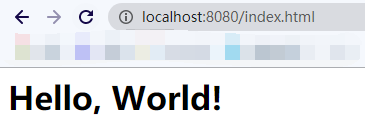
client请求效果:
自定义协议
组成要素
- 魔数: 用来在第一时间判断接受的数据是否为无效数据包,其实就是通信双方关注是否是自己业务的消息
- 版本号: 可以支持协议的升级
- 序列化算法: 消息正文到底采用哪种序列化反序列化方式
- 如: json、protobuf、hession、jdk
- 指令类型: 比如登陆、注册、单聊、群聊… 跟业务有关的
- 请求序号: 为了双工通信,提供异步能力
- 正文长度
- 消息正文
编码器与解码器
package com.xlg.component.netty.apply.protocol; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.util.List; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import com.xlg.component.netty.apply.message.Message; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.ByteToMessageCodec; /** * 自定义编码器与解码器. 其实就是一套通信协议, 就是一个handler * 注意: 这个是不能加 @Sharable 也即是线程共享. * 因为父类害怕, 子类中存在一些有状态的编解码. * @author wangqingwei * Created on 2022-06-19 */ public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message> { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MessageCodec.class); @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { // 1. 设置默数 4字节 out.writeBytes(new byte[] {'Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'}); // 2. 版本号 1字节 out.writeByte(1); // 3. 序列化算法 1字节 0: jdk 1:protobuf out.writeByte(0); // 4. 指令类型 1字节 0: 登陆 out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType()); // 5. 请求序号 4字节 out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId()); // 为了补齐16字节, 加一个 out.writeByte(0xff); // 6. 正文长度 4字节 // 7. 消息正文 // 获取序列化后的msg ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(msg); // 得到jdk序列化后的数据 byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); out.writeInt(bytes.length); out.writeBytes(bytes); logger.debug("编码"); } @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { // 获取魔数 final int magic = in.readInt(); // 获取版本号 final byte version = in.readByte(); // 获取序列化算法 final byte seqType = in.readByte(); // 获取指令类型 final byte messageType = in.readByte(); // 请求序号 final int sequenceId = in.readInt(); // 额外数据 final byte extData = in.readByte(); // 四字节的正文长度 final int length = in.readInt(); // 正文内容 byte[] bytes = new byte[length]; in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length); ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes)); Message msg = (Message)objectInputStream.readObject(); logger.debug("解码: {}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magic, version, seqType, messageType, sequenceId, extData, length, msg); // 下一个handler处理 out.add(msg); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
编写测试类
package com.xlg.component.netty.apply.protocol; import com.xlg.component.netty.apply.message.LoginRequestMessage; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBufAllocator; import io.netty.channel.embedded.EmbeddedChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder; import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler; /** * @author wangqingwei * Created on 2022-06-19 */ public class TestMessageCodec { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel( new LoggingHandler(), // 长度字段. 解决半包与粘包问题. new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 12, 4, 0,0), new MessageCodec() ); // 添加编码器 LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage("zhangsan", "123", "张三"); // channel.writeOutbound(message); // 测试解码 ByteBuf byteBuf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer(); new MessageCodec().encode(null, message, byteBuf); final ByteBuf slice1 = byteBuf.slice(0, 100); final ByteBuf slice2 = byteBuf.slice(100, byteBuf.readableBytes() - 100); slice1.retain(); channel.writeInbound(slice1); // release 1 channel.writeInbound(slice2); // channel.writeInbound(byteBuf); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 测试类中用到了LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,避免粘包半包问题
- 通过MessageCodec的encode方法将附加信息与正文写入到ByteBuf中,通过channel执行入站操作。入站时会调用decode方法进行解码
@Sharable注解
这个编解码器能否在多个channel中共享呢?
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG); // 不同的channel中使用同一个handler对象,提高复用率 channel1.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler); channel2.pipeline().addLast(loggingHandler);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
不行, 因为
但是实际情况我们并不能添加该注解,会抛出异常信息ChannelHandler cn.nyimac.study.day8.protocol.MessageCodec is not allowed to be shared
因为MessageCodec继承自ByteToMessageCodec,ByteToMessageCodec类的注解如下
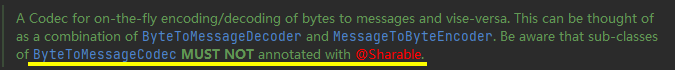
改造:package com.xlg.component.netty.apply.protocol; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.util.List; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import com.xlg.component.netty.apply.message.Message; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler.Sharable; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageCodec; /** * msgToMsg 不会出现需要多个channel共享时出现半包记录数据问题. * * 需要和 new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 一起使用. 确保buf数据是完整的. * @author wangqingwei * Created on 2022-06-19 */ @Sharable public class MessageShareCodec extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MessageShareCodec.class); @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { final ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(); // 1. 设置默数 4字节 buf.writeBytes(new byte[] {'Q', 'W', 'E', 'R'}); // 2. 版本号 1字节 buf.writeByte(1); // 3. 序列化算法 1字节 0: jdk 1:protobuf buf.writeByte(0); // 4. 指令类型 1字节 0: 登陆 buf.writeByte(msg.getMessageType()); // 5. 请求序号 4字节 buf.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId()); // 为了补齐16字节, 加一个 buf.writeByte(0xff); // 6. 正文长度 4字节 // 7. 消息正文 // 获取序列化后的msg ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(msg); // 得到jdk序列化后的数据 byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); buf.writeInt(bytes.length); buf.writeBytes(bytes); logger.debug("编码"); out.add(msg); } @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
配置:

三、聊天室
https://nyimac.gitee.io/2021/04/25/Netty%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80/#%E8%BF%9E%E6%8E%A5%E5%81%87%E6%AD%BB
-
相关阅读:
小程序添加分享和禁用分享功能
教你使用华为云函数进行签名校验
Spring框架学习
处理死锁的策略-预防死锁
VVC代码阅读 帧内预测部分(1) xCheckRDCostIntra()函数(部分)
机器学习过程&四要素
springboot 自动注入servlet原理
民商法领域的论文选题求推荐?
前端css实现特殊日期网页变灰功能
数字时代的保险创新与升级 | 创新场景50
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41773026/article/details/125627803