-
开源ffmpeg(三)——音频拉流、解码以及重采样
前言
对于ffmpeg介绍和如何输出ffmpeg日志可以参照之前的博客。
该篇博客是用于学习如何使用ffmpeg进行读取音频(包括本地和远端),并对读取流进行音频解码、以及进行重采样的操作。如果现在看官对于音频解码不是很熟悉,建议可以多看看雷神的文章,膜拜+缅怀雷神。
这里有对于音频解码基础的介绍:
视音频编解码技术零基础学习方法
PCM音频数据格式介绍|版本声明:山河君,未经博主允许,禁止转载
一、API介绍
1.主要API介绍
API 释义 备注 av_log_set_level 设置log等级 具体参数参照log.h头文件 avformat_alloc_context 分配封装上下文 使用avformat_free_context释放上下文 av_frame_alloc 申请解码后数据缓存区 使用av_frame_free释放 swr_alloc 申请重采样上下文 使用swr_free释放 av_packet_alloc 申请数据包缓存区 使用av_packet_free释放 avformat_open_input 打开一个媒体流,并获取头信息 使用avformat_close_input关闭流 avformat_find_stream_info 获取流信息 一个媒体流中可能存在多个流 avcodec_find_decoder 注册编解码器 参数为编解码器ID avcodec_alloc_context3 分配编解码器上下文 使用avcodec_free_context释放 avcodec_parameters_to_context 填充编解码器上下文参数 avcodec_open2 使用注册的编解码器初始化编解码器上下文 swr_alloc_set_opts2 设置重采样参数 swr_init 初始化重采样上下文 av_read_frame 从流里读取下个包 最终存放在av_packet avcodec_send_packet 将一个包放入解码器 avcodec_receive_frame 从解码器读取解码后的数据 最终存放在av_frame里 swr_convert 进行重采样 会返回每个通道的采样数 av_samples_get_buffer_size 获取给定音频参数所需的缓冲区大小 这个值理论上不会发生变化 av_packet_unref 清空数据包 为了不频繁删除数据包缓冲区,只做清除 2.流程介绍
上文把一些主要的API已经做了介绍了,但其实这些API的主要目的就是为了获取:流上下文、解码器、重采样。
以下流程每个框都代表一个线程,当然,播放并未体现在本文中。而且值得注意的是:读包后塞入编码器,和获取解码数据可以放在不同的线程中,特别是在做视频工作的时候。因为在做解码工作和重采样时,是一件十分耗时的事情,我们不应该让解码阻塞住读包的过程。 相对于视频解码,音频解码是一个快速的事情。
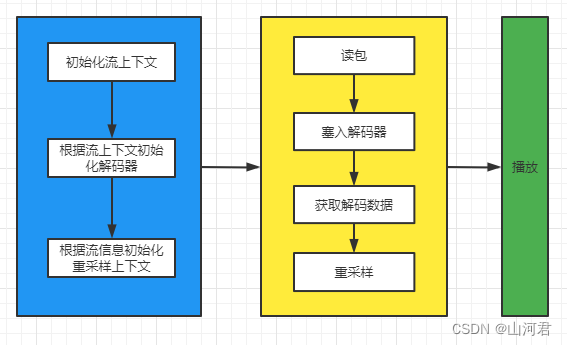
3.备注
由于笔者这边使用的是ffmpeg 4.4,与老版本是有一些差别的,例如:
一些API是已经废弃的,例如以下API是为了初始化ffmpeg的库:- av_register_all
- avformat_network_init
又有一些API是被替换了的,例如以下API是为了对于寻解码器、释放包等:
- avcodec_decode_audio4
- av_free_packet
- avcodec_alloc_context3
虽然已经废弃,但是还是接口还是保留下来的,只要在使用的时候小心一点即可
二、代码实例
1.头文件
#pragma once extern "C" { #include "include/libavformat/avformat.h" #include "include/libavcodec/avcodec.h" #include "include/libavutil/avutil.h" #include "include/libswresample/swresample.h" } #include <iostream> #include <mutex> #include <Windows.h> namespace AudioReadFrame { #define MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE 192000 // 1 second of 48khz 16bit audio 2 channel //自定义结构体存储信息 struct FileAudioInst { long long duration; ///< second long long curl_time; ///< second int sample_rate; ///< samples per second int channels; ///< number of audio channels FileAudioInst() { duration = 0; curl_time = 0; sample_rate = 0; channels = 0; } }; //拉流线程状态 enum ThreadState { run = 1, exit, }; class CAudioReadFrame { public: CAudioReadFrame(); ~CAudioReadFrame(); public: //加载流文件 bool LoadAudioFile(const char* pAudioFilePath); //开始读流 bool StartReadFile(); //停止读流 bool StopReadFile(); private: //释放资源 bool FreeResources(); //改变拉流线程的装填 void ChangeThreadState(ThreadState eThreadState); //拉流线程 void ReadFrameThreadProc(); //utf转GBK std::string UTF8ToGBK(const std::string& strUTF8); private: typedef std::unique_ptr<std::thread> ThreadPtr; //目的是为了重定向输出ffmpeg日志到本地文件 #define PRINT_LOG 0 #ifdef PRINT_LOG private: static FILE* m_pLogFile; static void LogCallback(void* ptr, int level, const char* fmt, va_list vl); #endif //目的是为了将拉流数据dump下来 #define DUMP_AUDIO 1 #ifdef DUMP_AUDIO FILE* decode_file; #endif // DUMP_FILE private: bool m_bIsReadyForRead; int m_nStreamIndex; uint8_t* m_pSwrBuffer; std::mutex m_lockResources; std::mutex m_lockThread; FileAudioInst* m_pFileAudioInst; ThreadPtr m_pReadFrameThread; ThreadState m_eThreadState; private: SwrContext* m_pSwrContext; //重采样 AVFrame* m_pAVFrame; //音频包 AVCodec* m_pAVCodec; //编解码器 AVPacket* m_pAVPack; //读包 AVCodecParameters * m_pAVCodecParameters; //编码参数 AVCodecContext* m_pAVCodecContext; //解码上下文 AVFormatContext* m_pAVFormatContext; //IO上下文 }; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
2.源文件
#include "CAudioReadFrame.h" #include <sstream> namespace AudioReadFrame { #ifdef FFMPEG_LOG_OUT FILE* CAudioReadFrame::m_pLogFile = nullptr; void CAudioReadFrame::LogCallback(void* ptr, int level, const char* fmt, va_list vl) { if (m_pLogFile == nullptr) { m_pLogFile = fopen("E:\\log\\log.txt", "w+"); } if (m_pLogFile) { vfprintf(m_pLogFile, fmt, vl); fflush(m_pLogFile); } } #endif CAudioReadFrame::CAudioReadFrame() { std::cout << av_version_info() << std::endl; #if DUMP_AUDIO decode_file = fopen("E:\\log\\decode_file.pcm", "wb+"); #endif } CAudioReadFrame::~CAudioReadFrame() { #if DUMP_AUDIO if (decode_file) { fclose(decode_file); decode_file = nullptr; } #endif StopReadFile(); } bool CAudioReadFrame::LoadAudioFile(const char* pAudioFilePath) { #ifdef FFMPEG_LOG_OUT if (m_pLogFile != nullptr) { fclose(m_pLogFile); m_pLogFile = nullptr; } time_t t = time(nullptr); struct tm* now = localtime(&t); std::stringstream time; time << now->tm_year + 1900 << "/"; time << now->tm_mon + 1 << "/"; time << now->tm_mday << "/"; time << now->tm_hour << ":"; time << now->tm_min << ":"; time << now->tm_sec << std::endl; std::cout << time.str(); av_log_set_level(AV_LOG_TRACE); //设置日志级别 av_log_set_callback(LogCallback); av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, time.str().c_str()); #endif ChangeThreadState(ThreadState::exit); FreeResources(); av_log_set_level(AV_LOG_TRACE); //设置日志级别 av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "the debug line:%d, string:%s", __LINE__, "hello"); m_nStreamIndex = -1; m_pAVFormatContext = avformat_alloc_context(); m_pAVFrame = av_frame_alloc(); m_pSwrContext = swr_alloc(); m_pFileAudioInst = new FileAudioInst; m_pSwrBuffer = (uint8_t *)av_malloc(MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE); m_pAVPack = av_packet_alloc(); //Open an input stream and read the header if (avformat_open_input(&m_pAVFormatContext, pAudioFilePath, NULL, NULL) != 0) { av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Couldn't open input stream.\n"); return false; } //Read packets of a media file to get stream information if (avformat_find_stream_info(m_pAVFormatContext, NULL) < 0) { av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Couldn't find stream information.\n"); return false; } for (unsigned int i = 0; i < m_pAVFormatContext->nb_streams; i++) { //因为一个url可以包含多股,如果存在多股流,找到音频流,因为现在只读MP3,所以只找音频流 if (m_pAVFormatContext->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO) { m_nStreamIndex = i; break; } } if (m_nStreamIndex == -1) { av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Didn't find a audio stream.\n"); return false; } m_pAVCodecParameters = m_pAVFormatContext->streams[m_nStreamIndex]->codecpar; m_pAVCodec = (AVCodec *)avcodec_find_decoder(m_pAVCodecParameters->codec_id); // Open codec m_pAVCodecContext = avcodec_alloc_context3(m_pAVCodec); avcodec_parameters_to_context(m_pAVCodecContext, m_pAVCodecParameters); if (avcodec_open2(m_pAVCodecContext, m_pAVCodec, NULL) < 0) { av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not open codec.\n"); return false; } //初始化重采样 采样率为双通 short, 48k AVChannelLayout outChannelLayout; AVChannelLayout inChannelLayout; outChannelLayout.nb_channels = 2; inChannelLayout.nb_channels = m_pAVCodecContext->ch_layout.nb_channels; if (swr_alloc_set_opts2(&m_pSwrContext, &outChannelLayout, AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, 48000, &inChannelLayout, m_pAVCodecContext->sample_fmt, m_pAVCodecContext->sample_rate, 0, NULL) != 0) { av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "swr_alloc_set_opts2 fail.\n"); return false; } swr_init(m_pSwrContext); //保留流信息 m_pFileAudioInst->duration = m_pAVFormatContext->duration / 1000;//ms m_pFileAudioInst->channels = m_pAVCodecParameters->ch_layout.nb_channels; m_pFileAudioInst->sample_rate = m_pAVCodecParameters->sample_rate; m_bIsReadyForRead = true; return true; } bool CAudioReadFrame::StartReadFile() { if (!m_bIsReadyForRead) { av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "File not ready"); return false; } if (m_pReadFrameThread != nullptr) { if (m_pReadFrameThread->joinable()) { m_pReadFrameThread->join(); m_pReadFrameThread.reset(nullptr); } } ChangeThreadState(ThreadState::run); m_pReadFrameThread.reset(new std::thread(&CAudioReadFrame::ReadFrameThreadProc, this)); return true; } bool CAudioReadFrame::StopReadFile() { ChangeThreadState(ThreadState::exit); if (m_pReadFrameThread != nullptr) { if (m_pReadFrameThread->joinable()) { m_pReadFrameThread->join(); m_pReadFrameThread.reset(nullptr); } } FreeResources(); return true; } void CAudioReadFrame::ReadFrameThreadProc() { while (true) { if (m_eThreadState == ThreadState::exit) { break; } //读取一个包 int nRet = av_read_frame(m_pAVFormatContext, m_pAVPack); if (nRet != 0) { std::stringstream logInfo; logInfo << "read frame no data error:" << nRet << std::endl; av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, logInfo.str().c_str()); ChangeThreadState(ThreadState::exit); continue; } //判断读取流是否正确 if (m_pAVPack->stream_index != m_nStreamIndex) { std::stringstream logInfo; logInfo << "read frame no data error:" << std::endl; av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, logInfo.str().c_str()); continue; } //将一个包放入解码器 nRet = avcodec_send_packet(m_pAVCodecContext, m_pAVPack); if (nRet < 0) { std::stringstream logInfo; logInfo << "avcodec_send_packet error:" << nRet << std::endl; av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, logInfo.str().c_str()); continue; } //从解码器读取解码后的数据 nRet = avcodec_receive_frame(m_pAVCodecContext, m_pAVFrame); if (nRet != 0) { std::stringstream logInfo; logInfo << "avcodec_receive_frame error:" << nRet << std::endl; av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, logInfo.str().c_str()); continue; } //重采样,采样率不变 memset(m_pSwrBuffer, 0, MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE); nRet = swr_convert(m_pSwrContext, &m_pSwrBuffer, MAX_AUDIO_FRAME_SIZE, (const uint8_t **)m_pAVFrame->data, m_pAVFrame->nb_samples); if (nRet <0) { std::stringstream logInfo; logInfo << "swr_convert error:" << nRet << std::endl; av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, logInfo.str().c_str()); continue; } #if DUMP_AUDIO //获取重采样之后的buffer大小 int buffSize = av_samples_get_buffer_size(NULL, 2, nRet, AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, 1); fwrite((char*)m_pSwrBuffer, 1, buffSize, decode_file); #endif av_packet_unref(m_pAVPack); } } bool CAudioReadFrame::FreeResources() { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_lockResources); if (m_pSwrBuffer) { av_free(m_pSwrBuffer); m_pSwrBuffer = nullptr; } if (m_pFileAudioInst) { delete m_pFileAudioInst; m_pFileAudioInst = nullptr; } if (m_pSwrContext) { swr_free(&m_pSwrContext); m_pSwrContext = nullptr; } if (m_pAVFrame) { av_frame_free(&m_pAVFrame); m_pAVFrame = nullptr; } if (m_pAVPack) { av_packet_free(&m_pAVPack); m_pAVPack = nullptr; } if (m_pAVFormatContext) { avformat_free_context(m_pAVFormatContext); m_pAVFormatContext = nullptr; } if (m_pAVCodecParameters) { avcodec_parameters_free(&m_pAVCodecParameters); m_pAVCodecParameters = nullptr; } if (m_pAVCodecContext) { avcodec_close(m_pAVCodecContext); m_pAVCodecContext = nullptr; } m_bIsReadyForRead = false; return true; } void CAudioReadFrame::ChangeThreadState(ThreadState eThreadState) { std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_lockThread); if (m_eThreadState != eThreadState) { m_eThreadState = eThreadState; } } std::string CAudioReadFrame::UTF8ToGBK(const std::string& strUTF8) { int len = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, strUTF8.c_str(), -1, NULL, 0); wchar_t* wszGBK = new wchar_t[len + 1]; memset(wszGBK, 0, len * 2 + 2); MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, strUTF8.c_str(), -1, wszGBK, len); len = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, wszGBK, -1, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL); char *szGBK = new char[len + 1]; memset(szGBK, 0, len + 1); WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, wszGBK, -1, szGBK, len, NULL, NULL); //strUTF8 = szGBK; std::string strTemp(szGBK); delete[]szGBK; delete[]wszGBK; return strTemp; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
3.使用
#include "CAudioReadFrame.h" int main() { AudioReadFrame::CAudioReadFrame cTest; cTest.LoadAudioFile("E:\\原音_女声.mp3"); cTest.StartReadFile(); system("pause"); return 0; }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
现在看一下音谱:

总结
以上就是对于音频的拉流、解码以及重采样的流程了,该例子中,拉取的是本地流,不过如果给一个远端直播流是同样可以成功的。
当然这些只是入门的操作,在实际使用,在拉起直播流、本地流、远端文件流的处理方案都应该是不同的,毕竟场景不同,方案也不同。至于为什么使用不同的方案,会在接下来的文章中再做解释。
如果对您有所帮助,请帮忙点个赞吧!
-
相关阅读:
数据结构 - 线段树的运用
酷开科技持续推动智能投影行业创新发展
B站韩顺平的正则表达式学习
ROS2自学笔记:通信接口
yolov6训练完模型如何得到每个类别的ap值
Golang常用语法糖
因果图测试用例设计方法介绍(超全的总结笔记错过就没有了)
关于时间日期
文科生的爬藤神器:HIEEC哈佛国际经济学论文比赛
“2022年度科技行业CEO”!
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42956179/article/details/124983029
