-
JAVASE语法零基础——Comparable接口、Comparator接口
Java系列文章目录

Write once,Runanywhere.🔥🔥🔥
这篇文章的接口用于实现自定义类的比较。💥 💥 💥如果你觉得我的文章有帮助到你,还请【关注➕点赞➕收藏】,得到你们支持就是我最大的动力!!!
💥 💥 💥⚡版权声明:本文由【马上回来了】原创、在CSDN首发、需要转载请联系博主。
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「马上回来了」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
🚀🚀🚀 新的知识开始喽🚀🚀🚀

1.Comparable接口
现在先创建一个学生类,学生类的基本信息:名字、年龄、成绩。
class Student{ //实例成员 public String name; public int age; public double score; //构造方法 public Student(String name, int age, double score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } //对象打印 @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + '}'; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
然后实例化两个学生对象:
class Student{ public String name; public int age; public double score; public Student(String name, int age, double score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + '}'; } } public class Test0 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student("小王",19,85.0); Student student1 = new Student("小李",18,90.0); if(student.compareTo(student1)>0){ System.out.println("student>student1"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
现在要比较这三个学生对象的大小,也就是给这三个对象排序,应该怎么弄呢?
排序的对象是我们自定义的学生类对象,这个学生类引用的对象有三个成员属性,因此我们必须选取一个成员属性来排序,我们选取age然后用Comparable接口实现排序。class Student implements Comparable<Student> {//自定义比较类实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 //实例成员 public String name; public int age; public double score; //构造方法 public Student(String name, int age, double score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } //重写对象打印 @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + '}'; } //实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 必须重写compareTo这个方法 来选择自定义类型排序选择的方式,这里选择age @Override public int compareTo(Student o) {//排升序 //return this.age - o.age; if (this.age > o.age) { return 1; } else if (this.age == o.age) { return 0; } else { return -1; } } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student("小王",19,85.0); Student student1 = new Student("小李",18,90.0); //student引用调用重写的compareTo方法,student1引用作为参数 if(student.compareTo(student1)>0){ System.out.println("student>student1"); }else if(student.compareTo(student1)<0){ System.out.println("student>student1"); }else{ System.out.println("student=student1"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
运行结果:

现在创建一个是Student类型的数组进行,也按照age来进行比较:class Student implements Comparable<Student> {//自定义比较类实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 //实例成员 public String name; public int age; public double score; //构造方法 public Student(String name, int age, double score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } //重写对象打印 @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + '}'; } 实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 必须重写compareTo这个方法 来选择自定义类型排序选择的方式,这里选择age @Override public int compareTo(Student o) {//排序为升序 //return this.age - o.age; if (this.age > o.age) { return 1; } else if (this.age == o.age) { return 0; } else { return -1; } // if (o.age > this.age){ // return 1; // }else if(this.age == o.age){ // return 0; // }else{ // return -1; // } // } } } public class Test { public static void main1(String[] args) { Student[] student = new Student[3]; //每一个数组元素都是一个学生对象 student[0] = new Student("小王",19,85.0); student[1] = new Student("小李",17,75.0); student[2] = new Student("小刘",18,95.0); System.out.println("排序前"+Arrays.toString(student)); Arrays.sort(student); System.out.println("排序后"+Arrays.toString(student)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
运行结果:
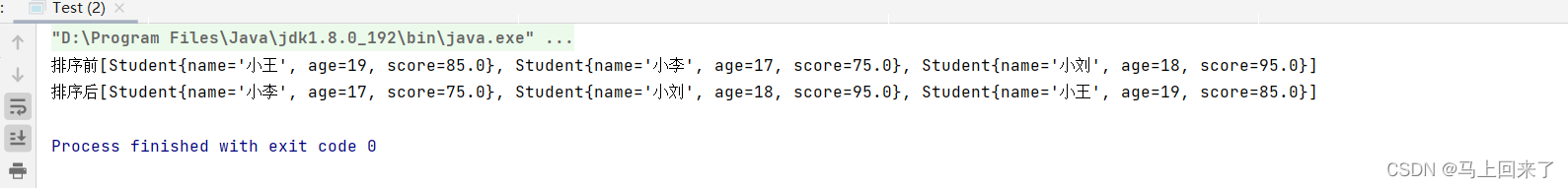
如果不实现Comparable接口,数组排序直接使用 Arrays.sort:

compareTo也无法重写,运行报错:


可以看到错误提醒我们Comparable接口,并且ComparableTimSort试图强行帮我们进行类型转换和调用compareTo方法。2.Comparator接口
Comparator接口:比较器。比Comparable接口更为灵活,Comparable接口一般用于设置默认的比较自定义类成员的方式。比较器可以
接着Compara接口那段按年龄大小比较的代码,现在我们又想按照成绩、名字比较大小,这时我们则需要使用CompareTo接口来实现。Comparator接口需要重写compare方法。
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {//自定义比较类实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 //实例成员 public String name; public int age; public double score; //构造方法 public Student(String name, int age, double score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } //重写对象打印 @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + '}'; } //实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 必须重写compareTo这个方法 @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { //return this.age - o.age; if (this.age > o.age) { return 1; } else if (this.age == o.age) { return 0; } else { return -1; } if (o.age > this.age){ return 1; }else if(this.age == o.age){ return 0; }else{ return -1; } } } } class ScoreComparetor implements Comparator<Student>{ @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { return (int)(o1.score-o2.score); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Student student = new Student("小王",19,85.0); Student student1 = new Student("小李",18,90.0); ///比较器先实例化出对象,然后调用compare这个比较方法 ScoreComparetor scoreComparetor = new ScoreComparetor(); int ret = scoreComparetor.compare(student,student1); System.out.println(ret); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
运行结果:

数组的比较:
class Student implements Comparable<Student> {//自定义比较类实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 //实例成员 public String name; public int age; public double score; //构造方法 public Student(String name, int age, double score) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.score = score; } //重写对象打印 @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", score=" + score + '}'; } 实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 必须重写compareTo这个方法 来选择自定义类型排序选择的方式,这里选择age @Override public int compareTo(Student o) {//排序为升序 //return this.age - o.age; if (this.age > o.age) { return 1; } else if (this.age == o.age) { return 0; } else { return -1; } // if (o.age > this.age){ // return 1; // }else if(this.age == o.age){ // return 0; // }else{ // return -1; // } // } } } public class Test { public static void main1(String[] args) { Student[] student = new Student[3]; //每一个数组元素都是一个学生对象 student[0] = new Student("小王",19,85.0); student[1] = new Student("小李",17,75.0); student[2] = new Student("小刘",18,95.0); //实例化出比较器的对象 ScoreComparetor scoreComparetor = new ScoreComparetor(); System.out.println("排序前"+Arrays.toString(student)); //自定义对象的引用,比较器的引用 Arrays.sort(student,scoreComparetor); System.out.println("排序后"+Arrays.toString(student)); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
运行结果:

3.总结
对于自定义类型的比较大小,需要通过Comparable接口、Comparator接口来实现。
Comparab接口需要重写compareTo方法,由于compareTo方法是在自定义类里实现,所以一般用于设置默认规则的比较设置。
Comparator接口又称为比较器,需要重写compare方法,相比Comparable接口Comparator接口更为灵活,通过创建一个新的比较规则类去与自定义类相结合,使比较形式更为灵活。
Comparable接口语法形式:class 类 implements Comparable<自定义类名>{ ..... //实现Comparable<自定义类>接口 必须重写compareTo这个方法 @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { //return this.age - o.age; if (this.age > o.age) { return 1; } else if (this.age == o.age) { return 0; } else { return -1; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
Comparator接口语法形式:
// 比较规则类名 接口<自定义类> class ScoreComparetor implements Comparator<Student>{ //重写compare方法 注意返回值类型 @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { //通过引用来选取比较器要比较的成员属性 return (int)(o1.score-o2.score); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
🌏🌏🌏今天的你看懂这里又学到了很多东西吧🌏🌏🌏

🌔 🌔 🌔下次见喽🌔 🌔 🌔

-
相关阅读:
基于Python实现的糖尿病预测系统
SQLSERVER基础--存储过程
那些不易解释的互联网知识
剑指offer面试题35 第一个只出现一次的字符
Shell脚本学习笔记
学不会的博弈论——进阶篇
通俗易懂的ChatGPT的原理简介
Maven常用命令、坐标、依赖管理、依赖范围
【论文阅读】Twin Neural Network Regression
vscode提交git代码总是需要输入账号密码问题
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_62160964/article/details/125569735
