-
synchronized关键字在同步代码块中的应用(下)
类Class的单例性
每一个*.java文件对应Class类的实例都是一个,在内存中是单例的,测试代码如下:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { MyTest test1 = new MyTest(); MyTest test2 = new MyTest(); MyTest test3 = new MyTest(); MyTest test4 = new MyTest(); System.out.println(test1.getClass() == test1.getClass()); System.out.println(test1.getClass() == test2.getClass()); System.out.println(test1.getClass() == test3.getClass()); System.out.println(test1.getClass() == test4.getClass()); SimpleDateFormat format1 = new SimpleDateFormat(); SimpleDateFormat format2 = new SimpleDateFormat(); SimpleDateFormat format3 = new SimpleDateFormat(); SimpleDateFormat format4 = new SimpleDateFormat(); System.out.println(format1.getClass() == format1.getClass()); System.out.println(format1.getClass() == format2.getClass()); System.out.println(format1.getClass() == format3.getClass()); System.out.println(format1.getClass() == format4.getClass()); } } output: true true true true true true true true- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
Class类用于描述类的基本信息,包括有多少个字段,有多少个构造方法,有多少个普通方法等,为了减少对内存的高占用率,在内存中只需要存在一份Class类对象就可以了,所以被设计成单例的。
静态同步synchronized方法与synchronized(class)代码块
关键字synchronized还可以应用在static静态方法上,如果这样写,那是对当前*.java文件对应的Class类对象进行持锁,Class类的对象是单例的,更具体地说,在静态static方法上使用synchronized关键字声明同步方法时,使用当前静态方法所在类对应Class类的单例对象作为锁。
public class Service { synchronized public static void printA() { try { System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "进入printA"); Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "离开printA"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } synchronized public static void printB() { System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "进入printB"); System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "离开printB"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
public class ThreadA extends Thread { @Override public void run() { Service.printA(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
public class ThreadB extends Thread { @Override public void run() { Service.printB(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) { ThreadA a = new ThreadA(); a.setName("A"); a.start(); ThreadB b = new ThreadB(); b.setName("B"); b.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
output: 线程名称为:A在1655824945776进入printA 线程名称为:A在1655824948791离开printA 线程名称为:B在1655824948791进入printB 线程名称为:B在1655824948791离开printB- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
synchronized关键字加到static静态方法上的方式是将Class类对象作为锁,而synchronized关键字加到非static静态方法上的方式是将方法所在类的对象作为锁。
public class Service { synchronized public static void printA() { try { System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "进入printA"); Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "离开printA"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } synchronized public static void printB() { System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "进入printB"); System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "离开printB"); } synchronized public void printC(){ System.out.println("线程名称为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"在"+System.currentTimeMillis()+"进入printC"); System.out.println("线程名称为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"在"+System.currentTimeMillis()+"离开printC"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
public class ThreadC extends Thread{ private Service service; public ThreadC(Service service){ super(); this.service = service; } @Override public void run(){ service.printC(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
output: 线程名称为:A在1655825737790进入printA 线程名称为:C在1655825737790进入printC 线程名称为:C在1655825737790离开printC 线程名称为:A在1655825740805离开printA 线程名称为:B在1655825740805进入printB 线程名称为:B在1655825740805离开printB- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
异步运行的原因是持有不同的锁,一个是将类Service的对象作为锁,另一个是将Service类对应Class类的对象作为锁,A、B线程和C线程是异步的关系,而A线程和B线程是同步的关系。
同步syn static方法可以对类的所有对象实例起作用
Class锁可以对类的所有对象实例起作用。
public class Service { synchronized public static void printA() { try { System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "进入printA"); Thread.sleep(3000); System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "离开printA"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } synchronized public static void printB() { System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "进入printB"); System.out.println("线程名称为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "在" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "离开printB"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
public class ThreadA extends Thread { private Service service; public ThreadA(Service service) { super(); this.service = service; } @Override public void run() { service.printA(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
public class ThreadB extends Thread { private Service service; public ThreadB(Service service) { this.service = service; } @Override public void run() { service.printB(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
output: 线程名称为:A在1655826421956进入printA 线程名称为:A在1655826424967离开printA 线程名称为:B在1655826424967进入printB 线程名称为:B在1655826424967离开printB- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
同步syn(class)代码块可以对类的所有对象实例起作用
同步synchronized(class)代码块的作用其实和synchronized static方法的作用一样。
String常量池特性与同步相关的问题与解决方案
JVM具有String常量池的功能,所以如下代码结果为true
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { String a = "a"; String b = "a"; System.out.println(a == b); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
当synchronized(string)同步块与String联合使用时,要注意常量池会带来一些意外。
public class Service { public static void print(String stringParam) { try { synchronized (stringParam) { while (true) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(1000); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
public class ThreadA extends Thread { private Service service; public ThreadA(Service service) { super(); this.service = service; } @Override public void run() { service.print("AA"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
public class ThreadB extends Thread { private Service service; public ThreadB(Service service) { this.service = service; } @Override public void run() { service.print("AA"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Service service = new Service(); ThreadA t1 = new ThreadA(service); t1.setName("A"); t1.start(); ThreadA t2 = new ThreadA(service); t2.setName("B"); t2.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
output: A A A A A A A A A A- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
出现这种情况的原因是String的两个值都是AA,两个线程持有相同的锁,造成B线程不能执行。这就是String常量池所带来的问题,所以大多数情况下同步synchronized代码块不适用String作为锁对象,而改用其他,例如,new Object()实例化一个新的Object对象,它并不放入缓存池中,或者执行new String()创建不同的字符串对象,形成不同的锁。
public class Service { public static void print(Object obj) { try { synchronized (obj) { while (true) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); Thread.sleep(1000); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
output: A B A B B A B A A B B A- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
同步synchronized方法无限等待问题与解决方案
使用同步方法会导致锁资源被长期占用,得不到运行的机会,如下:
public class Service { synchronized public void methodA(){ System.out.println("methodA begin"); boolean isContinueRun = true; while(isContinueRun){} System.out.println("methodA end"); } synchronized public void methodB(){ System.out.println("methodB begin"); System.out.println("methodB end"); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
output: methodA begin- 1
- 2
B线程永远得不到运行的机会,这时可以使用同步块来解决这样的问题:
public class Service { Object o1 = new Object(); public void methodA(){ synchronized (o1){ System.out.println("methodA begin"); boolean isContinueRun = true; while(isContinueRun){} System.out.println("methodA end"); } } Object o2 = new Object(); public void methodB(){ synchronized (o2){ System.out.println("methodB begin"); System.out.println("methodB end"); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
output: methodA begin methodB begin methodB end- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
多线程的死锁
java线程死锁是一个经典的多线程问题,因为不同的线程都在等待根本不可能被释放的锁,从而导致所有的任务都无法继续完成。在多线程技术中,“死锁”是必须避免的,因为这会造成线程“假死”。
public class DealThread implements Runnable { public String username; public Object lock1 = new Object(); public Object lock2 = new Object(); public void setFlag(String username) { this.username = username; } @Override public void run() { if (username.equals("a")) { synchronized (lock1) { try { System.out.println("username = " + username); Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (lock2){ System.out.println("按lock1 -> lock2代码顺序执行了"); } } } if(username.equals("b")){ synchronized (lock2){ try { System.out.println("username = "+username); Thread.sleep(3000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (lock1){ System.out.println("按lock2->lock1代码顺序执行了"); } } } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Service service = new Service(); ThreadA t1 = new ThreadA(service); t1.setName("A"); t1.start(); ThreadB t2 = new ThreadB(service); t2.setName("B"); t2.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
output: username = a username = b- 1
- 2
- 3
可以使用jdk自带工具来监测是否有死锁现象,执行jps命令和jstack命令

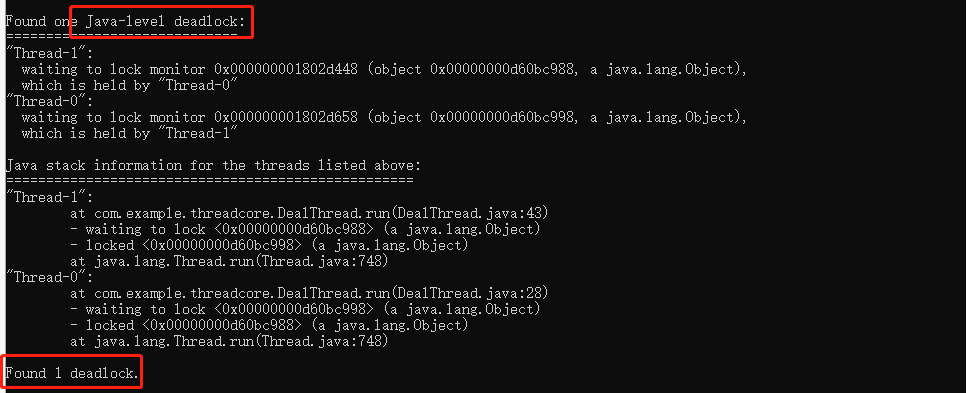
死锁是程序设计的bug,在设计程序时要避免双方互相持有对方的锁,只要互相等待对方释放锁,就有可能出现死锁。
内置类与同步
- 内置类中有两个同步方法,但使用的是不同的锁,输出结果也是异步的。
- 同步代码块synchronized(lock)对lock上锁后,其他线程只能以同步的方式调用lock中的同步方法。
锁对象改变导致异步执行
在将任何数据类型作为同步锁时,需要注意是否有多个线程同时争抢锁对象。如果多个线程同时争抢相同的对象,则这些线程之间就是同步的;如果多个线程分别获得自己的锁,则这些线程之间就是异步的。
通常情况下,一旦持有锁后就不再对锁对象进行更改,因为一旦更改就有可能出现一些错误。
public class Service { private String lock = "123"; public void testMethod() { try { synchronized (lock) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " begin " + System.currentTimeMillis()); lock = "456"; Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " end " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
public class Run { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Service service = new Service(); ThreadA a = new ThreadA(service); a.setName("a"); ThreadB b = new ThreadB(service); b.setName("b"); a.start(); Thread.sleep(50); b.start(); } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
output: a begin 1656170359345 b begin 1656170359408 a end 1656170361360 b end 1656170361423- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
50ms后,B线程取得的锁是“456”。
去掉50ms后,可能出现同步,也可能出现异步。
锁对象不改变依然同步执行
如果锁是一个User对象,其中一个线程持有该锁后,修改了User对象的属性。与其他线程依然是同步执行,因为持有的锁对象为同一个,仅仅对象的属性改变了,但对象未发生改变。
同步写法案例比较多
使用关键字synchronized的写法比较多,常用的有以下几种:
public class MyService { synchronized public static void testMethod1(){} public void testMethod2(){ synchronized (MyService.class){} } synchronized public void testMethod3(){} public void testMethod4(){ synchronized (this){} } public void testMethod5(){ synchronized ("abc"){} } }- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
上面代码出现了3种类型的锁对象:
- testMethod1()和testMethod2()持有的锁是同一个,即MyService.java对应Class类的对象。
- testMethod3()和testMethod4()持有的锁是同一个,即MyService.java类的对象。
- testMethod5()持有的锁是字符串abc。
相同的锁是同步关系,不相同的锁是异步关系。
-
相关阅读:
百度网盘vip免费领取一天活动链接2024最新
【我的百度实习总结】百度网盘——一刻相册实习
chrome浏览器关闭书签栏右侧的所有书签
智慧园区信息化管理系统发展现状及难题
关于NDK
Rust实战系列-Rust介绍
【愚公系列】2022年07月 Tabby集成终端的使用
轻量级多级菜单控制框架程序(C语言)
SpringBoot 源码分析(四) 内置Tomcat分析
蓝桥杯每日一题2023.10.21
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/wozaibohaibian/article/details/125465494
