-
项目一:使用 Spring + SpringMVC + Mybatis + lombok 实现网络五子棋
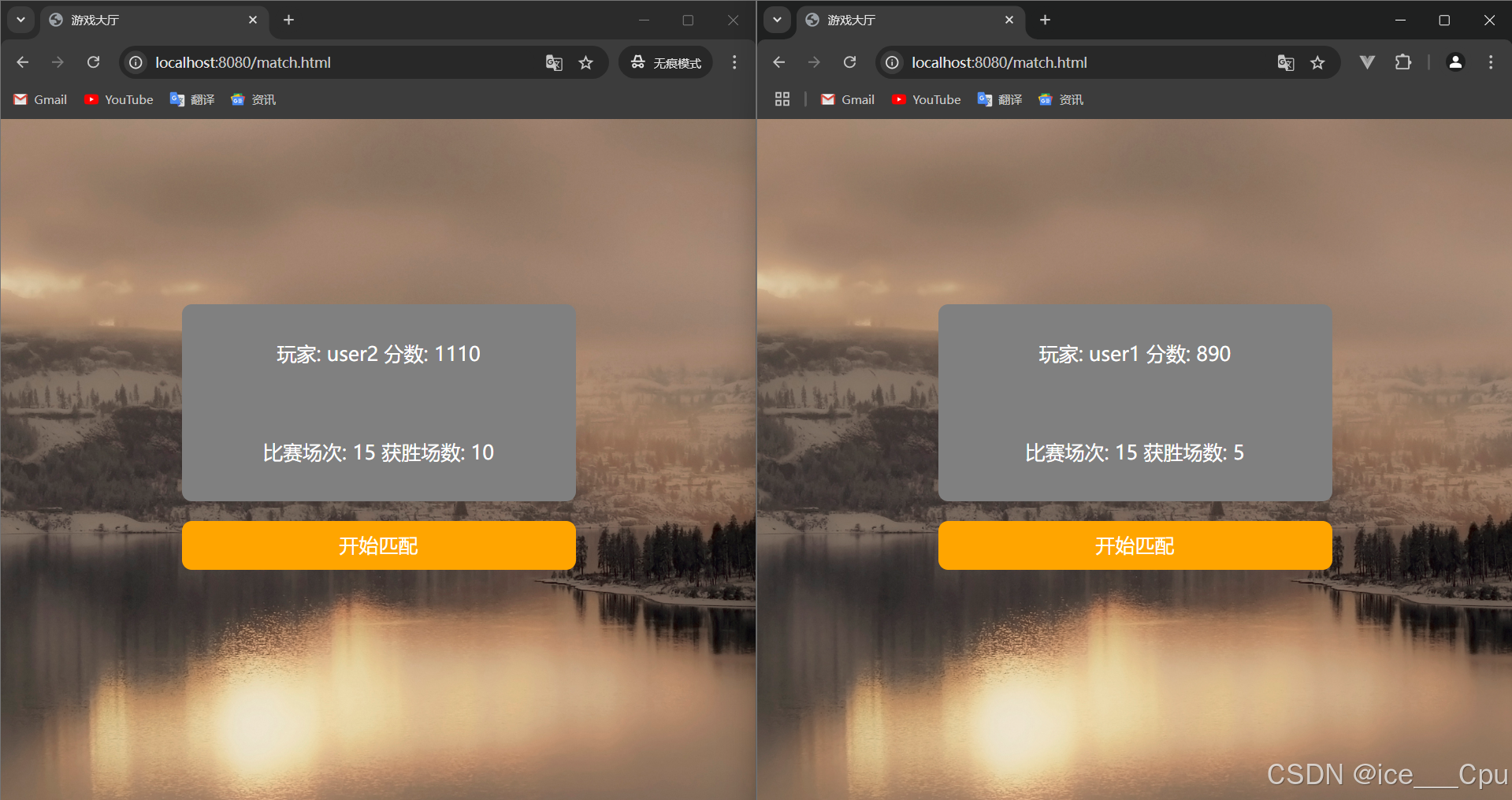
一:系统展示:




二:约定前后端接口
2.1 登陆
登陆请求:
GET /login HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded username=zhangsan&password=123登陆响应:
- 正常对象:正常对象会在数据库中存储,直接从数据库中取出即可,无需通过 set 方法进行设置
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: application/json { "userid": 1, "username": "zhangsan", "password": "123", "score": 1000, "totalcount": 0, "wincount": 0 }- 登陆失败返回空对象
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: application/json { "userid": 0, "username": null, "score": 0, "totalcount": 0, "wincount": 0 }2.2 注册
- 注册请求
GET /register HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded username=zhangsan&password=123- 注册响应
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: application/json { "userid": 1, "username": "zhangsan", "password": "123", "score": 1000, "totalcount": 0, "wincount": 0 }- 获取当前用户信息
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json { "userid": 1, "username": "zhangsan", "score": 1000, "totalcount": 0, "wincount": 0 }2.2 匹配
- 匹配请求
ws://127.0.1:8080/Match { "message": "startMatch" / ”stopMatch“ //startMatch 代表开始匹配,stopMatch 代表停止匹配 }请求不必带有用户的信息。因为在登陆成功后会把用户信息保存在 httpsession 中,websocket 可以拿到这个 httpseesion中存储的数据。
- 匹配响应 1
ws://127.0.0.1:8080/Match { "ok": true, // 进入成功为 true 匹配成功,否则为 false "reason": "失败原因", // 失败原因(若匹配失败则返回此字段) "message": "startMatch" / "stopMatch"/'matchSuccess'/'repeatConnection' //startMatch 代表开始匹配,stopMatch 代表停止匹配 ,matchSuccess 代表匹配成功 ,'repeatConnection 代表用户多开 }2.3 对战
对战和匹配使用两套逻辑,使用不同的 websocket 路径处理,能够更好的解耦合
- 响应 1 gameready
{ "message": "gameReady", "ok": true, // 匹配成功为 true,否则为 false,false 代表有某些问题 "reason": "", // 出错原因(若匹配失败则返回此字段) "roomid": "123456", // 房间 ID "thisuserid": 1, // 自己的用户 ID "thatuserid": 2, // 对手的用户 ID "whiteuser": 1 // 先手玩家 ID,1 表示自己先,2 表示对手先 }这个请求是玩家匹配成功后,由服务器生成的内容,把这个内容返回给浏览器
- 下棋请求 1
{ "message": "putChess", "userid": 1, "row": 0, "col": 0 }- 下棋响应
{ "message": "putChess", "userid": 1, "row": 0, // 行 "col": 0, // 列 "winner": 0 // 当前是否分出胜负,0 代表无胜负,非 0 代表获胜方用户 ID }三: websocket 前置知识
对于 http 来说,能够实现客户端向服务器发送数据,但是很难实现服务器向客户端发送数据,虽然可以通过轮转实现,但是这种实现太消耗cpu,性能也不好,而且实现起来也比较麻烦,所以我们选择使用 websocket 协议,websocket 协议能实现客户端和服务器的双向通信,符合我们目前的需求场景。
WebSocket 与 HTTP 的区别
- 持久连接:WebSocket 连接建立后会一直保持,直到显式关闭,减少了多次连接开销。
- 双向通信:WebSocket 支持全双工通信,即客户端和服务器可以在任意时间发送消息。
- 低延迟:WebSocket 的头部信息少,通信延迟低,非常适合实时性要求高的应用场景。
使用 WebSocket 的场景
- 实时聊天系统(如在线客服、聊天应用)
- 在线游戏(如棋类对战、竞技游戏)
- 实时数据推送(如股票行情、天气更新、体育比分)
3.1 websocket 连接流程
使用 WebSocket 连接的步骤:
- 后端配置 WebSocket 端点:定义 WebSocket 端点的 URL,客户端通过该 URL 连接到服务器。
- 实现 TextWebSocketHandler 类:处理 WebSocket 连接事件,包括连接建立、接收消息、连接关闭等。
- 前端建立 WebSocket 连接:前端使用 JavaScript 创建 WebSocket 连接,发送和接收消息。
步骤一:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.EnableWebSocket; import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketHandlerRegistry; @Configuration @EnableWebSocket public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer { @Override public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) { registry.addHandler(new ChatHandler(), "/chat"); // 将 /chat 端点与 ChatHandler 绑定 } }- /chat:这是客户端连接的 WebSocket URL(端点)。
- ChatHandler:我们自定义的 WebSocket 处理器,用来处理 WebSocket 的事件。
步骤 2:实现 TextWebSocketHandler 类
import org.springframework.web.socket.TextMessage; import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketSession; import org.springframework.web.socket.handler.TextWebSocketHandler; public class ChatHandler extends TextWebSocketHandler { //TextWebSocketHandler 是 Spring 提供的一个辅助类,用于处理 WebSocket 的文本消息。 // 1. 连接建立时调用 @Override public void afterConnectionEstablished(WebSocketSession session) throws Exception { System.out.println("连接已建立:" + session.getId()); } // 2. 接收到消息时调用 @Override protected void handleTextMessage(WebSocketSession session, TextMessage message) throws Exception { System.out.println("收到消息:" + message.getPayload()); // 将收到的消息返回给客户端 session.sendMessage(new TextMessage("服务器响应:" + message.getPayload())); } // 3. 连接关闭时调用 @Override public void afterConnectionClosed(WebSocketSession session, CloseStatus status) throws Exception { System.out.println("连接已关闭:" + session.getId()); } // 4. 处理错误时调用 @Override public void handleTransportError(WebSocketSession session, Throwable exception) throws Exception { System.err.println("传输错误:" + exception.getMessage()); } }- afterConnectionEstablished:当客户端成功连接时调用,比如用户打开 WebSocket
页面。这时候我们可以进行一些初始化操作。 - handleTextMessage:当服务器接收到客户端发送的消息时调用。这里我们简单地把接收到的消息再发送回客户端。
- afterConnectionClosed:当 WebSocket 连接关闭时调用,比如用户关闭页面或断开连接。我们可以在这里进行一些清理操作。
- handleTransportError:当连接出错时调用,例如网络故障。可以在这里记录错误日志或进行错误处理。
步骤三:前端实现
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>WebSocket 示例title> head> <body> <h2>WebSocket 简单示例h2> <div> <input type="text" id="messageInput" placeholder="输入消息"> <button onclick="sendMessage()">发送消息button> div> <div id="response">div> <script> // 1. 创建 WebSocket 连接 let websocket = new WebSocket("ws://" + location.host + "/chat");//建立连接 // 2. 连接建立时调用 websocket.onopen = function() { console.log("WebSocket 连接已建立"); }; // 3. 接收消息时调用 websocket.onmessage = function(event) { console.log("收到消息:" + event.data); document.getElementById("response").innerText = "服务器:" + event.data; }; // 4. 连接关闭时调用 websocket.onclose = function() { console.log("WebSocket 连接已关闭"); }; // 5. 出错时调用 websocket.onerror = function(error) { console.error("WebSocket 出现错误:" + error); }; // 发送消息给服务器 function sendMessage() { let message = document.getElementById("messageInput").value; websocket.send(message); // 发送消息 } script> body> html>- new WebSocket(“ws://” + location.host + “/chat”):创建 WebSocket 连接到服务器 /chat 端点绑定的 WebSocket 处理器上。
- onopen:当连接成功时调用,可以在这里通知用户连接已建立。
- onmessage:当接收到服务器发送的消息时调用。我们将接收到的消息显示在页面上。
- onclose:当连接关闭时调用,可以在这里通知用户连接已关闭。
- onerror:当连接出错时调用。
通过这三个步骤就可以把特定的前端页面和特定的后端类进行连接并通信了
3.2 客户端和服务器互发数据
在 WebSocket 通信中,客户端和服务器都可以通过特定的方法发送数据。
3.2.1 客户端发送数据给服务器
在前端,客户端使用 WebSocket.send() 方法向服务器发送数据。
// 假设已经创建了 WebSocket 连接 let websocket = new WebSocket("ws://" + location.host + "/chat"); // 定义一个函数,通过 WebSocket 向服务器发送消息 function sendMessage() { let message = document.getElementById("messageInput").value; // 获取输入框中的消息 websocket.send(message); // 使用 send 方法发送消息给服务器 console.log("发送消息给服务器:" + message); }
3.2.2 服务器发送数据给客户端
在 Spring Boot 中,服务器使用 WebSocketSession.sendMessage() 方法向客户端发送数据。
import org.springframework.web.socket.TextMessage; import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketSession; public class ChatHandler extends TextWebSocketHandler { @Override protected void handleTextMessage(WebSocketSession session, TextMessage message) throws Exception { System.out.println("收到客户端消息:" + message.getPayload()); // 构造服务器的响应消息 TextMessage responseMessage = new TextMessage("服务器响应:" + message.getPayload()); // 发送响应消息给客户端 session.sendMessage(responseMessage); System.out.println("发送消息给客户端:" + responseMessage.getPayload()); } }数据通过 sendMessage 发送数据后,前端会调用 onmessage 方法
3.3 Json数据 Java对象 JS对象的互相转换
在 Web 开发中,我们经常需要在客户端(JavaScript)和服务器端(Java)之间传递数据,通常会使用 JSON 格式。以下是 JSON 字符串与 JavaScript 对象、Java 对象之间的互相转换方法。
在前端,前端需要 JS 对象,而在后端,后端需要 Java 对象,而他们传输的数据都是 Json 格式的数据,所以当我们传输数据的时候就涉及到了这三个对象的互相转换
- 前端发送数据:JavaScript 对象 → JSON 字符串 → 发送给后端。
- 后端接收数据:JSON 字符串 → Java 对象 → 处理。
- 后端返回数据:Java 对象 → JSON 字符串 → 发送给前端。
- 前端接收数据:JSON 字符串 → JavaScript 对象 → 处理。
3.3.1 JSON 字符串与 JavaScript 对象的转换
3.3.1.1 JavaScript 对象转为 JSON 字符串
使用 JSON.stringify() 方法将 JavaScript 对象转换为 JSON 字符串。
let jsObject = { name: "张三", age: 25, city: "北京" }; // 将 JavaScript 对象转换为 JSON 字符串 let jsonString = JSON.stringify(jsObject); console.log(jsonString); // 输出: {"name":"张三","age":25,"city":"北京"}3.3.3.2 JSON 字符串转为 JavaScript 对象
使用 JSON.parse() 方法将 JSON 字符串转换为 JavaScript 对象。
let jsonString = '{"name":"张三","age":25,"city":"北京"}'; // 将 JSON 字符串转换为 JavaScript 对象 let jsObject = JSON.parse(jsonString); console.log(jsObject.name); // 输出: 张三
3.3.2、JSON 字符串与 Java 对象的转换
3.3.2.1 引入 Jackson 依赖
如果使用 Maven 项目,在 pom.xml 中添加 Jackson 的依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId> <artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId> <version>2.12.3version> dependency>3.2.2.2 JSON 字符串转为 Java 对象
使用 ObjectMapper 类的 readValue() 方法将 JSON 字符串转换为 Java 对象。
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; public class JsonExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String jsonString = "{\"name\":\"张三\",\"age\":25,\"city\":\"北京\"}"; // 创建 ObjectMapper 实例 ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 将 JSON 字符串转换为 Java 对象 Person person = objectMapper.readValue(jsonString, Person.class); System.out.println(person.getName()); // 输出: 张三 } } class Person { private String name; private int age; private String city; // Getters and Setters public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } }3.2.2.3 Java 对象转为 JSON 字符串
使用 ObjectMapper 类的 writeValueAsString() 方法将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 字符串。
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; public class JsonExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建一个 Java 对象 Person person = new Person(); person.setName("张三"); person.setAge(25); person.setCity("北京"); // 创建 ObjectMapper 实例 ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 字符串 String jsonString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person); System.out.println(jsonString); // 输出: {"name":"张三","age":25,"city":"北京"} } }四:会话的相关知识
会话创建和持续时间
- 当用户第一次访问服务器(例如第一次登录或访问某个页面)时,服务器会为用户创建一个新的会话,并生成一个唯一的会话 ID。
- 服务器会将这个会话 ID 发送给客户端。
- 在这个会话期间,用户的所有请求都会携带这个会话 ID,服务器通过这个 ID 识别请求来自同一用户,继续使用相同的会话对象。
会话过期或手动销毁
- 会话有一个过期时间(通常设置在服务器的配置中,例如 30 分钟或其他时间),如果用户在过期时间内没有任何活动(即没有请求发给服务器),会话将自动失效。
- 用户也可以通过主动“退出登录”来销毁会话,此时服务器会手动调用 session.invalidate() 方法,立即销毁会话,并清除所有会话中的数据。
再次登录会创建新会话
- 如果用户退出登录或会话过期,用户再进行登录时,服务器通常会创建一个新的会话。
- 新的会话会重新生成会话 ID,不再使用之前的 ID,因此之前的会话数据不会继续保留。
五:源代码
-
相关阅读:
【mediasoup-sfu-cpp】5: SfuDemo:分发ok
Android逆向fiddler抓包工具——理解HTTP协议
Qt交叉编译到另一台电脑执行报错重新编译
PTA 甲级 1039 Course List for Student
MySQL阻塞与死锁
R语言 | 安装ggpubr R包时编译语句中出现 WARNING: ignoring environment value of R_HOME 而报错
虹科工业树莓派应用案例之在石油开采中的应用
Antd中Table列表行默认包含修改及删除功能的封装
【考研】数据结构考点——链式基数排序
【11】基础知识:React脚手架
- 原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_73232539/article/details/143253967