-
lombok @EqualsAndHashCode 注解如何让对象.equals()方法只比较部分属性
实体类
import lombok.Data; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; @Data @EqualsAndHashCode public class Cs { private int id; private String name; public Cs(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
运行
public static void main(String[] args) { Cs cs1=new Cs(1,"小小"); Cs cs2=new Cs(1,"小小"); System.out.println(cs1.equals(cs2)); }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
查看生成的class文件
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.hieasy.rftools.common; public class Cs { private int id; private String name; public Cs(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } public int getId() { return this.id; } public String getName() { return this.name; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String toString() { return "Cs(id=" + this.getId() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ")"; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } else if (!(o instanceof Cs)) { return false; } else { Cs other = (Cs)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } else if (this.getId() != other.getId()) { return false; } else { Object this$name = this.getName(); Object other$name = other.getName(); if (this$name == null) { if (other$name != null) { return false; } } else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) { return false; } return true; } } } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Cs; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = true; int result = 1; int result = result * 59 + this.getId(); Object $name = this.getName(); result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); return result; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
如果我们去掉注解是一样的,全部比较的话可以不要@EqualsAndHashCode注解
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.hieasy.rftools.common; public class Cs { private int id; private String name; public Cs(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } public int getId() { return this.id; } public String getName() { return this.name; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) { return true; } else if (!(o instanceof Cs)) { return false; } else { Cs other = (Cs)o; if (!other.canEqual(this)) { return false; } else if (this.getId() != other.getId()) { return false; } else { Object this$name = this.getName(); Object other$name = other.getName(); if (this$name == null) { if (other$name != null) { return false; } } else if (!this$name.equals(other$name)) { return false; } return true; } } } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Cs; } public int hashCode() { int PRIME = true; int result = 1; int result = result * 59 + this.getId(); Object $name = this.getName(); result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); return result; } public String toString() { return "Cs(id=" + this.getId() + ", name=" + this.getName() + ")"; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
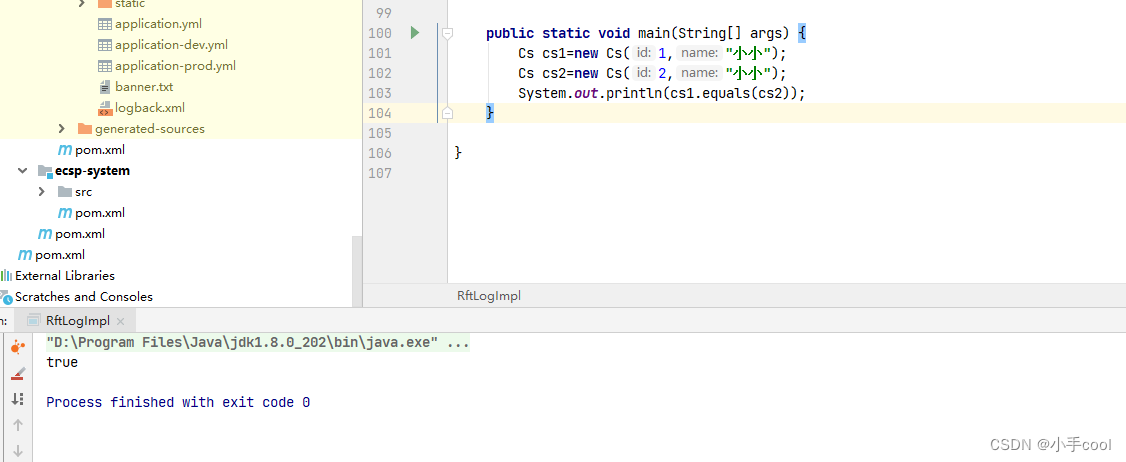
但是我们如果只想比较name属性的话,类上需要加入@EqualsAndHashCode(onlyExplicitlyIncluded = true),想只比较哪些属性就在属性上加@EqualsAndHashCode.Include
import lombok.Data; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; /** * @author Zc * @date 2022年06月24日 16:04 */ @Data @EqualsAndHashCode(onlyExplicitlyIncluded = true) public class Cs { private int id; @EqualsAndHashCode.Include private String name; public Cs(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
结果
-
相关阅读:
数据集读取与划分
阿里面试——机器学习岗四个面试案例
加密项目是否采用DAO模式 首先考量这8个因素
为什么ping不通,而traceroute却可以通
基于Web的盾构机盾尾变形远程监测系统
智能方案设计——智能跳绳方案
(附源码)计算机毕业设计SSM教学团队管理系统
Linux下安装oracle11.2.0.4
Docker Swarm总结
程序员的人生
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38030465/article/details/125447630
